Households and Workers
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are households?
Consumers of goods and services and suppliers of factors of production
What is disposable income?
The amount of income that households have left to spend or save after paying direct taxes (like income tax) and receiving benefits (like pensions or welfare payments)
What is consumption?
The total spending by households on goods and services to satisfy their wants and needs
What is real disposable income?
The purchasing power of disposable income, taking into consideration inflation
What is inflation?
A sustained rise in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over time, meaning that money buys fewer goods and services
What is saving?
When people delay consumption until some later time when they withdraw and spend savings plus any interest
What is the saving ratio and how do you calculate it?
The percentage of disposable income that households save rather than spend on consumption
Calculation: Savings - Disposable Income x 100
What is dissaving?
When households spend more than their disposable incomes, often by using past savings or borrowing money
What is wealth?
The total value of assets (such as houses, savings, shares, and possessions) owned by a person or household, minus any debts owed
What is consumer confidence?
A measure of how optimistic consumers feel about the future of the economy and their personal finances
What are interest rates?
The cost of borrowing money or the reward for saving money
What is division of labour?
When the production process is split into different tasks, and each worker specializes in one particular task
List and explain factors affecting consumer expenditure
Disposable income
Wealth
Consumer confidence
Interest rates
Age
Gender
Different tastes
Real incomes have risen
People work fewer hours than they did years ago
Social attitudes have changes
Population trends
People have become more health conscious
Concern for the environment is growing
Technology is advancing rapidly
Why do wages differ between different occupations?
Different abilities and qualifications
“Dirty” jobs and unsociable hours
Job satisfaction
Lack of information about other jobs and wages
Labour immobility
Fringe benefits
Why do wages differ within the same occupation?
Regional differences in labour demand and supply
Length of service
Local pay agreements
Non-monetary rewards differ
Discrimination
List and explain factors that affect saving patterns
Saving for future consumption
Interest rates
Consumer confidence
Availability of saving schemes
List and explain factors that affect borrowing
Interest rates
Wealth
Consumer confidence
Ways of borrowing and availability of credit
List and explain non-wage factors when choosing an occupation
Hours of work
More hours of work: shift left in supply
Less hours of work: shift right in supply
Holiday entitlement
More holiday entitlement: shift right in supply
Less holiday entitlement: shift left in supply
Promotion prospects (opportunities for promotion)
Promotion prospects refers to the opportunity for workers to be promoted within a company
More promotion prospects: shift right in supply
Less promotion prospects: shift left in supply
Flexible working arrangements
More flexible working arrangements: shift right in supply
Less flexible working arrangements: shift left in supply
Qualifications required
More qualifications required: shift left in supply
Less qualifications required: shift right in supply
Quality of working environment
Higher quality of working environment: shift right in supply
Less quality of working environment: shift left in supply
Job security
More secure: shift right in supply
Less secure: shift left in supply
Job satisfaction
More satisfying: shift right in supply
Less satisfying: shift left in supply
Fringe benefits (such as health insurance, paid time off, retirement plans..)
More fringe benefits: shift right in supply
Less fringe benefits: shift left in supply
Training opportunities
More training opportunities: shift right in supply
Less training opportunities: shift left in supply
Pension entitlement
Pension entitlement: shift right in supply
No pension entitlement: shift left in supply
Interesting and varied tasks
More interesting and varied tasks: shift right in supply
Less interesting and varied tasks: shift left in supply
Distance or time it takes to travel to and from work
More distance or time: shift left in supply
Less distance or time: shift right in supply
List and explain factors affecting demand of labour
Changes in consumer demand for goods for labour
Changes in the productivity of labour
Changes in the price and productivity of capital
Changes in non-wage employment costs
List and explain factors affecting supply of labour
Changes in the net advantages of an occupation
Changes on the provision and quality of education and training
Demographic changes
List and explain advantages of division of labour
1. More goods and services can be produced
Division of labour increases skill and speed
2. Full use made of employees abilities
Increase skills and become more productive
3. Time is saved
More productive, less training needed
4. Allows use of machinery
It becomes worthwhile to use machinery and allows further saving of time and effort
List and explain disadvantages of division of labour
1. Work may become boring (monotony)
Workers doing the same thing are likely to become bored, meaning work quality may go down
2. Workers may feel alienated
Workers may feel undervalued and lose pride in their work because they can’t see final result of their efforts
3. Products become too standardized
Whether or not this is a disadvantage is up to peoples own opinion
4. Firms are unable to use labour flexibly
If workers are not multi-skilled, they are unable to cover staff absences
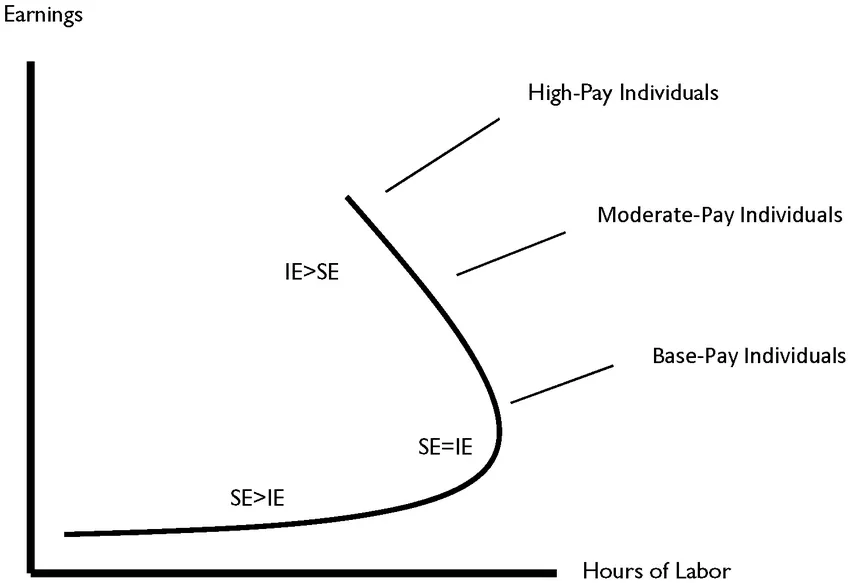
Explain the backward bending supply curve of labour
As wages rise, workers may initially choose to work more
At a certain point, workers might decide they earn enough money and would like more leisure time
As wages increase, they work less since they can take more time off and earn a lot of money