Carboxyl groups and derivatives as electrophiles
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
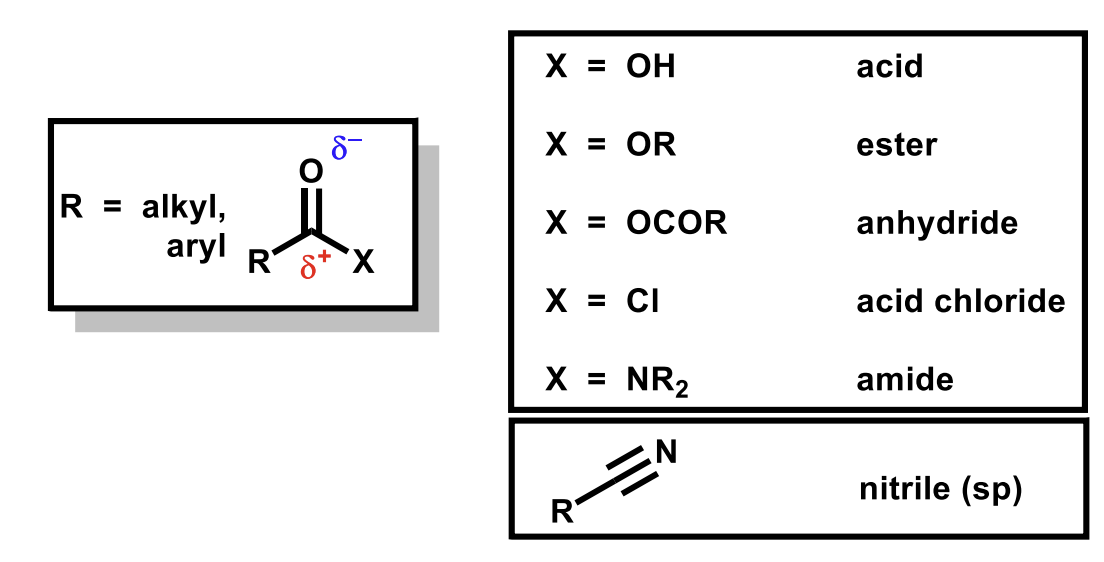
Examples of these groups - carbonyls with an additional heteroatom
The nitrile group has the same oxidation level on the carbon (3 bonds to heteroatoms from carbon in all)
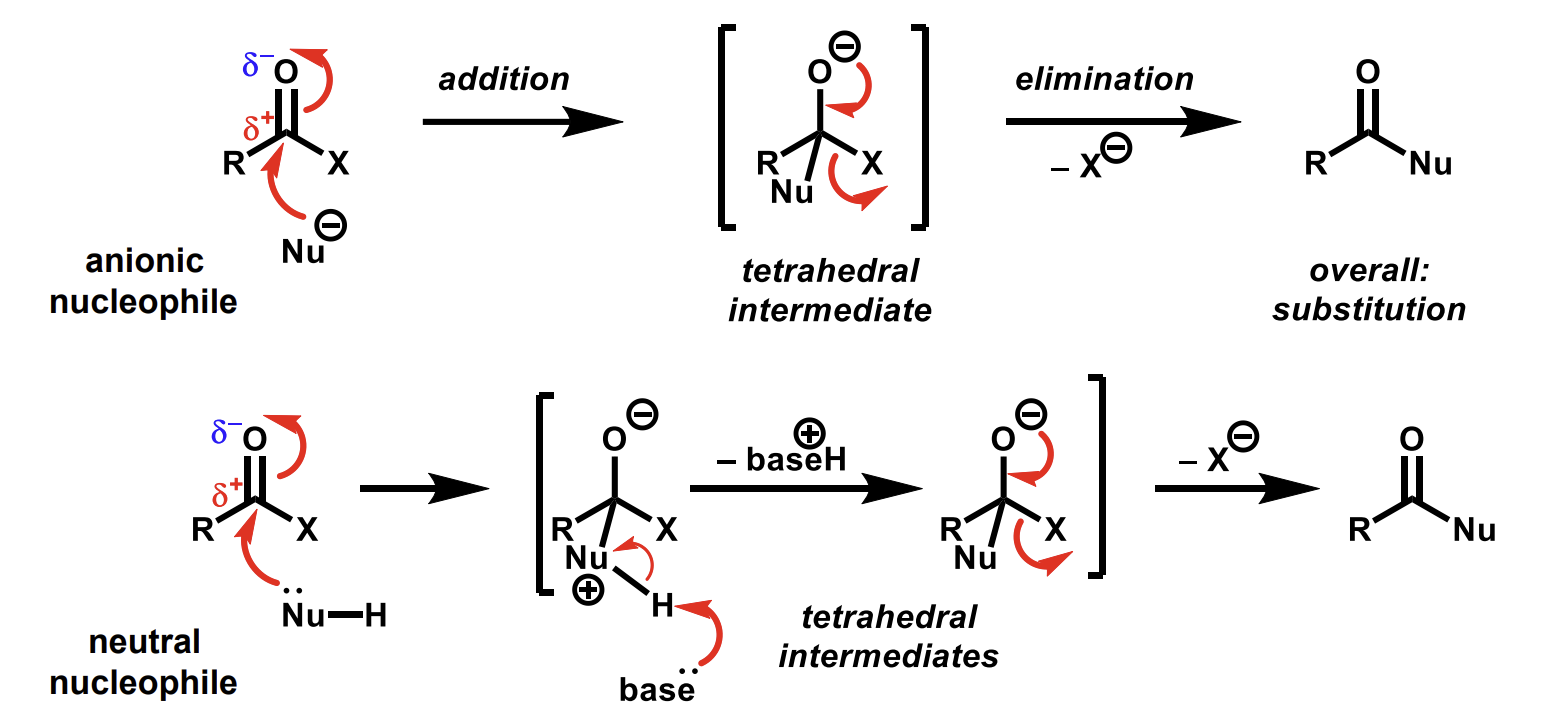
Nucleophilic addition-elimination
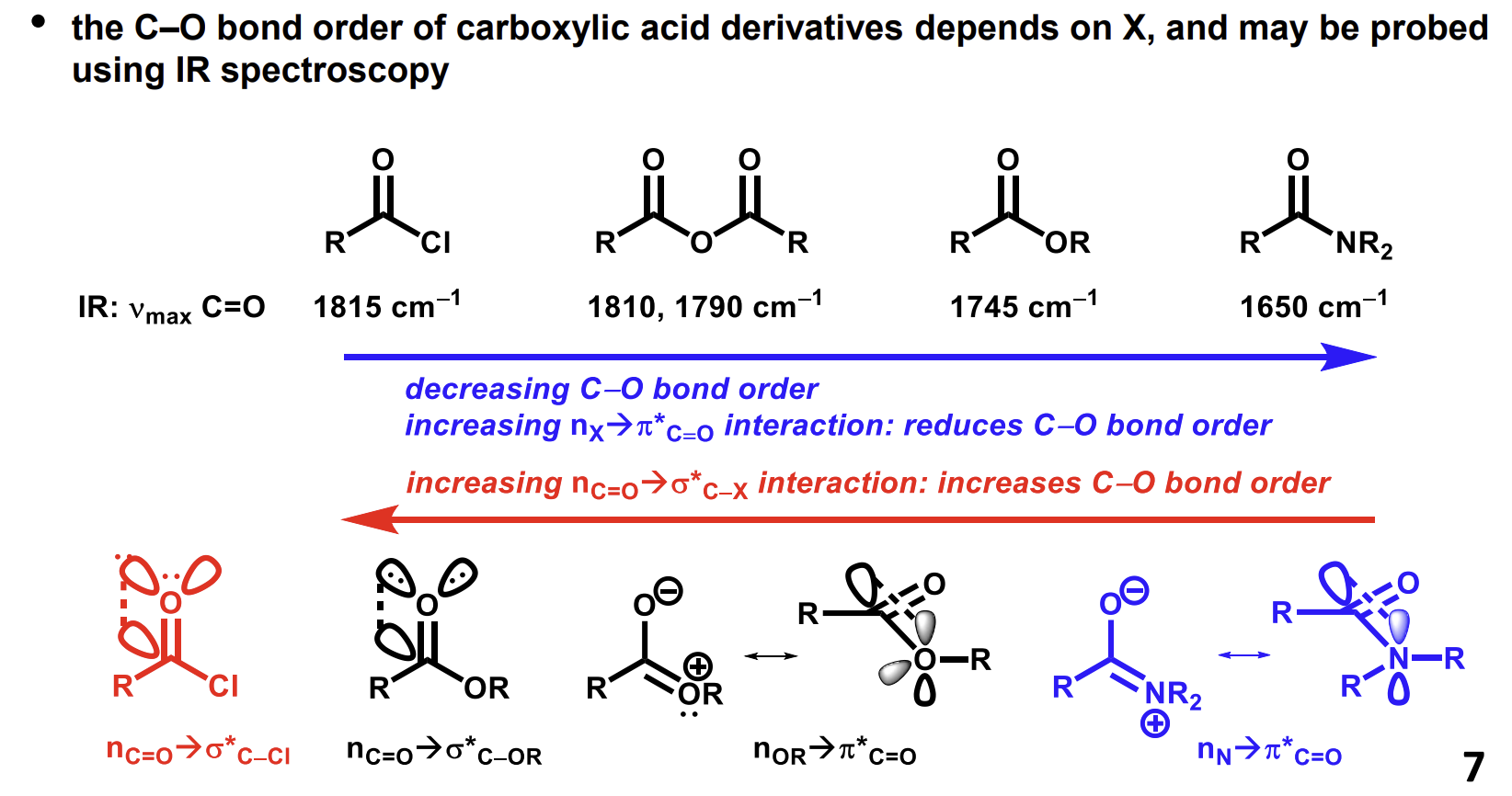
How do the infrared characteristics of the C=O bonds vary across groups and why
Increased electron donation from X decreases the bond order. (look at the resonance form at the bottom second from right.
Higher bond order means stronger bond and a higher stretching frequency.
Why are acyl chlorides more reactive than amides
The interaction of the nitrogen lone pair reduces the electrophilicity of the amide, making the oxygen more electron dense and hence a better nucleophile.
Lower pKas of conjugate acids suggests a better leaving group. In the case of acyl chlorides, the leaving group is much better than in amides
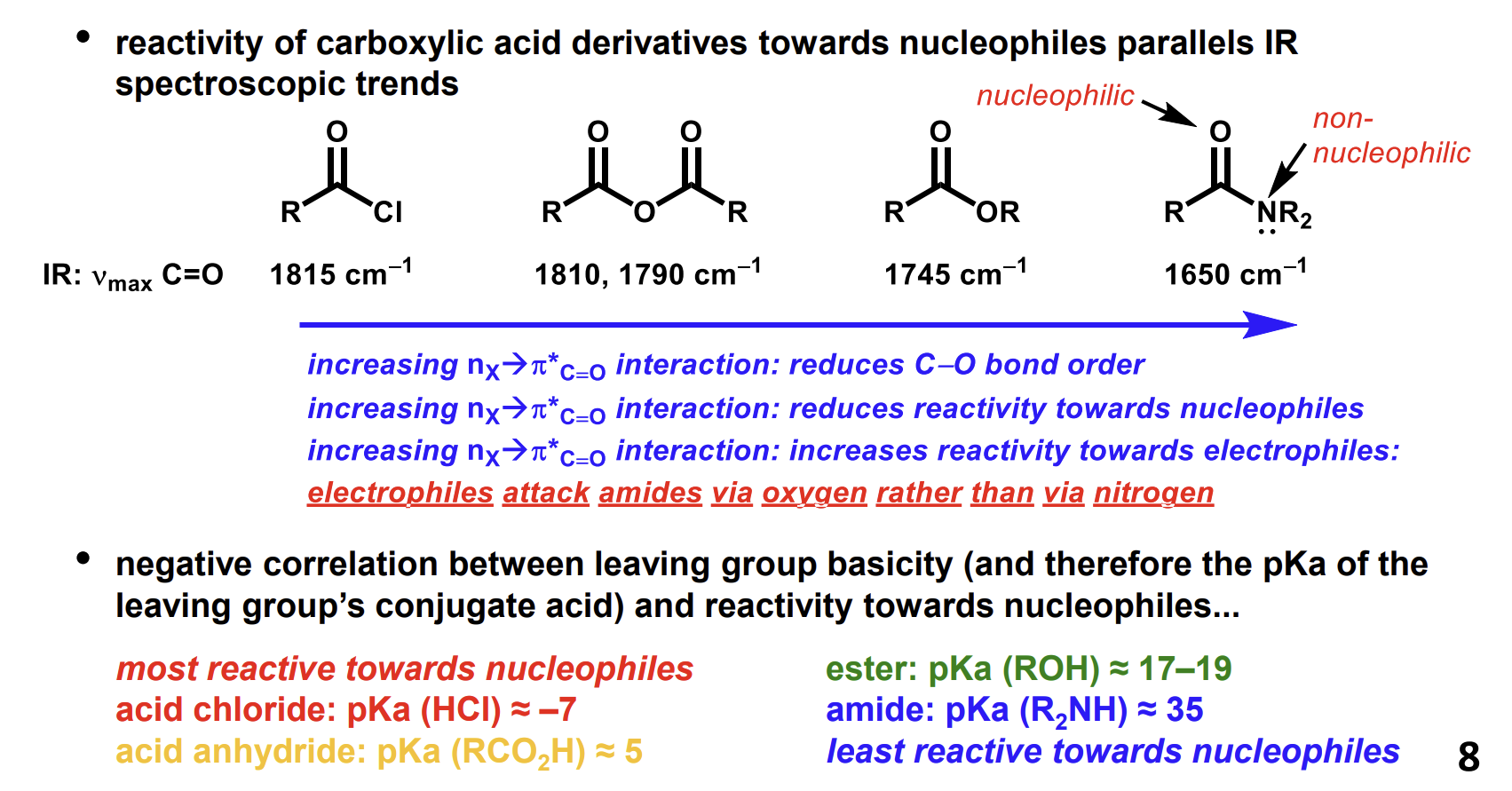
Acyl chlorides reaction with amines and practical optimisations
Forms an amide.
The amide will be protonated by the HCl formed so another base will frequently be used to avoid protonating a large proportion of the amine reagent. Pyridine is very good for this purpose as it is also a solvent and a nucleophilic catalyst which makes the carbonyl carbon more electrophilic.
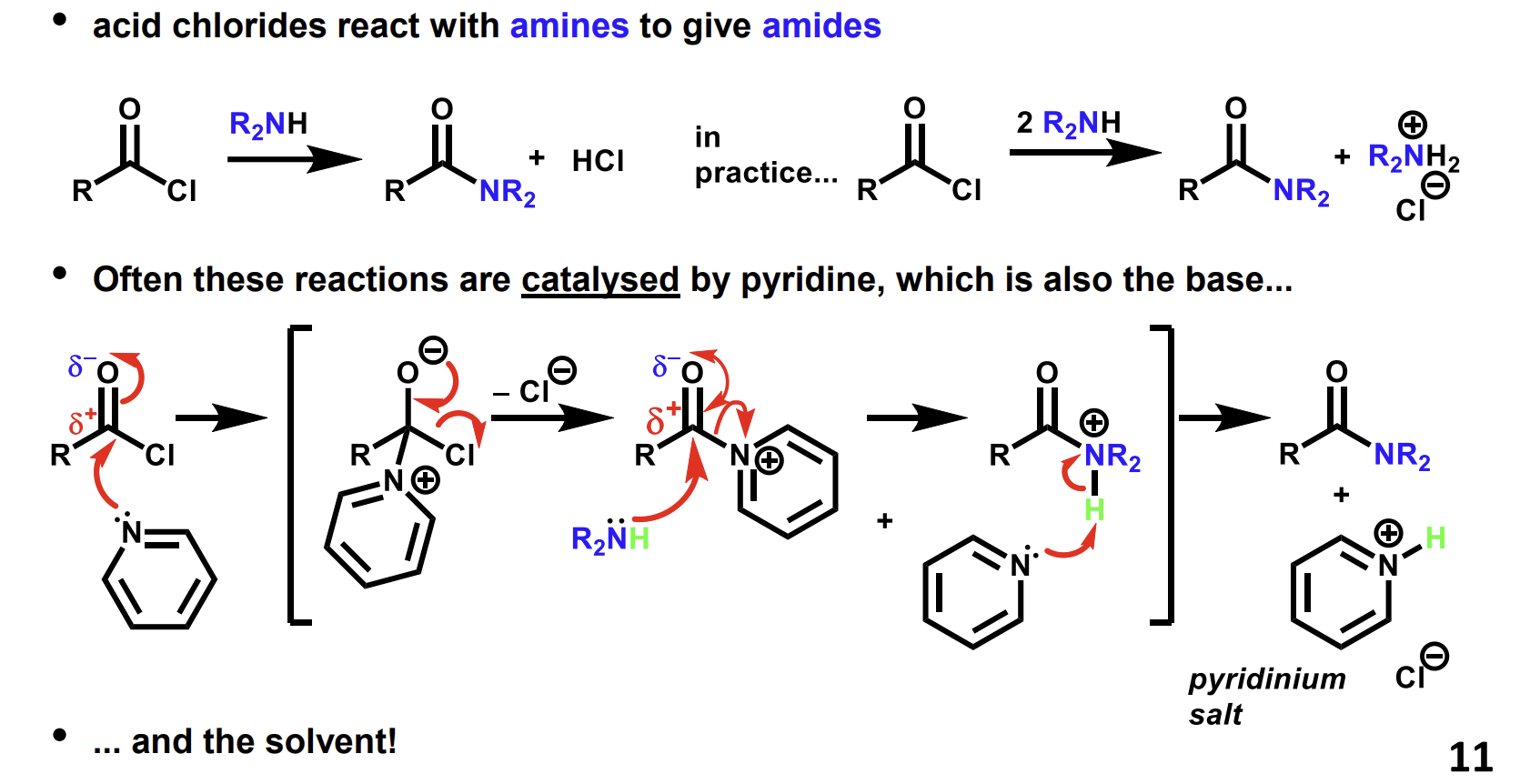
Mechanism for synthesis of acid chlorides using carboxylic acids and thionyl chloride
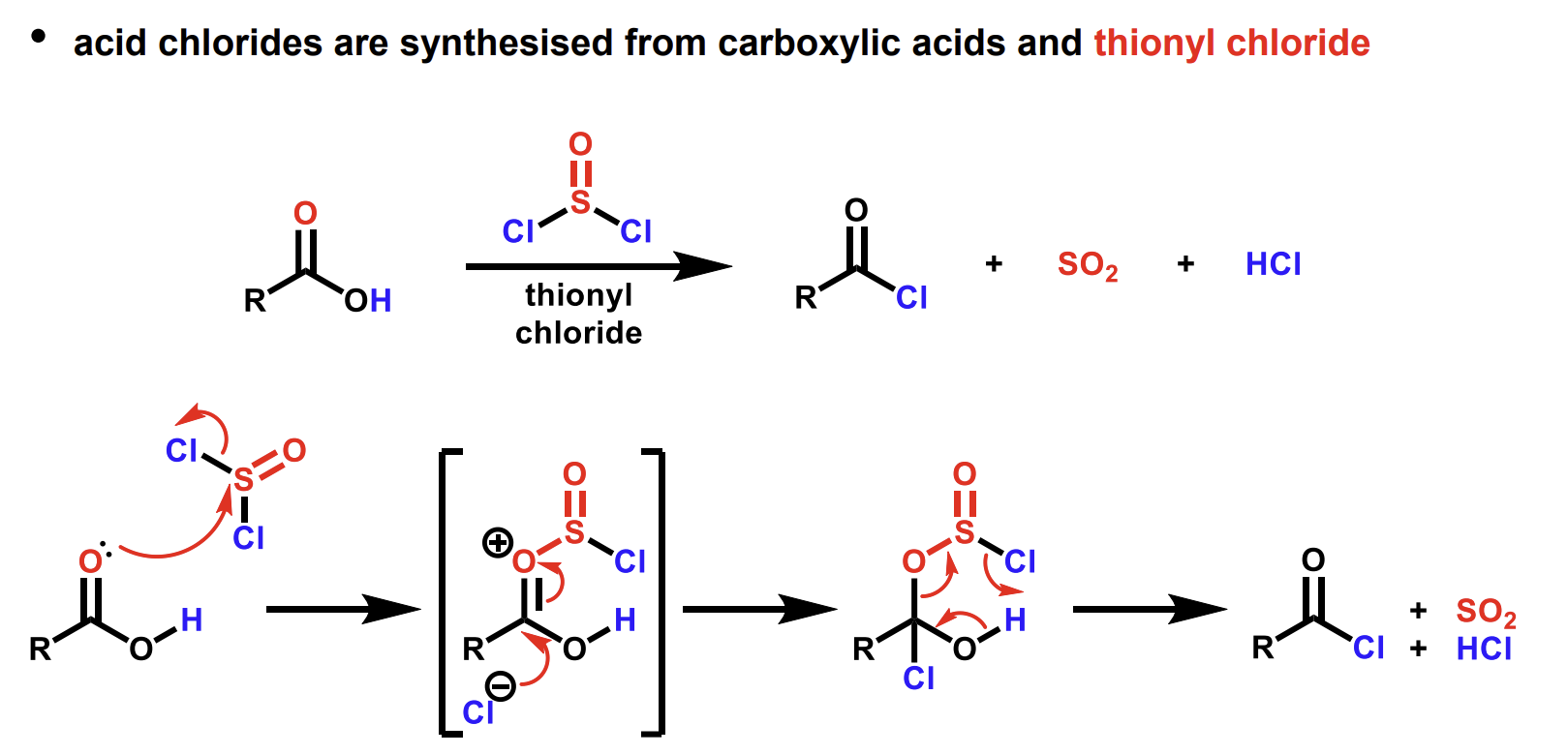
Mechanism for synthesis of esters using carboxylic acids and alcohols in the presence of acid
Sulfuric acid is good here as it is a good dehydrating agent so shifts the equilibrium
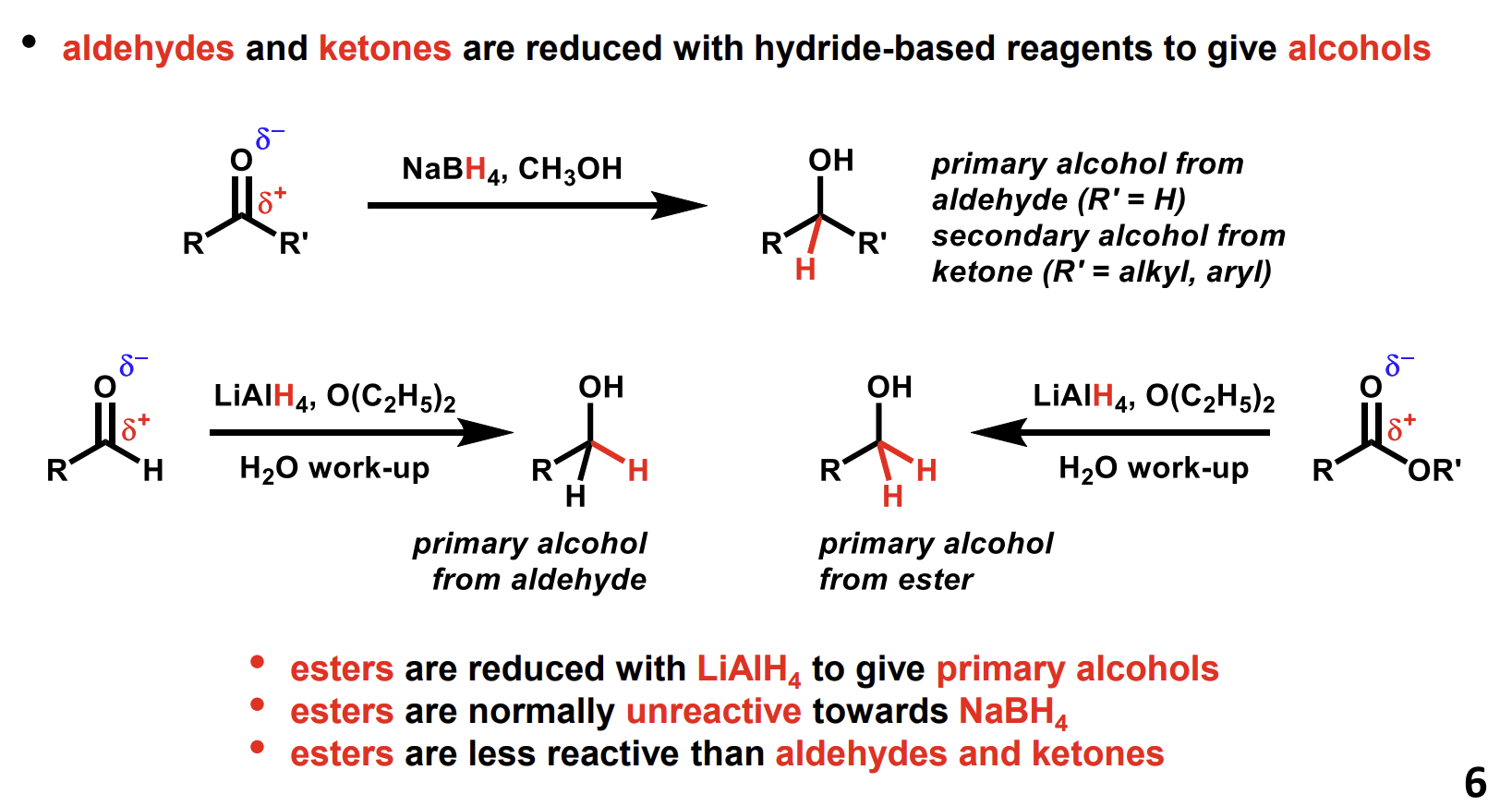
Reduction of aldehydes, ketones and esters using hydride-based reagents
Produces alcohols. NaBH4 is not usually strong enough to reduce esters, LiAlH4 must be used. Note that an additional alcohol product, HOR’ is formed in the ester reaction
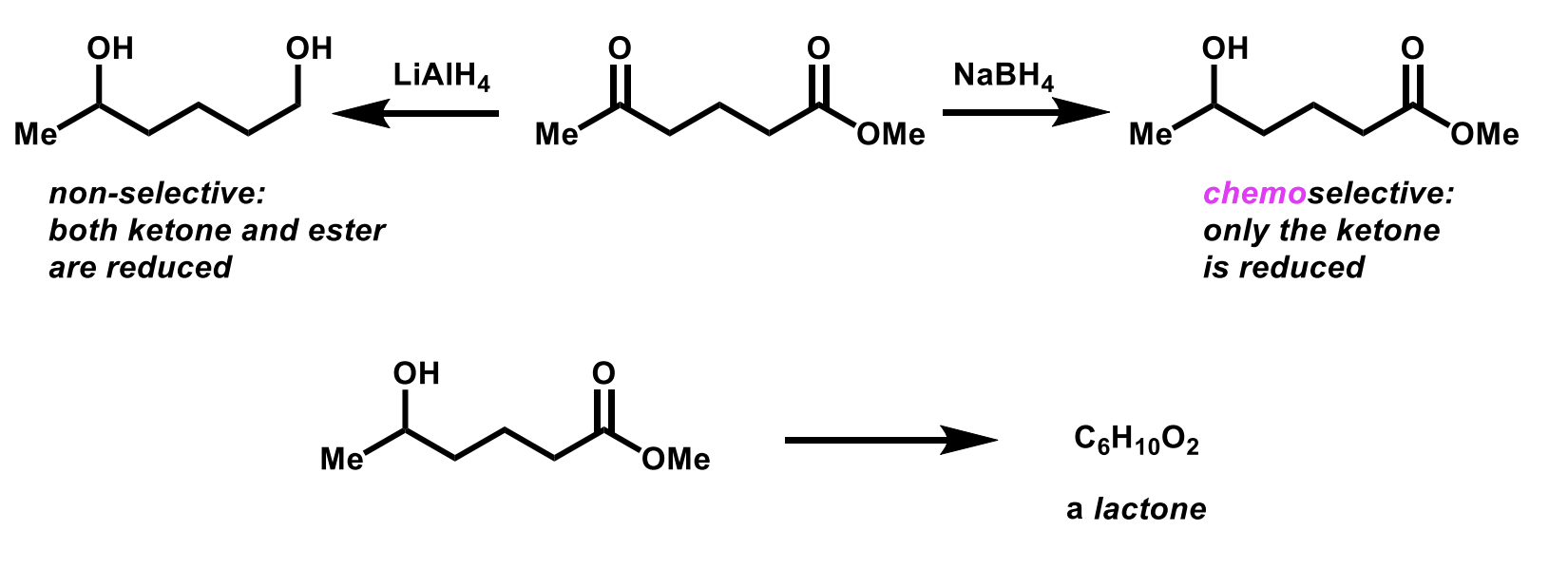
Chemoselective reaction
More than one functional group which are distinguished by the reagent.
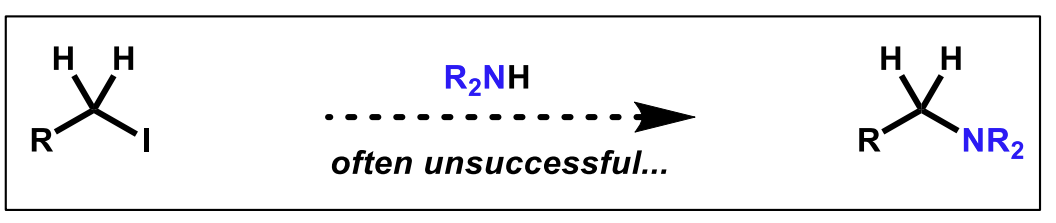
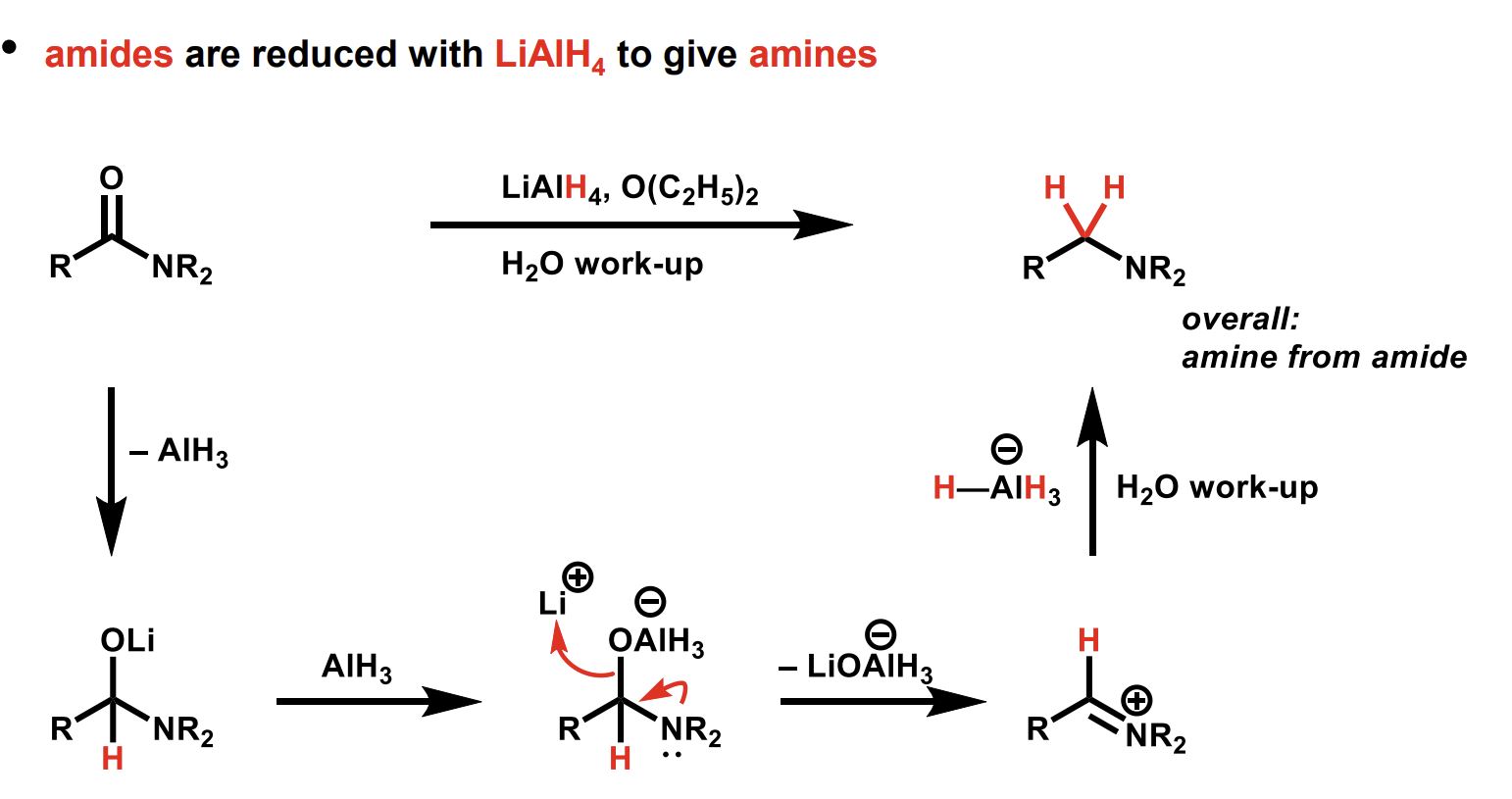
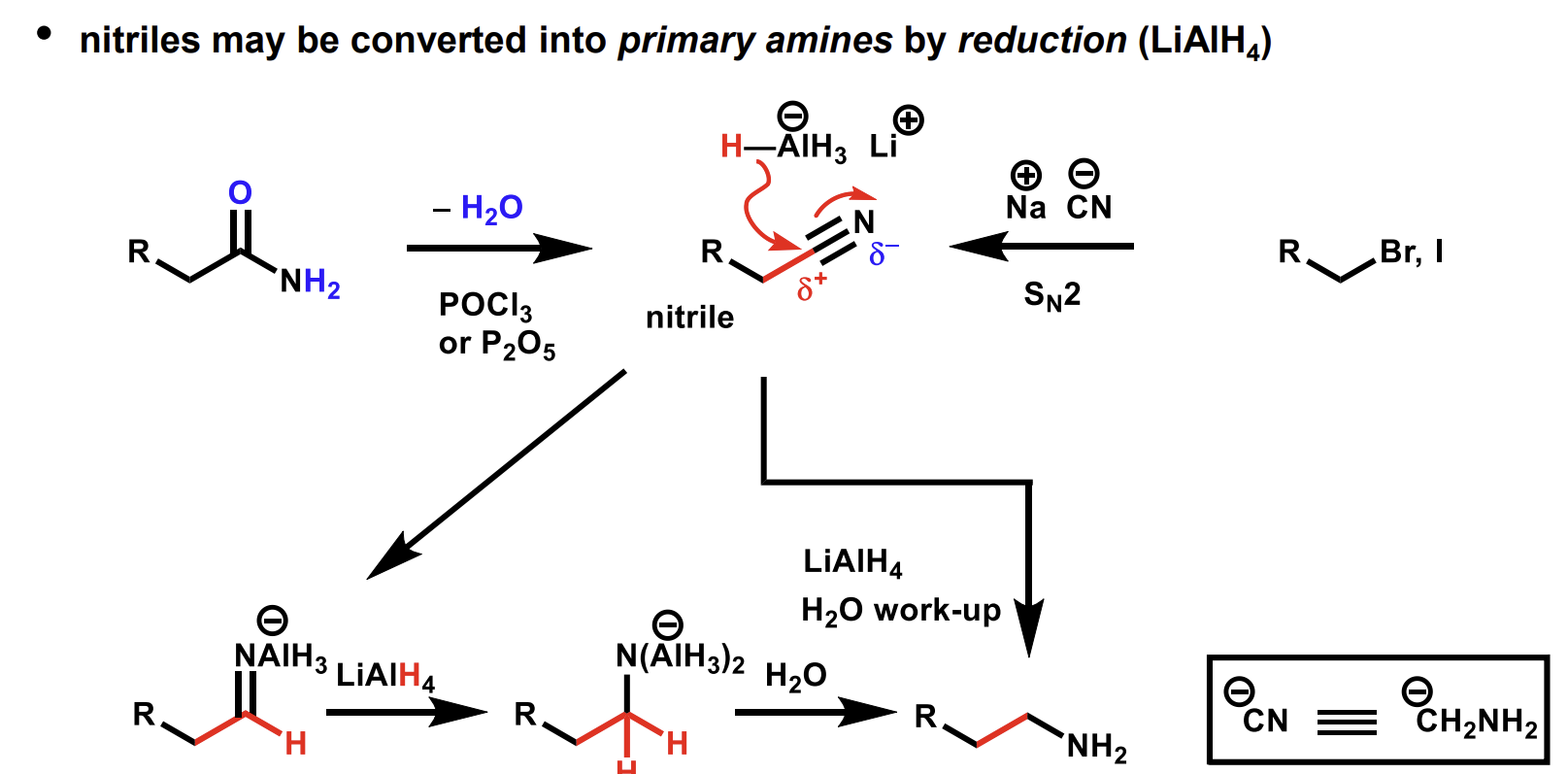
What is an alternative way to generate this amine
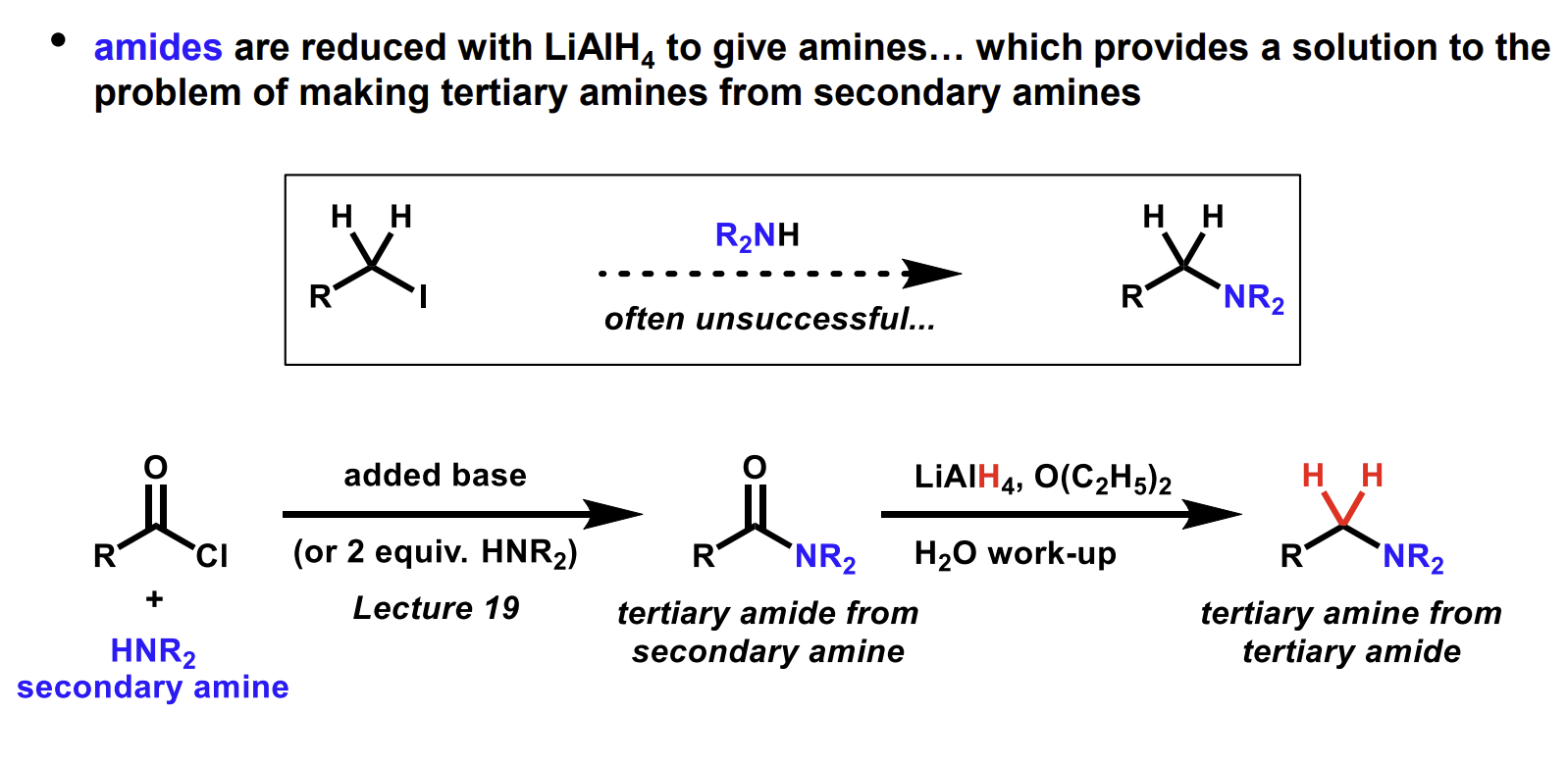
Mechanism for this reduction
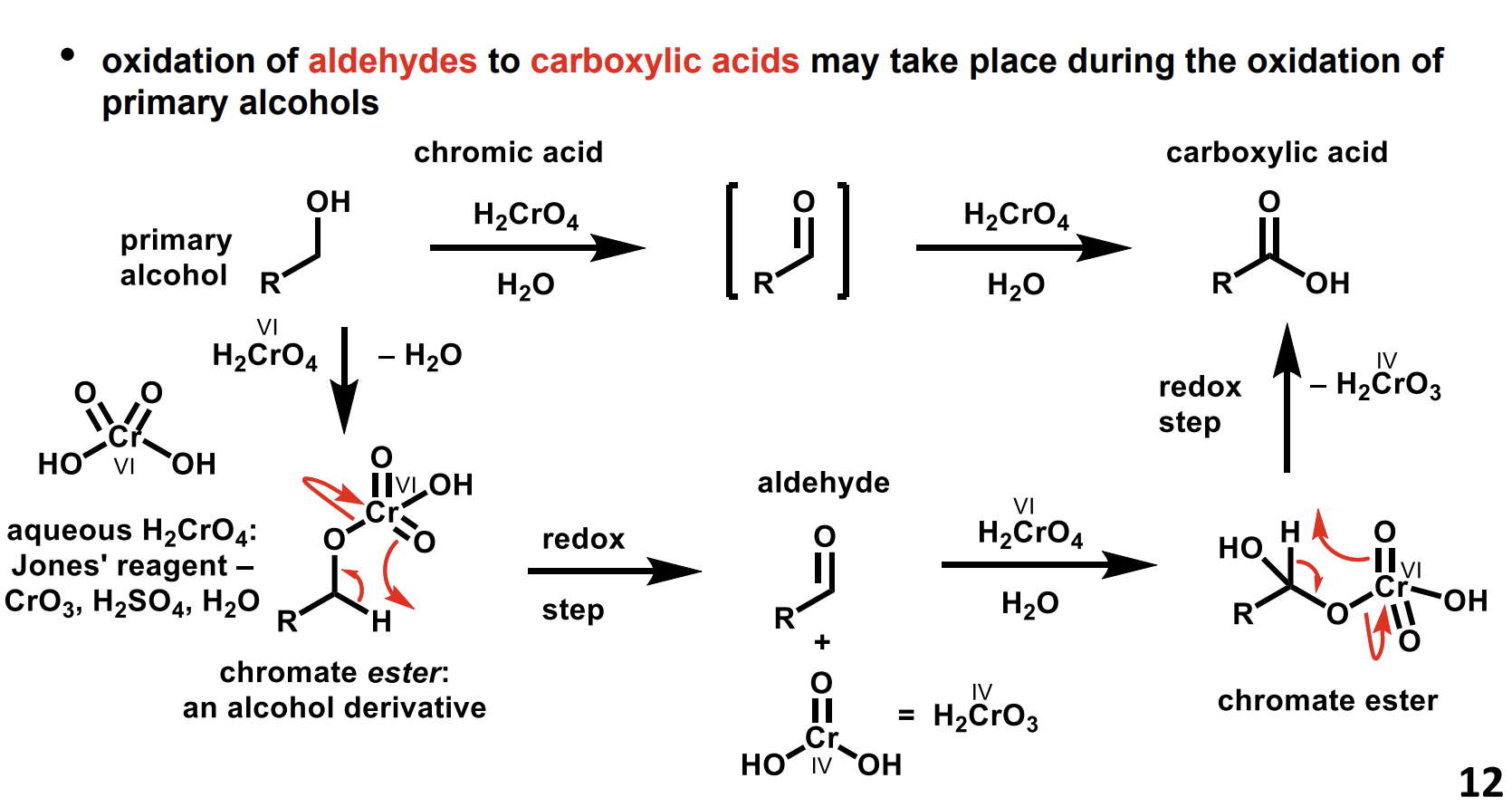
Method to convert a primary alcohol into a carboxylic acid via an aldehyde
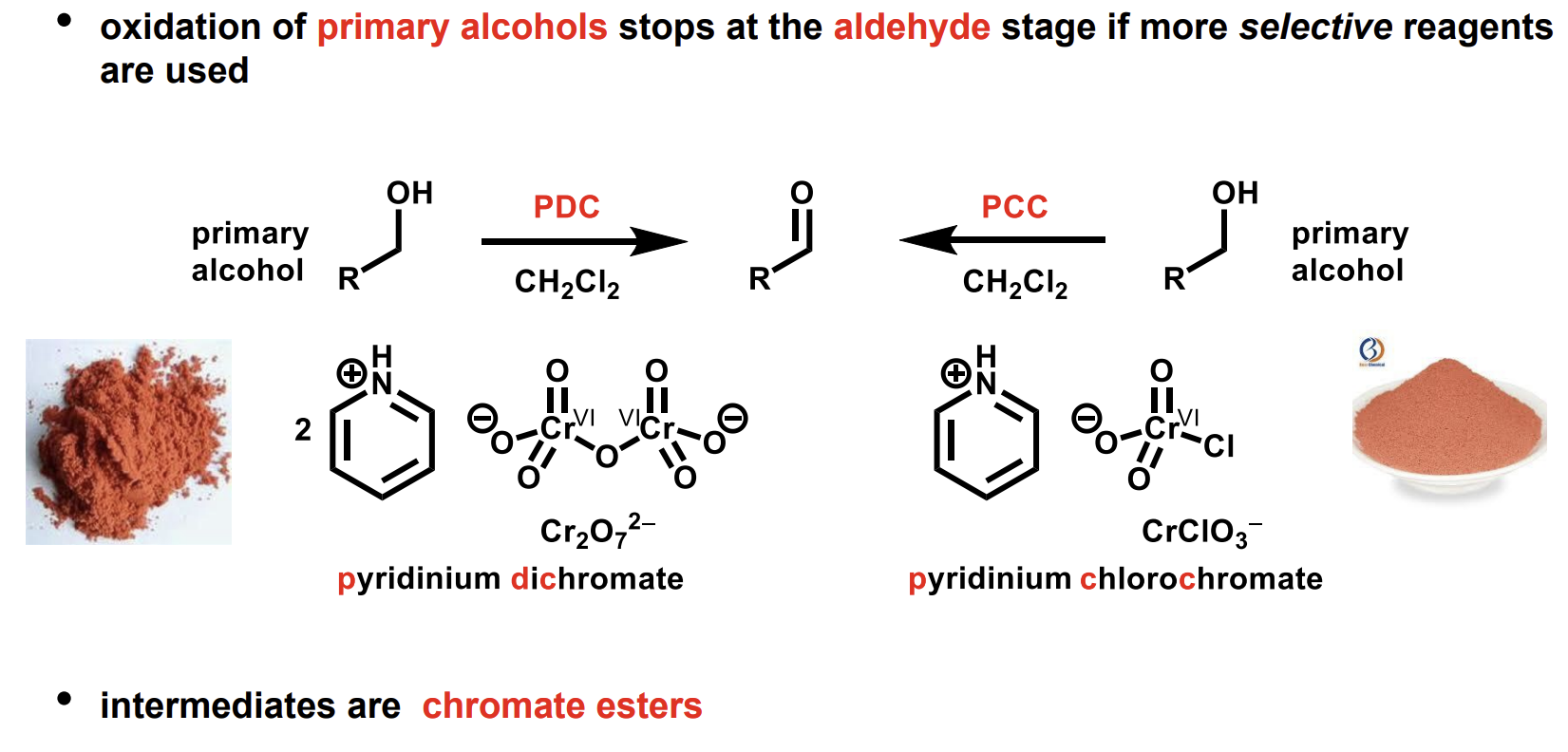
How can we stop this oxidation at the aldehyde level
Using more selective reagents.
Oxidation of secondary alcohols to ketones

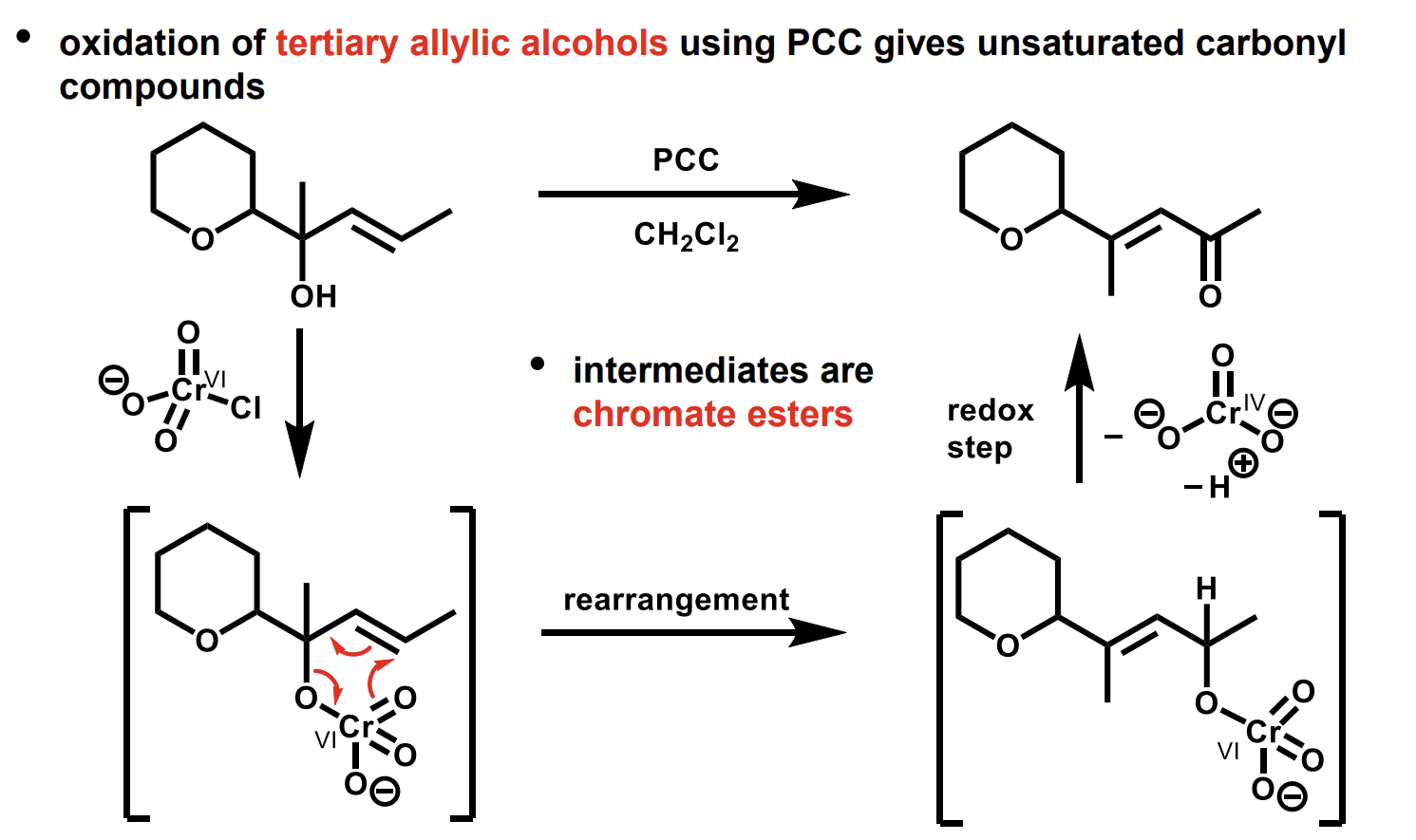
What does oxidation of tertiary allylic alcohols using PCC give
Oxidation of ketones to give esters
Uses a peracid
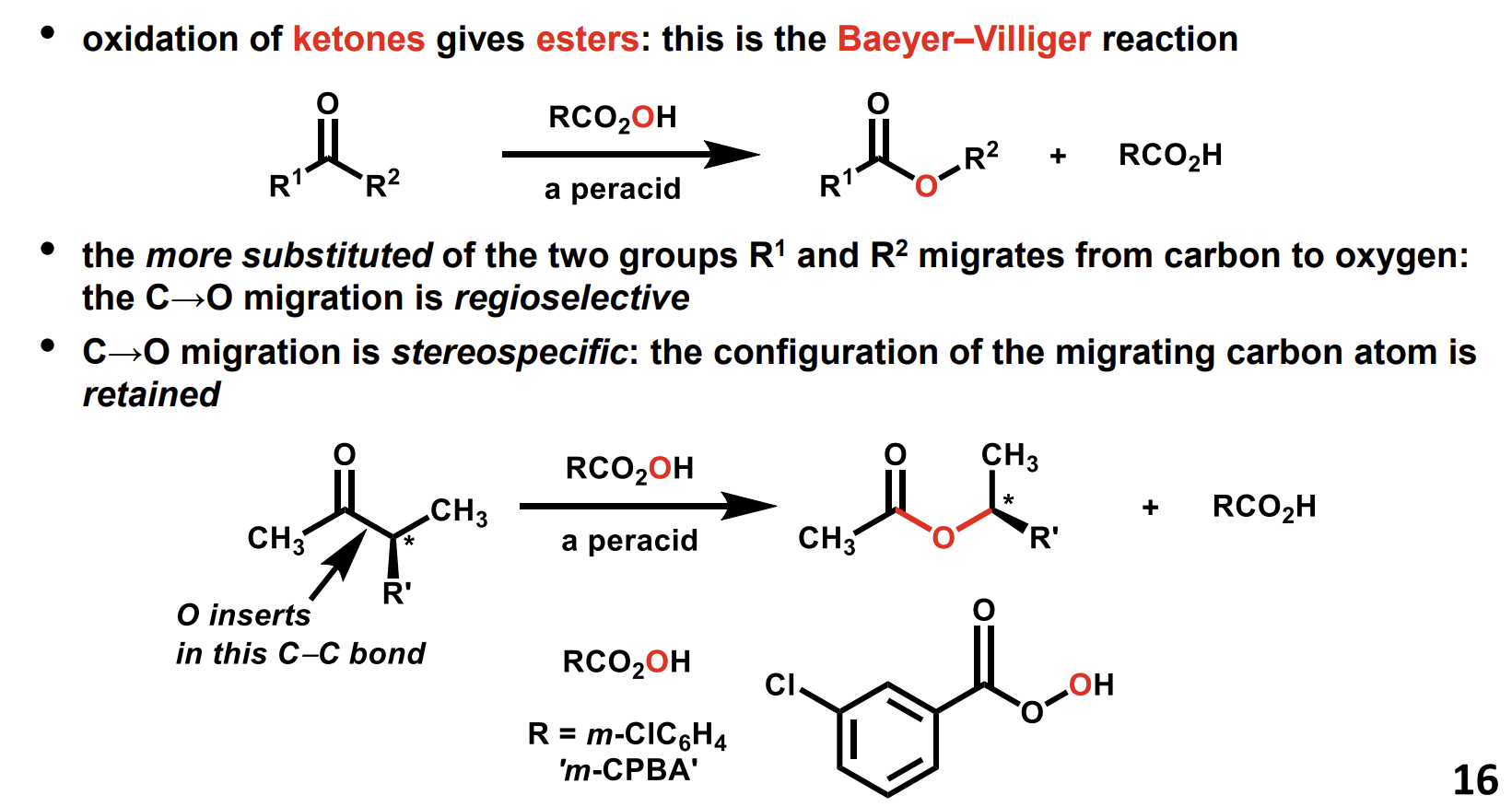
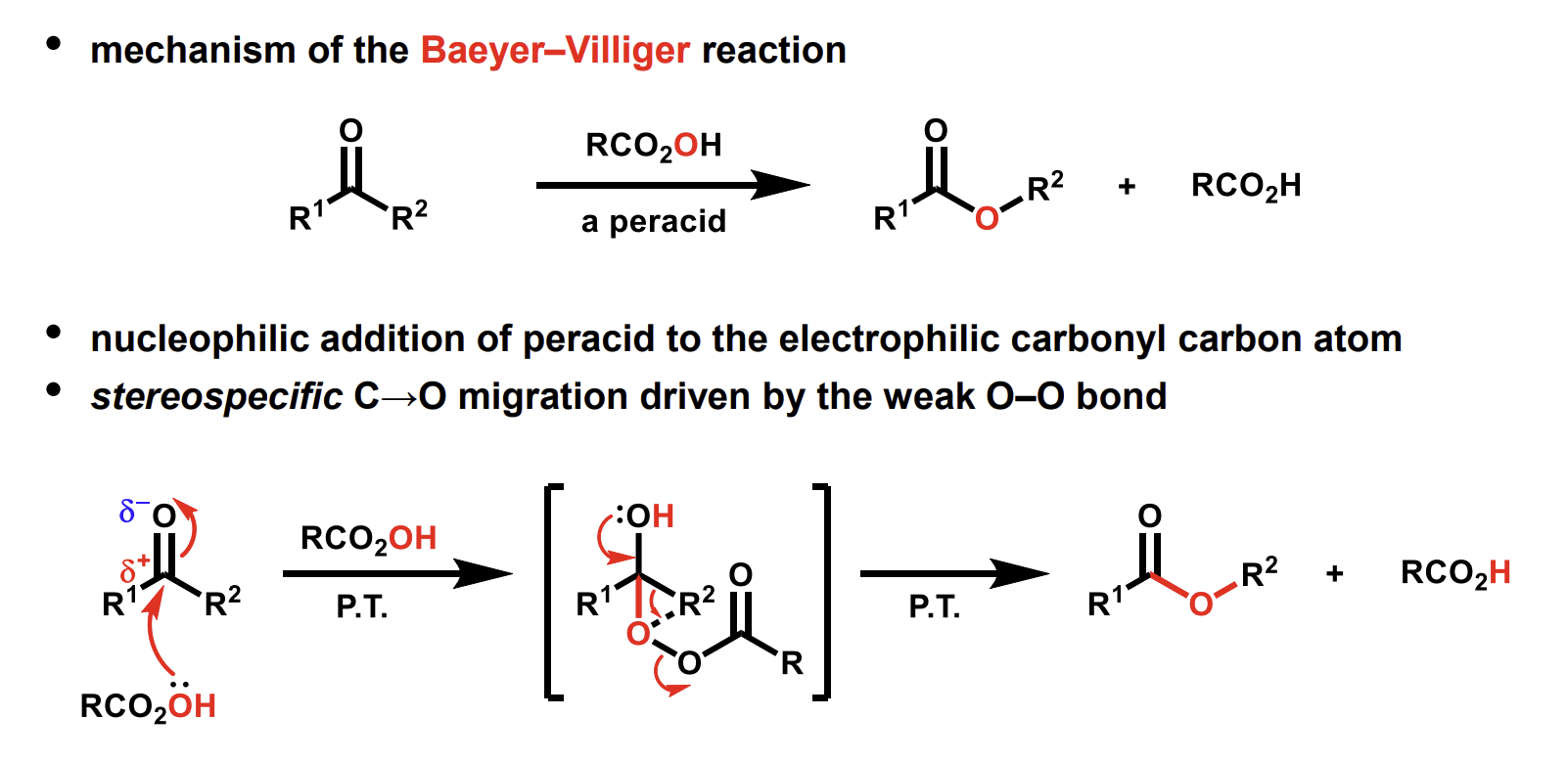
Mechanism of this oxidation
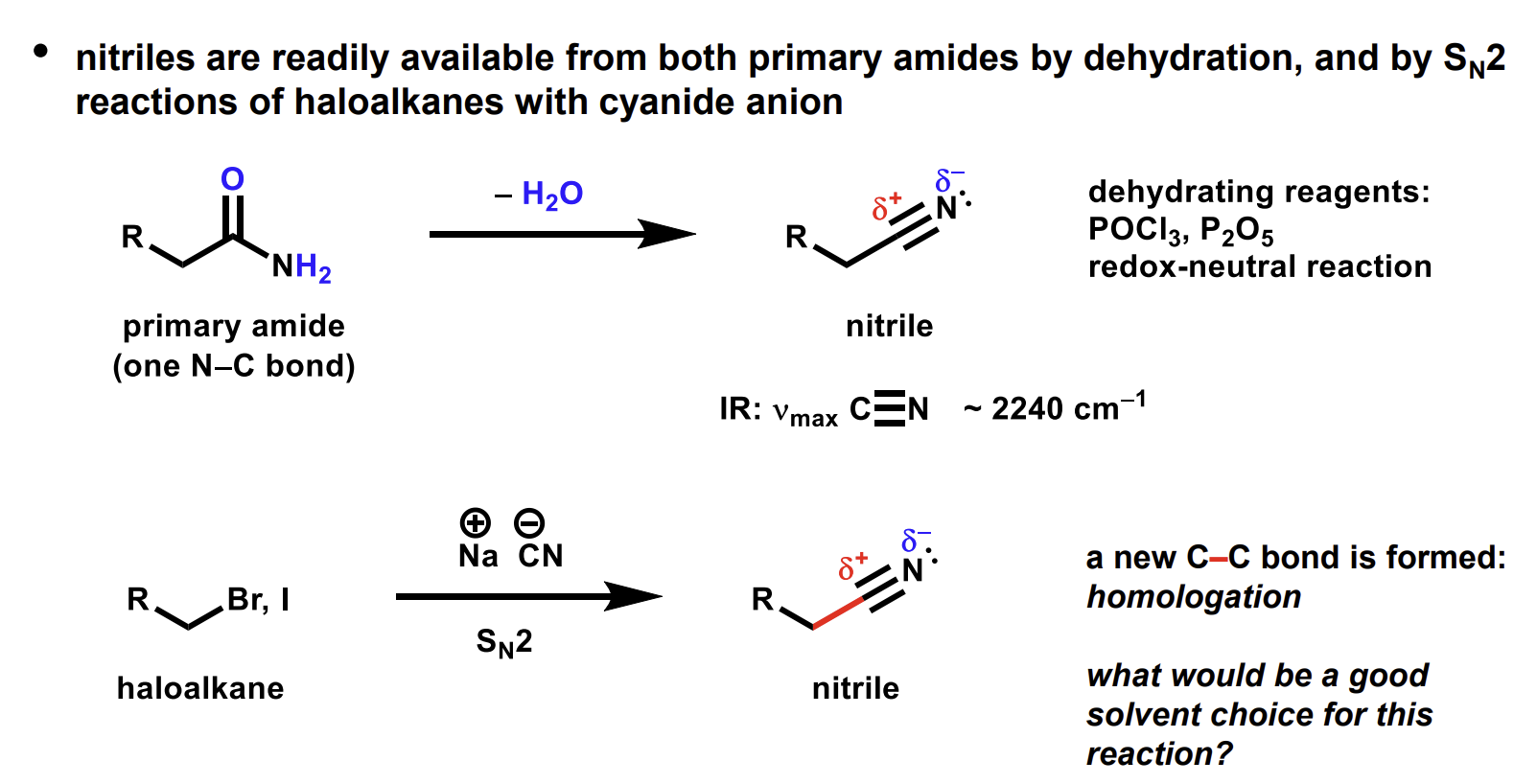
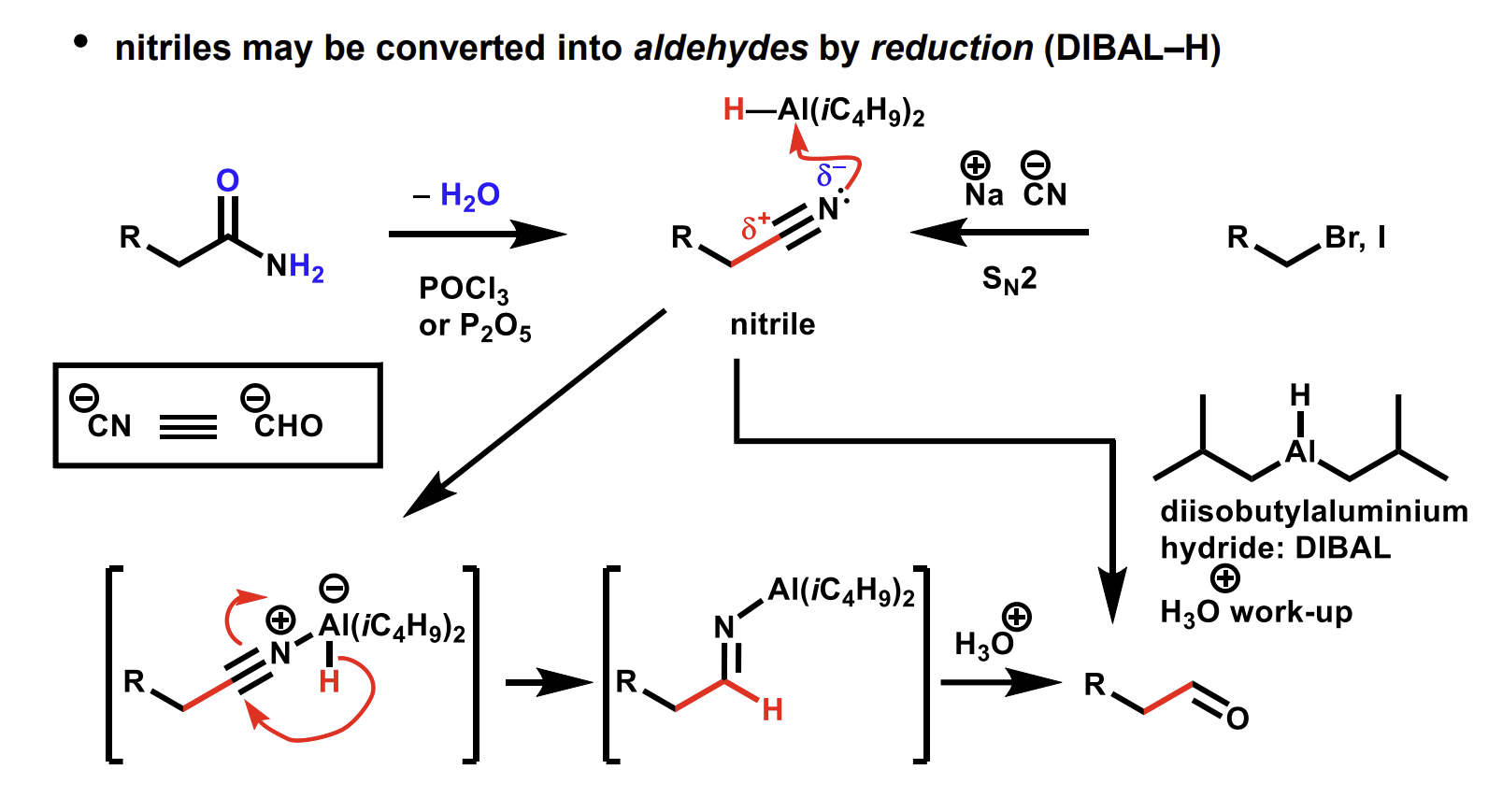
Methods to make nitriles
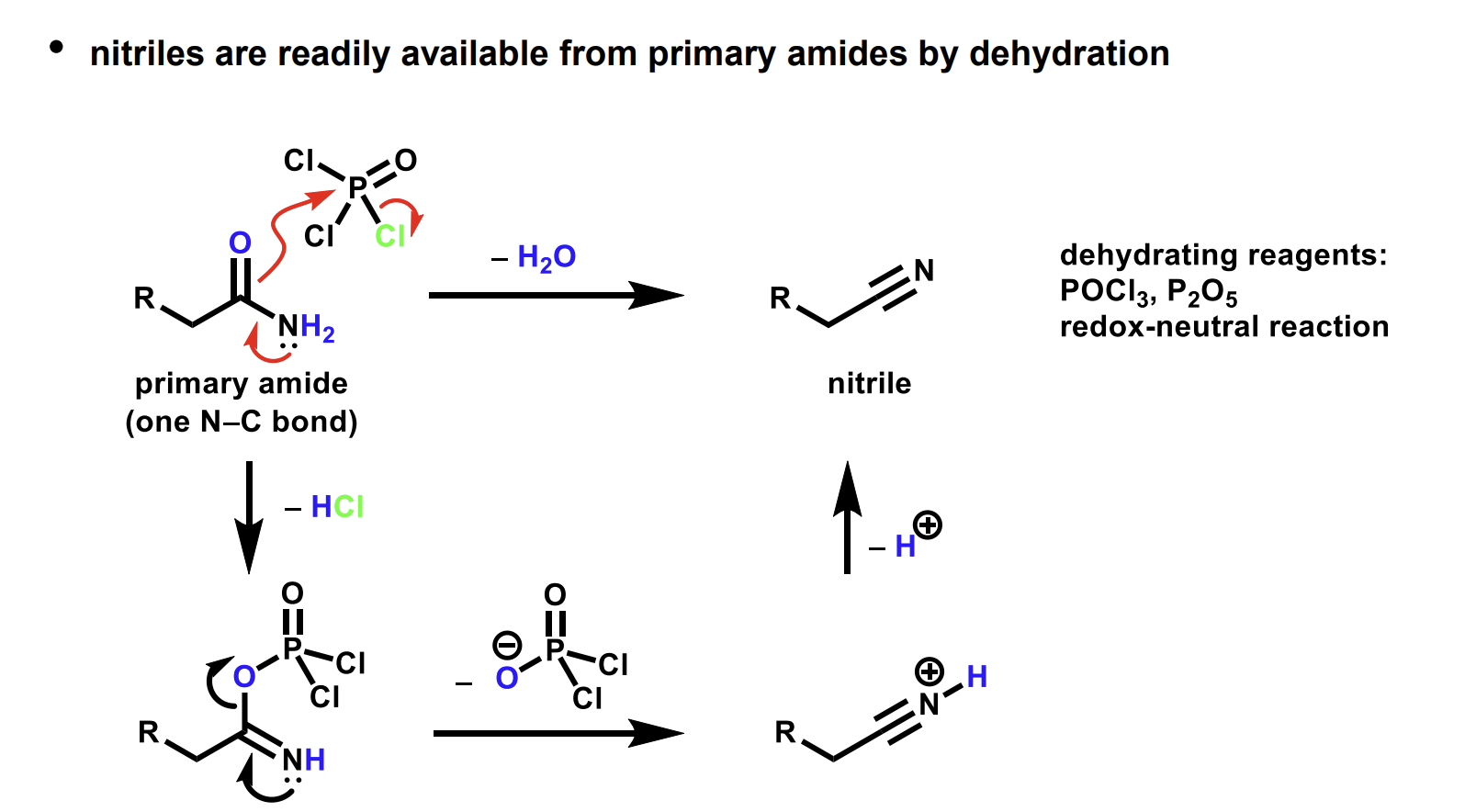
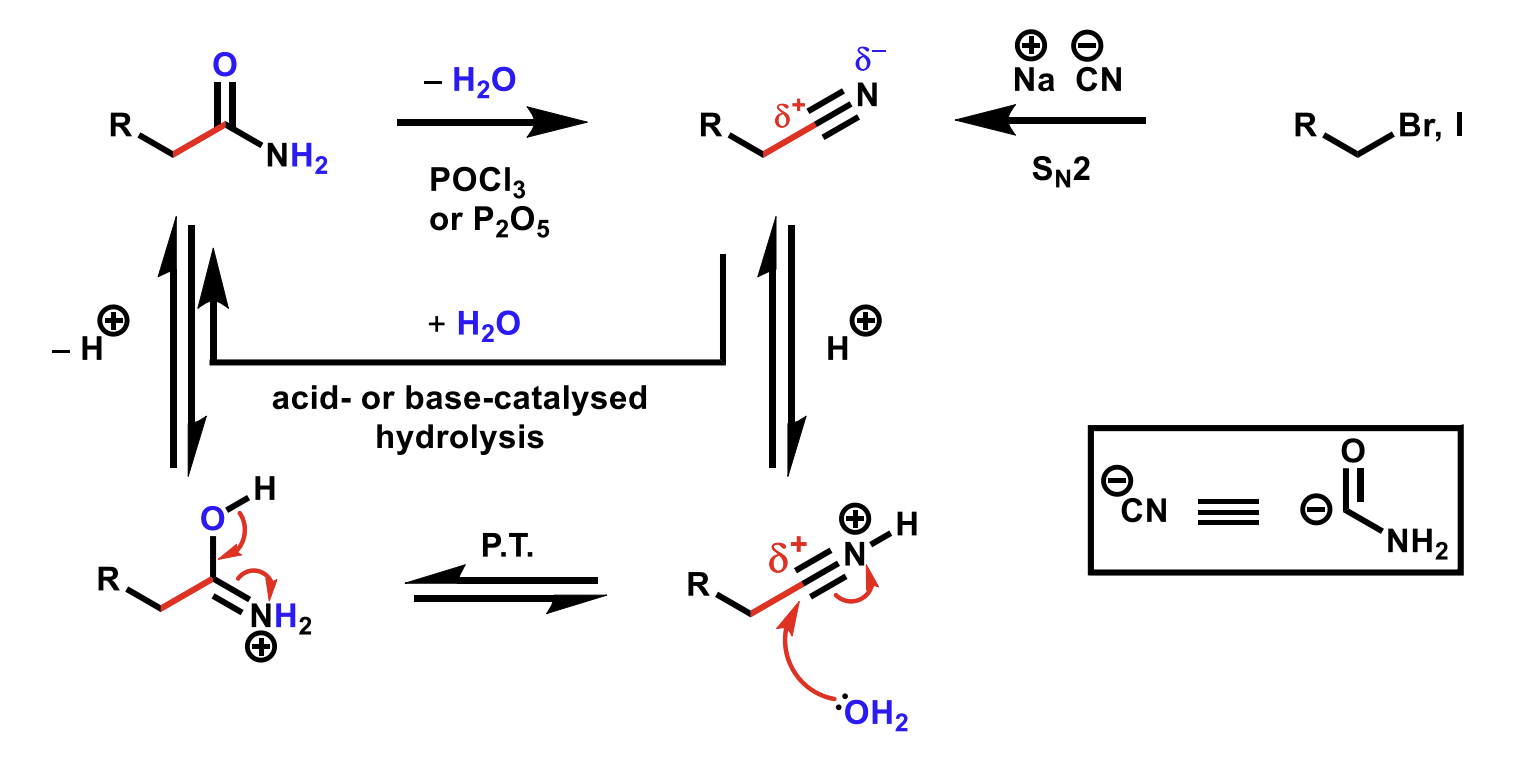
Dehydration of amides mechanism
Summary of reactions of nitriles
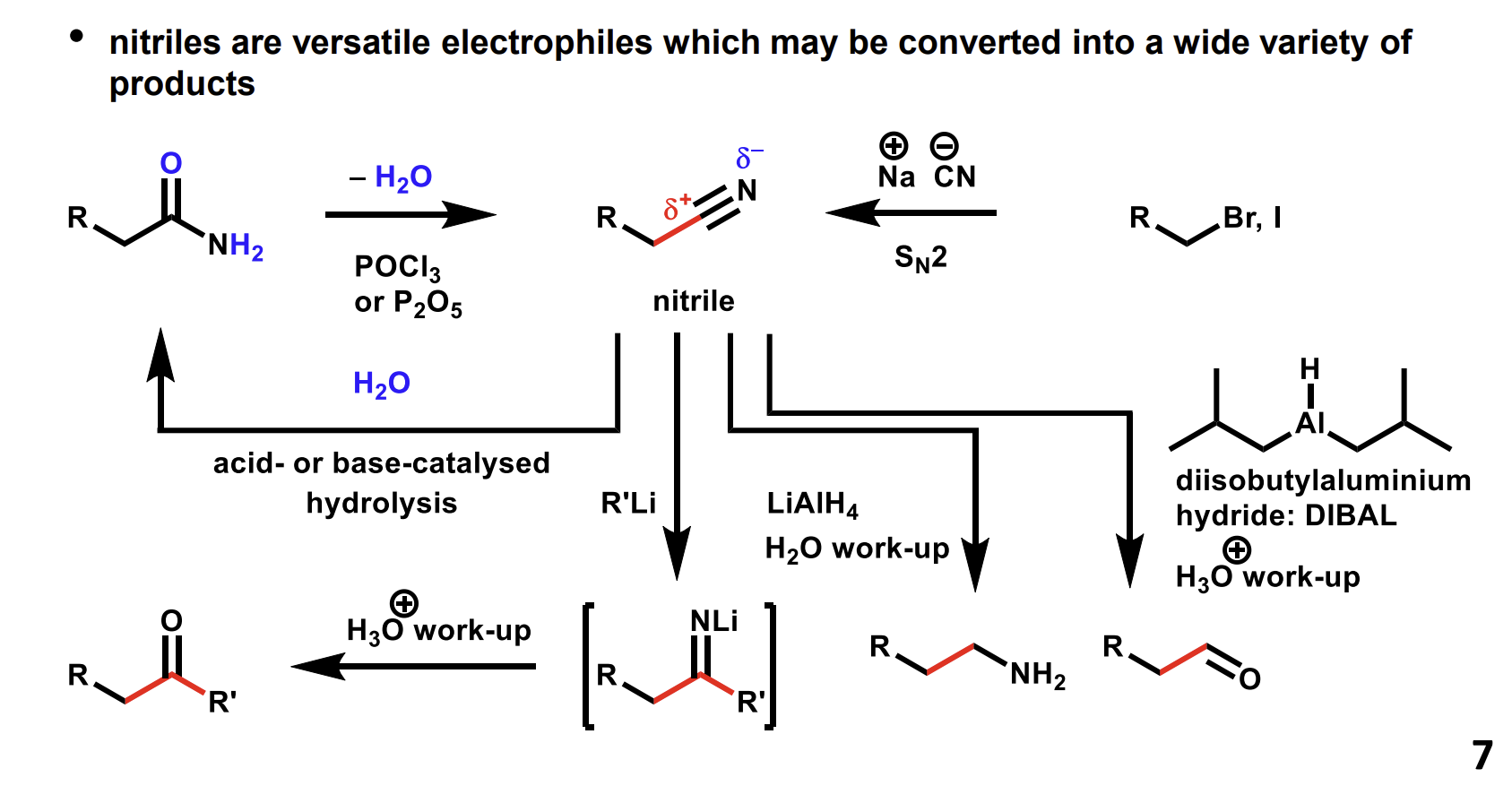
Converting nitriles into amides mechanism
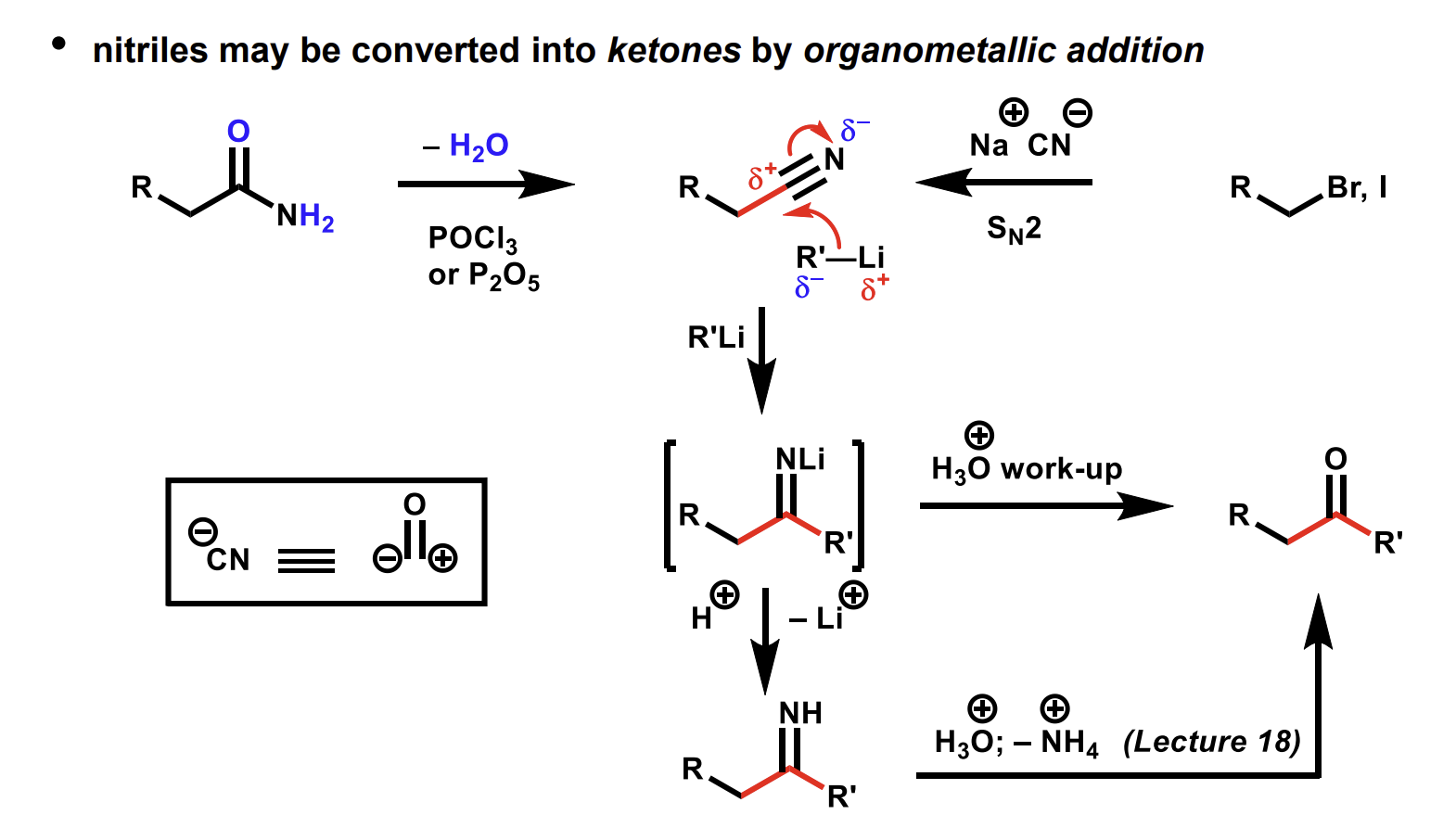
Conversion of nitriles to ketones using organometallic reagents.
Reduction of nitriles into primary amines
Reduction of nitriles into aldehydes using DIBAL
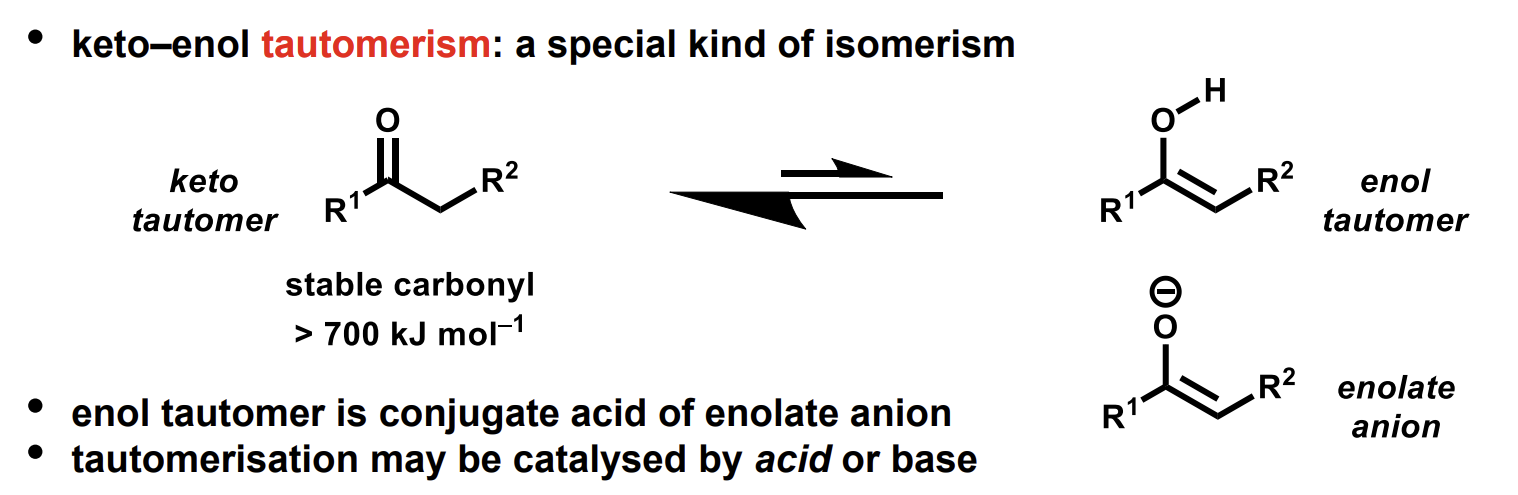
what do keto-enol tautomers look like
enol and enolate are distinct - not isomers and do not freely interconvert in isolation
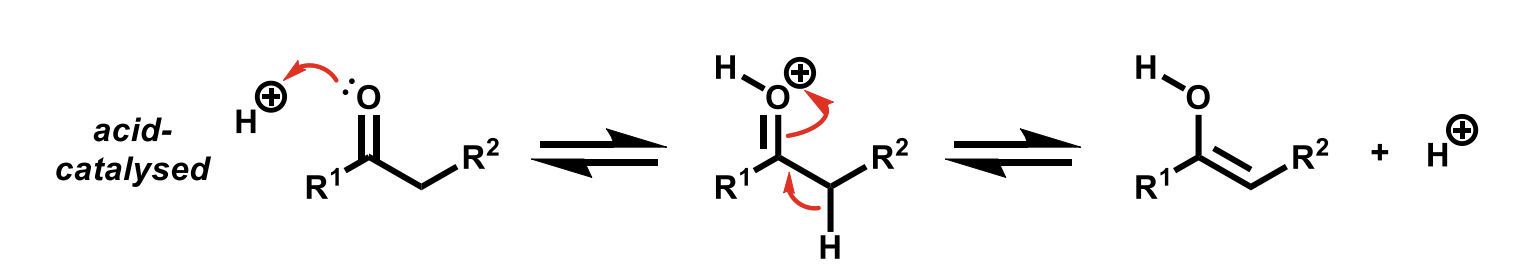
Acid catalysed tautomerisation
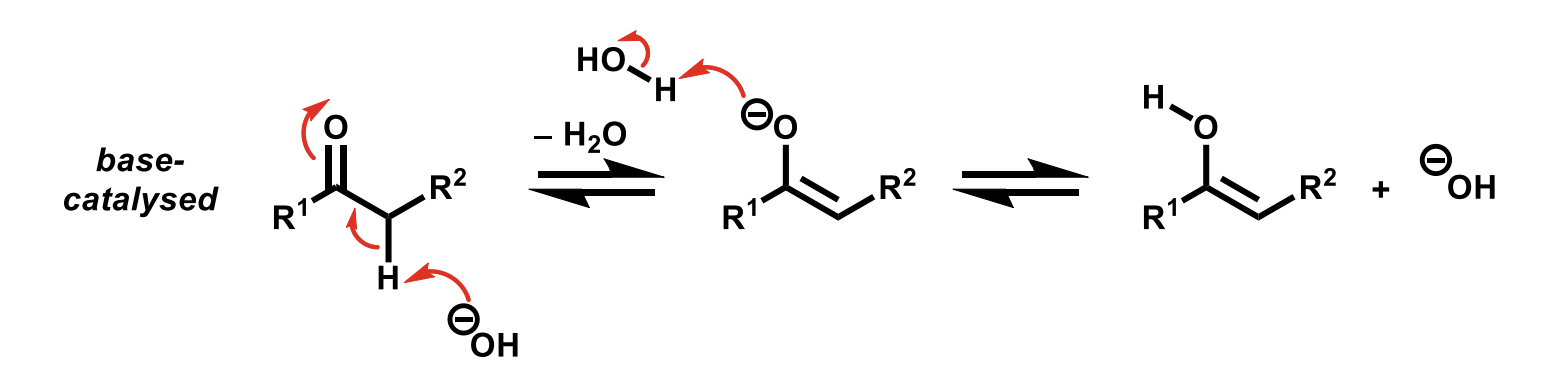
Base-catalysed tautomerisation
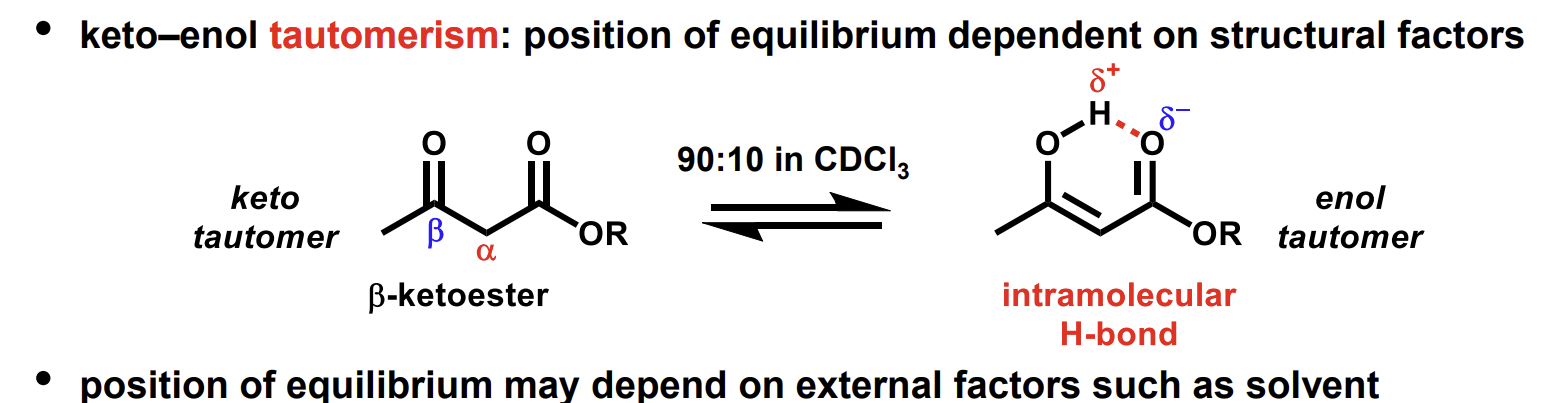
Factors affecting tautomerisation equilibrium
Certain structures like this one favours the enol more than others - in acetone a tiny proportion of enol tautomer would exist.
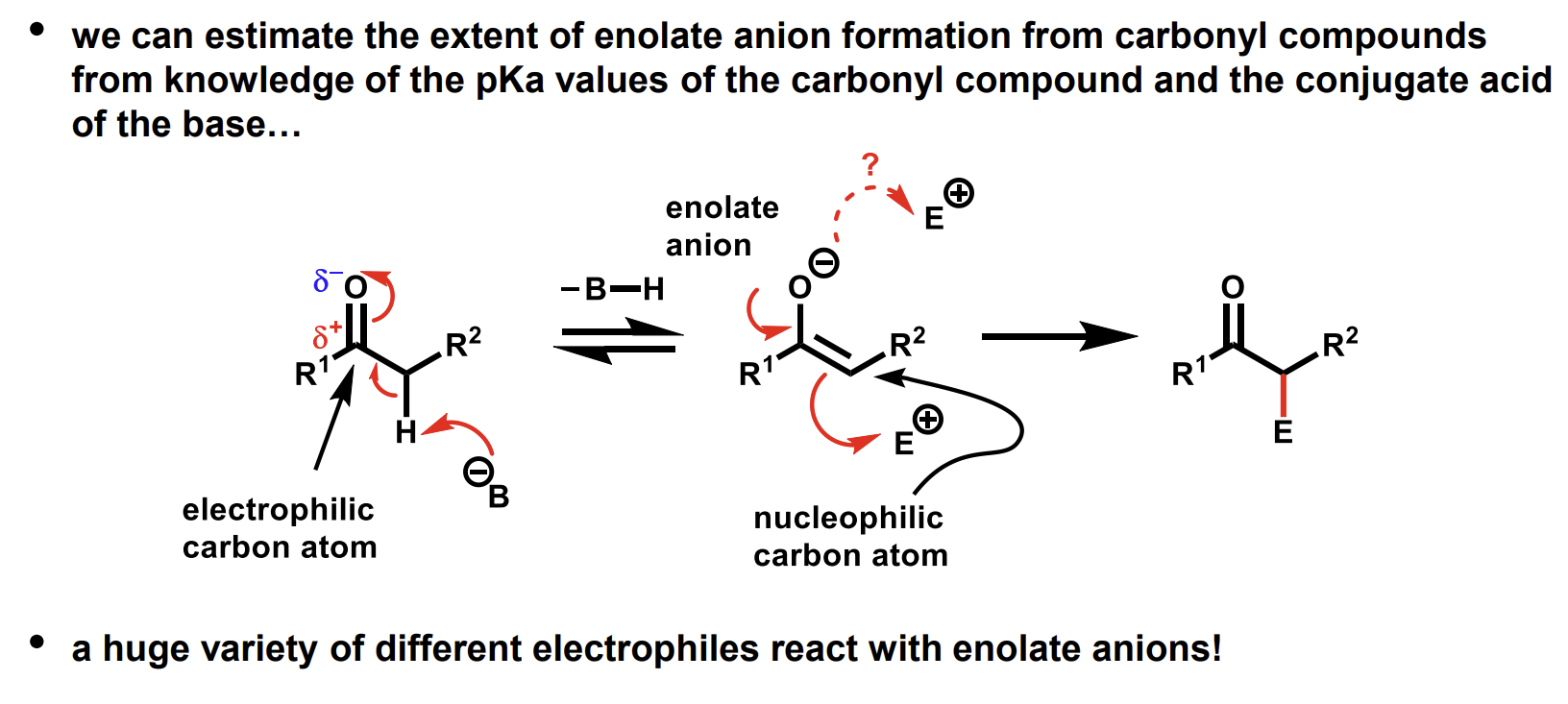
Enolate reactions with electrophiles
Enolates are ambident nucleophiles - they have 2 points at which they can act as nucleophiles.