Joints and articulations
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
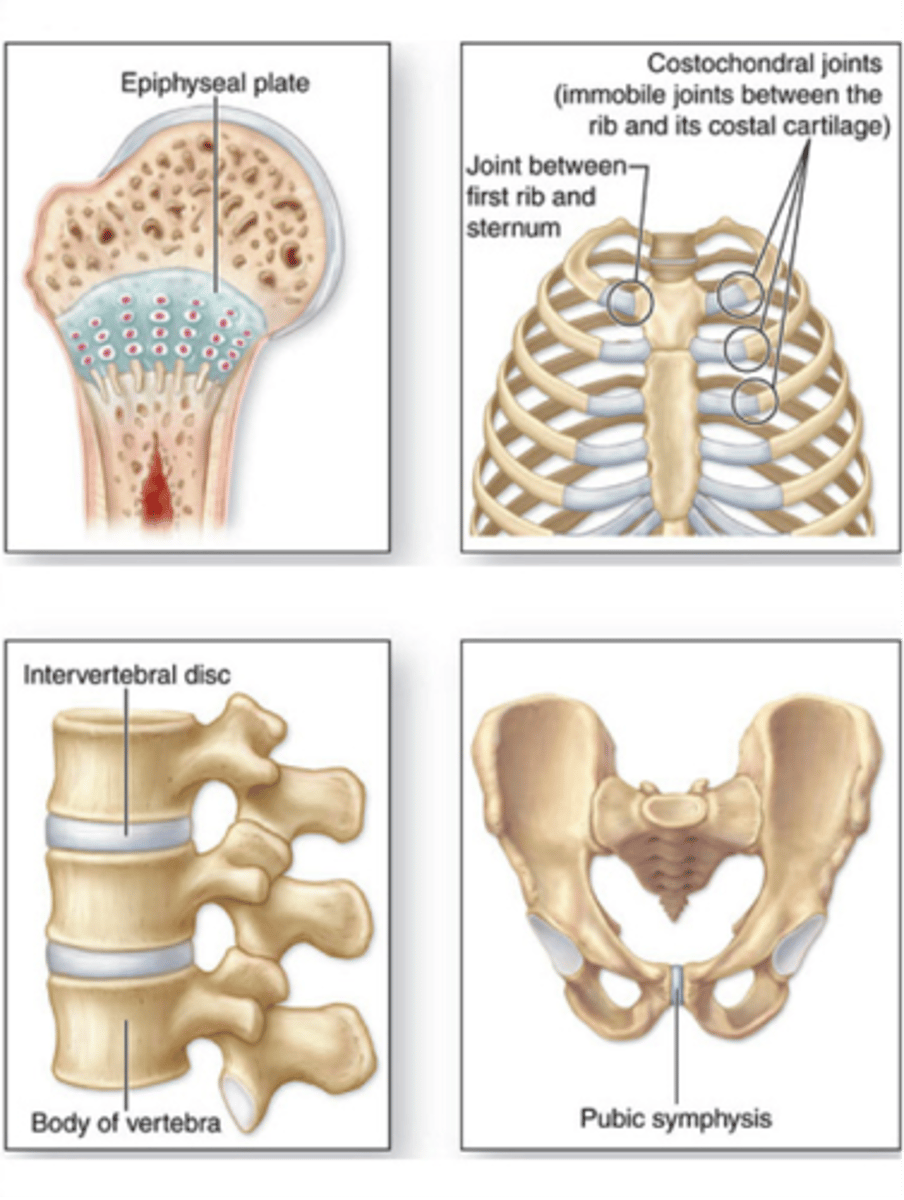
synathroses
immovable joints composed of joints, fibrocartilage, or hyaline cartilage. synarthrotic ex: Epiphyseal plates, sternocostal joint between manubrium and first rib
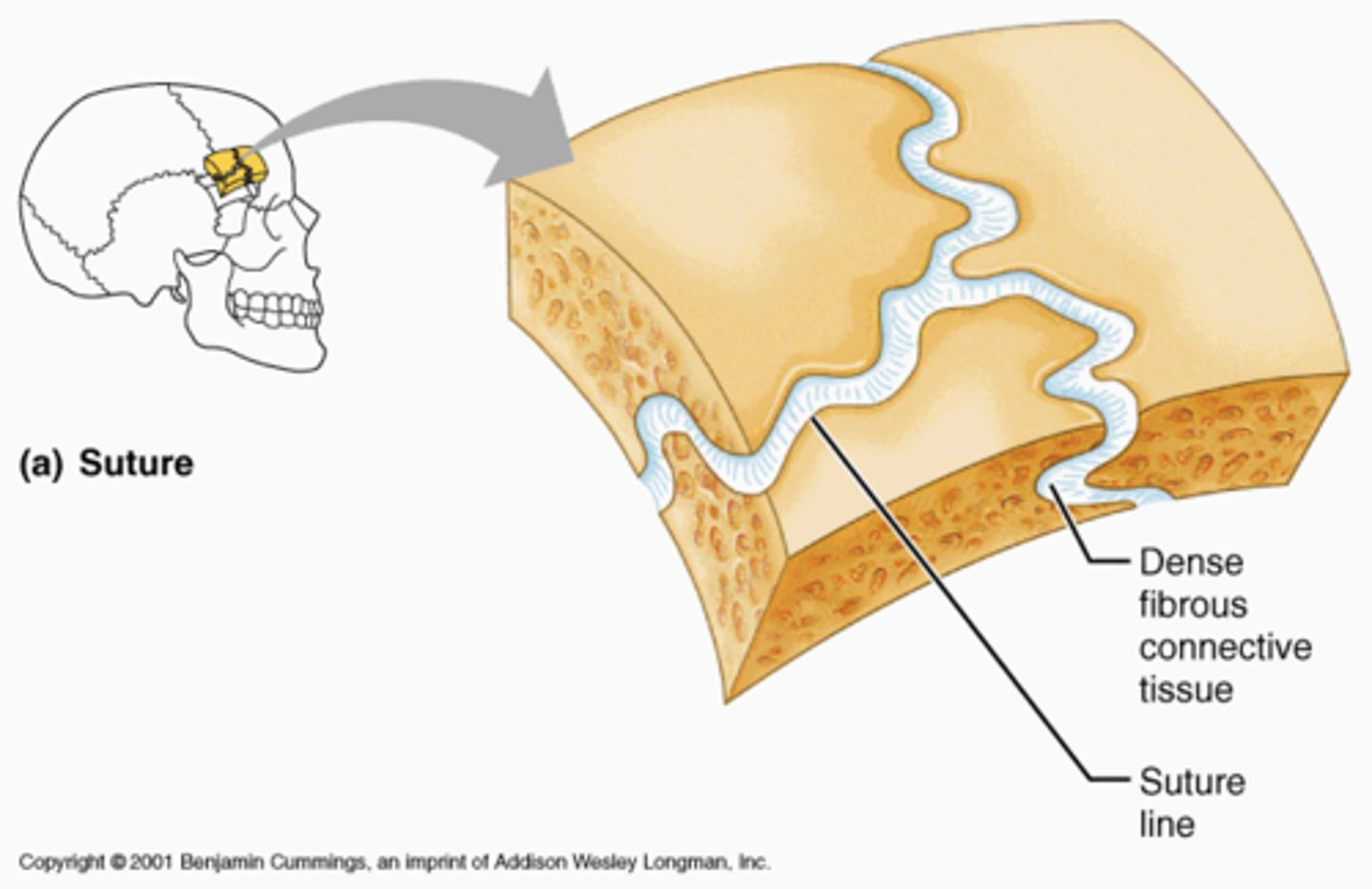
amphiarthrosis
slightly movable joints composed of cartilage or fibrocartilage aka cartilaginous
ie. where the fibula and tibia meet
public symphysis
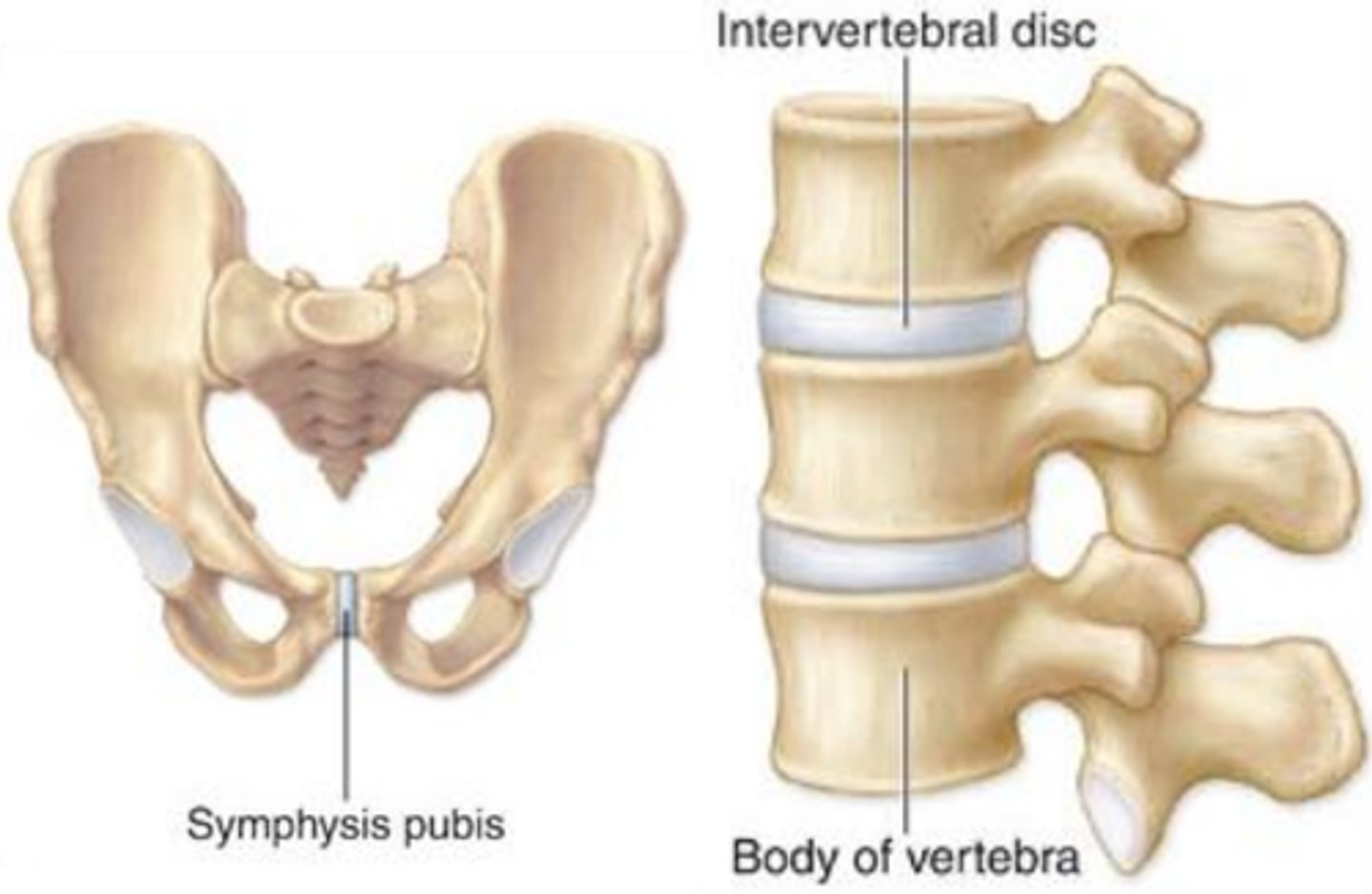
diarthroses
free moveable synovial joint composed of articular cartilage aka synovial
ie. tibia, hips, femur, hands
synovial fluid
in the diarthroses in which it lubricates the joint
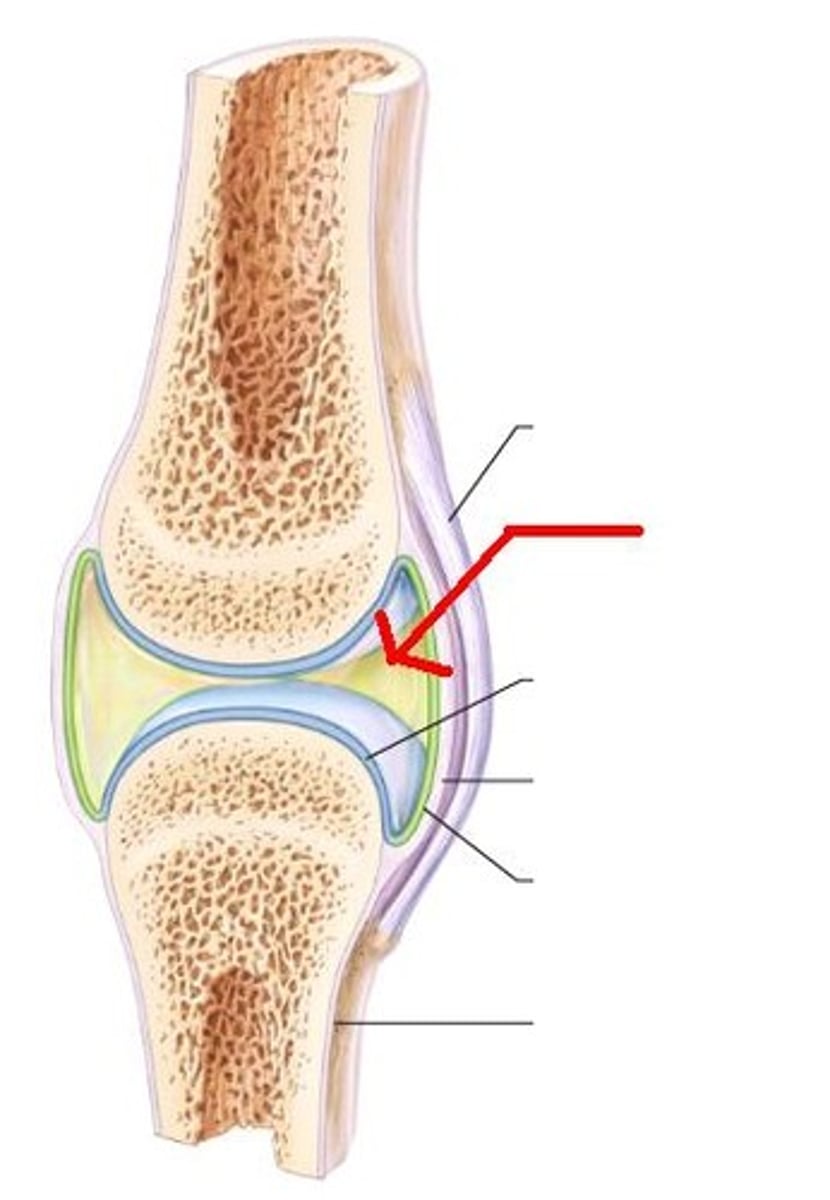
synovial sac
contains the synovial fluid and makes a gap so joints can move
extension
type of angular movement when you bend your arm back, increasing the angle
hyperextension
type of angular movement when you move your arm further back than normal anatomical positioning
abduction
type of angular movement is when you raise your arms away from your body
circumduction
type of angular movement that combines all 5 angular movements that allow the forearm to move in a circle while the elbow remains stable
adduction
type of angular movement when you move your arms back down to your body
rotational
when you move your whole arm to turn the bone around its axis
supination
being able to turn the palm of your hand anteriorly
pronation
being able to turn your hand backward or posteriorly
dorsiflexion
Flexion of a body part in an upward (dorsal) direction
joint
the sites where two or more bones meet
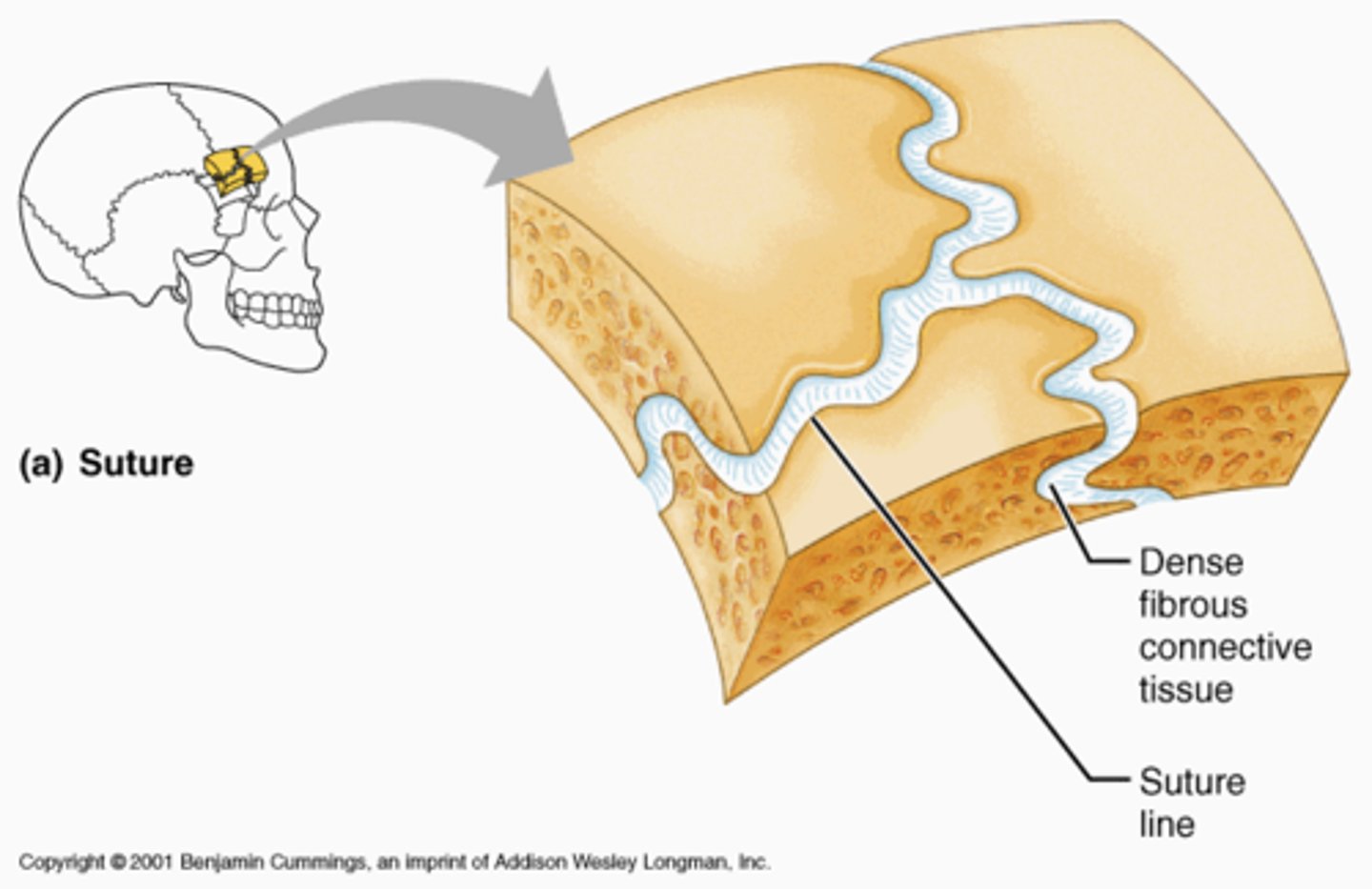
fibrous joint
a fibrous joint is where the bone ends are held together by fibrous connective tissue ( primarily composed of collagen fibers)
cartilaginous joint
the articulating bones are held together by a pad or disc of cartilage.
synarthroses joint
Immovable joints
diarthroses joint
freely moveable joint
amphiarthroses joint
Slightly movable
ligaments
Connect bone to bone
gliding joint
allows one bone to slide over another; found in wrist and ankles
saddle joint
Two concave surfaces fit against a convex surface
Thumbs
hinge joint
Joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane
pivot joint
a freely moving joint in which movement is limited to rotation
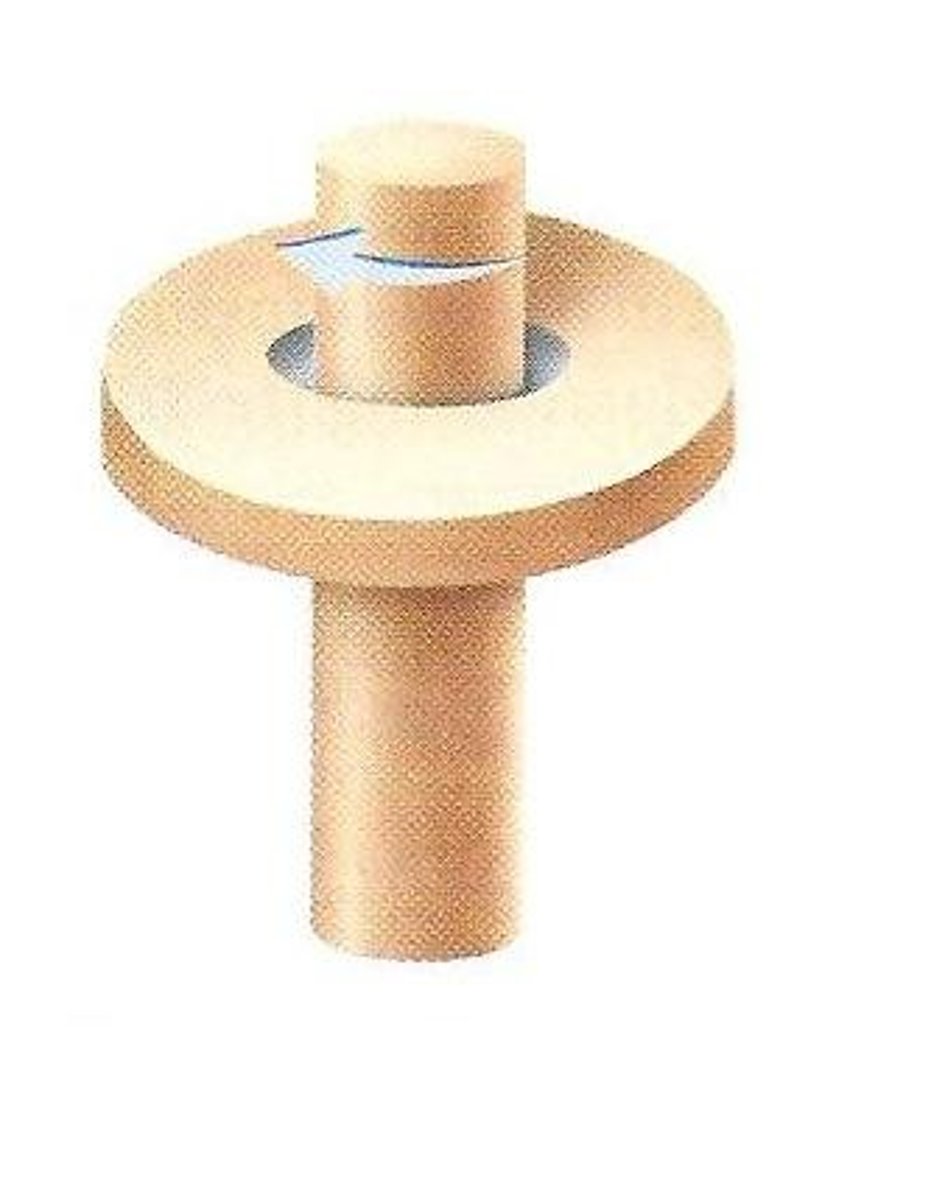

Conyloid Joint
side to side movement and back and forth (knuckle joints)
gliding joint
allows one bone to slide over another; found in wrist and ankles
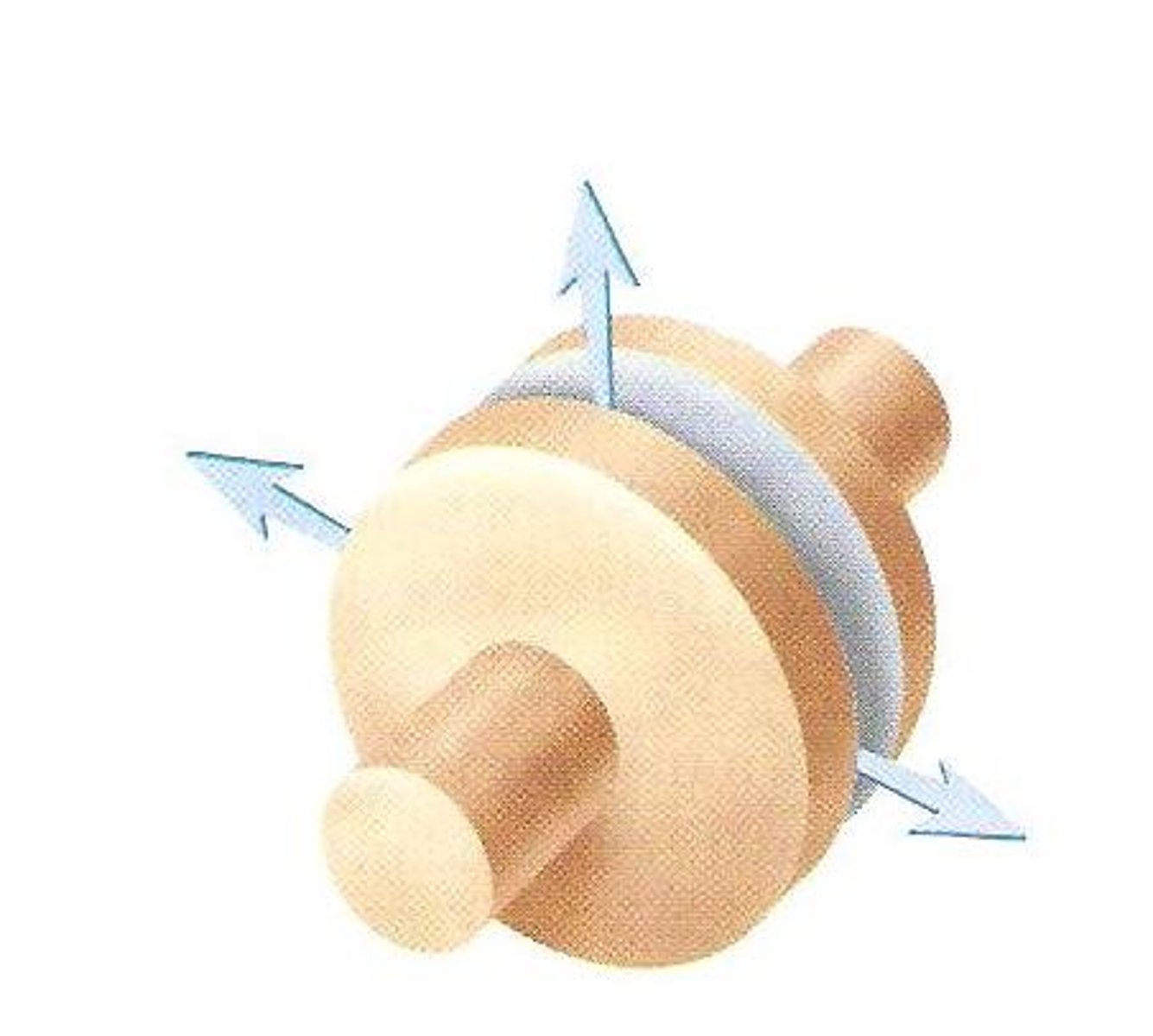
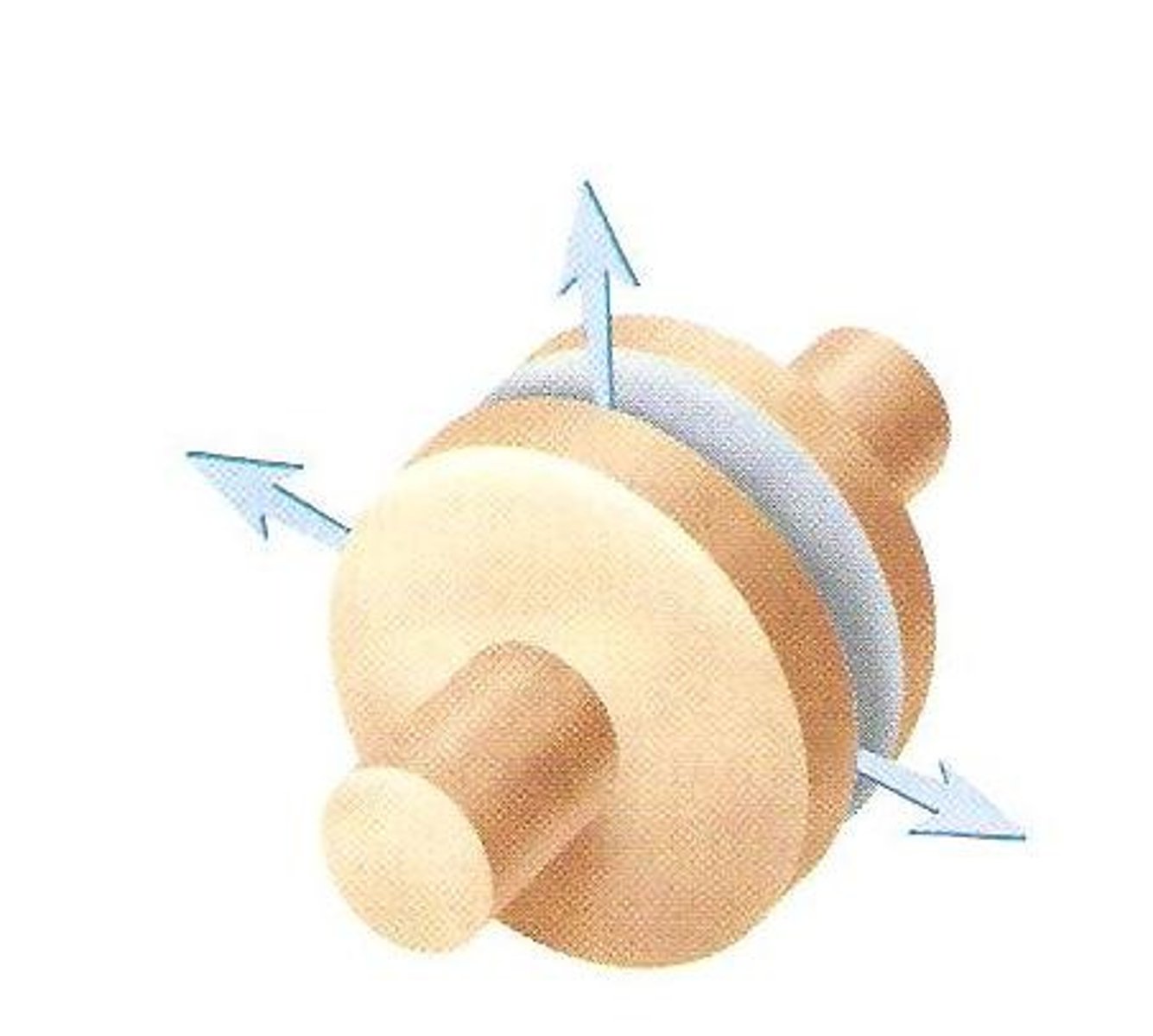
saddle joint
Two concave surfaces fit against a convex surface
Thumbs
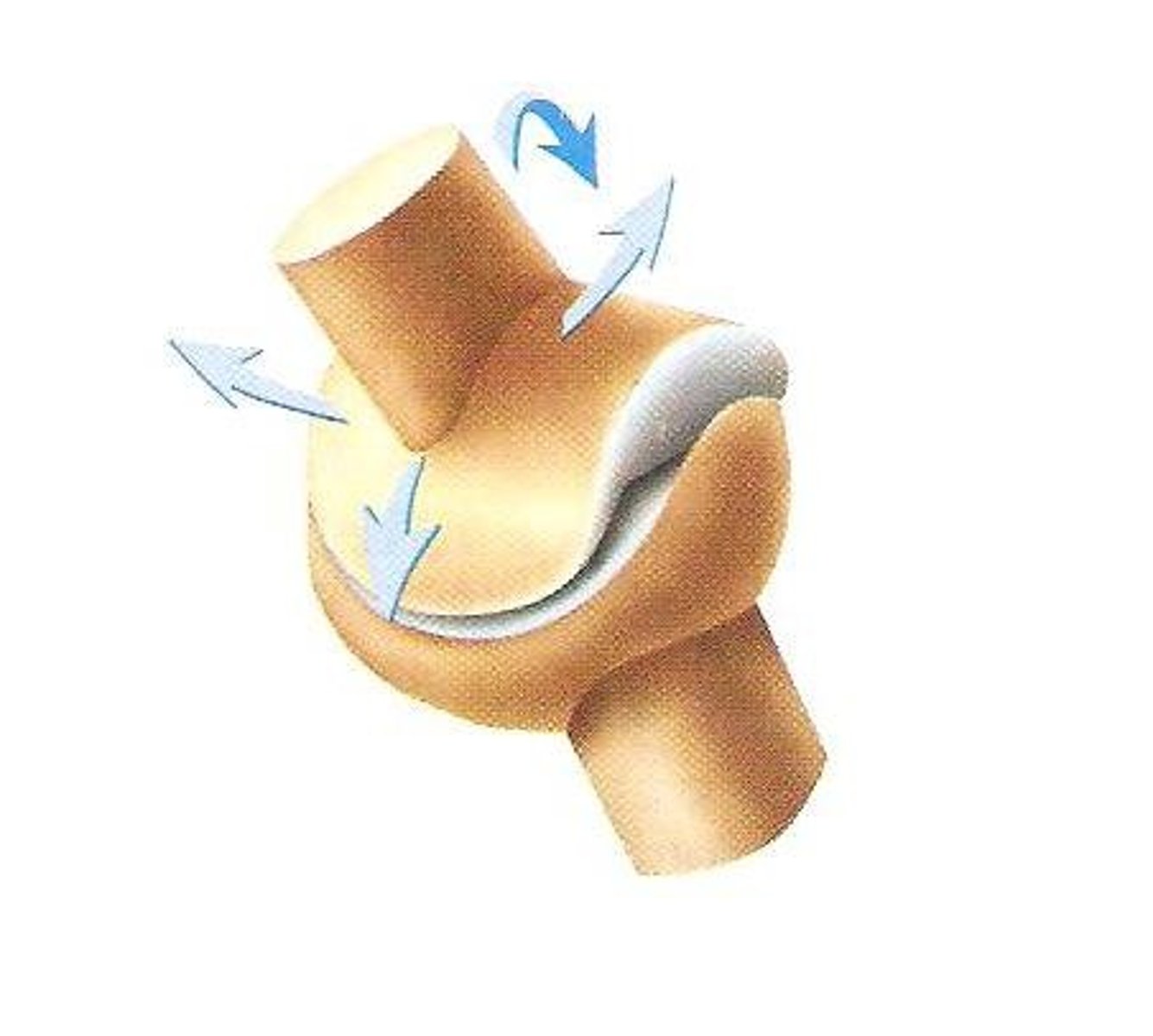
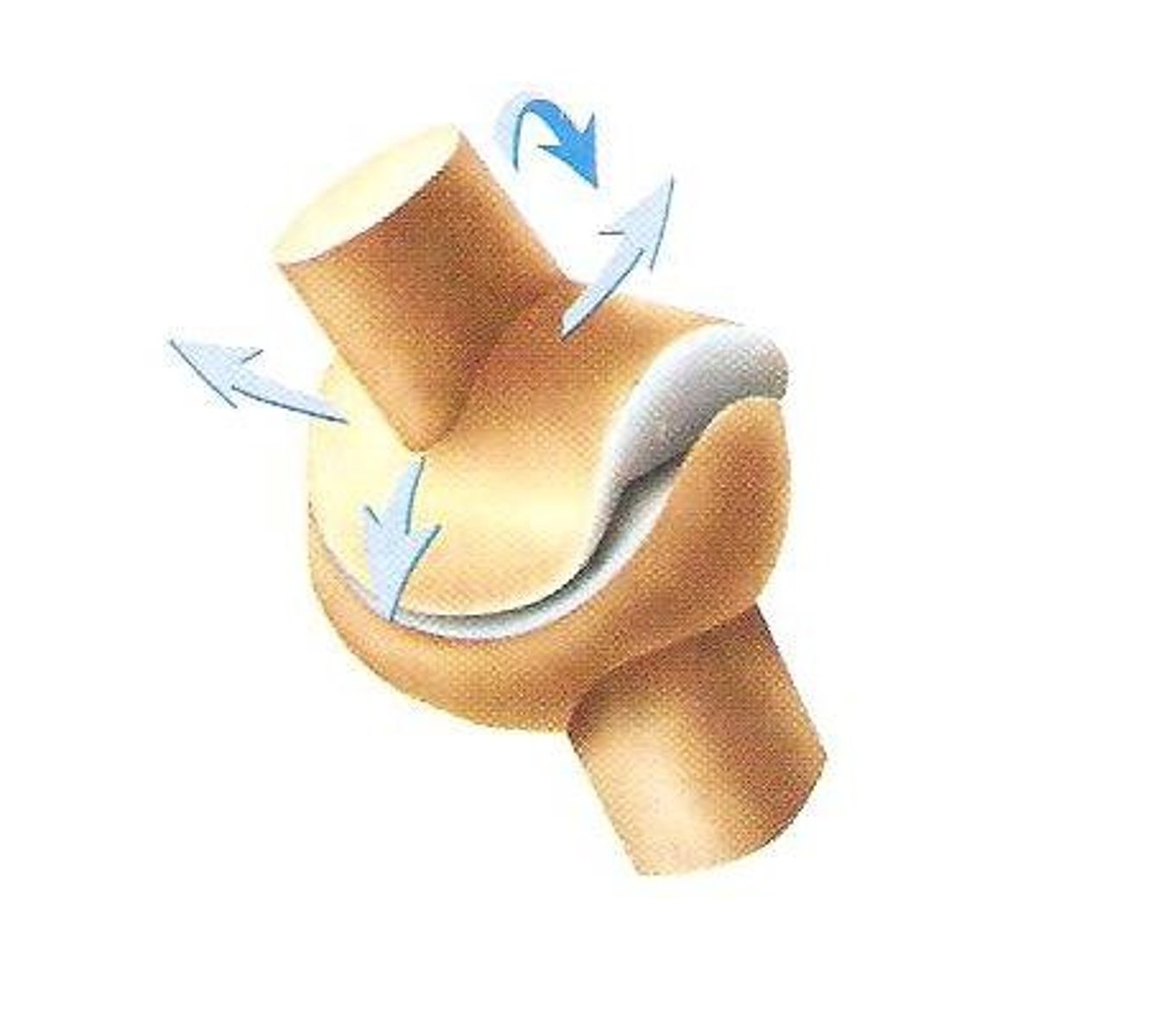
hinge joint
Joint between bones (as at the elbow or knee) that permits motion in only one plane
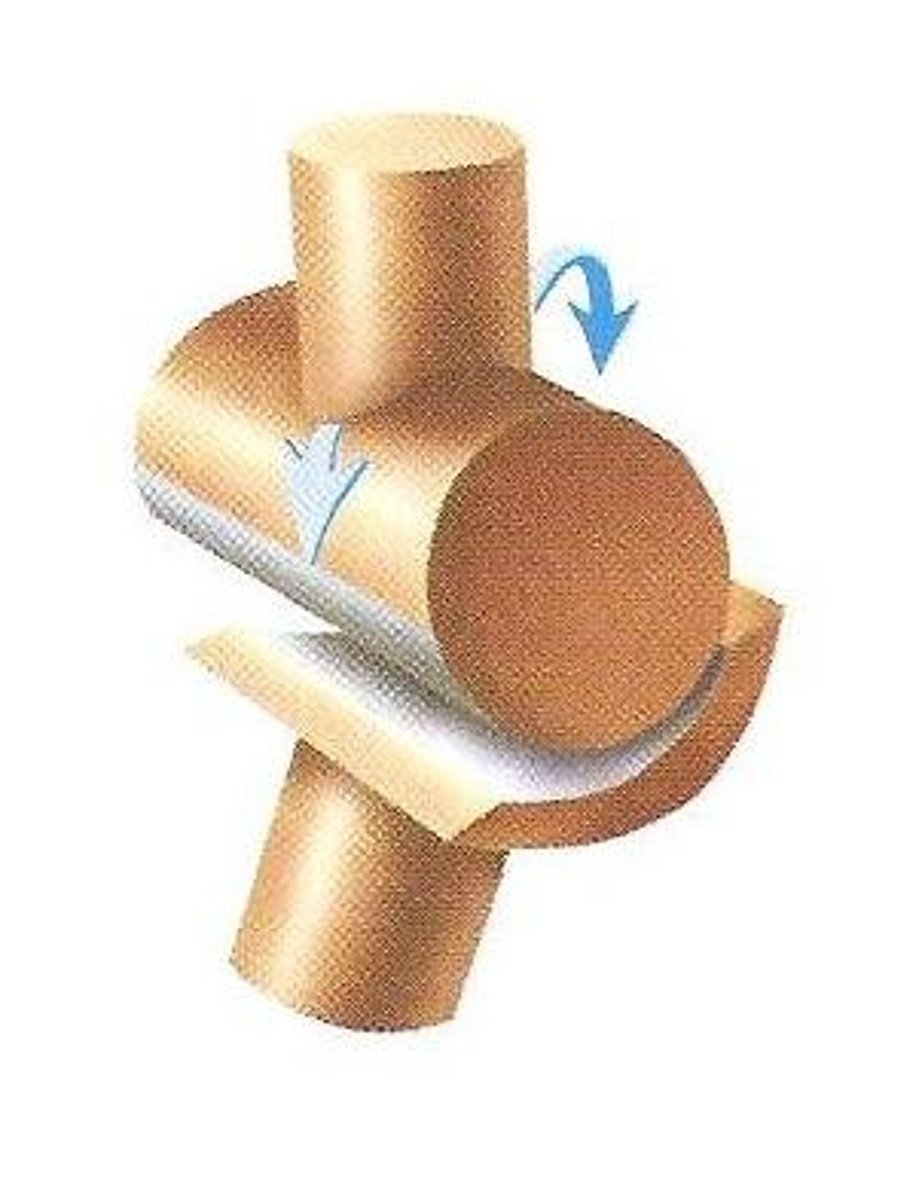
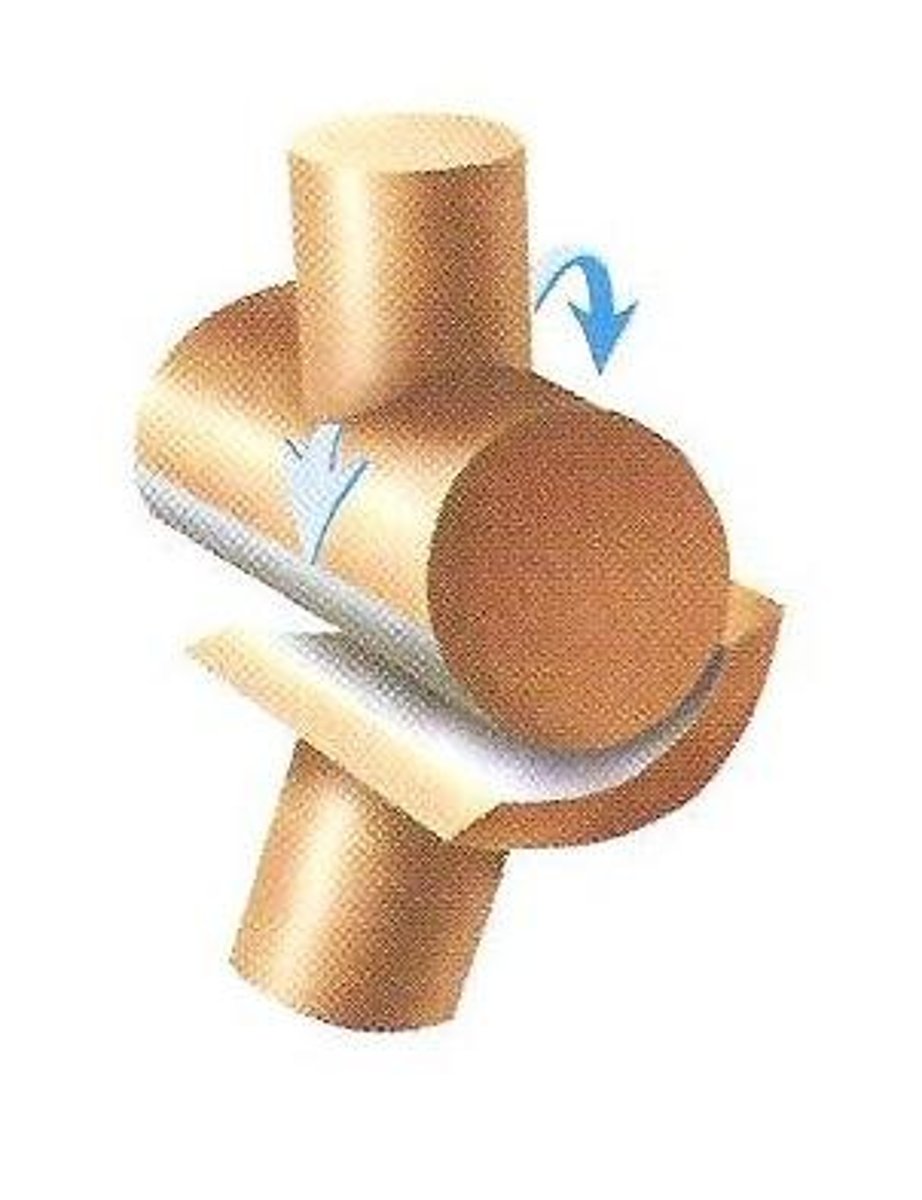
pivot joint
a freely moving joint in which movement is limited to rotation

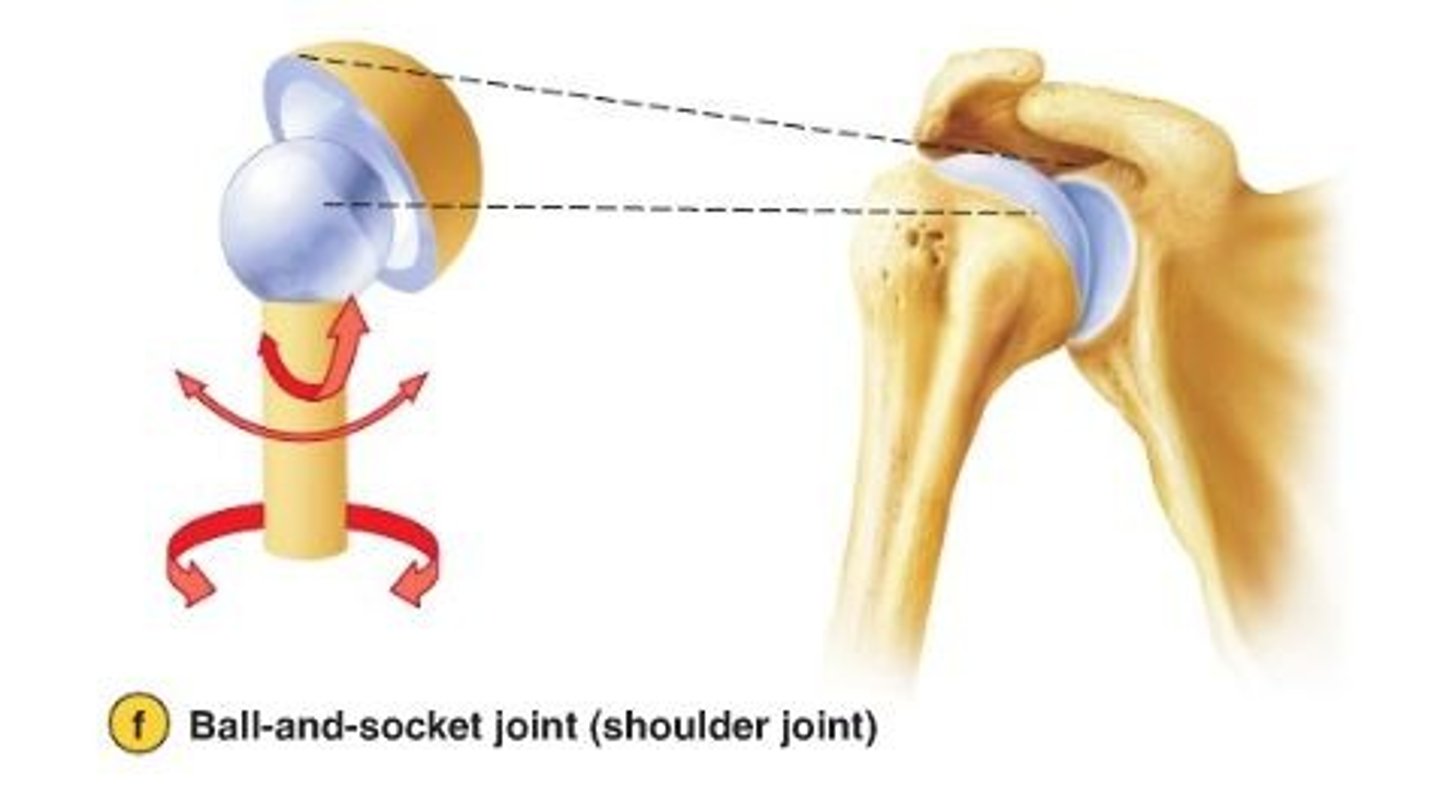
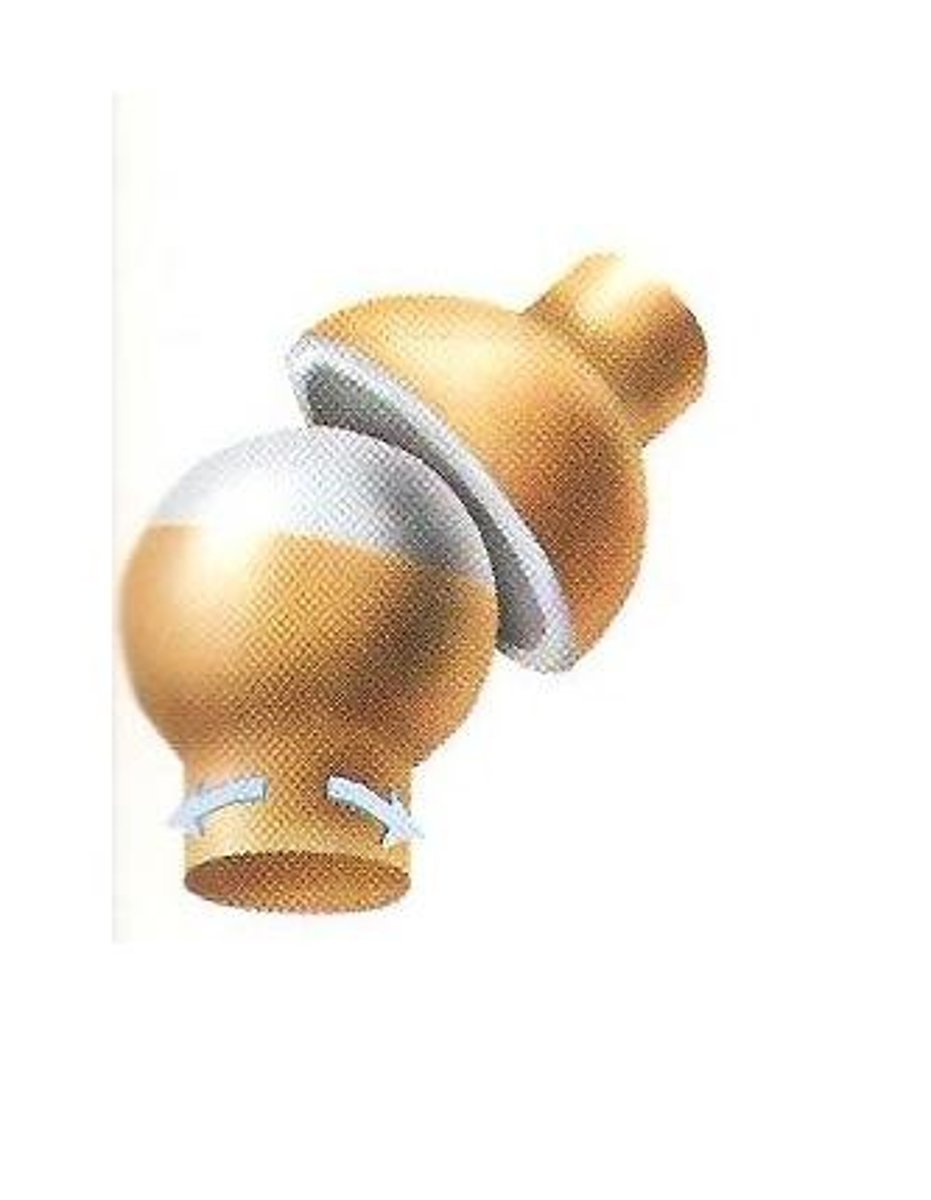
ball and socket joint
allow complete rotation to move in all directions; hips and shoulders

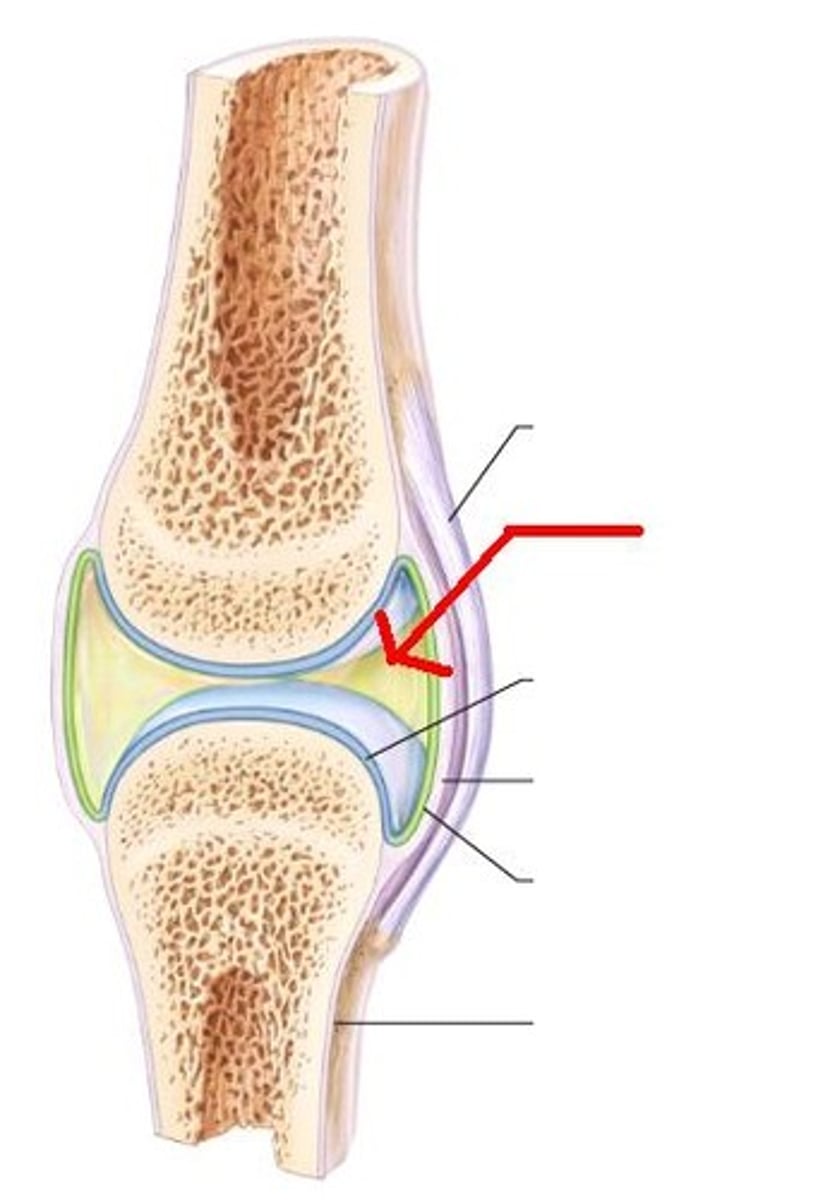
synovial joints
fluid filled freely movable joints cavities, all diathrosis,
synovial joint features
joint cavity, articular cartilage, membrane, fluid, reinforcing ligaments, tendons, and bursae. blood vessels and nerves.