ap hug: unit 1
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
TODALSIGS
Title, Orientation, Date, author, Legend, Scale, Index, Grid, Source
Title
Explains what info the map is displaying
Orientation
A way of figuring out how to orient the map (ex. compass rose)
Date
Tells when the map was made to help reader get frame of reference
Author
The people who made the map to prove authenticity
Legend
Shows what the markings on the map mean
Map Scale
The ratio between distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the Earth
Cartographic scale/written/ratio
The way the map communicates scale
Index
Collection of major sites and location to help reader find locations (not on every map)
Grid
Series of lines on a map that match index
Source
Explains where author got info from to establish credibility
Site
Physical characteristics
Situation
The location of a place relative to other places
Problem with maps
Contortion
Reference maps
Show information (direction): boundaries, geographic features, places
Thematic maps
Tell a story about quantifiable data (ex. People)
Isoline
Map connected with contour lines
Contour lines
Lines connecting data points of the same value
Graduated Symbol
The bigger the dot, the bigger the percentage
Dot
Place a dot representing a value in its approximate location (ex. One dot per 100 people)
Cartogram
Presents a visual but distorted representation of size
Choropleth
Use colours or shading to represent data (typically the darker the area, the more there is)
Flow Line
Shows movement of goods/animals/services,etc.
Absolute direction
The exact direction you are heading
Absolute Distance
The exact distance between two places
Absolute location
The exact spot where something is located
Relative direction
The direction depends on the surrounding area
Relative distance
An approximate measurement between two places Ex. measured in time or direction
Clustered patterns
Grouped, nucleated, clumped or concentrated
Dispersed patterns
Distributed, scattered and spread out
Uniform Pattern
Evenly spaced
Random Pattern
No discernable pattern
Distance Decay
The farther away one place is from another the less interaction those two places will have with one another
Time-space compression
The reduction of time it takes for something to get from one place to another, mostly due to technology
GPS
Constellation of 24 satellites that orbit the earth to make it possible for people with ground receivers to pinpoint their geographic absolute location
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Computer system designed to gather and analyse particular kinds of data (ex. Map to show changes to a community over time)
Remote sensing
Seeing or measuring something from a considerable distance (ex. satellite)
Place
A specific point with particular physical and human characteristics
Toponym
Name given to a location that often hints at the culture of a place
Cultural Ecology
Study of Human-Environmental Interactions
Environmental Determinism Theory
The old theory that solely physical environment caused social development
Environmental Possibilism Theory
The physical environment may limit some human actions, but people have the ability to adjust to their environment.
Small scale
Small details → zoomed out
Large scale
Large details → zoomed in
Scale of data
Refers to the level of scale that data is organised by within the map (ex. County, state,nation, etc.)
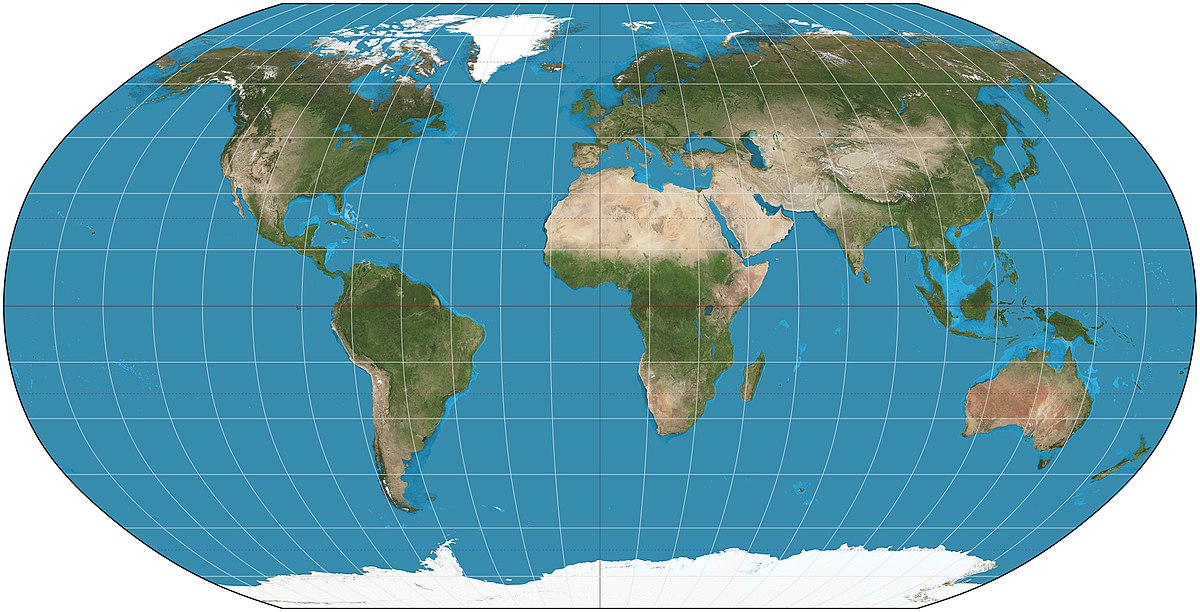
Mecrator
Used for navigation because distance accurate
Increased size distortion the further away from the equator (ex. North looks a lot bigger than it is)
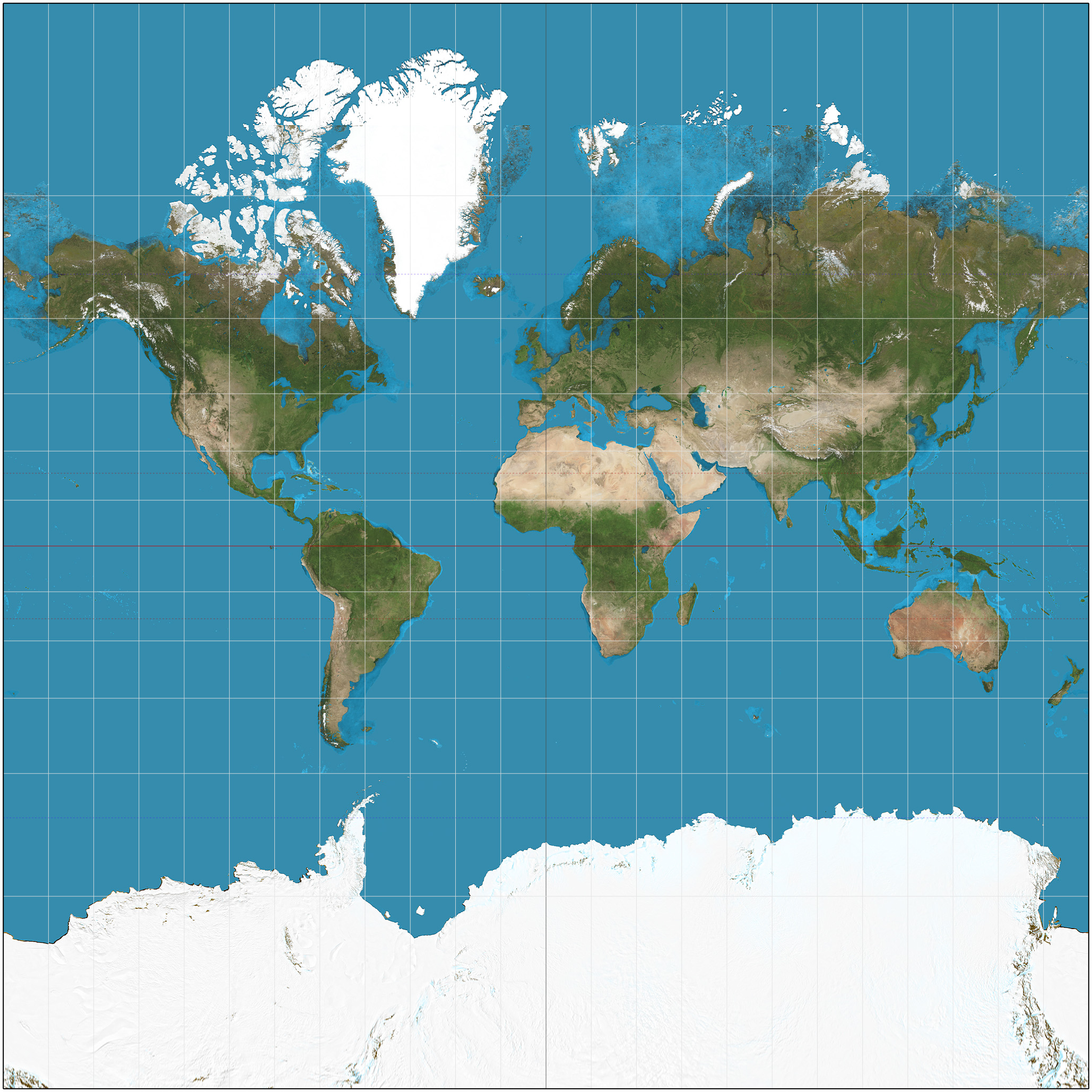
Goode Homolosine Projection
Interrupted map
True size and shape
Distortion with distance and distortion near the edges
Not useful for directions due to distortion
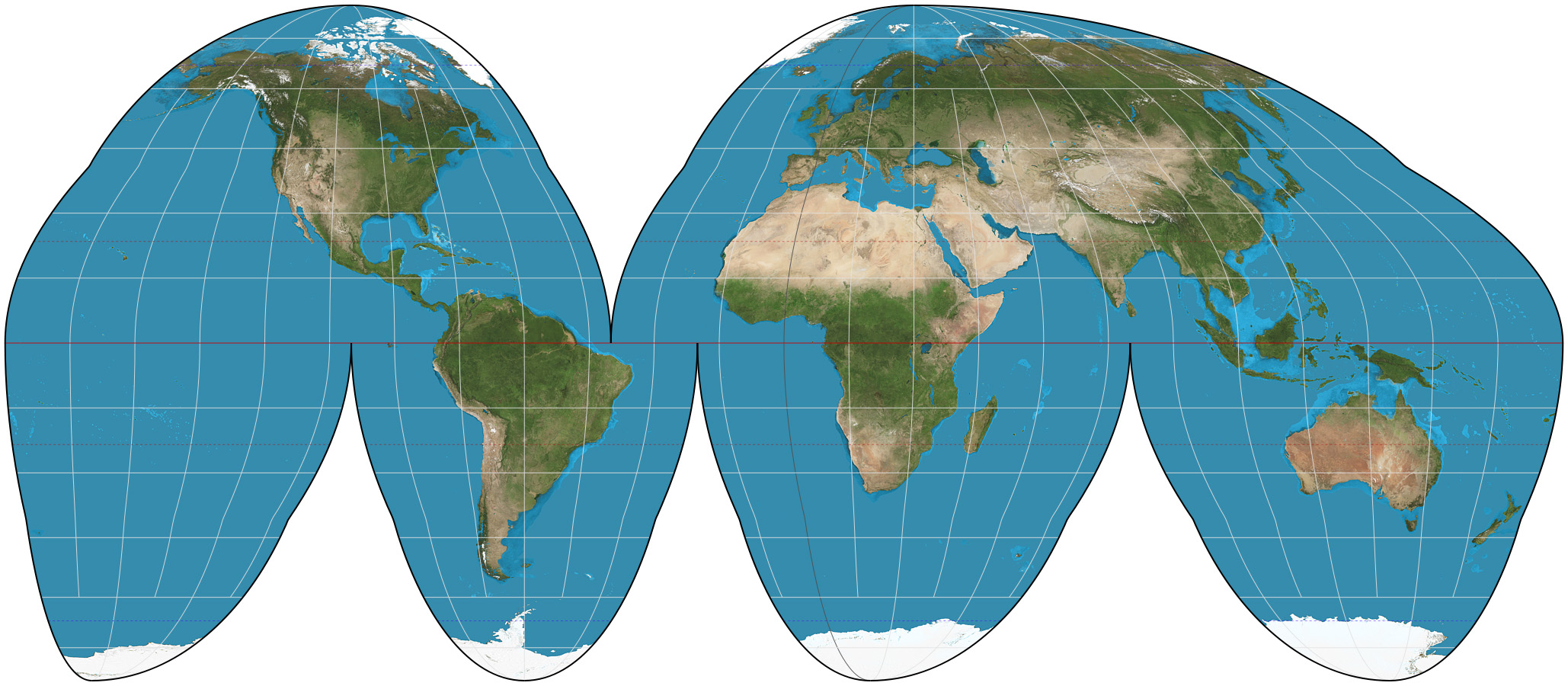
Gall-Peters Projection
Land area accuracy
Areas near the poles are stretched horizontally
More accurately shows southern hemisphere as larger than Northern Hemisphere
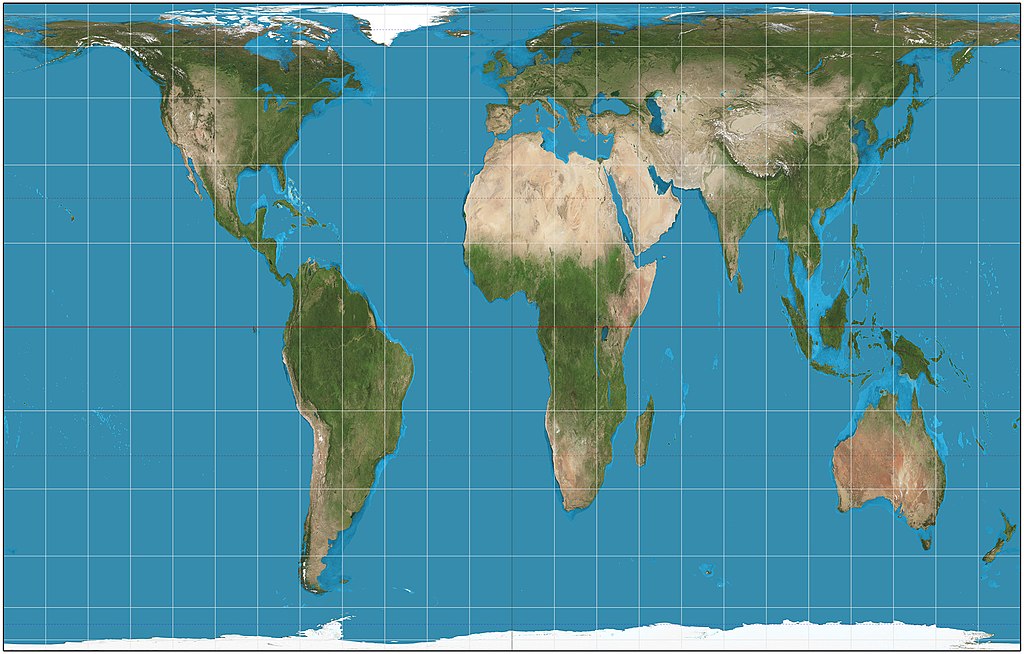
Robinson Projection
More accurately shows the area near the poles
Distorts cardinal directions and distance at the poles
Inturrupted Map
Have places that have been split
Uninterrupted Map
Do not have places that have been split
Geospatial technologies
Technology that allows people to visualize geographic data
Methods of acquiring geographic data
Field observations, personal interview, media reports, government documents, travel narratives, landscape analysis, photo analysis
Spatial Association
Relationships among variables over space
Concentration
Spread of a feature through space
Density
# of a feature within a given area
Patterns
Arrangements of features in relation to e/o
Flow
Movement of resources
Sense of place
Perception of a place due to its characteristics and familiarity
Agricultural
Production of agricultural products for human or animal consumption
Industrial
Produce/manufacture products
Commercial
Selling final goods/services
Residential
For people to build homes and live in
Recreational
Relaxing
Transportational
Helping people/goods get around
Renewable Resources
Can be reused infinitely
Non-renewable resources
Cannot be reused infinitely
Scale of Analysis
How the scale is split up
Graphic Scale
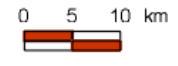
Verbal Scale
1cm : 1km
Representative Fraction / Ratio
1:100 000 000
Formal (Uniform) Region
Areas in which certain measurable characteristics are found throughout
Functional (Nodal) Region
Central Place and area around which is affected by it or uses its services
Vernacular (Perceptual)
Defined by People’s feelings and attitudes about an area
Sustainability
Sustainability consists of fulfilling the needs of current generations without compromising the needs of future generations
Aristotle
Came up with the theory the earth was spherical
Eratosthenes
Calculated the circumference of the earth
First to use the word Geography
Claudius Ptolemy
Wrote book called Geography and came up with idea of latitude and longitude
Muhammad al-Idrisi
Worked for the king of Sicily to make a accurate description of the Earth
George Perkins Marsh
Described how natural systems are impacted by human actions.
Considered to be the first modern environmentalist
Carl Sauer
Argued that cultural landscapes, the interactions between people and their environment, should be the focus of geographic study.
Geography
Study of the world (Place and space) and asking about humans’ relationships to the environment and other humans
What is Where
Describing where things are located
Why There
Describing why that phenomenon is here and not there
Why Care
Making connections – why should I care about this?
Physical Geography
The environment/natural things
Human Geography
People and things related to people or that they build (i.e. cities, transportation etc.)
Location
Ways of describing where something is
Site
The ground that the location occupies
Place
The ways of describing and identifying the characteristics of an area
Physical Characteristics
Natural features of an area
Human Characteristics
Human contributions to an area
Direct Human Impacts
Humans live there
Indirect Human Impacts
Humans do not live there, but influence through things like drifting air pollution
Human-Environment Interaction
How the Human world and the physical world impact each other
Adaptations
Changes humans have made to survive in their environments
Impacts
How human activities change the environment, and how environmental changes impact humans
Resources
How humans use the Earth’s natural resources for the own benefits
Movement and Globalization
How people and places interact