SZ 17 Reliability and validity of diagnosis 1
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Explain the key concepts of reliability and validity of diagnosis and classification of schizophrenia (5)
* Diagnosis: whether someone has SZ
* Classification: what SZ is
* Reliability: consistency, e.g., inter- rater reliability
* Validity: truth, measures what it is supposed to measure
* i.e., accurate diagnosis of well- defined illness
Identify and define 2 types of misdiagnosis and their effects in the case of schizophrenia (2x3)
* False positive
* Diagnosed with SZ but don't have it
* Unnecessary drug treatment, side effects
* False negative
* Not diagnosed with SZ but do have it
* Lack of treatment
Explain what research has shown about changes in reliability of diagnosis of schizophrenia over time (in 3 'waves') (3x2)
* 1950-70s
* Low reliability due to vague criteria
* 1980s-2010s: moderate reliability due to increased clarity, but subjectivity still a problem
* 2019: high reliability, but only in ideal conditions (time, training and discussion)
* Osorio: +0.97 correlation between doctors in diagnosis
Explain similarities and corresponding differences between DSM and ICD in how they classify / diagnose schizophrenia (2x2)
* Both require 2 symptoms, with a set of core symptoms
* ICD has 1 more on the 'core' list
* Both need 1 month of full symptoms
* DSM needs 6 months of 'signs of disturbance'...
... ICD doesn't
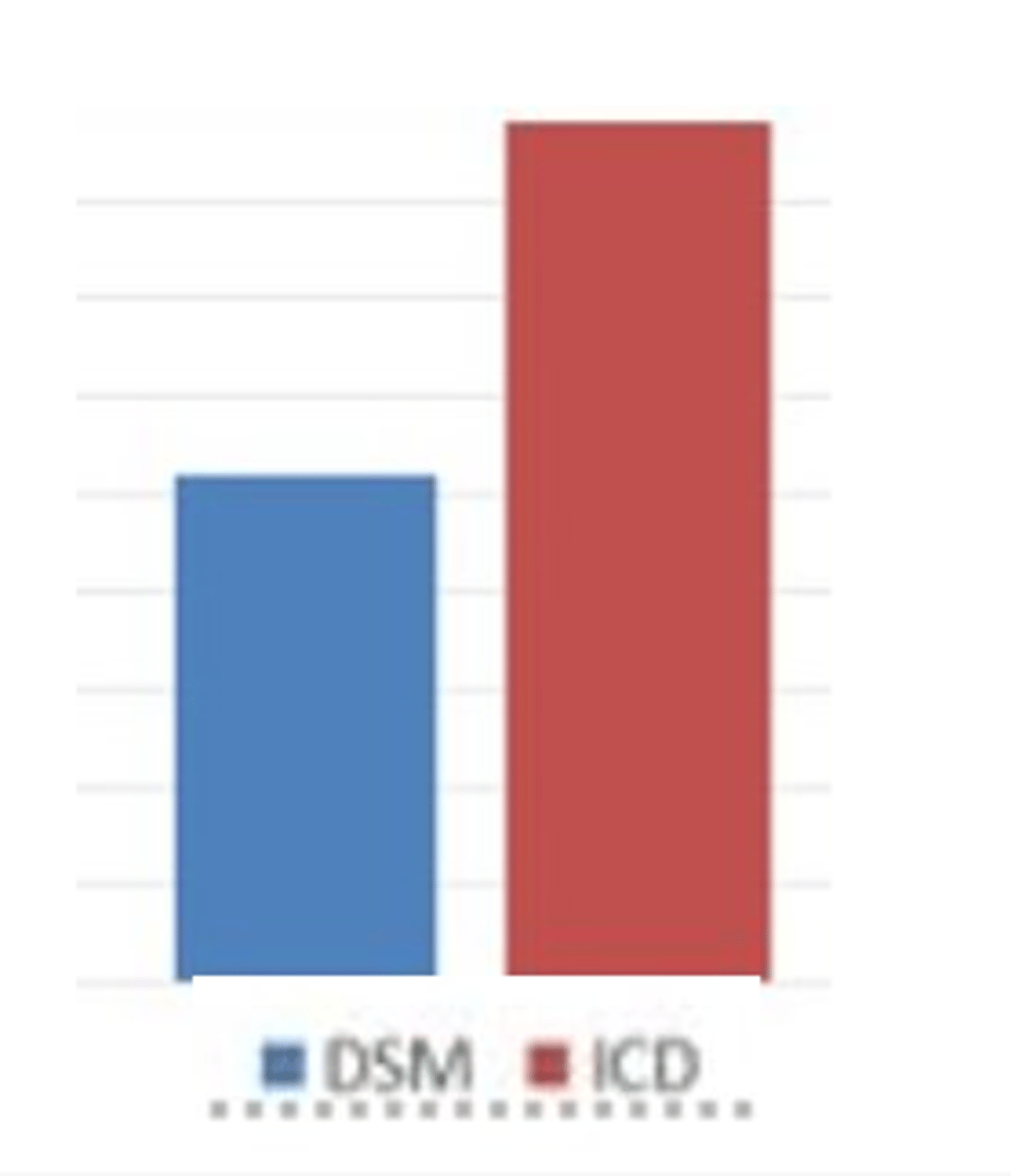
Explain what research (e.g., Cheniaux) has shown about differences in diagnosis of schizophrenia between DSM and ICD, and hence their validity (4)
* Diagnosis rates 2x as high for ICD as DSM
* Due to differences in diagnostic criteria
* DSM underdiagnoses / false negatives / Type 2 errors?
* ICD overdiagnoses / false positives / Type 1 errors?
* At least one of the systems gives invalid results