Ch. 7 Gross Domestic Product
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a specific time period (usually a year)
Market value:
uses prices to measure worth.
Final goods/services
avoids double counting; excludes intermediate goods.
Produced within a country
only domestic production counts.
During a time period:
only current production is included.
What is included in GDP?
Final goods and services
New goods produced this year
Value of services (like repairs, real estate, etc.)
What is not included in GDP?
Used goods
Financial transactions (stocks, bonds)
Intermediate goods (inputs)
Underground economy (unreported cash jobs)
What are the two ways we can measure GDP?
Expenditure approach: .
Income approach:
Expenditure approach
Add up total spending on goods and services.
Income approach
Add up all income earned from producing goods and services
Expenditure approach (Y = C + I + G + NX):
C (Consumption): Household spending on goods/services.
I (Investment): Business spending on capital goods, new buildings, inventory.
G (Government): Spending by all government levels on goods/services (not transfer payments).
NX (Net Exports): Exports − Imports
A family buying groceries is a ?
Consumption
A company buying new machines is a ?
Investment
The government paying for roads is ?
Government
U.S. selling jets overseas is a ?
Net Exports
Nominal GDP
Measured in current prices (includes inflation).
Real GDP
Adjusted for price changes (shows true output).
Real Value Calculation
Nominal Value/Price Index x 100
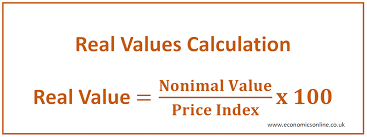
What is the consumer price index (CPI)
Measures the average price change of a fixed “market basket” of goods and services bought by typical urban households.
what is the GDP Deflator?
Measures the average price level of all goods and services included in GDP, not just consumer items.
How do you calculate the inflation rate?
Inflation Rate= New Price Index - Old Price Index / Old Price Index x 100
inflation rate Example: If the CPI increased from 200 last year to 210 this year:
210-200/200 × 100 = 5%
Problems with GDP as a measure of human well-being
Nonmarket production:
Underground economy:
Leisure and human costs:
Quality changes & new goods:
Harmful side effects:
Information age benefits:
Nonmarket production
Ignores household work and volunteer services.
Underground economy
Misses unreported legal or illegal transactions.
Leisure and human costs
Doesn’t count shorter work hours or safer conditions.
Quality changes & new goods
Hard to measure improvements (like better tech).
Harmful side effects
Pollution, crime, and disasters raise GDP but hurt welfare.
Information age benefits
Free digital goods and convenience not captured