Astronomy Final - multiple choice
5.0(6)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:57 PM on 2/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
What is the distance between the Earth and the sun?
A. 1 AU
B. 1 Lightyear
C. Less than 7
D. We haven't been able to make that measurement yet
A. 1 AU
B. 1 Lightyear
C. Less than 7
D. We haven't been able to make that measurement yet
A. 1 AU
2
New cards
What happens when you compress a gas?
A. The pressure increases, therefore the temperature increases
B. The pressure decreases, therefore the temperature increases
C. The temperature increases with no effect on the overall pressure
D. The pressure increases with no effect on the overall temperature
A. The pressure increases, therefore the temperature increases
B. The pressure decreases, therefore the temperature increases
C. The temperature increases with no effect on the overall pressure
D. The pressure increases with no effect on the overall temperature
A. The pressure increases, therefore the temperature increases
3
New cards
Which of the following is not a stellar property depicted by the HR diagram?
A. Temperature
B. Color
C. Mass
D. Luminosity
A. Temperature
B. Color
C. Mass
D. Luminosity
C. Mass
4
New cards
4. At What distance from a celestial object would the apparent (m) and absolute (M) magnitude be equal?
A. 1 parsec
B. 10 parsecs
C. 100 Parsecs
D. 1 kiloparsec
A. 1 parsec
B. 10 parsecs
C. 100 Parsecs
D. 1 kiloparsec
B. 10 parsecs
5
New cards
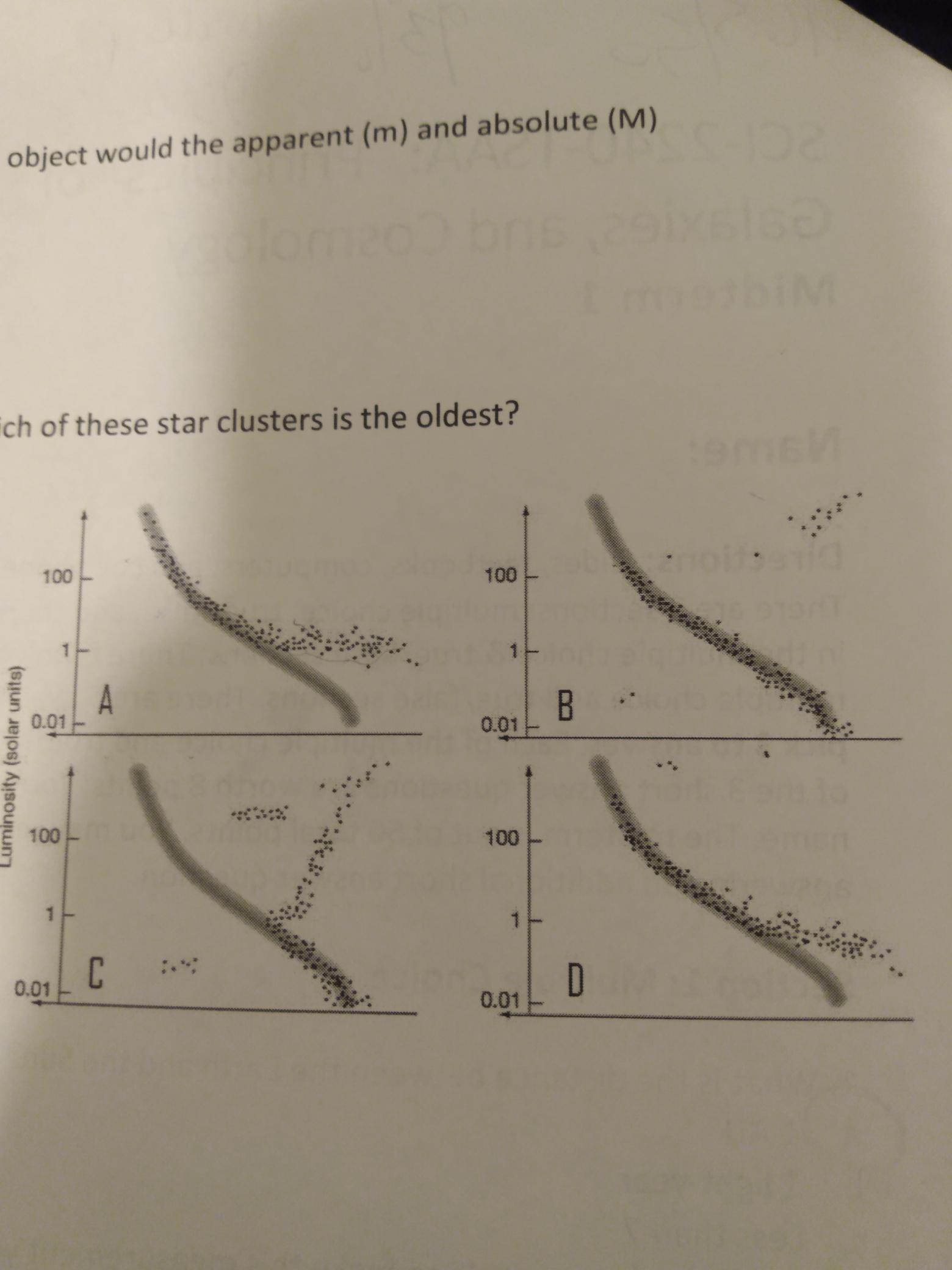
Given the HR diagrams below, which of these star clusters is the oldest
C
6
New cards
What is the Chandrasekhar Limit?
A. A mass limit for a neutron star
B. A mass limit for a white dwarf
C. A radius limit for a neutron star
D. A radius limit for a white dwarf
A. A mass limit for a neutron star
B. A mass limit for a white dwarf
C. A radius limit for a neutron star
D. A radius limit for a white dwarf
B. A mass limit for a white dwarf
7
New cards
How is the apparent magnitude of a celestial object defined?
A. The flux as measured from the surface of the sun?
B. The flux as measured from 10 parsecs
C. The flux as measured from the surface of an object
D. The flux as measured from Earth
A. The flux as measured from the surface of the sun?
B. The flux as measured from 10 parsecs
C. The flux as measured from the surface of an object
D. The flux as measured from Earth
D. The flux as measured from Earth
8
New cards
Which of the following is not listed on the x-axis of an HR diagram?
A. Wavelength
B. Color
C. Radius
D. Temperature
A. Wavelength
B. Color
C. Radius
D. Temperature
C. Radius
9
New cards
If you replaced the mass of the Sun with a black hole of equal mass, what would happen to the solar system?
A. Everything in the solar system would be sucked in
B. All of the planets' orbital speeds would significantly increase
C. Nothing would change about the orbits in the Solar System
A. Everything in the solar system would be sucked in
B. All of the planets' orbital speeds would significantly increase
C. Nothing would change about the orbits in the Solar System
C. Nothing would change about the orbits in the Solar System
10
New cards
What is the correct order of the stellar spectral types from highest to lower temperature
A. AGKMOBF
B. OBAFGKM
C. MOBFAKG
C. BAGMOKF
A. AGKMOBF
B. OBAFGKM
C. MOBFAKG
C. BAGMOKF
B. OBAFGKM
11
New cards
In what part of the EM spectrum is the sun emitting spectral types from highest to lower temperatures?
A. Gamma
B. Optical
C. Ultraviolet
D. Infrared
A. Gamma
B. Optical
C. Ultraviolet
D. Infrared
B. Optical
12
New cards
What does a spectrum do?
A. Splits an atom into 2 smaller atoms
B. Refracts white light into the colors of the rainbow
C. Causes an electron to descend 1 or more energy levels, emitting a photon in the process
D. counts the number of photons at every wavelength (or frequency)
A. Splits an atom into 2 smaller atoms
B. Refracts white light into the colors of the rainbow
C. Causes an electron to descend 1 or more energy levels, emitting a photon in the process
D. counts the number of photons at every wavelength (or frequency)
D. counts the number of photons at every wavelength (or frequency)
13
New cards
I am observing 2 galaxies. The first has an apparent magnitude of m=12, and the second m=17. How many times brighter is the first galaxy than the second?
A. 10
B. 50
C. 100
D. 500
A. 10
B. 50
C. 100
D. 500
C. 100
14
New cards
what is the distance modulus of an object at a distance of 1 kiloparsec?
A. 10
B. 100
C. 1,000
D. 10,000
A. 10
B. 100
C. 1,000
D. 10,000
A. 10
15
New cards
I am observing 2 identical stars. If one star is 5 times further from me, I observe that star to be ____ times dimmer than the closer star
A. 5
B. 25
C. 125
D. 625
A. 5
B. 25
C. 125
D. 625
B. 25
16
New cards
T/F Magnitudes are defined such that 10 steps is equivalent to 100 steps in brightness
false
17
New cards
T/F All fusion in the cores of stars stops at magnesium
false
18
New cards
T/F low mass stars can fuse and produce elements all the way up to iron (Fe) before transitioning into the red giant phase
false
19
New cards
T/F The sun's luminosity will rise to 1000 times its current level during evolution
true
20
New cards
T/F most elements present on the periodic table are produced by stars, either in cores by stellar explosions
true
21
New cards
T/F Each time a high-mass star turns out of a heavier element to fuse, it fuses heavier elements more rapidly in the core due to a large increase in temperature.
false
22
New cards
T/F A star's radius has the greatest effect on its luminosity
false
23
New cards
T/F A nearby star's spectrum reveals that its peak wavelength is 1000 nm, placing most of its emitted photons in the infrared. Therefore, I can conclude that this star is hotter than the sun.
false
24
New cards
T/F An electron will absorb a photo if it descends one or more energy level of an atom
false
25
New cards
T/F It is extremely rare to find a white dwarf in a binary star system
false
26
New cards
What is not a reason why main sequence fitting works
A. All stars in a cluster are the same age at the same distance
B. Every MS has roughly the same inherent shape, the differences are the number of stars and where they appear on the MS
C. All main sequences of every star cluster are the same
D. Any difference in apparent magnitude between two clusters is due to distance
A. All stars in a cluster are the same age at the same distance
B. Every MS has roughly the same inherent shape, the differences are the number of stars and where they appear on the MS
C. All main sequences of every star cluster are the same
D. Any difference in apparent magnitude between two clusters is due to distance
C. All main sequences of every star cluster are the same
27
New cards
which of the following cannot be listed on the x-axis of an HR diagram?
A. Age
B. Color
C. Radius
D. Wavelength
A. Age
B. Color
C. Radius
D. Wavelength
C. Radius
28
New cards
Which of the following correctly lists all the galaxy types from youngest to oldest
A. Elliptical, Spiral, Lenticular
B. Elliptical, Lenticular, Spiral
C. Lenticular, Spiral, Elliptical
D. Spiral, Lenticular, Elliptical
A. Elliptical, Spiral, Lenticular
B. Elliptical, Lenticular, Spiral
C. Lenticular, Spiral, Elliptical
D. Spiral, Lenticular, Elliptical
D. Spiral, Lenticular, Elliptical
29
New cards
Where are stars made in the milky way
A. In the bulge
B. In the disk
C. In the halo
D. In the subhalo
A. In the bulge
B. In the disk
C. In the halo
D. In the subhalo
B. In the disk
30
New cards
What is cosmology
A. The study of the structure and evolution of stars
B. The study of the structure and evolution of the milky way
C. The study of the structure and evolution of galaxies
D. The study of the structure and evolution of universe
A. The study of the structure and evolution of stars
B. The study of the structure and evolution of the milky way
C. The study of the structure and evolution of galaxies
D. The study of the structure and evolution of universe
D. The study of the structure and evolution of universe
31
New cards
How are stars orbiting around a galaxy if they're located in a bar
A. Their orbits are similar to other stars in the galaxy, there is just an over dense region of stars in the bar
B. Their orbits are highly eccentric around the bar
C. Their orbits are more circular than disk or bulge stars
A. Their orbits are similar to other stars in the galaxy, there is just an over dense region of stars in the bar
B. Their orbits are highly eccentric around the bar
C. Their orbits are more circular than disk or bulge stars
B. Their orbits are highly eccentric around the bar
32
New cards
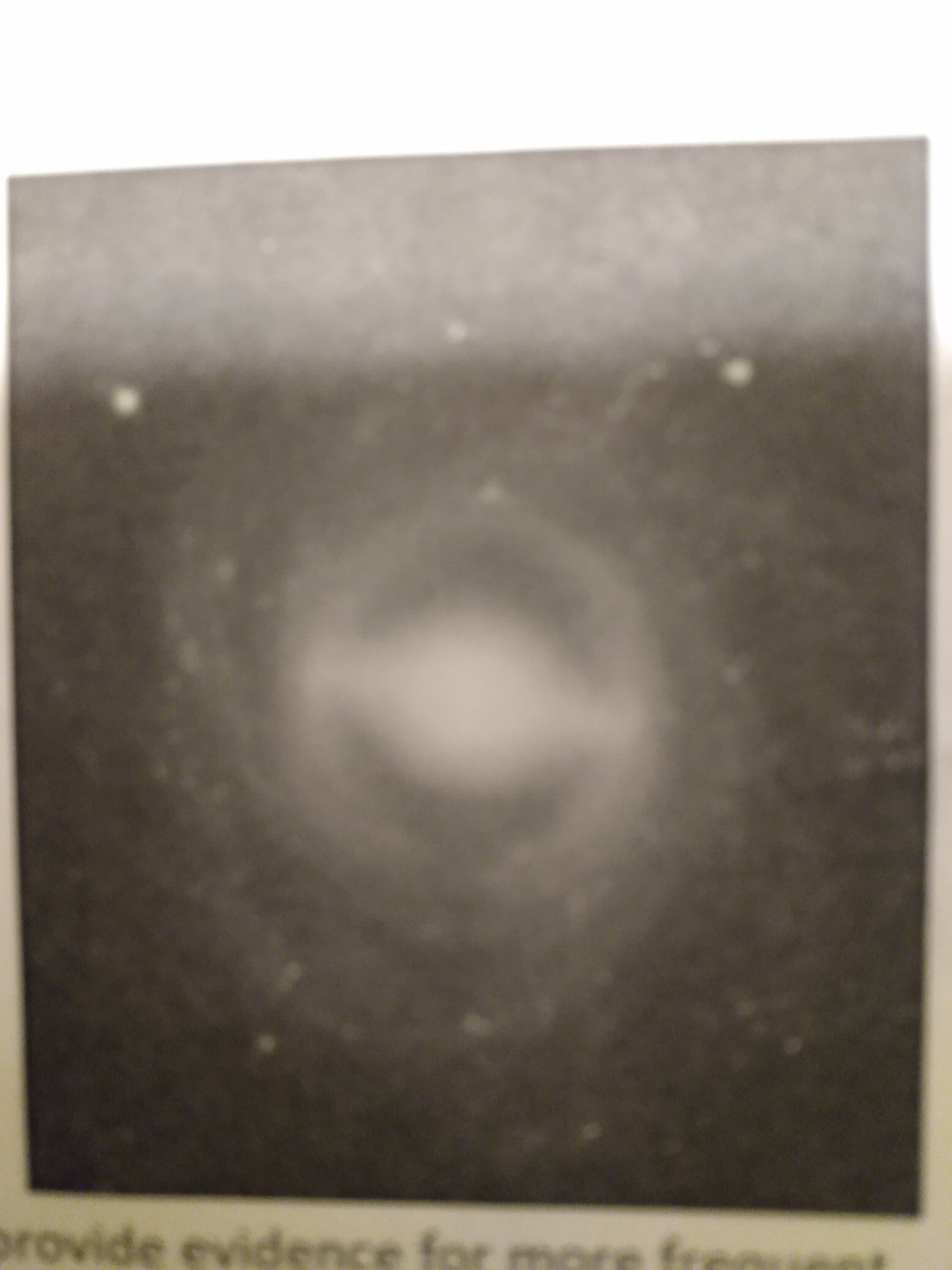
What would the hubble classification be for the the galaxy on the right?
A. SBd
B. E5
C. Sa
D. SBb
A. SBd
B. E5
C. Sa
D. SBb
D. SBb
33
New cards
Where are cepheids found on the HR diagram
A. Middle of the main sequence
B. Instability Strip
C. Red Giant Branch
D. Near the top
A. Middle of the main sequence
B. Instability Strip
C. Red Giant Branch
D. Near the top
B. Instability Strip
34
New cards
What features about distant galaxies do we observe that provide evidence for more frequent interactions in the early universe?
A. There were more prominent bulges in spirals compared to today
B. There were higher numbers of ellipticals in the early universe
C. There were more prominent disks in spirals compared to today
D. Distant galaxies appear to have disturbed morphologies
A. There were more prominent bulges in spirals compared to today
B. There were higher numbers of ellipticals in the early universe
C. There were more prominent disks in spirals compared to today
D. Distant galaxies appear to have disturbed morphologies
D. Distant galaxies appear to have disturbed morphologies
35
New cards
Molecular clouds, planetary nebulae, and supernovae all exhibit this type of spectrum
A. Absorption
2. Emission
C. Continuous
A. Absorption
2. Emission
C. Continuous
2. Emission
36
New cards
where will the milky way's gas be in 1 trillion years
A. Blown out of the galaxy
B. Still recycling like it is now
C. locked in white dwarfs and low mass stars
A. Blown out of the galaxy
B. Still recycling like it is now
C. locked in white dwarfs and low mass stars
C. locked in white dwarfs and low mass stars
37
New cards
If a protogalactic cloud has little to (approximately) no angular momentum, what will it likely turn into?
A. A spiral
B. An elliptical
C. A massive star
D. A black hole
A. A spiral
B. An elliptical
C. A massive star
D. A black hole
B. An elliptical
38
New cards
In which part of the EM spectrum would starburst galaxies shine the brightest?
A. Radio
B. Infrared
C. Ultraviolet
D. X-ray
A. Radio
B. Infrared
C. Ultraviolet
D. X-ray
B. Infrared
39
New cards
The furthest distances that Leavitt's Law can reach are
A. other universes
B. Other star clusters in the milky way
C. other stars in the milky way
D. other galaxies
A. other universes
B. Other star clusters in the milky way
C. other stars in the milky way
D. other galaxies
D. other galaxies
40
New cards
why does ongoing star formation in spiral galaxies lead to a blue appearance?
A. There aren't any yellow or red stars in spirals
B. Short-lived blue stars outshine the other stars
C. Gas in the disk preferentially scatters blue light
A. There aren't any yellow or red stars in spirals
B. Short-lived blue stars outshine the other stars
C. Gas in the disk preferentially scatters blue light
B. Short-lived blue stars outshine the other stars
41
New cards
T/F Spiral arms cannot be produced by gravitational interaction with another galaxy
false
42
New cards
T/F Irregular galaxies have no defined shape and usually no central bulge, but they can have ongoing star formation
True
43
New cards
T/F Tip of the red giant branch stars all share the same absolute magnitude in the V filter
False
44
New cards
T/F Stars in the disk of the milky way are typically younger than halo or bulge stars
true
45
New cards
T/F Lenticulars usually don't have spiral arms but they do have disks, which means lenticulars also have ongoing star formation
false
46
New cards
T/F Leavitt's Law cannot be used for distances outside of the milky way
false
47
New cards
T/F Spiral galaxies are much more commonly found in clusters
false
48
New cards
T/F protogalactic clouds that had leftover angular momentum are believed to have evolved into disk galaxies
true
49
New cards
T/F the faber-Jackson relation be applied to both elliptical and spiral galaxies
false
50
New cards
T/F the diameter of the milky way is roughly 30 kpc
true
51
New cards
Which of the following is not one of the conclusions of Hubble's Law?
A. The farther a galaxy's distance, the larger the redshift
B. The universe is expanding
C. The velocities of the Local Group show infall into the Virgo Cluster
D. Further galaxies have larger recessional velocities
A. The farther a galaxy's distance, the larger the redshift
B. The universe is expanding
C. The velocities of the Local Group show infall into the Virgo Cluster
D. Further galaxies have larger recessional velocities
C. The velocities of the Local Group show infall into the Virgo Cluster
52
New cards
2. If I assume He 70 km/s/Mpc, and 1 measure a galaxy's recessional velocity to be 3500 km/s, what is the distance to this galaxy in Mpt according to Hubble's Law?
A. 25 Mpc
B. 50 MpC
C. 75 MpC
D. 100 MpC
A. 25 Mpc
B. 50 MpC
C. 75 MpC
D. 100 MpC
B. 50 MpC
53
New cards
During what era of the early Universe were photons finally released?
A. Particle Era
B. Nucleosynthesis Era
C. Atoms Era
D. Galaxies Era
A. Particle Era
B. Nucleosynthesis Era
C. Atoms Era
D. Galaxies Era
C. Atoms Era
54
New cards
Which of the following galaxy characteristics has not been observed to correlate with supermassive black hole mass?
A. Bulge Mass
B. Bulge luminosity
C. Galaxy Stellar Mass
D. Cryonic Mass
E. None of the above
A. Bulge Mass
B. Bulge luminosity
C. Galaxy Stellar Mass
D. Cryonic Mass
E. None of the above
E. None of the above
55
New cards
Which rung of the distance ladder did Hubble use to prove Andromeda was its own galaxy separate from the Milky Way?
A. Type la supernovae
B. The Tully Fisher Relation
C.TRGB Stars
D. Leavitt's Law
A. Type la supernovae
B. The Tully Fisher Relation
C.TRGB Stars
D. Leavitt's Law
D. Leavitt's Law
56
New cards
Which of the following is not one of the 4 fundamental forces of the Universe?
A. Strong Force
B. Hydrostatic Force
C. Weak Force
D. Gravity
A. Strong Force
B. Hydrostatic Force
C. Weak Force
D. Gravity
B. Hydrostatic Force
57
New cards
Dark matter comprises approximately % of the Universe
A. 25%
B. 50%
C.75%
D. 100 %
A. 25%
B. 50%
C.75%
D. 100 %
A. 25%
58
New cards
In which type of galaxy are type la supernovae most likely to occur?
A. Spirals
B. Ellipticals
C. Lenticulars
d. Both a and b
A. Spirals
B. Ellipticals
C. Lenticulars
d. Both a and b
d. Both a and b
59
New cards
What is the observable Universe?
A. All photons which have had time to travel to us.
B. The portion of the sky unobscured by the disk of the Milky Way All
C. photons in the Universe which we have detected so far.
D. A term for all bodies in the Universe which emit photons.
A. All photons which have had time to travel to us.
B. The portion of the sky unobscured by the disk of the Milky Way All
C. photons in the Universe which we have detected so far.
D. A term for all bodies in the Universe which emit photons.
A. All photons which have had time to travel to us.
60
New cards
Which of the following is a possible conclusion from the disagreement between the values of Ho?
a. Something is possibly wrong with our models of the Universe
B. There is possibly new physics to understand about the inverse
C. Something is possibly wrong with our methods of observation.
d. All of the above
E. None of the above
a. Something is possibly wrong with our models of the Universe
B. There is possibly new physics to understand about the inverse
C. Something is possibly wrong with our methods of observation.
d. All of the above
E. None of the above
d. All of the above
61
New cards
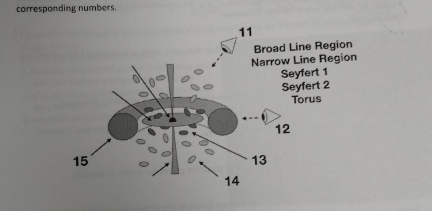
Consider the AGN Unified Model below, Match and fill in the designated components to the corresponding numbers
11. Seyfert 1
12. Seyfert 2
13. Broad Line Region
14. Narrow Line region
15. Torus
12. Seyfert 2
13. Broad Line Region
14. Narrow Line region
15. Torus
62
New cards
T/F The supermassive black hole at the center of Messier 87 is larger than our Solar System
True
63
New cards
T/F A Type IA supernova is the explosion of the outer layers of a massive star after the core collapses
False
64
New cards
T/F On large scales, the distribution of matter in the Universe is even without a center or edge.
True
65
New cards
T/F We have directly imaged both Sagittarius A and the supermassive black hole at the center of Messier 87 with the Event Horizon Telescope
True
66
New cards
T/F Hubble Flow gets weaker for galaxies at further distances while gravitational interactions get stronger
False
67
New cards
T/F As you move backwards in the Universe's timeline, the strength of gravity increases.
True
68
New cards
T/F The present day Universe has a closed geometry
False
69
New cards
T/F Supernova explosions can shine as bright as an entire galaxy for weeks to months
True
70
New cards
T/F From every galaxy's perspective, nearly every galaxy in the Universe is moving away from them
True