Microbiology Chapter 7: Fundamentals of Microbial Growth and Control
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
1
New cards
microbial growth
cell division that produces new (daughter) cells and increases the total cell population
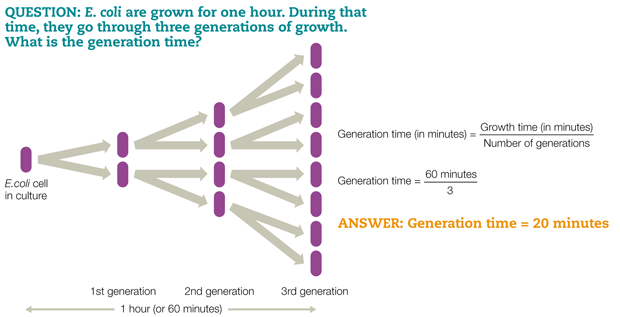
2
New cards
generation time
The time that it takes for a cells population to double
3
New cards
exponential growth
As bacteria divide by binary fission, they exhibit\______________.
4
New cards
20 minutes
Generation time for E. Coli is what?
5
New cards
15-20 hours
Generation time for mycobacterium tuberculosis is?
6
New cards
Lag phase
What is phase one of the bacteria growth phases
7
New cards
Phase one-lag phase
Which phase is the delay that occurs while cells adjust to their new environment?
8
New cards
log phase
What is phase two of the bacteria growth phases
9
New cards
Phase two- log phase
Which is the period of rapid exponential growth
10
New cards
Phase Three- stationary phase
Which occurs when the nutrients are depleted & waste accumulates? During this phase, population growth rate levels are off.
11
New cards
stationary phase
What is phase three of the bacteria growth phases?
12
New cards
death phase
What is the fourth phase of the bacteria growth phases?
13
New cards
Phase four- death phase
Which phase occurs when waste builds up, nutrients decease, & the cells begin to die?
14
New cards
low temperature
Decreases enzymatic reactions
15
New cards
increased temperature
What property speeds up enzymatic reaction and increase growth rate
16
New cards
high temperatures
what denatures cell proteins?
17
New cards
optimal temperature
Temperature where cellular growth is the highest
18
New cards
Psychrophiles
Thrive between -20 and 10 degrees Celsius
19
New cards
Psychrotrophs
Bacteria that grow at about 0-30 degrees Celsius and are associated with foodborne illness
20
New cards
Mesophiles
grow best around 10-50 degrees Celsius and are associated with most pathogens
21
New cards
Thermophiles
grow around 40-75 degrees Celsius are associated with compost piles and hot spring
22
New cards
Extreme thermophiles
thrive in very hot environments are grown around 65-120 degrees Celsius
23
New cards
Listeriosis
usually food borne infection; can be transmitted to fetus, reproduces in phagocytes, is a psychrotroph and can grow at refrigerator temps
24
New cards
Acidophiles
grow at PH 1 (or less) to PH 5, live in areas such as sulfur hot springs & volcanic vents are often maintain a fairly neutral cytoplasmic PH
25
New cards
Neutralophiles
grow best in a PH range of 5-8 make up majority of microorganisms
26
New cards
Alkaliphiles
grow in the basic PH range of 9-11 are associated with soda lakes
27
New cards
Halophiles
thrive in high salt environments are associated with the Dead Sea and the great salt lake of Utah
28
New cards
Facultative halophiles
tolerate higher salt but may not grow well. EX. staphylococcus aureus
29
New cards
Plasmolysis
Normal cells undergo ______, which is the process of cell losing water when placed in a hypertonic solution.
30
New cards
Cold
The suffix "psychro" means.......
31
New cards
Obligate aerobes
Organism with an absolute dependence on O2 for cellular processes
32
New cards
Microaerophiles
organisms that use only a small amount of O2 live in low O2 settings
33
New cards
falcultative anaerobes
organisms that grow with and without O2 and switch between using O2 and fermentation
34
New cards
aerotolerant anaerobes
organisms that tolerate O2, but don't use it and have ways to deactivate ROS
35
New cards
obligate anaerobes
Organisms that Do Not use O2 in their metabolism and can’t eliminate ROS; Tend to die in aerobic environments
36
New cards
Essential Nutrients
Elements such as sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, etc. that cell are required to have to build new cell.
37
New cards
Macronutrients
essential nutrients that are needed in large quantities for the cell, usually compose most of the dry weight.
38
New cards
Micronutrients
Nutrients used in very small amounts
39
New cards
Nutrients
Microbes use\__________from the environment go divide, and to build structural components, enzymes, and other factors.
40
New cards
90%
About\_______of a cells dry weight is carbon, hydrogen, nongaseous oxygen, and nitrogen.
41
New cards
Carbon
\_______is required by all organisms to form structural organic molecules and as a energy source.
42
New cards
Heterotroph & Autotroph
Two categories of organisms based on how they obtain organic carbon
43
New cards
Heterotrophs
Require and external source of organic carbon ( sugars, lipids, protiens)
44
New cards
Autotrophs
Do not require an external source of organic carbon and use carbon fixation to convert inorganic carbon into organic carbon
45
New cards
Nitrogen
\________is the limiting factor in many ecosystems and is found in amino acids and protiens
46
New cards
Sulfur
Found in amino acids, thiamine, and biotin
47
New cards
Phosphorus
Found in DNA, RNA, ATP, and membranes
48
New cards
growth factors
The necessary substances that a cell can't make on its own are called\_____________.
49
New cards
fastidious
Organisms that need multiple growth factors are said to be________.
50
New cards
phototrophs and chemotrophs
In order to carry out functions & construction, cells require energy including.....
51
New cards
Phototrophs
obtain energy from light
52
New cards
Chemotrophs
organisms that break down chemicals compounds for energy
53
New cards
Media
We classify\____________by their physical state, chemical composition, and their function.
54
New cards
liquid media
Ideal for growing large batches of microbes
55
New cards
solid media
Useful for isolating colonies and observing specific culture characteristics
56
New cards
semisolid media
Useful for motility testing of bacteria species
57
New cards
defined media
Synthetic media that has a precise chemical composition that is known and quantified to growth cultures
58
New cards
complex media
Media with a mixture of nutrients that are not fully defined and are used to grow fastidious organisms (EX. extracts and digests of yeasts, meat, or plants)
59
New cards
differential media
media formulated to visually distinguish one microbe from another
60
New cards
Blood Agar
Useful for distinguishing Steptococcus pyogenes
61
New cards
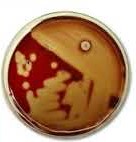
Beta hemolysis
Break down red blood cells
62
New cards

Alpha hemolysis
Partial breakdown of red blood cells by oxidation of hemoglobin
63
New cards
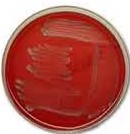
Gamma hemolysis
do not lyse red blood cells
64
New cards
selective media
suppress unwanted microbes and encourage desired microbes
65
New cards
Mannitol Salt Agar
selective due to its high salt content and differentiates organisms based on their ability to ferment a sugar called "mannitol"
66
New cards
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB)
dyes eosin and methylene blue limit gram-positive bacterial growth and differentiates based on ability to ferment lactose
67
New cards
38%
On average, anaerobes make up\_______of the bacterial population in a wound.
68
New cards
thioglycate
Reducing agent used for anaerobic organism; converts O2 to water
69
New cards
aseptic techniques
Methods designed to prevent introducing contaminating microbes to a patient, clinical sample, or others in the healthcare setting.
70
New cards
streak plate technique
most commonly used technique to isolate bacteria whose method is to dilute a culture on an agar plate
71
New cards
colony
As cells divide, their population increases to form a mound of cells called a\____________.
72
New cards
Direct Methods
Involve counting individual cells or colonies (plate counts)
73
New cards
Indirect Methods
rely on secondary reflections of overall population size
74
New cards
What are the consideration made when collecting clinical samples?
A patient primary diagnosis, stage & site of infection all affect how and when a sample is taken further more **Aseptic techniques**, **equipment used**, **taking a** **specific sample site** are all important to implement in the collection process.
75
New cards
Turbidity
The fast and easy way to indirectly measure cell numbers is to measure the\___________.
76
New cards
cloudiness
The term "turbidity" refers to.....
77
New cards
Physical Analysis
Involves staining and microscopy to observe morphological features
78
New cards
Biochemical analysis
Involves a collection of media that assess metabolic properties
79
New cards
Genetic methods
helps to quickly identify microbes and probes, PCR, DNA "fingerprinting", electrophoresis separation methods
80
New cards
Decontamination
Measures that remove or reduce microbial populations to render an object safe for handling
81
New cards
Sterilization
A measure that eliminates ALL bacteria, viruses, and endospores. Is required for drugs, objects used for medical procedures, and for lab media & glassware
82
New cards
Disinfection
Reduces microbial numbers on surfaces or objects and is used for cosmetics, foods, surfaces, and external medical equipment
83
New cards
Antiseptics
used to destroy pathogens on living tissue
84
New cards
Heat
Most microbes are sensitive to\__________.
85
New cards
Decimal Reduction Time (DRT)
The time, in minutes, it takes to kill 90% of a population of bacteria at a given temperature and is associated with disinfection
86
New cards
Thermal death time (TDT)
Shortest period of time at a certain temperature needed to kill all microbes in a sample
87
New cards
Thermal death point (TDP)
The minimum temperature needed to kill all microbes in a sample within 10 minutes
88
New cards
Autoclave
A machine that applies steam heat along with pressure to sterilize is used for microbiological media & assorted medical or lab equipment
89
New cards
20 minutes
Most substances are sterile after \________ using the standard autoclave settings.
90
New cards
What is autoclaving?
Steaming an object at 121 degrees Celsius (294 degrees Fahrenheit) with 15 pounds of pressure
91
New cards
Boiling
A highly affective decontaminating method used on heat resistant equipment **NOT** **sterilization**, that eliminates most microbial numbers, **BUT NOT** endospores.
92
New cards
Boiling water
\______________ for 5 minutes eliminates most pathogenic bacteria, protozoan, and viruses.
93
New cards
Pasteurization
Eliminates pathogens and reduces harmless microbes in dairy products that cause milk spoilage. EX. listeria, salmonella, and E. Coli
94
New cards
Incineration (dry heat)
\_________ or hot air ovens can also be used to sterilization or disinfection.
95
New cards
Radiation
Some physical decontamination methods involve __________, or high energy waves. Can serve as a disinfectant or sterilization tool depending on the protocol (either ionizing or non-ionizing).
96
New cards
Non-ionizing radiation
(ultraviolet light) causes thymine diners by altering structure of DNA leading to mutation used in sanitize drinking water & swimming pools, disinfecting surfaces in operating rooms, and disinfect biosafety cabinet surfaces
97
New cards
Ionizing radiation
generate reactive ions that kill microbes and inactivate viruses using gamma rays and x-rays but can damage nucleic acids. Can be used to in food (spices, meats, vegetables)and pharmaceutical industry, sterilizing medical supplies that cannot be autoclaved.
98
New cards
High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters
Remove microbes and allergens from the air is made of randomly arranged fibers hat remove 99.97% of airborne substances (does not sterilize the air)
99
New cards
Membrane filters
liquids can be sterilized using \_________________. (pore sizes range from 0.1 mm to filter out bacteria, to 0.01 mm to remove viruses)
100
New cards
"lifeStraws"
0.2 mm filters that remove pathogens from drinking water