PT 412 Intermittent Compression Devices
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
edema
presence of abnormal amounts of fluid in the extracellular tissue spaces
joint swelling, joint effusion
blood and joint fluid accumulated immediately following injury within joint capsule
lymphedema
swelling in subcutaneous tissues results from excessive accumulation of lymph(overdistension of lymph capillaries) occurring over several hours following injury
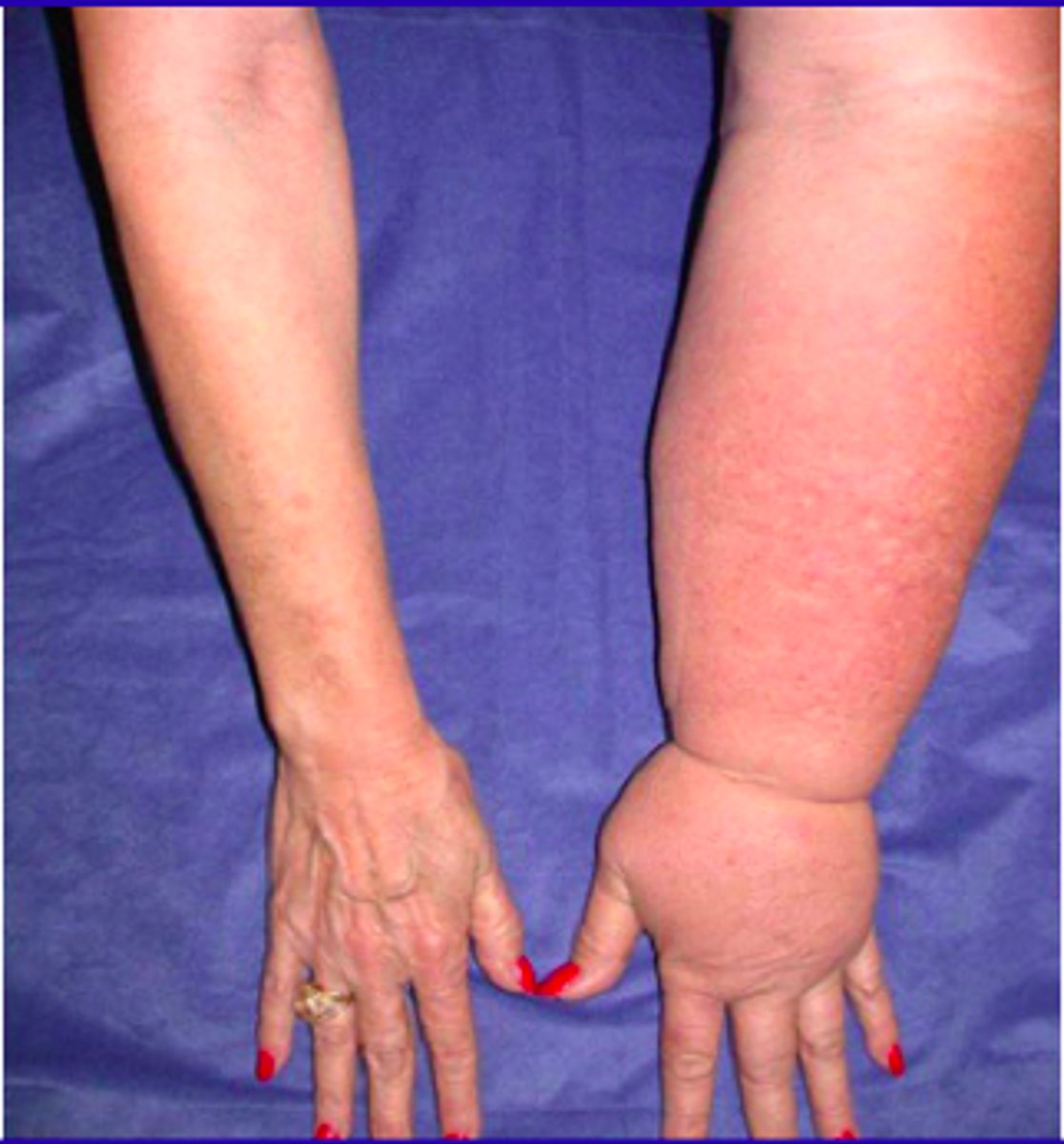
joint effusion
A type of swelling that occurs inside a joint/joint capsule
true
True or False? Edema and swelling are the same thing
pitting edema
indentation left after examiner depresses the skin over swollen edematous tissue, common with lymphedema
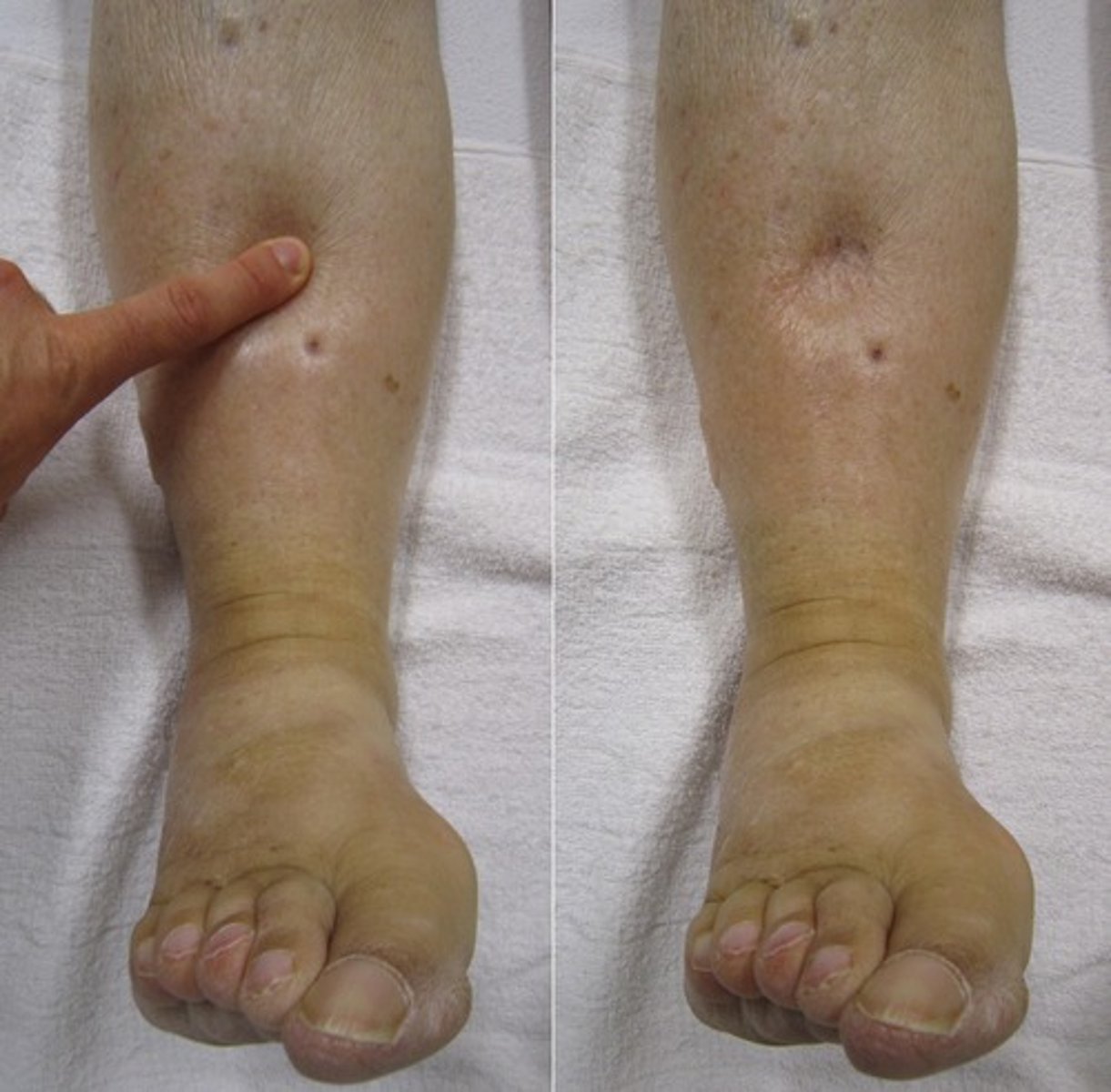
lymphatic system
As plasma and plasma proteins escape from small blood vessels they are picked up by what system to be returned to blood circulation?
safety valve for fluid overload
Lymphatic system acts as what?
interstitial fluid
The lymph system can be overwhelmed by sudden local increases in:
lymphatic system
Closedvascularsystem of endothelial cell lined tubes that parallel arterial and nervous system
circulatory
lymph vessels parallel what other system?
Interstitial fluid
What surrounds lymphatic capillaries?
terminal lymphatics
provide the entry way via valves into the lymphatic system for the excess interstitial fluid and plasma proteins
proximal
Are lymph nodes and structures more prominent in proximal or distal segments?
lymphatic capillaries → network of lymphatic vessels → collecting vessels → vascular system
Flow of lymph from distal to proximal
fibrils
The lymphatic capillaries are made of singlelayered endothelial cells with _____________ radiating from the junctions of the endothelial cells
support lymphatic capillaries, anchor to connective tissue
function of lymphatic fibrils
True
As intercellular fluid accumulates, the fibrils radiating from the seams in the lymphatic capillary pull the seam open to create a pore large enough for plasma proteins to enter. True or False?
lymph
what are the interstitial fluid and proteins called once they enter lymphatic capillaries?
muscle activity, active/passive movement, elevated positions, respiration and blood vessel pulsation, compression
Activities that can aid in the movement of lymph
Wolff's Law
#1 benefit of ROM exercises involves what concept?
mobilizing lymph and edema
#2 benefit of ROM exercises involves what concept?
first aid, PRICE
What can you do immediately after an injury to minimize edema
cold, compression, elevation, negative HV E-Stim
retards accumulation of fluid and keeps lymphatic system functioning at an optimum level
decreased plasma protein content
With tx that encourage lymph flow, what happens in the intercellular spaces?
bloodstream
Where does lymph fluid carry waste products and destroyed bacteria back to?
liver, kidneys
Once back into the bloodstream, waste products and destroyed bacteria are removed via what structures?
bowel movements, urine
How does the body expel waste products and destroyed bacteria?
gravity
can be used to augment normal lymph flow by encouraging its movement
higher
The _________ the elevation, the greater the effect on the lymph flow
ace wrap, tubi-grip, cryocuff, compression stockings/sleeves
What could we pair with elevation ti further aid lymph mobility?
Rhythmic internal compression/muscle contraction
will squeeze/pump lymph through lymph vessels improving its flow back to the vascular system
Retrograde massage, elastic compression, intermittent pressure devices
most often used external pressure devices
Jobst garments, Gottfried
Pressure dressings commonly used (custom)
PTs
Who measures/fits pts for custom pressure dressings?
non-custom, tubi-grip
Non-custom compression garments
inflation pressure, on/off time, total tx time
Intermittent Compression Treatment Parameters
reduce blood clot risk
What is a pneumatic boot in hospital mainly used for?
blood pressure
Therapeutic pressure settings on Jobst pumps are loosely correlated with what?
diastolic
A pressure on Jobst pumps approximating ___________ blood pressure is the MAX pressure, which we should not exceed
30 mmHg
Arterial capillary pressures during rest
30 mmHg
Any pressure exceeding what value should encourage reabsorption of the edema and movement of lymph
30-60 mmHg
Tx range pressure for UE
40-70 mmHg
Tx range pressure for LE
40-50 mmHg
what pressure may be best used for both LE and UE?
50 sec on/off
common and optimal on/off time sequences on jobst pumps
30-60 min
Typical tx time with jobst pumps
AAROM
What should we instruct patients to do during compression tx OFF cycle?
patient comfort
Primary deciding factor during on on/off cycle for jobts pump
half leg/arm, full leg/arm
Variations of compression sleevs
rubber hose and valve
Deflated compression sleeve is connected to compression unit via what devices?
Sequential Compression Pumps
Incorporates sequentially inflated multiple
compartment designs
distal → proximal
With Sequential Compression Pumps, where does the pressure build first?
20 mmHg
pressure difference at each hose on a Sequential Compression Pump
DBP
What should the highest pressure, on the distal sleeve of a Sequential Compression Pump, be determined by?
30/50 sec on, 30/50 sec off
Sequential Compression Pumps tx on/off time
False ("Unlike ice, cannot really do Tx too long")
True or false? You should be concerned with using Sequential Compression Pumps for too long?
30-60 min
Typical tx time for Sequential Compression Pumps
skin integrity, patient tolerance
What should be inspected before/during tx with compression pumps?
cold + compression
has been shown to be clinically effective in treating many edema conditions
inhibition (NOT shrinking)
Effect of cold on edema
cryo-cuff, game ready system
devices which make use of a combination of cold and compression which provides an inexpensive means of treating edema
lymphedema, traumatic edema, chronic edema, stasis ulcers, wound healing
Indications for Intermittent Pneumatic Compression
compartment syndrome, PVD, DVT, blood clot, superficial infection, congestive heart failure, acute pulmonary edema, displaced fractures, do not exceed DBP
Contraindications for Intermittent Pneumatic Compression
Blood flow restriction
restrict arterial inflow while occluding venous return, typically used for muscle growth and recovery; NOT for edema