Pediatric Patient PD I
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
neonate age
0-28 days
post-neonatal period
29 days to 1 year
young child age
1-4 years
middle child age
5-10 years
adolescent age
11-20 years
name same factors that can affect development
physical, social, environmental, disease
health promotion
the process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve, their health. It moves beyond a focus on individual behaviour towards a wide range of social and environmental interventions
health literacy
the degree to which an individual has the capacity to obtain, communicate, process, and understand basic health information and services to make appropriate health decisions
what is the schedule for well child checks?
Birth
First week of life
1, 2, 4, 6, 9 and 12 months
Annually
the AAP recommends use of a standardized tool for development milestones. it measures 4 domains of development, what are they?
Personal- social
Fine motor- adaptive
Language
Gross motor
what developmental milestones for 1 mo?
Head control
Spontaneous smile
what developmental milestones for 2 mo?
Head up when prone
Eyes follow object to midline
Responsive smile
what developmental milestones for 4 mo?
Rolls over
Eyes follow object past midline
Laughs
Preferential social smile
what developmental milestones for 6 mo?
Sits unsupported
Transfer objects between hands
Babbles
Stranger anxiety
what developmental milestones for 9 mo?
Stands with help
Pincher grasp
Repetitive sounds
Social games (peek-a-boo)
what developmental milestones for 12 mo?
Walks
Stacks cubes
10 words
Separation anxiety
what developmental milestones for 2 yr?
Walks backwards
Copies a line
Use of pronouns
Self centered
what developmental milestones for 3 yr?
Rides a tricycle
Copies a circle
Complete sentences
Group play
what developmental milestones for 4 yr?
Hops on one foot
Copies a cross
Tell stories
Imitates adults
what developmental milestones for 5 yr?
Partially dresses self
Copies a square
Asks for word meaning
Conforms to peers
what developmental milestones for 6 yr?
Skips
Copies a triangle
Expanding vocab
Rules are important
what is the number of immunizations recommended as of 2024?
37-42 doses + annual flu and COVID-19 vaccines
when are APGAR scores accessed? whats the max score?
assessed at 1 minute and 5 minutes of life, and every 5 minutes after until > 7 or intervention is initiated. Max score 10.
Ballard Scoring System
standardized method used to estimate gestational age and is based on neuromuscular and physical maturity
by year 1 birth weight and height should increase by?
weight should triple
height should increase by 50%
what is the average heart rate for
0-2 mo
0-6 mo
6-12 mo
140
130
115
what is the average respiratory rate range for an infant?
30-60 rpm
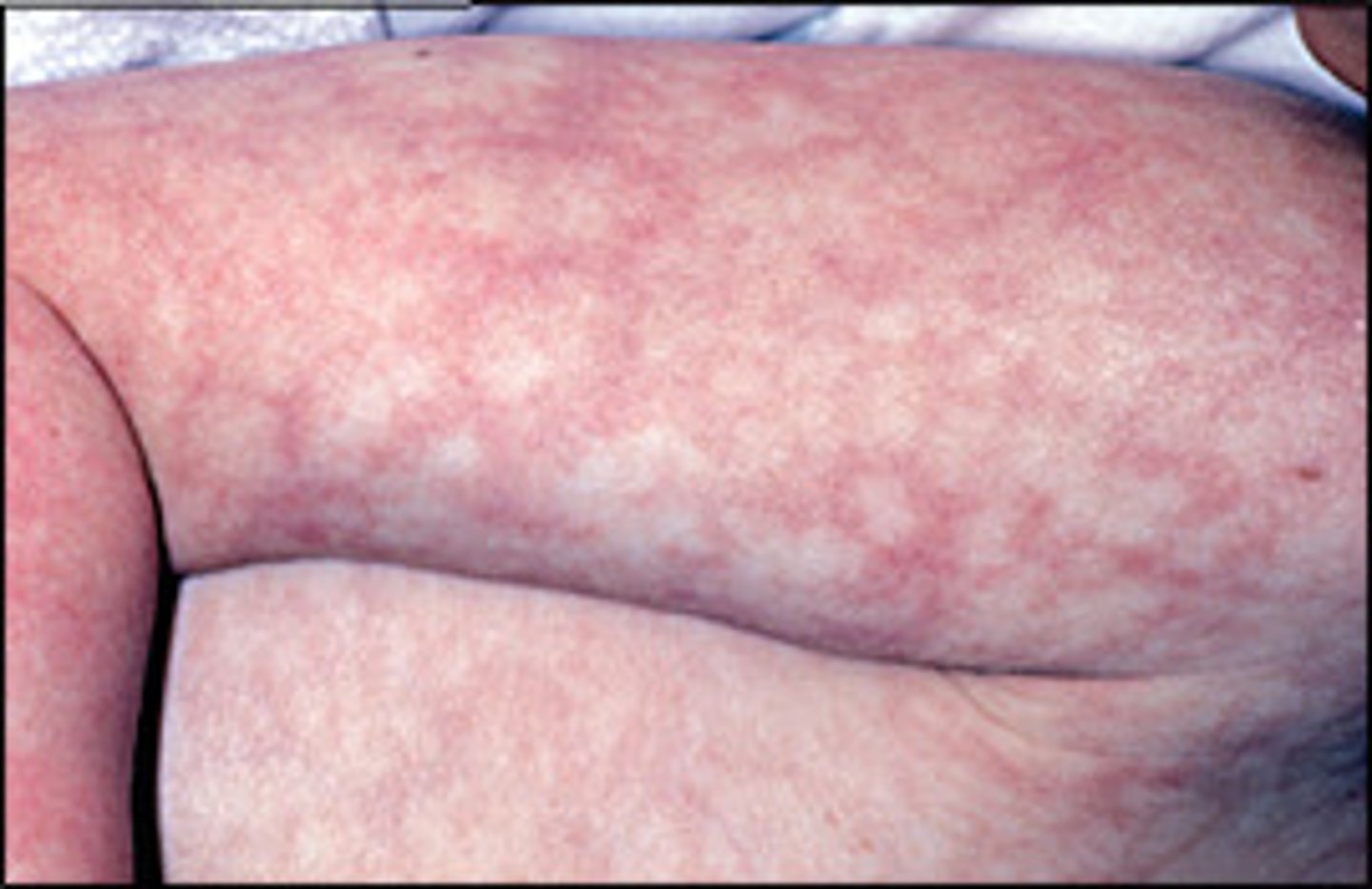
Cutis marmorata
common to see, due to cold - will disappear with warmth
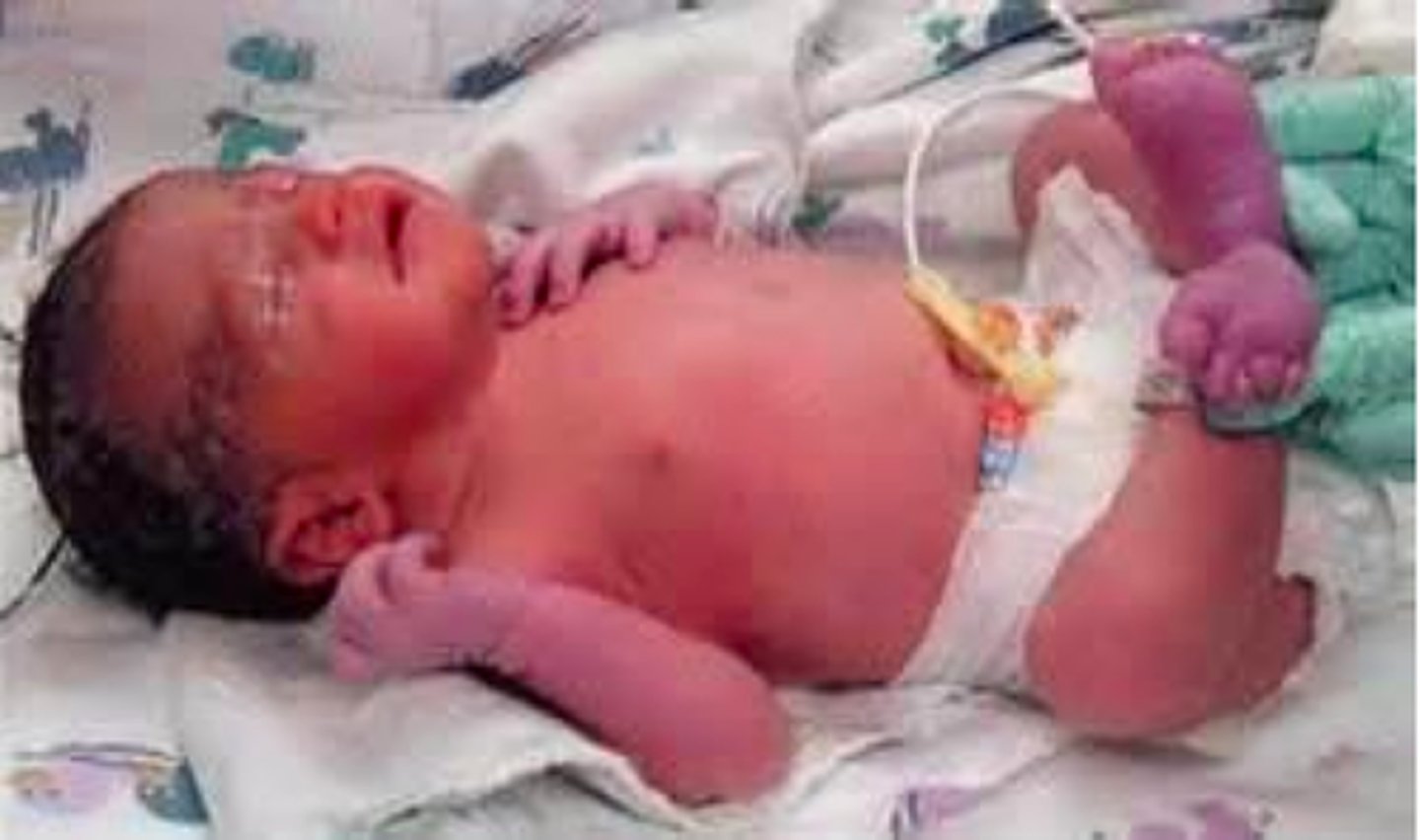
Acrocyanosis
blue skin, typically the extremeites
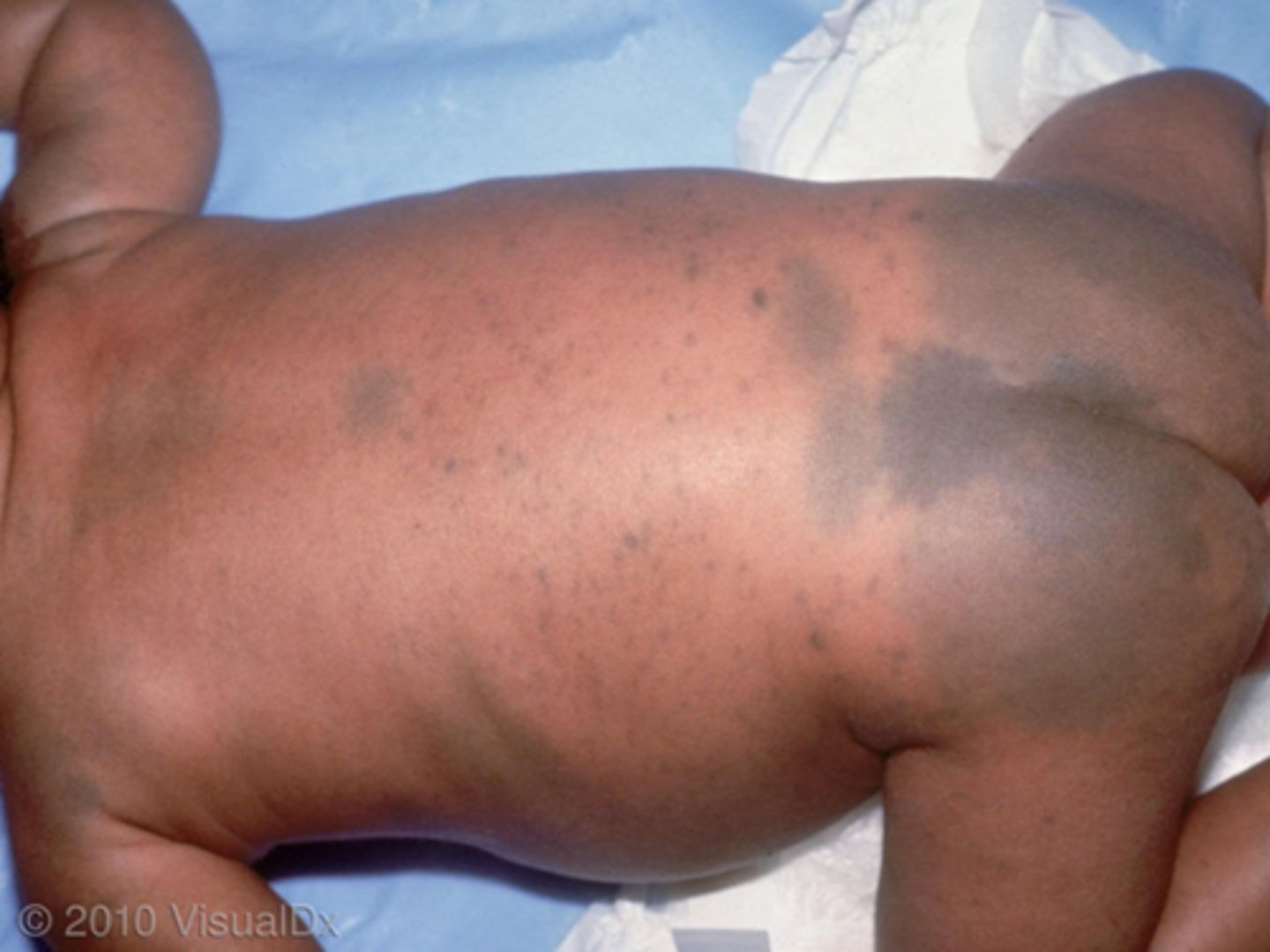
Mongolian spots
bluish purple spots of pigmentation
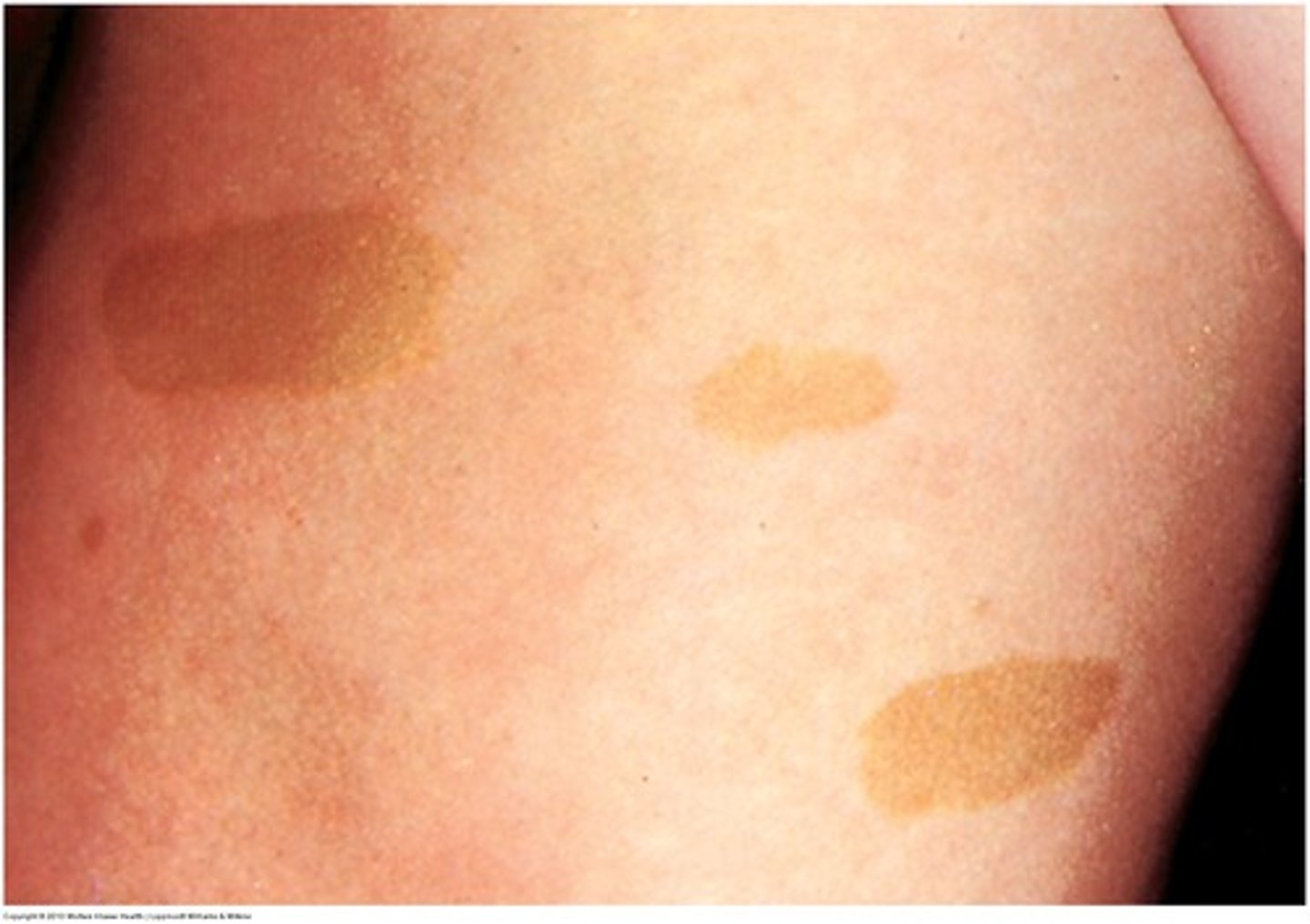
Café-au-lait spots
birthmarks
>6 - consider neurofibromatosis
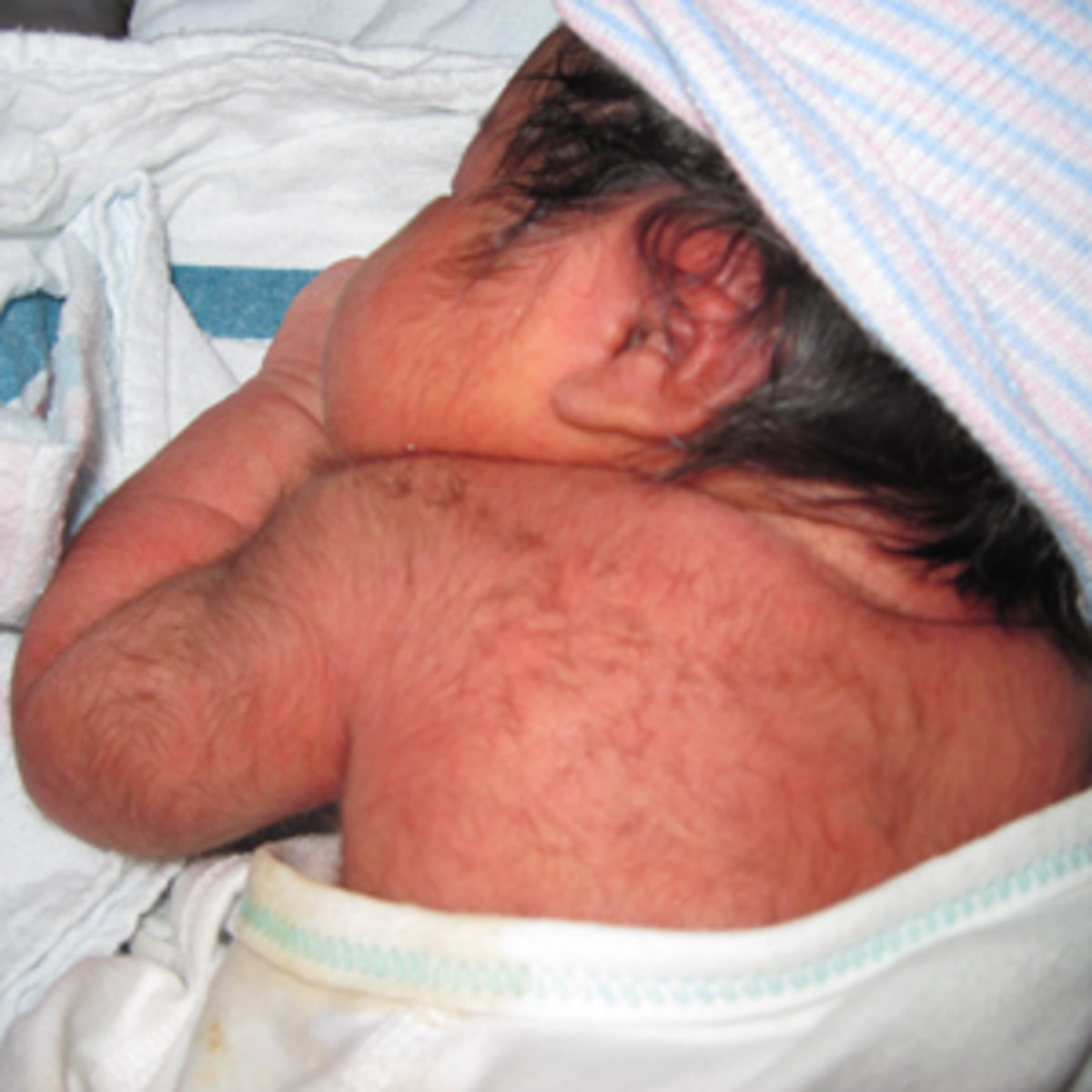
Lanugo
peach fuzz hair that sheds on its own, common in premature kiddos
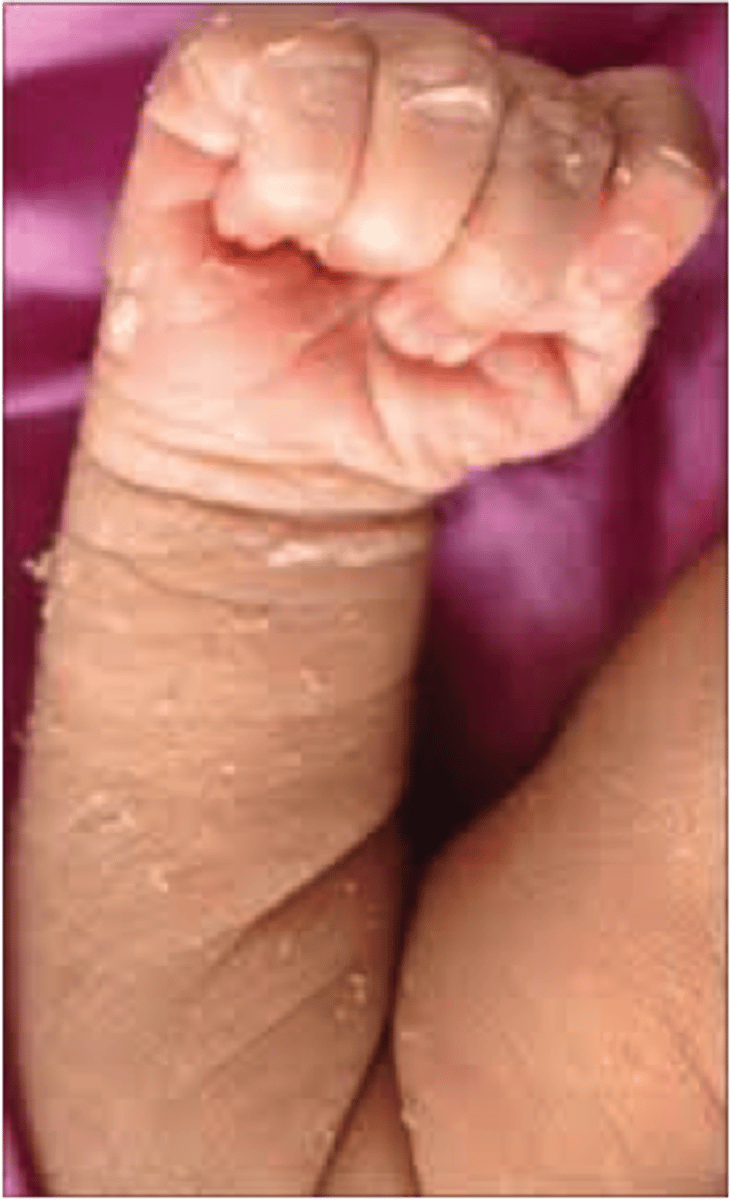
Desquamation
peeling/flaking skin, more common in post term kiddos
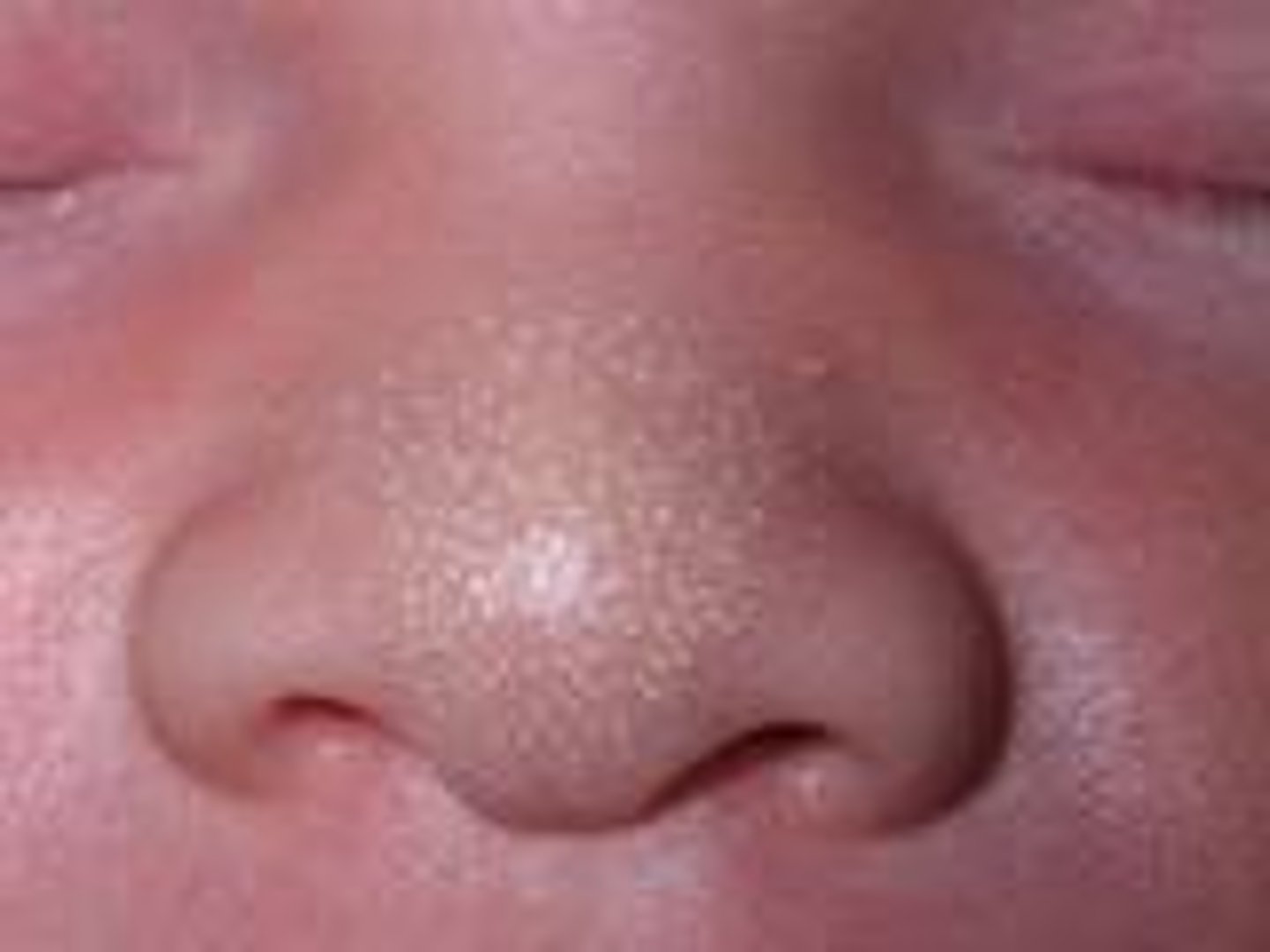
Milia
tiny epidermal cysts that occur in half of babies and will go away on their own
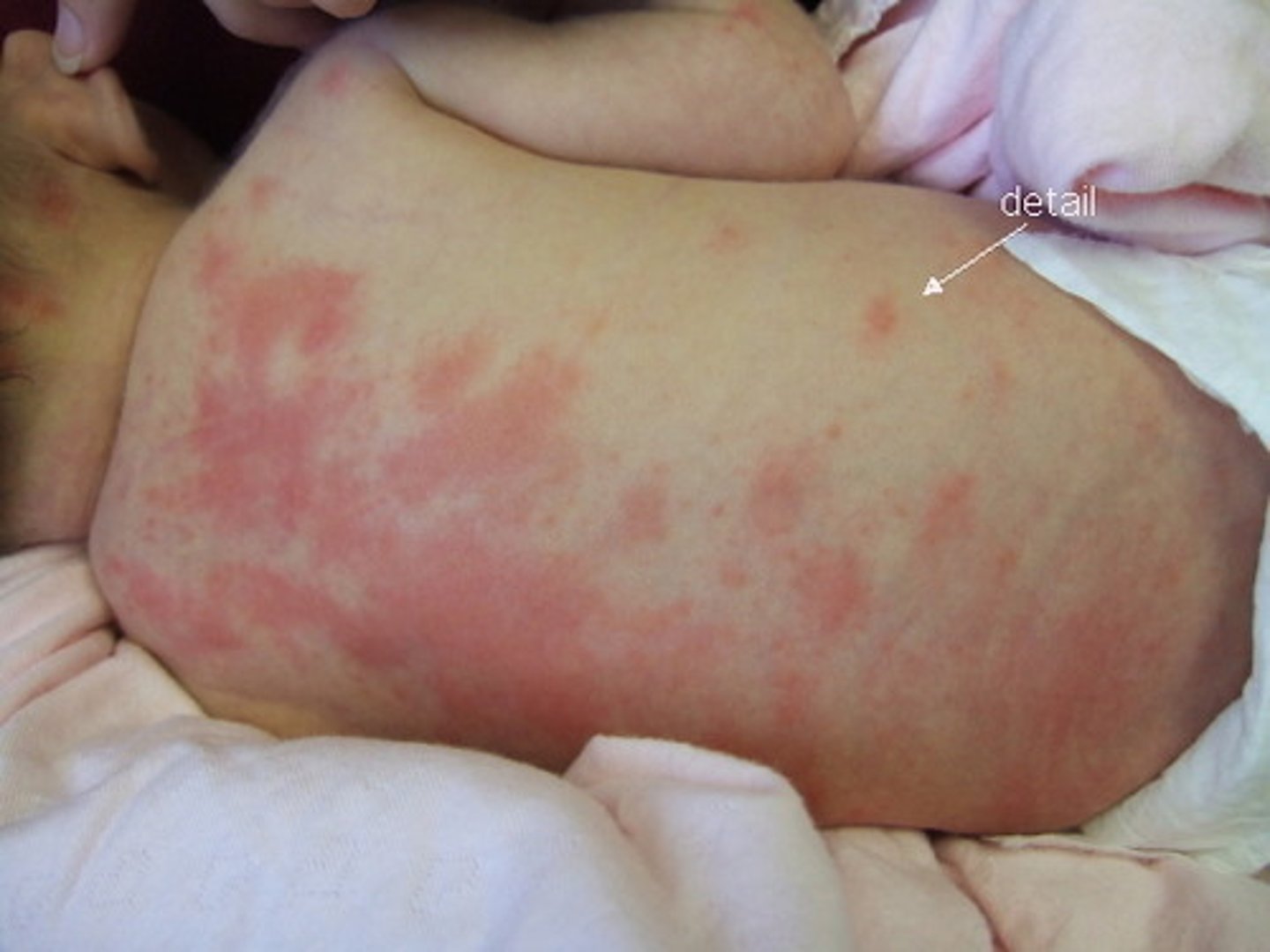
Erythema toxicum
blotchy red macules seen on the chest, back, and face in full term babies
Physiologic jaundice is seen in half of all newborns and is more common in breastfed babies t/f
true
1 multiple choice option
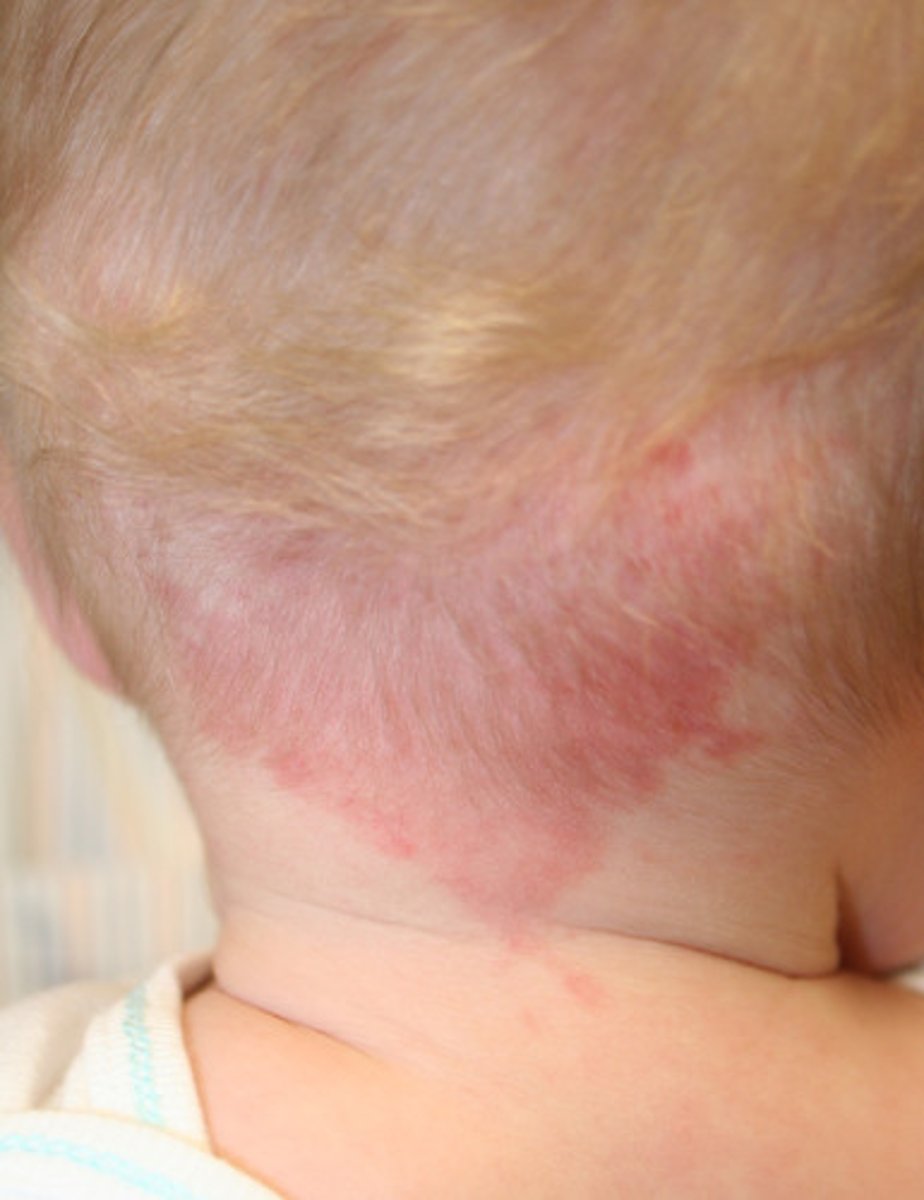
Nevus simplex
flat pink area that can be seen on the nape of neck (stork bite), upper eyelids, forehead (salmon patch)
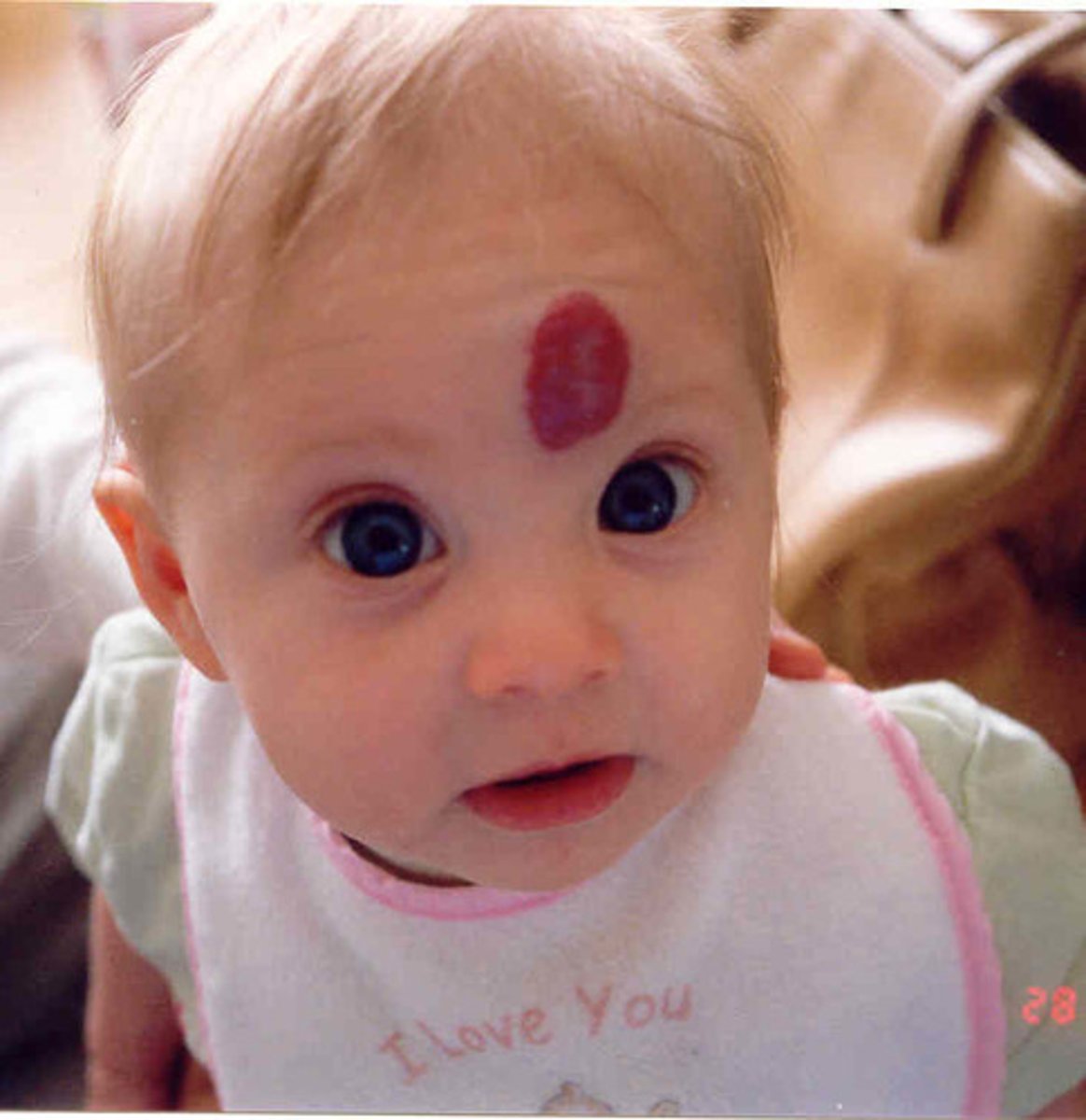
Capillary hemangioma
raised, red rubbery texture mark; appear in 2-4 weeks as a red nodule and typically resolves by age 9 - benign, best to wait it out
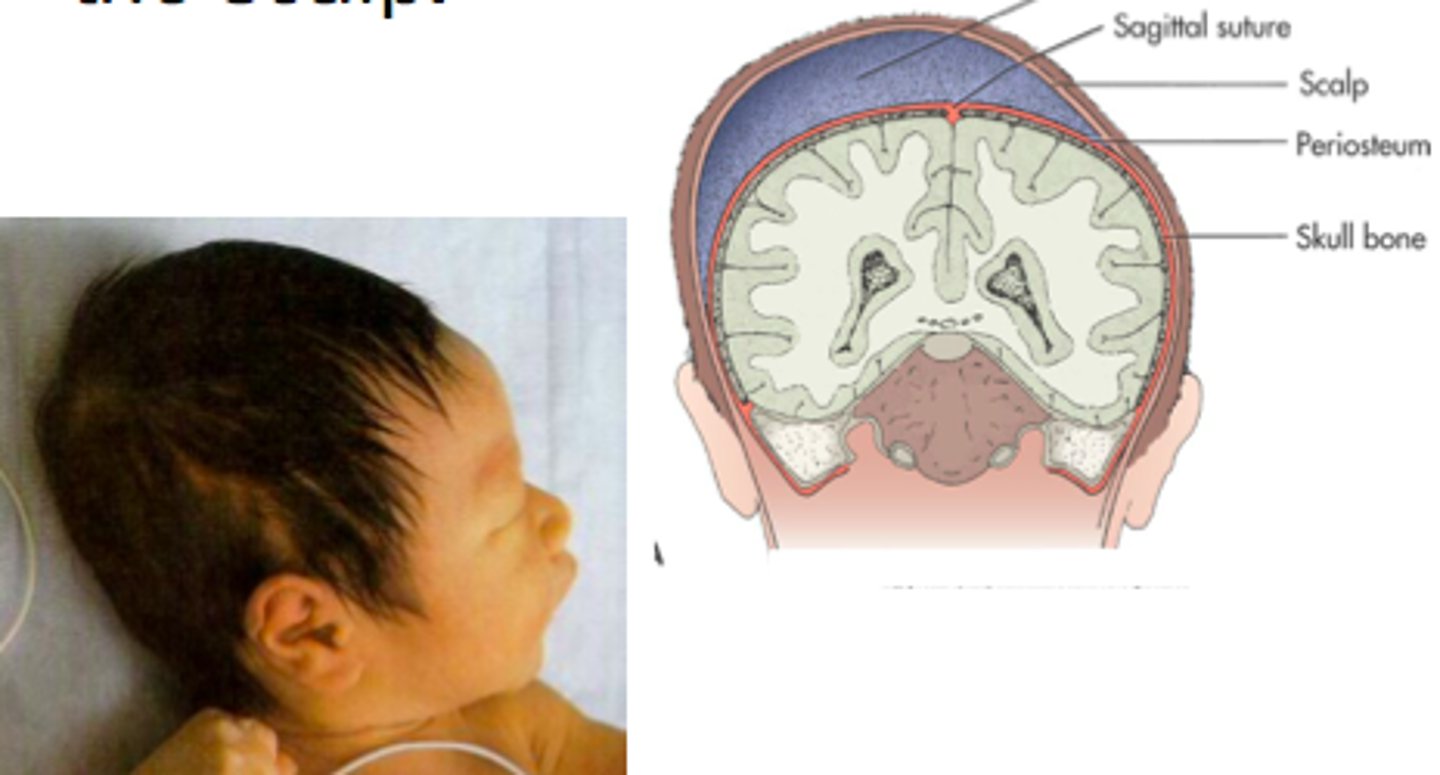
fontanelles
soft spots
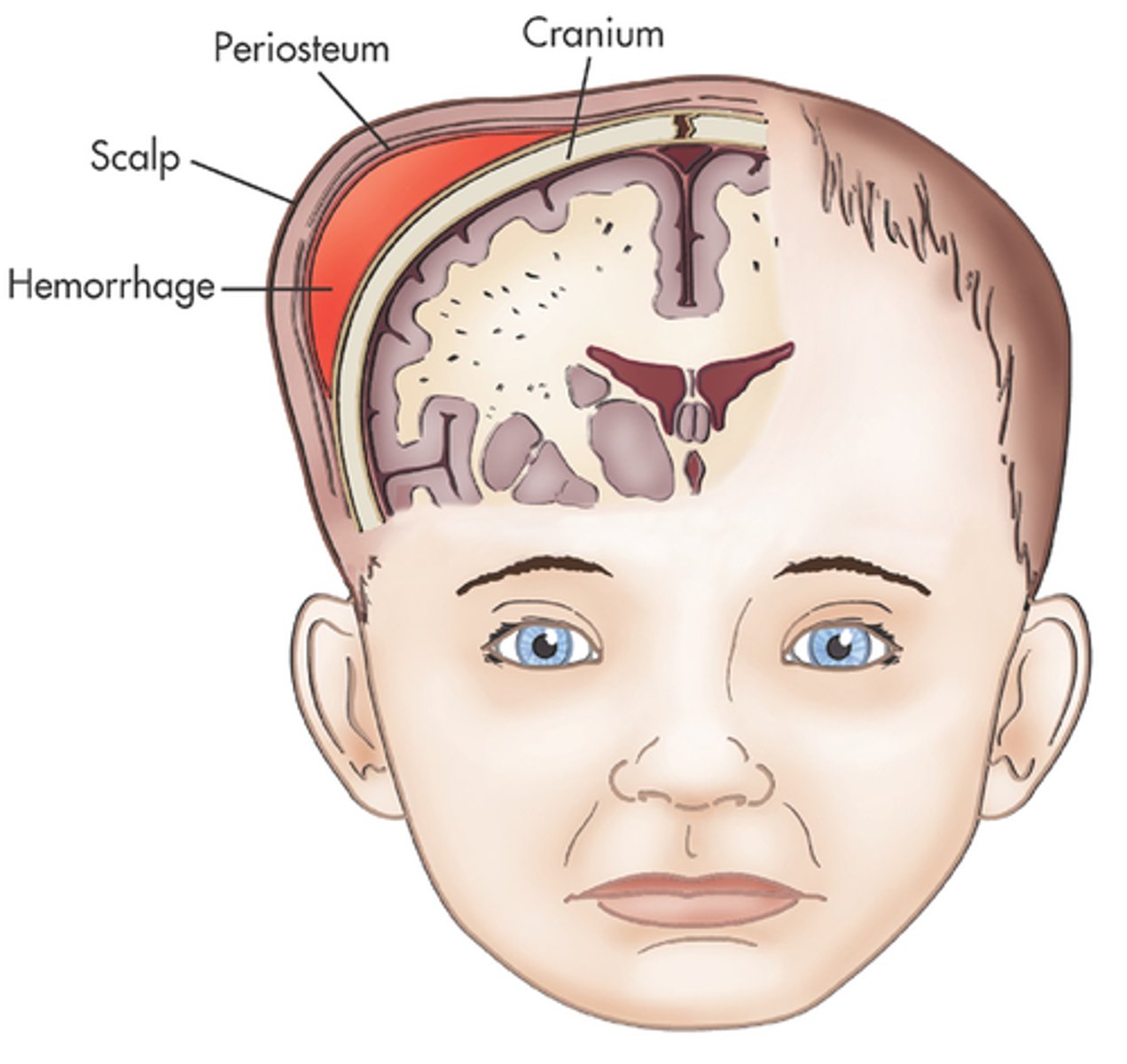
Caput succedaneum
crosses suture lines
Cephalohematoma
does not cross suture lines
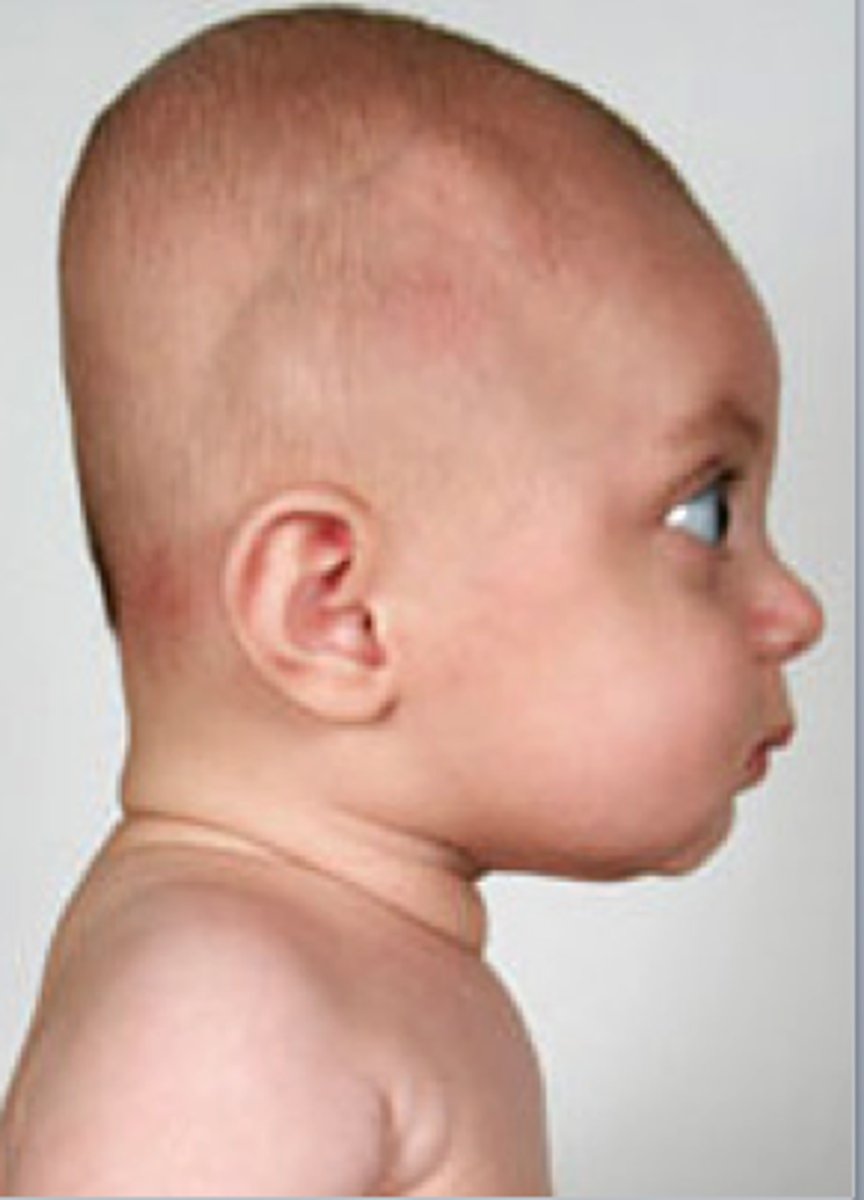
Plagiocephaly
flattening of the head
what is the visual milestone for birth?
blinks, may regard
what is the visual milestone for 1 mo?
fixes on object
what is the visual milestone for 1.5-2 mo?
coordinated eye movement
what is the visual milestone for 3 mo?
eyes converge, baby reaches
what is the visual milestone for 12 mo?
20/60 - 20/80 acuity
you are doing an ophthalmoscopic exam on an infant and they have a dark reflex, what could that indicate?
cataract, retinopathy of prematurity
you are doing an ophthalmoscopic exam on an infant and they have a white reflex, what could that indicate?
cataract, retinal detachment (separation of the retina from underlying layer), chorioretinitis or retinoblastoma
what are signs in a 0-2 mo year old that they can hear?
Startle response/blink; Calm with soothing voice
what are signs in a 2-3 mo year old that they can hear?
Change in body mvmt or facial expression in response to sound Turn eyes/head to sound
what are signs in a 3-4 mo year old that they can hear?
Turn to listen to voices/conversation
what are signs in a 6-7 mo year old that they can hear?
Appropriate language development
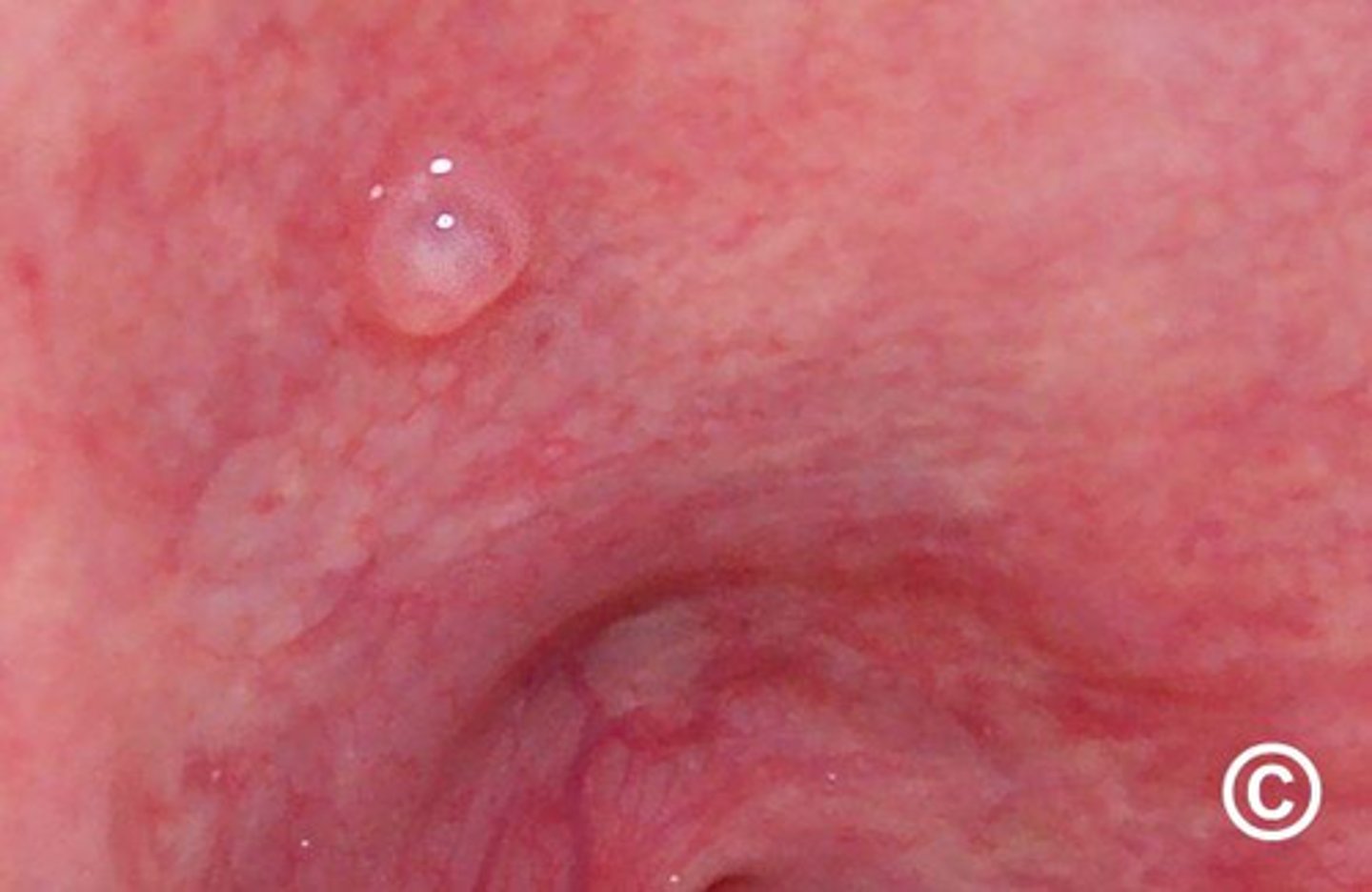
retention cyst
fluid-filled sac on the soft palate
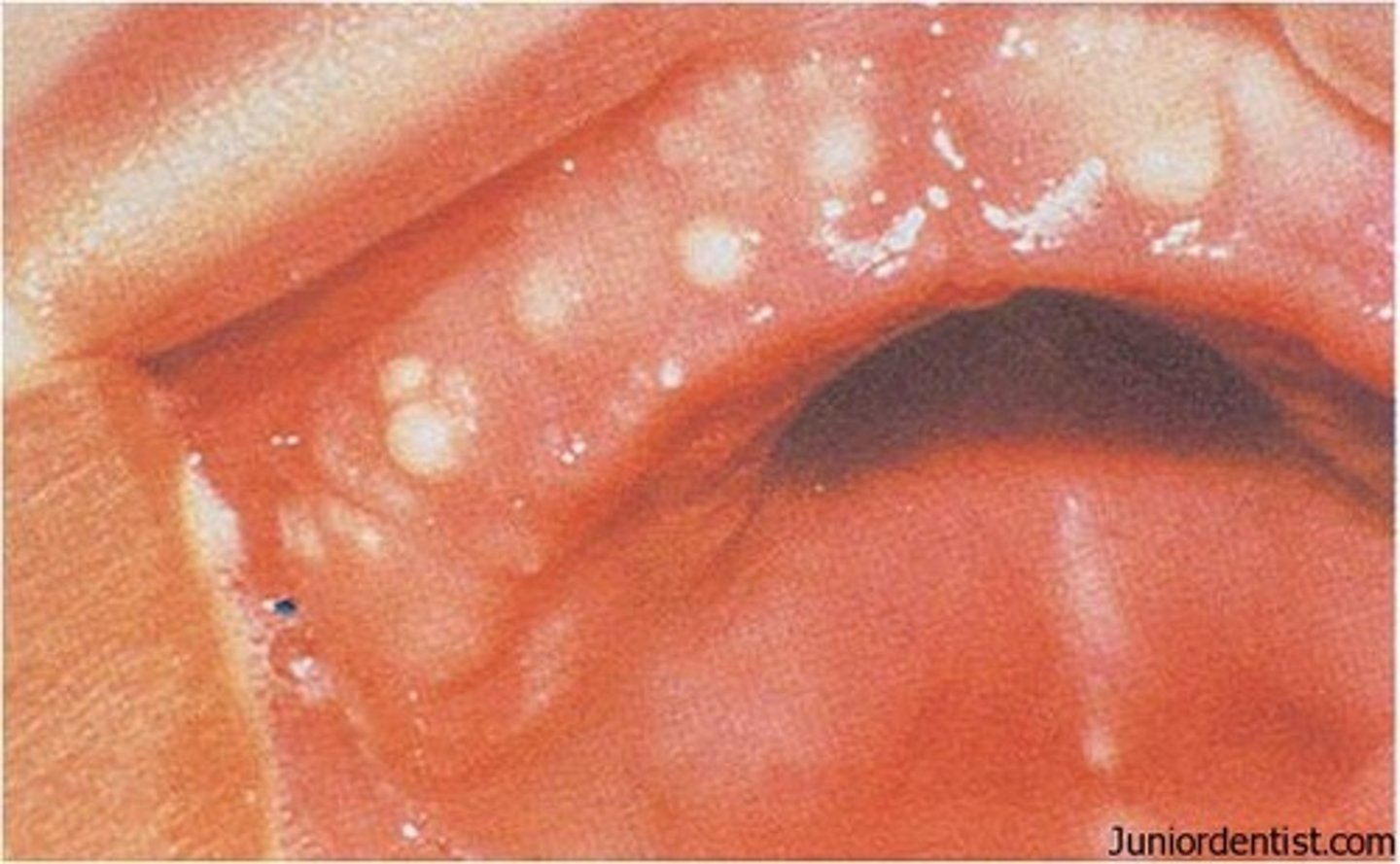
Epstein pearls
white/yellow cysts on hard palate
Ankyloglossia
tongue tied
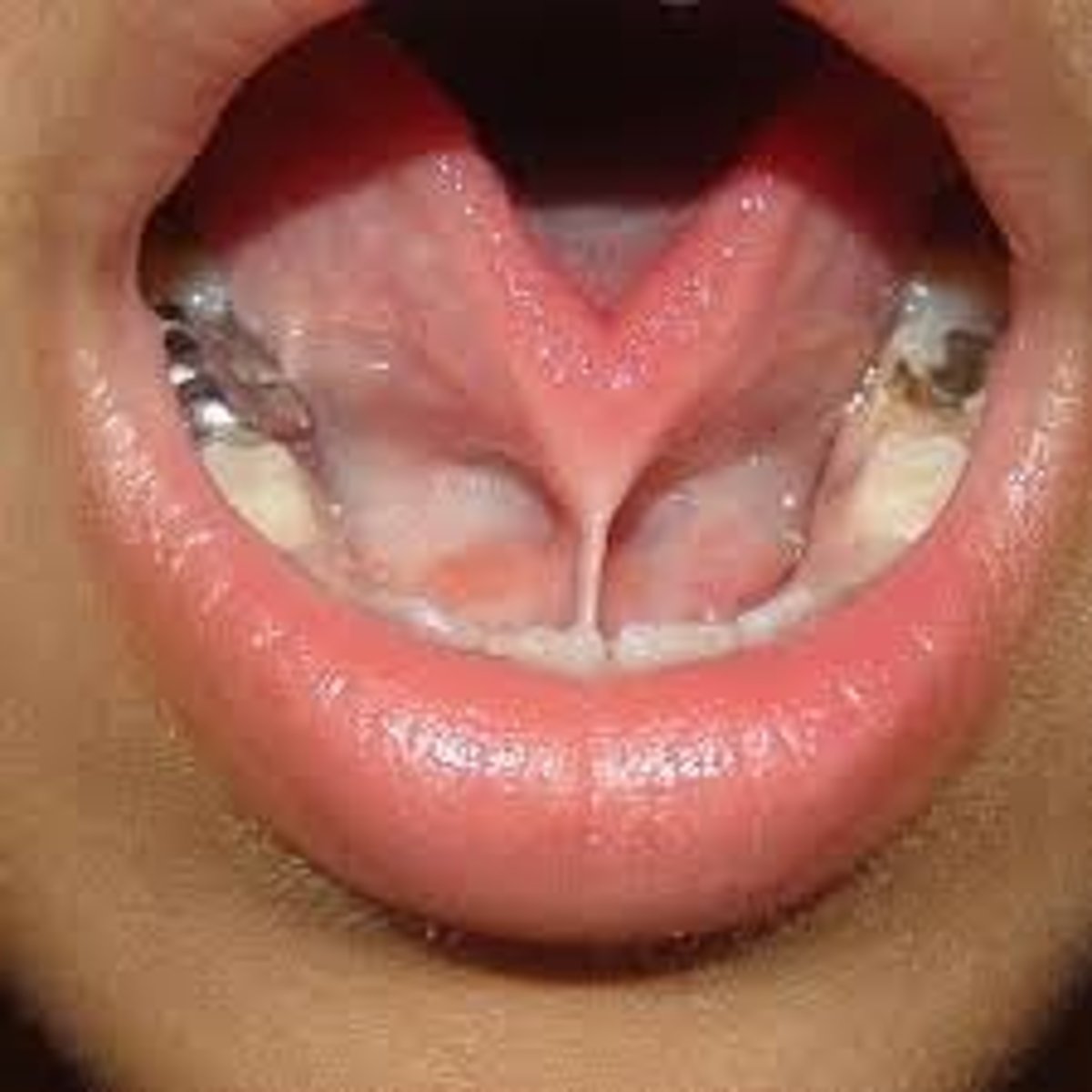
Macroglossia
enlarged tongue
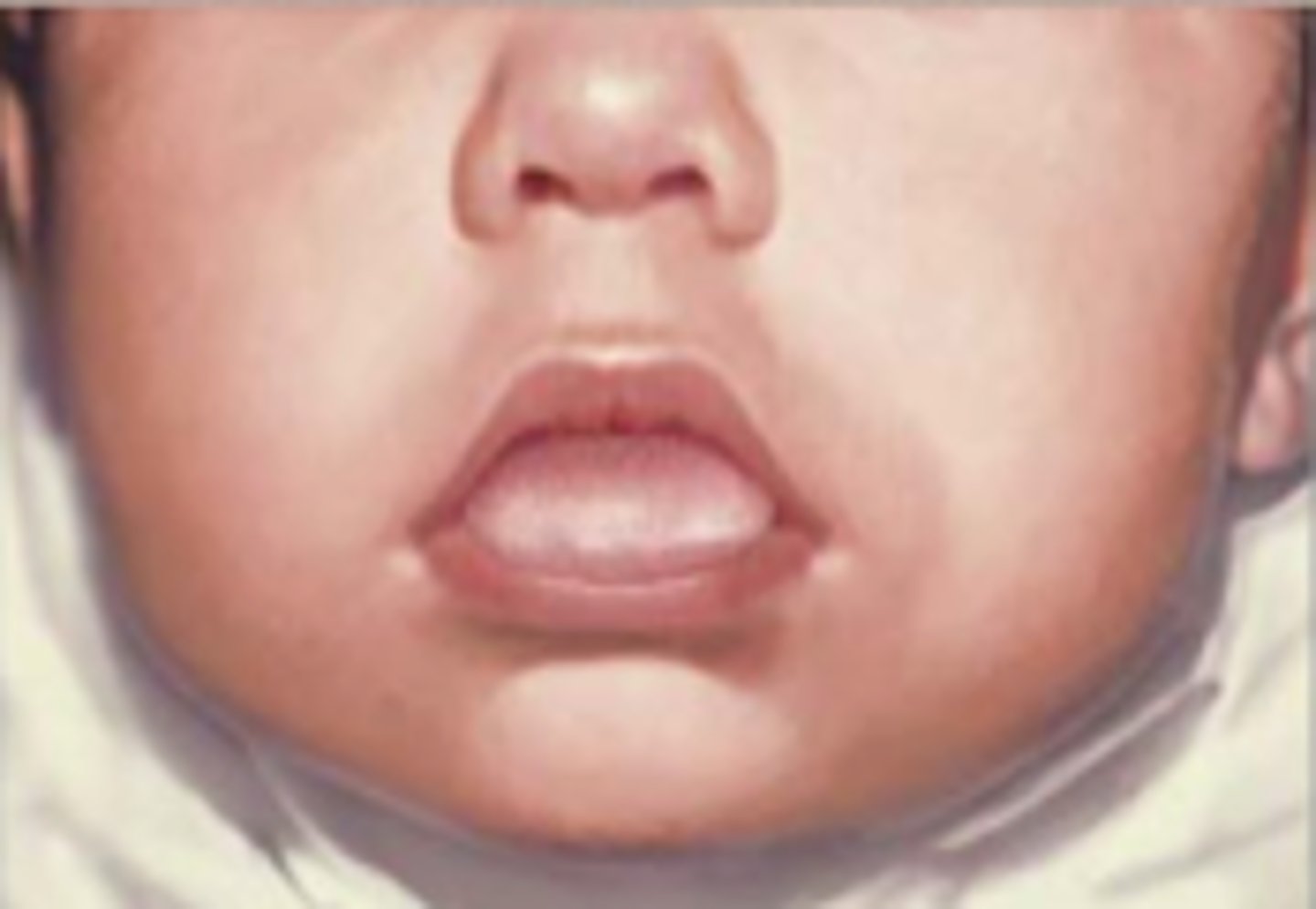
what could a raspberry tongue indicate in an infant?
desaturation
describe the heart sounds that might be heard during an infant heart exam
S1 and S2 should be crisp
Splitting of S2 heard with quiet or sleeping infant
S3 is low pitched, early diastolic, heard best at the apex
name 3 acyanotic heart murmurs seen in infants
ventricular septal defect (VSD)
patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)
atrial septal defect (ASD)
ventricular septal defect (VSD)
Defect in septum
Blood goes from left ventricle to right ventricle
patent ductis arteriosus (PDA)
Ductus arteriosus does not close at birth
Blood flows from aorta to pulmonary artery
Machinery sounding
atrial septal defect (ASD)
Opening in atrial septum
Blood shunts from left to right atria
Splitting of S2
name 2 cyanotic heart murmurs seen in infants
transposition of the great vessels
tetralogy of fallot
transposition of the great vessels
Aorta rises from the right ventricle
Pulmonary artery rises from the left ventricle
what are the 4 defects tetralogy of fallot?
Ventricular septal defect
Malposition of the aorta
Pulmonic stenosis
Right ventricular hypertrophy
amniotic portion of the umbilical cord
dries up and falls off by 2 weeks
cutaneous portion of the umbilical cord
retracts to abdominal wall
Diastasis recti
separation of rectus abdominis muscles
what are major and minor defects of spina bifida occulta?
Major defects- meningomyelocele
Minor defects-Pigmented spots, hairy patches, pits
what are the 2 tests to test for congenital hip dysplasia?
barlow and ortolani test
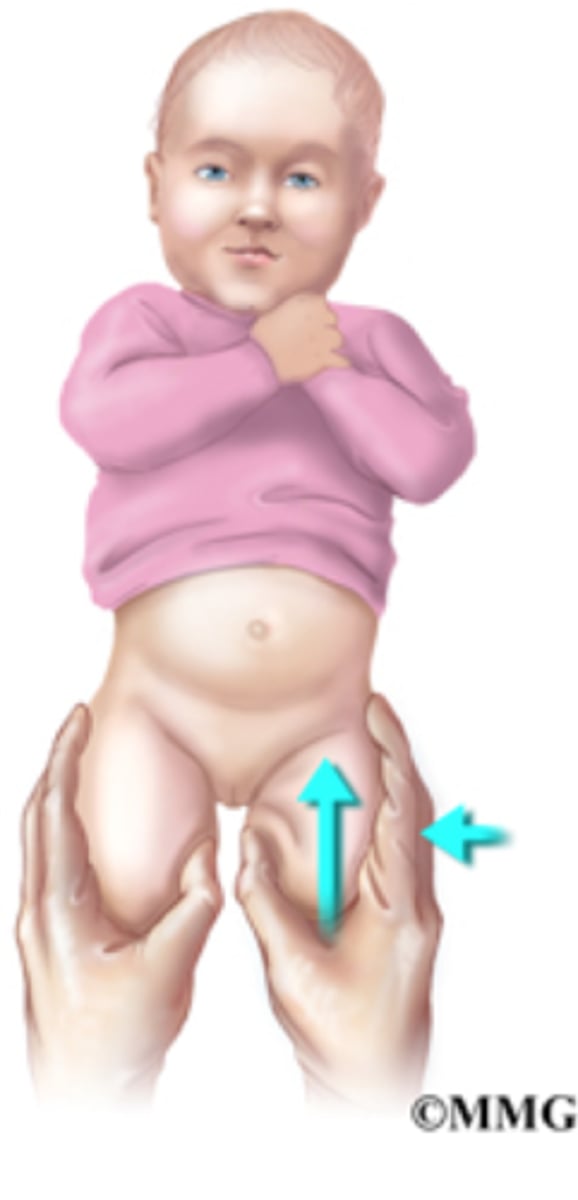
Barlow test
Tests for hip instability
Adduct both hips simultaneously while applying posterior pressure
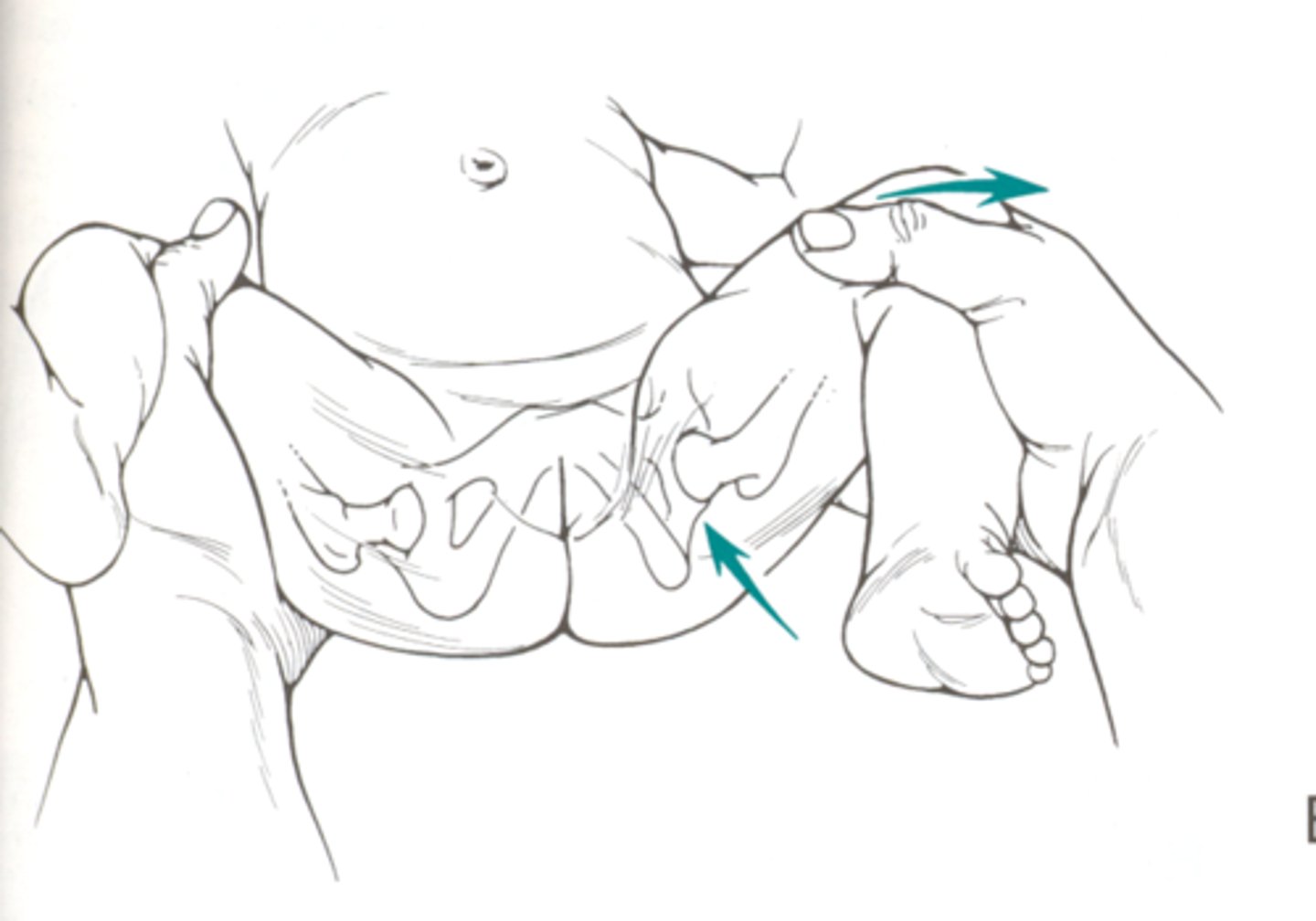
Ortolani test
Confirm hip dislocation
Abduct both hips simultaneously
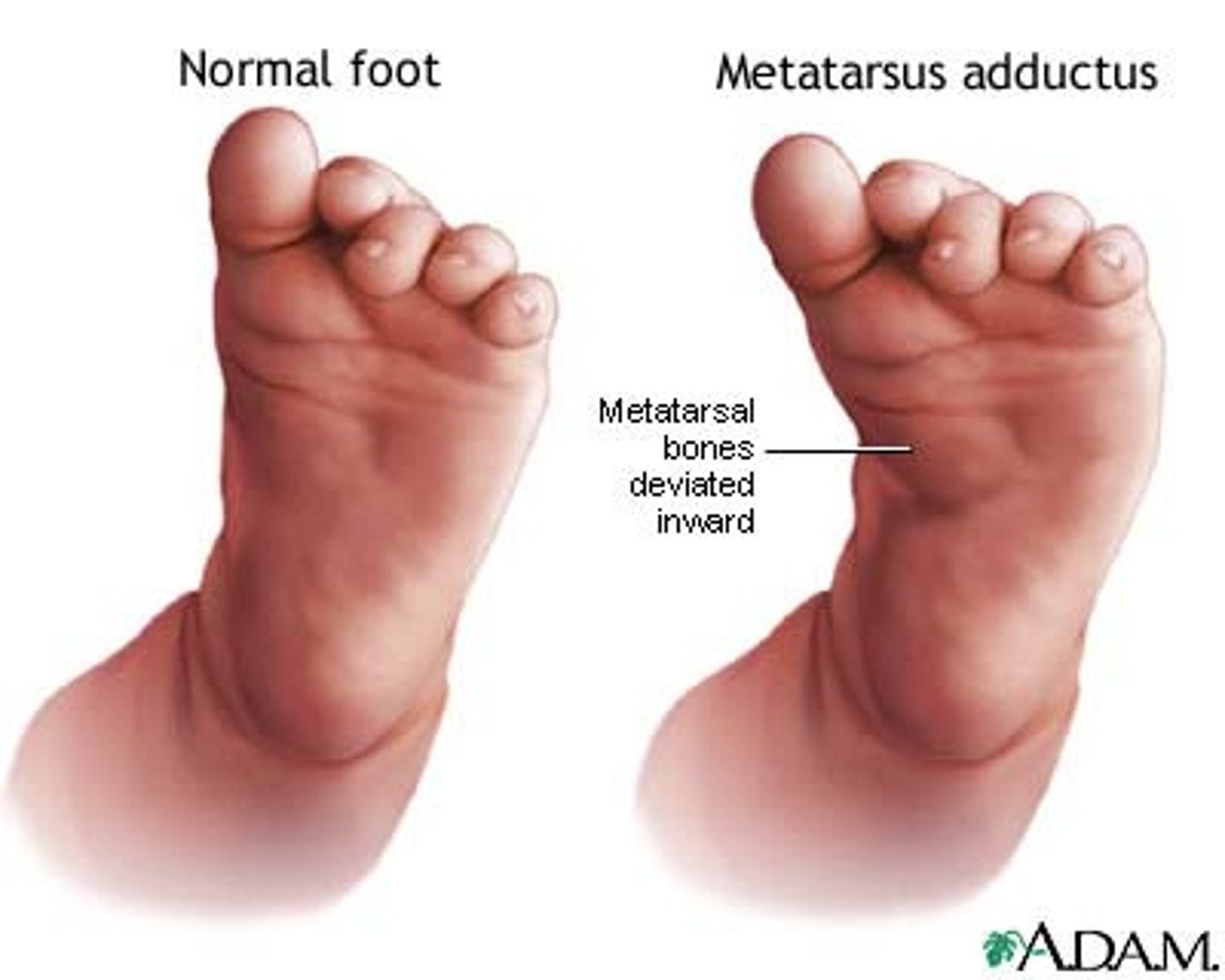
Metatarsus adductus
adduction without inversion of whole forefoot
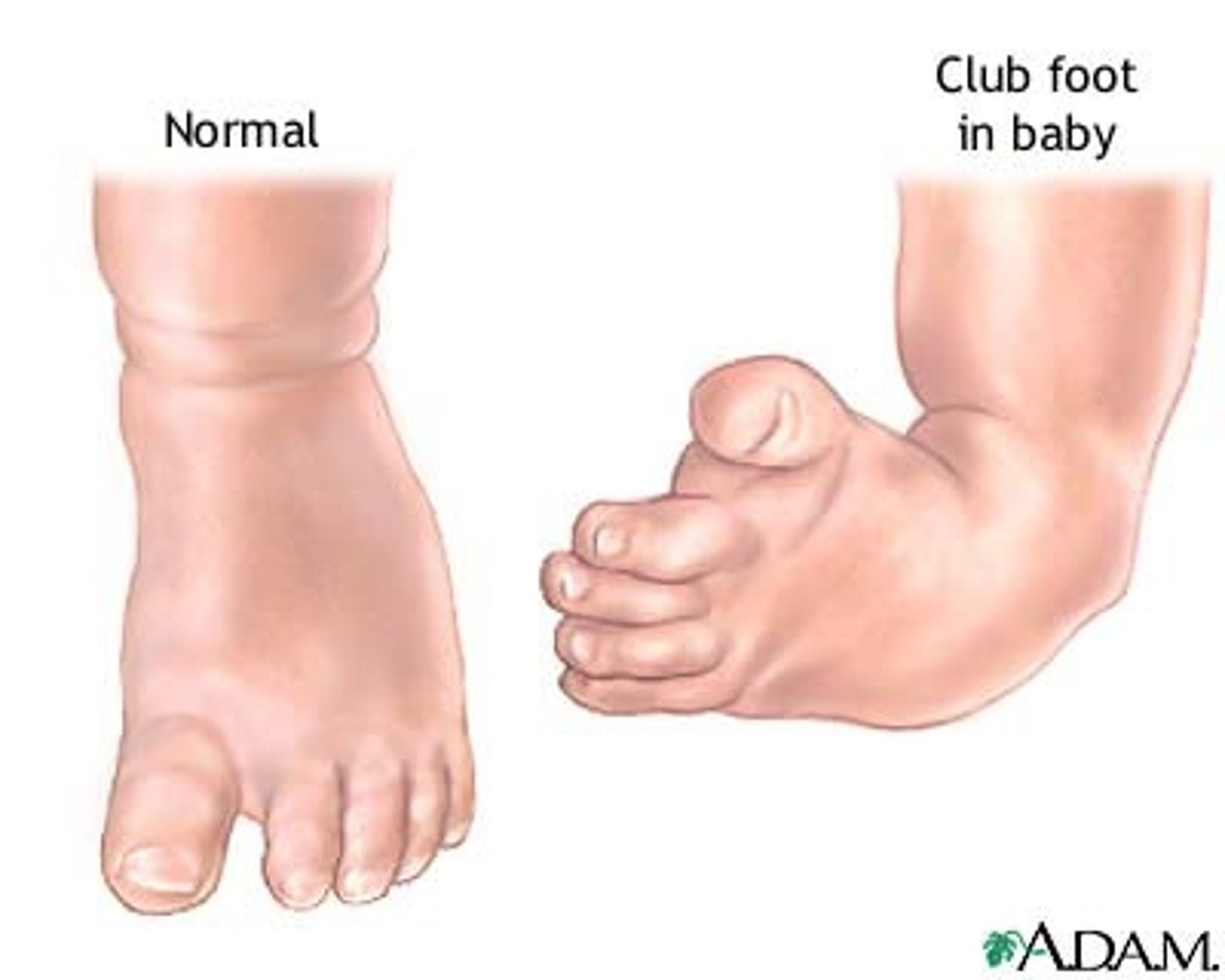
Talipes equinovarus
(clubfoot) full inversion, cannot recorrect it
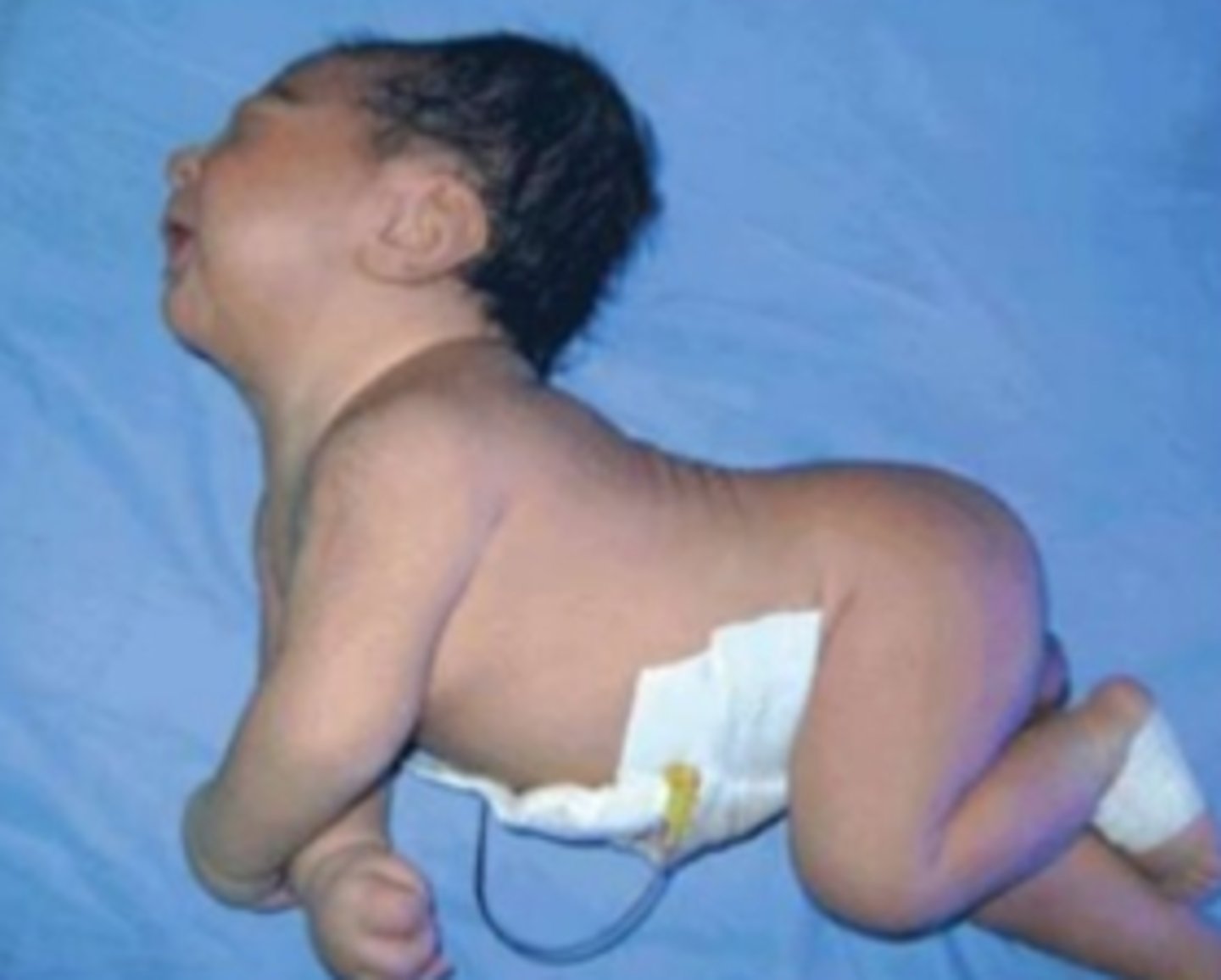
Hypertonia
Spasticity
Increase resistance
Stiff limps
Lack of flexibility
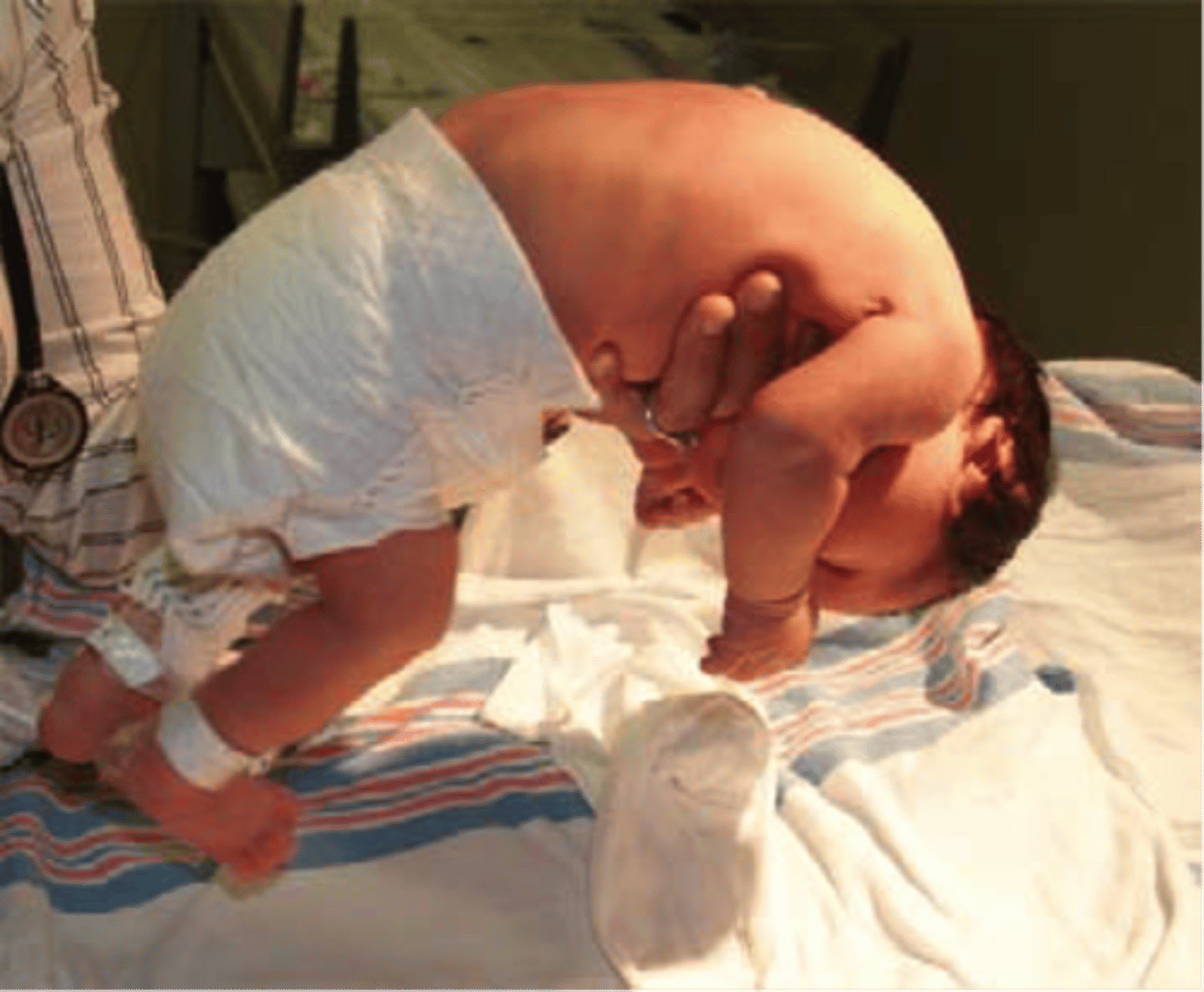
Hypotonia
Floppy" baby
Decreased resistance
Pronation
Increased flexibility
what result would the babinski reflex be in an infant?
positive
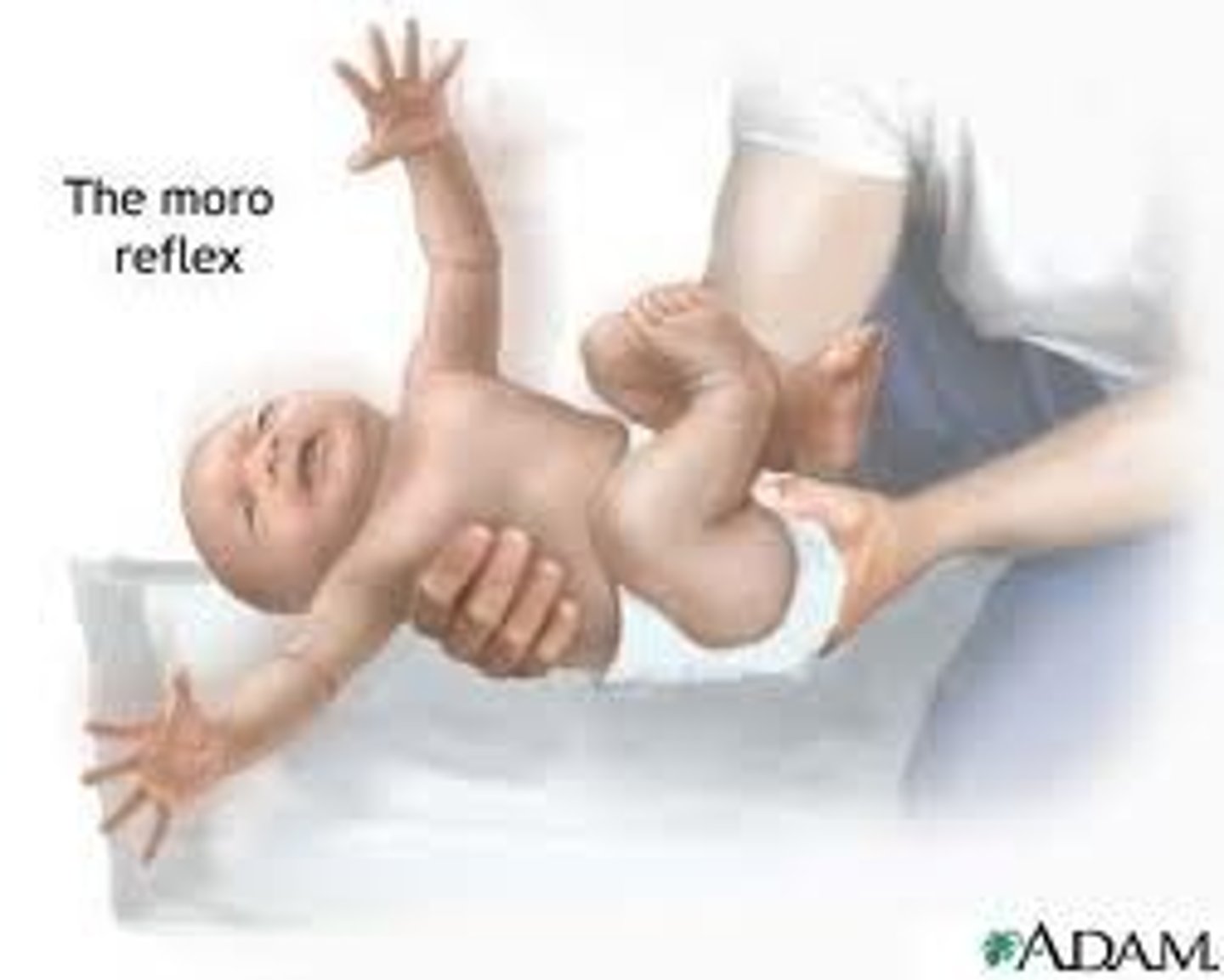
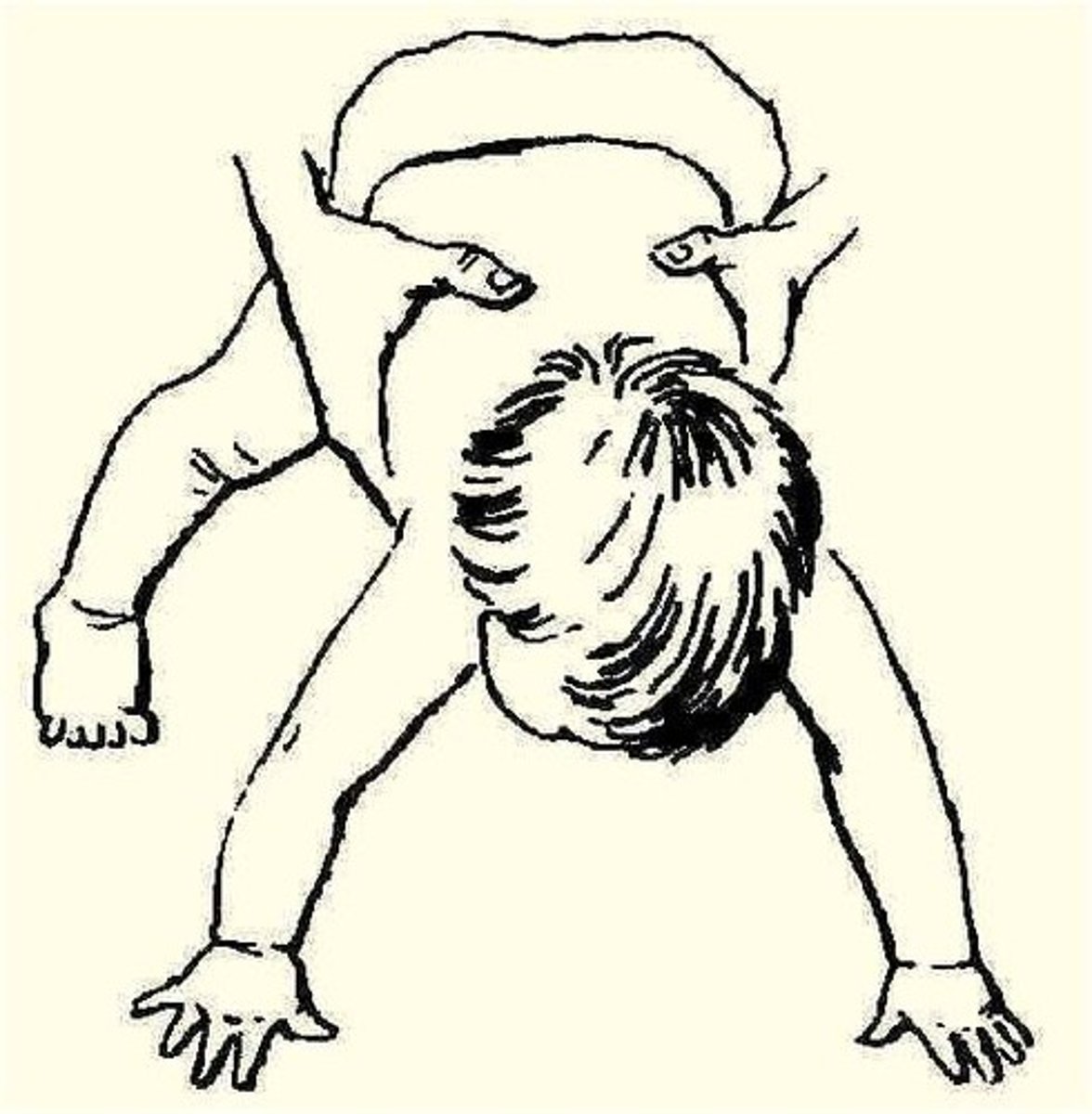
Moro reflex
Fight or Flight
Birth to 2-4 mo
Baby is lowered rapidly, head is thrown back, arms extend, cries
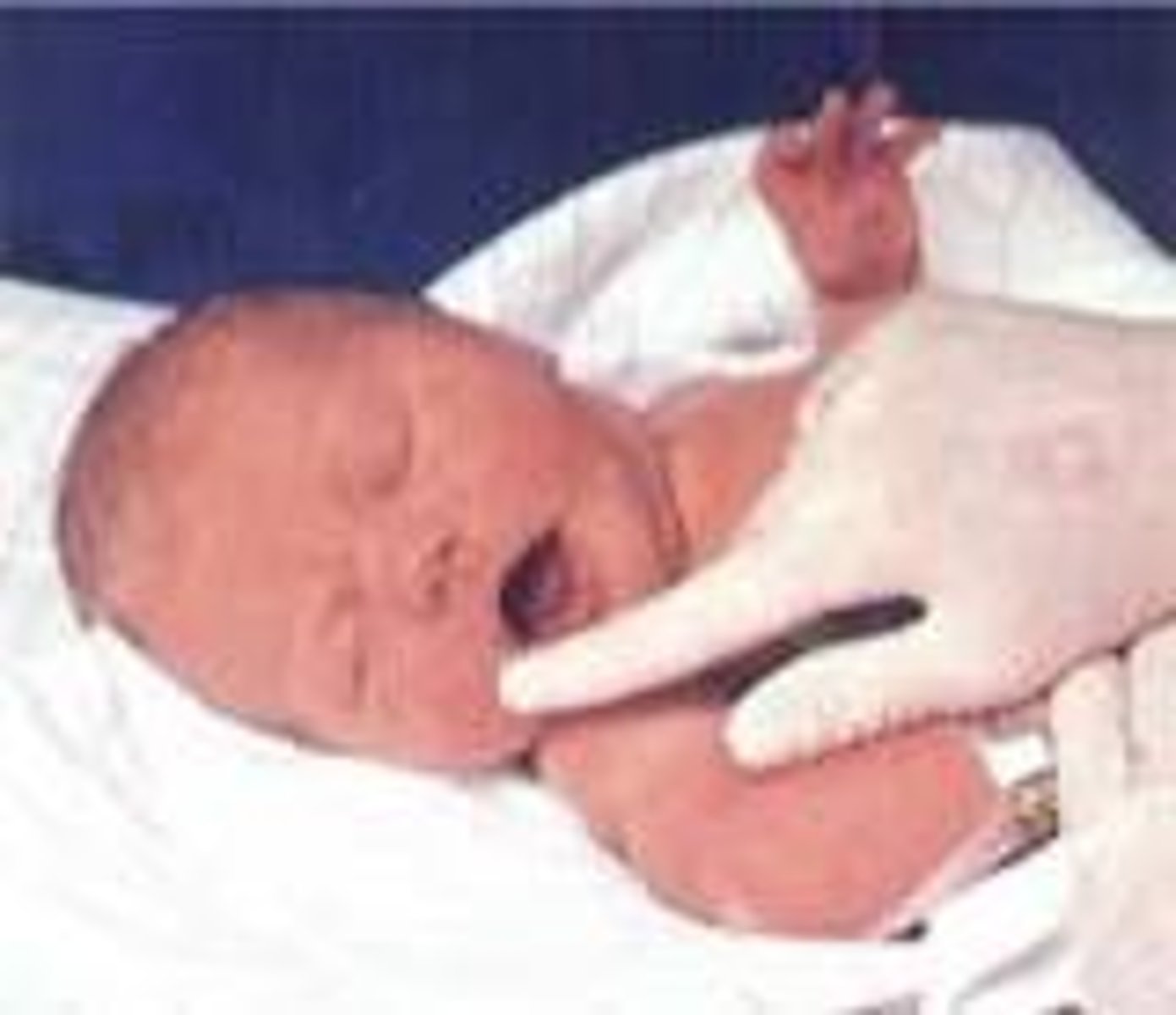
Rooting reflex
Locate food
Birth to 3-6 mo
Stroking corner of the mouth, the mouth will open and head will turn toward stimulus
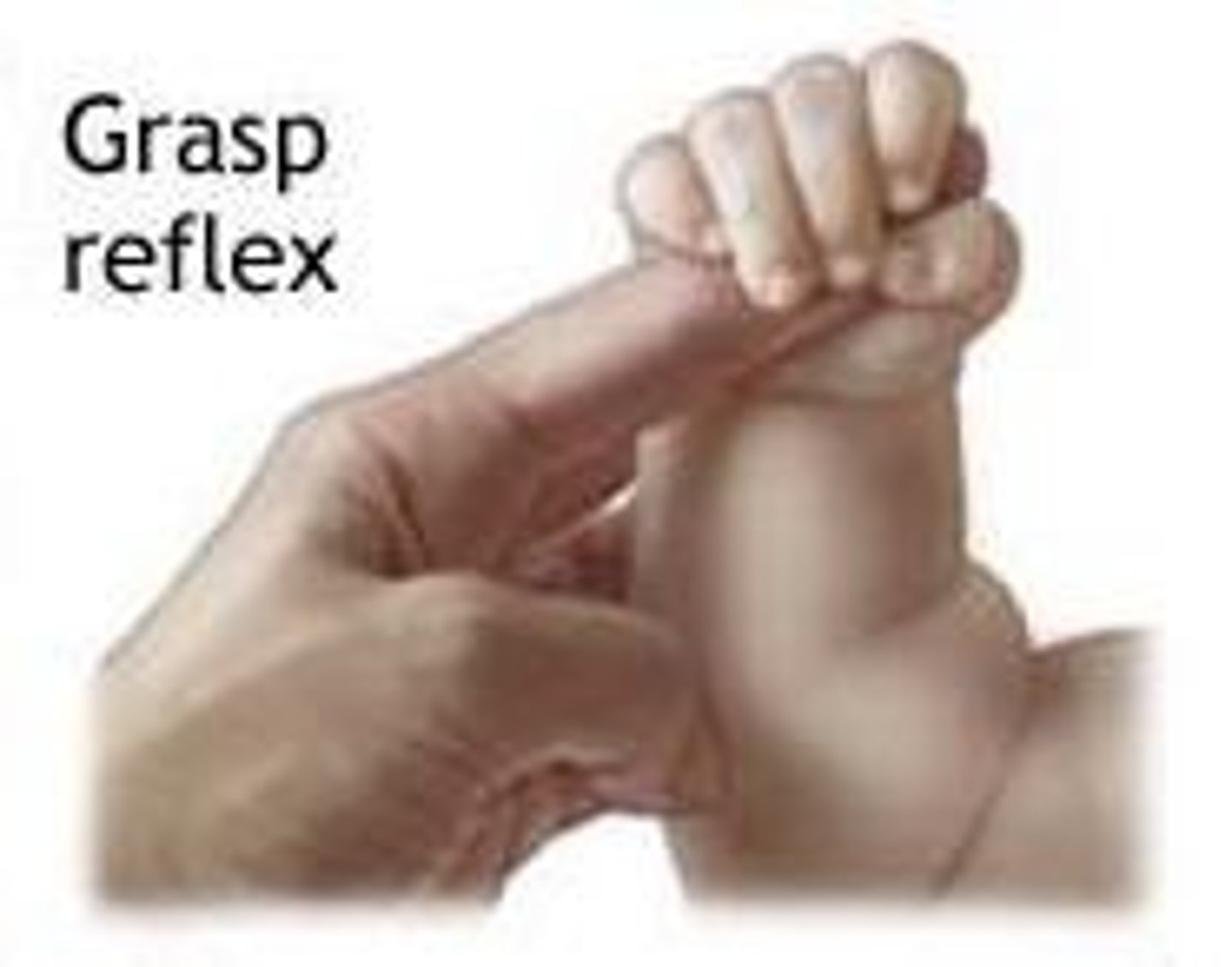
Palmar grasp
Grasping
Birth to 6 mo
Fingers close around an object placed in the palm
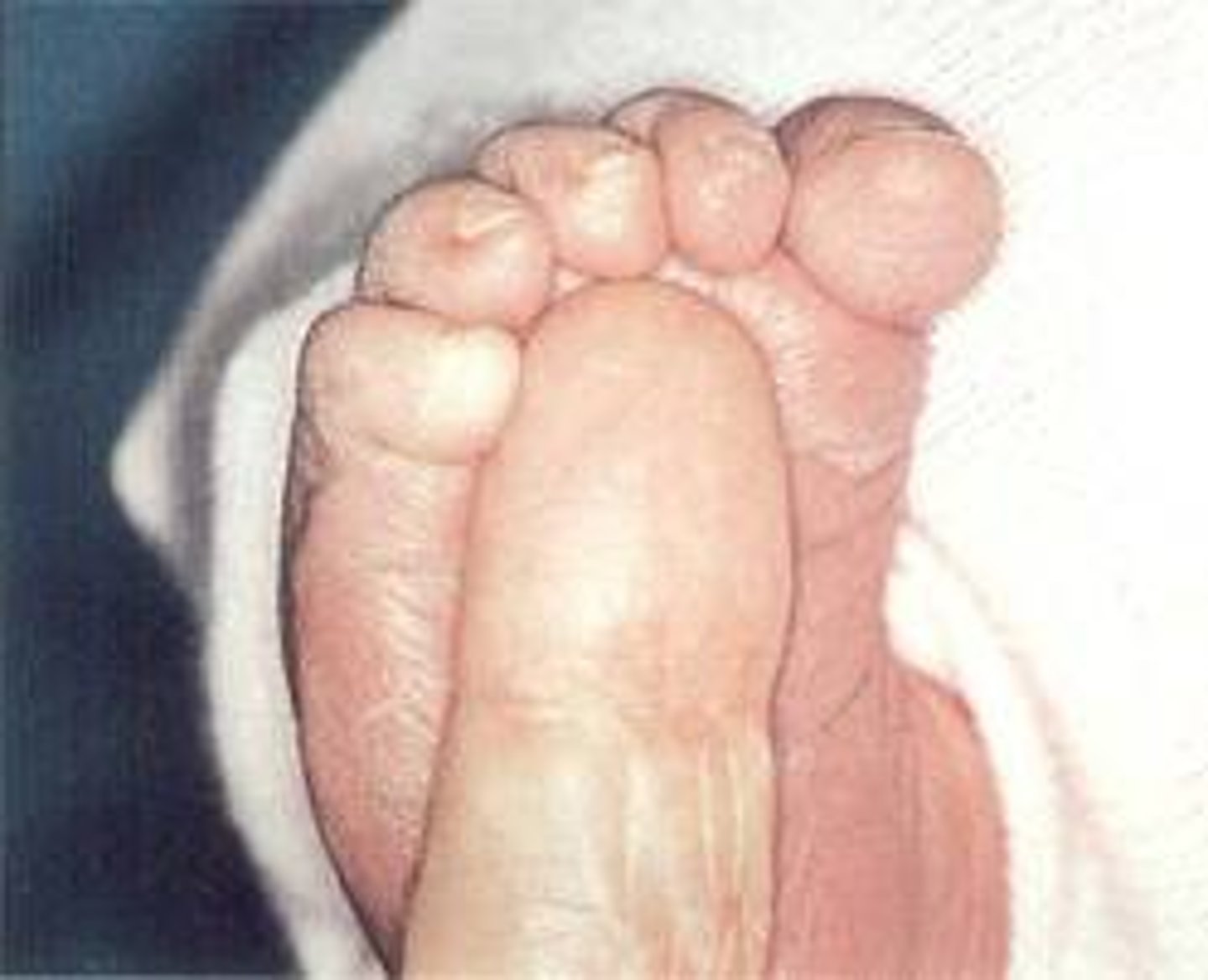
Plantar grasp
Protect the foot
Birth to 6 mo
Toes curl downward when sole is gently pressed
Asymmetric tonic neck reflex
Passage through birth canal
Birth to 3-9 mo
Supine turn head to one side, arms and legs on that side extend
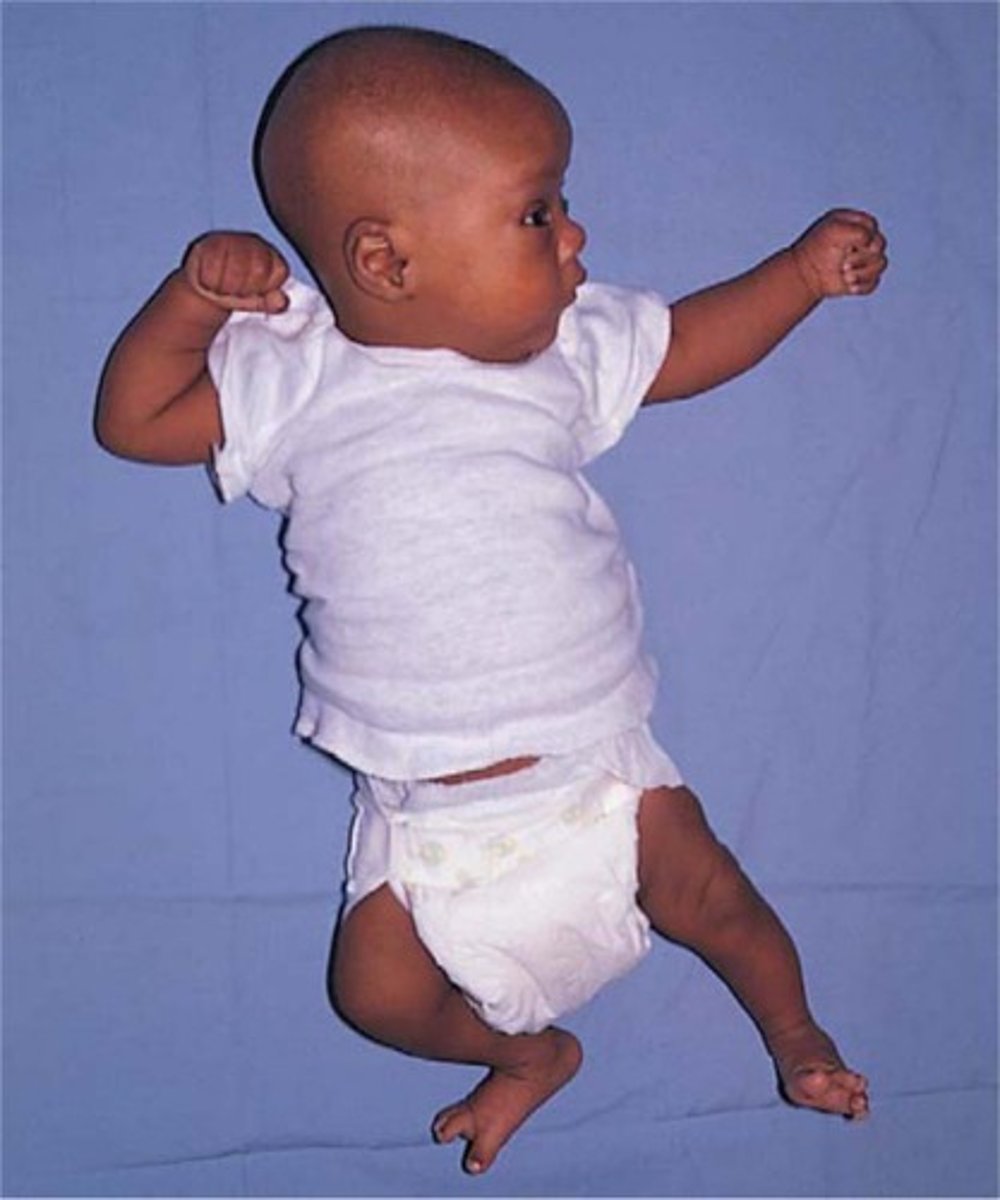
Stepping reflex
Instinct for walking
Birth to 2 mo
Appear to walk when held upright with feet on flat surface
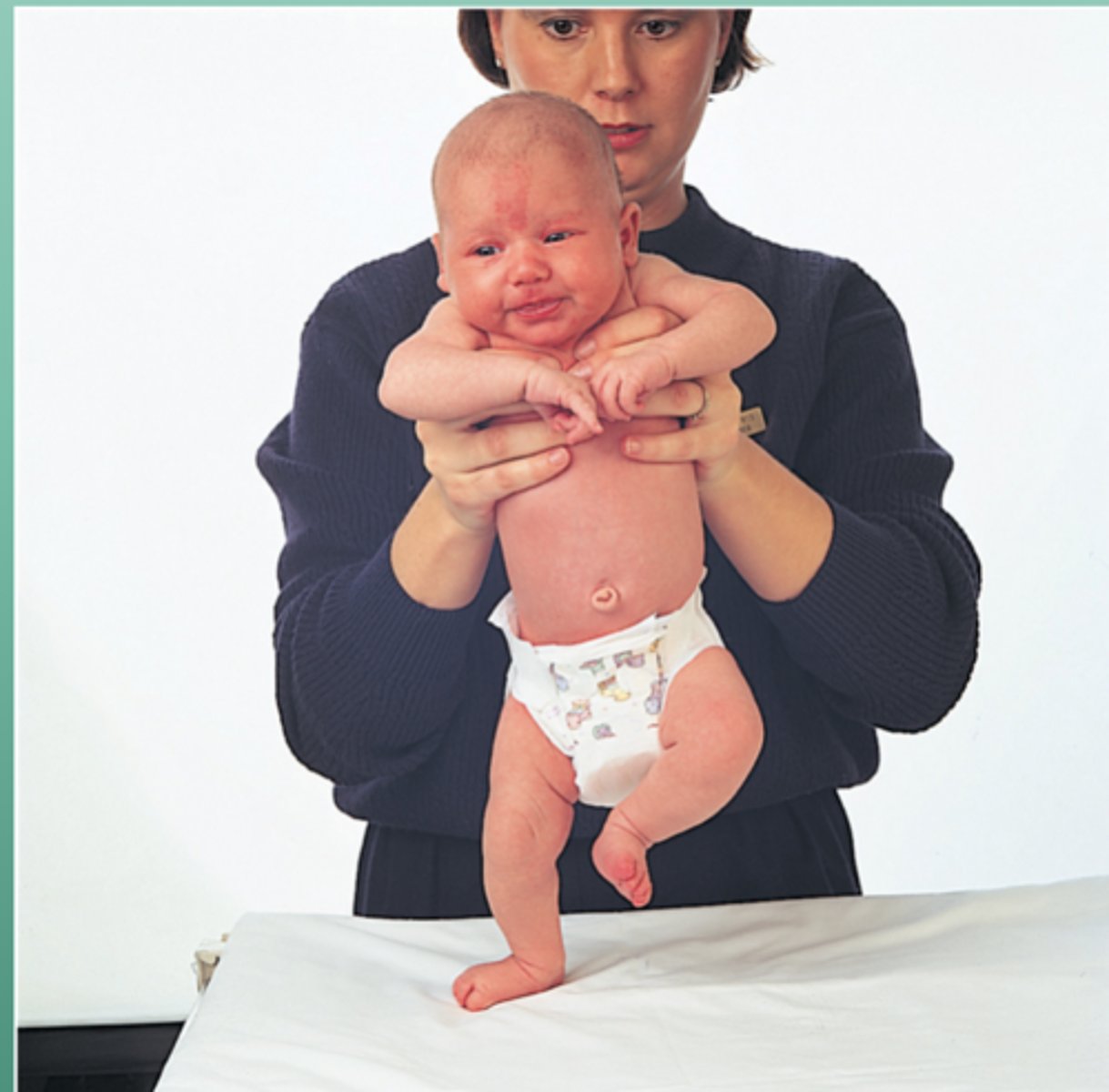
Landau reflex
Postural stability
4-5 mo to 1 yr
Holding baby prone, head will lift up and spine will straighten
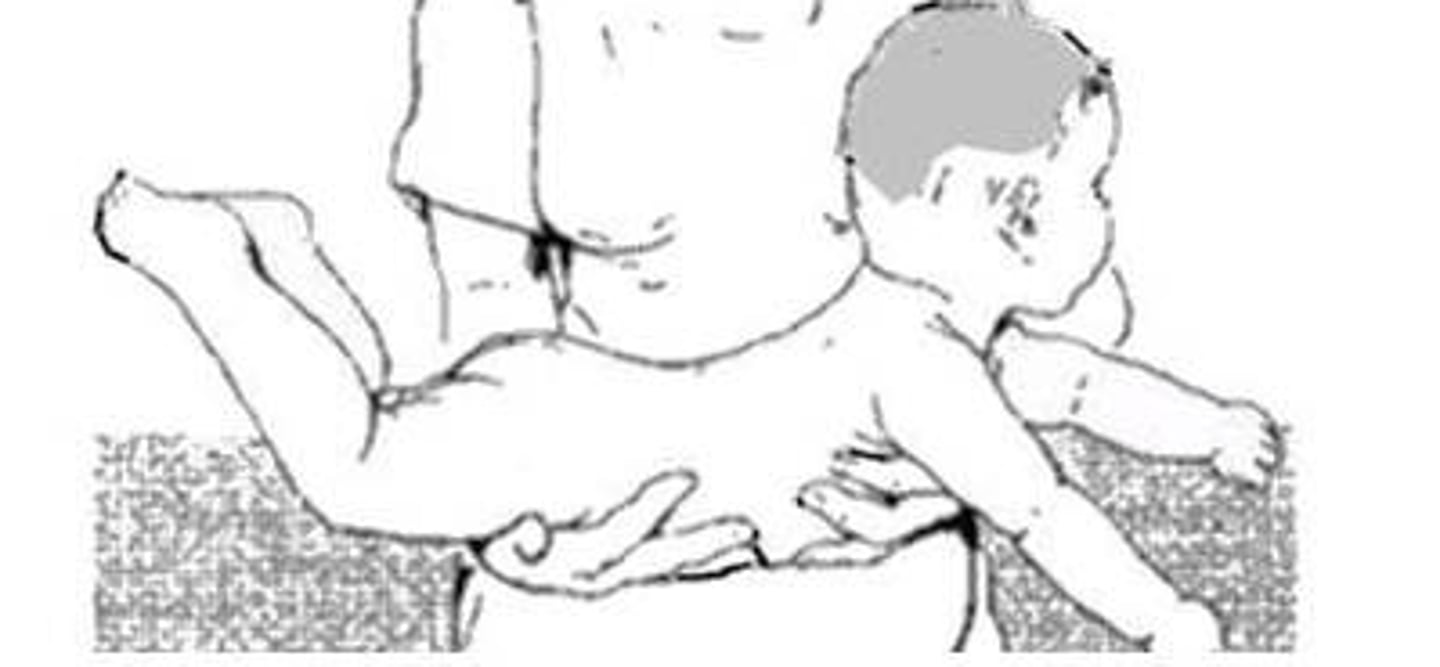
Parachute reflex
Instinct for catching oneself
8-9 mo through life
Holding baby prone and tipping head down, arms and legs extend
what is a normal pulse in early childhood?
110 bpm (1-2 years old)
103 bpm ( 2-6 years old)
95 bpm (6-10 years old)
what is a normal respiratory rate in early childhood?
20-40 rpm early childhood, 15- 25 late childhood, 14-20 from 15yr+
a toddler comes in with a hyper nasal voice. what do you suspect?
Submucosal cleft palate
a toddler comes in with a nasal voice and snoring. what do you suspect?
Adenoid hypertrophy mouth
a toddler comes in with a hoarse voice and cough. what do you suspect?
Viral infection
a toddler comes in with "rocks in their mouth". what do you suspect?
Tonsillitis
a toddler comes in with a "hot potato voice". what do you suspect?
Peritonsillar abscess
still's murmur
grade I-II/IV musical/vibratory, early-midsystolic, mid-lower LSB, radiates to carotids, may be eliminated with carotid compression
venous hum
soft, hollow, continuous. Louder in diastole, below the right clavicle, eliminated with jugular compression