L6: Synthesis of Carbohydrate and Fatty Acid Metabolism
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering the synthesis of carbohydrates from CO2 via various pathways, the Reductive Acetyl CoA pathway, and details on fatty acid synthesis and breakdown (beta-oxidation).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Name 3 pathways by which autotrophic bacteria convert CO2 to carbohydrate.
The Calvin cycle
Hydroxypropionate pathway
Reductive acetyl CoA pathway
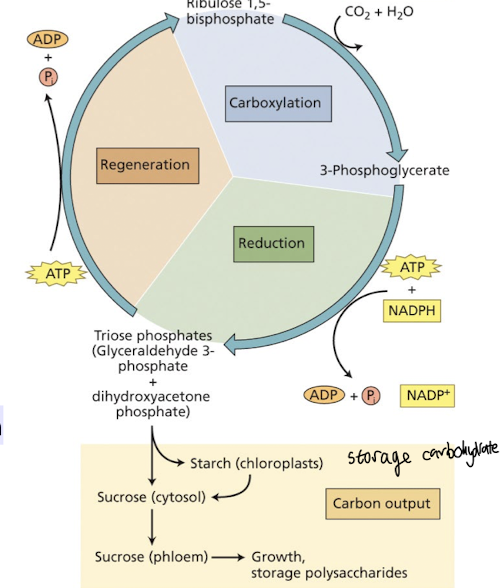
What is the Calvin Cycle?
Anabolic; it builds sugar from smaller molecules by using ATP + the reducing power of NADPH
C enters the cycle as CO2 and leaves as a sugar named glyceraldehyde 3-phospate (G3P)
Consists of 3 phases:
Carboylation by Rubisco + attaches to 5C sugar ribulose biphosphate
Reduction of NADPH + phosphorylation of 3PG produce G3P, reversal of glycolytic steps creates F6P
Regeneration of the CO2 acceptor (RuBP) by excess G3P
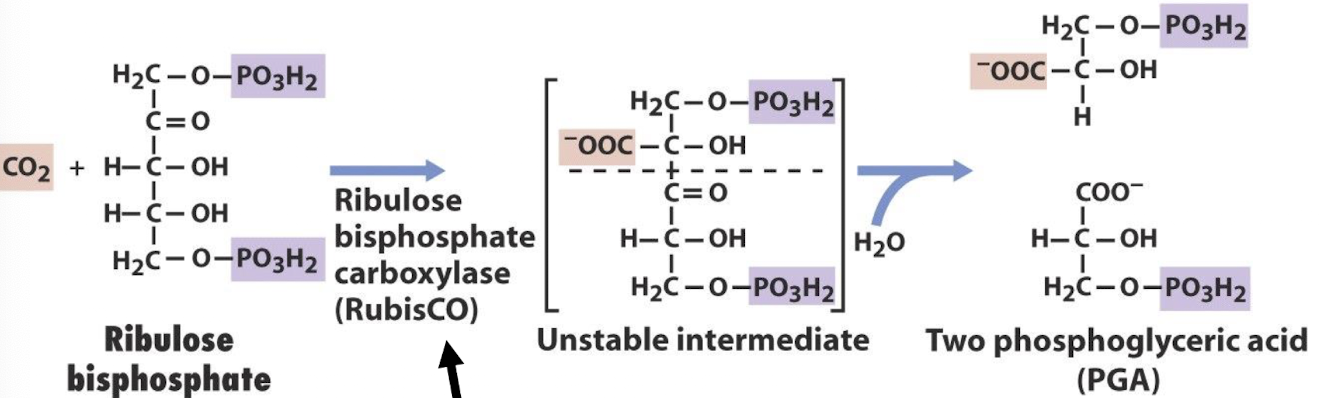
How is ribulose bisphosphate carboxylated by RubisCO?
Ribulose bisphosphate is carboxylated by RubisCO to form 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) during the carbon fixation phase of the Calvin cycle, enabling the incorporation of CO2 into an organic molecule.
-Very slow enzyme, catalyses only 3 carboxylations per second
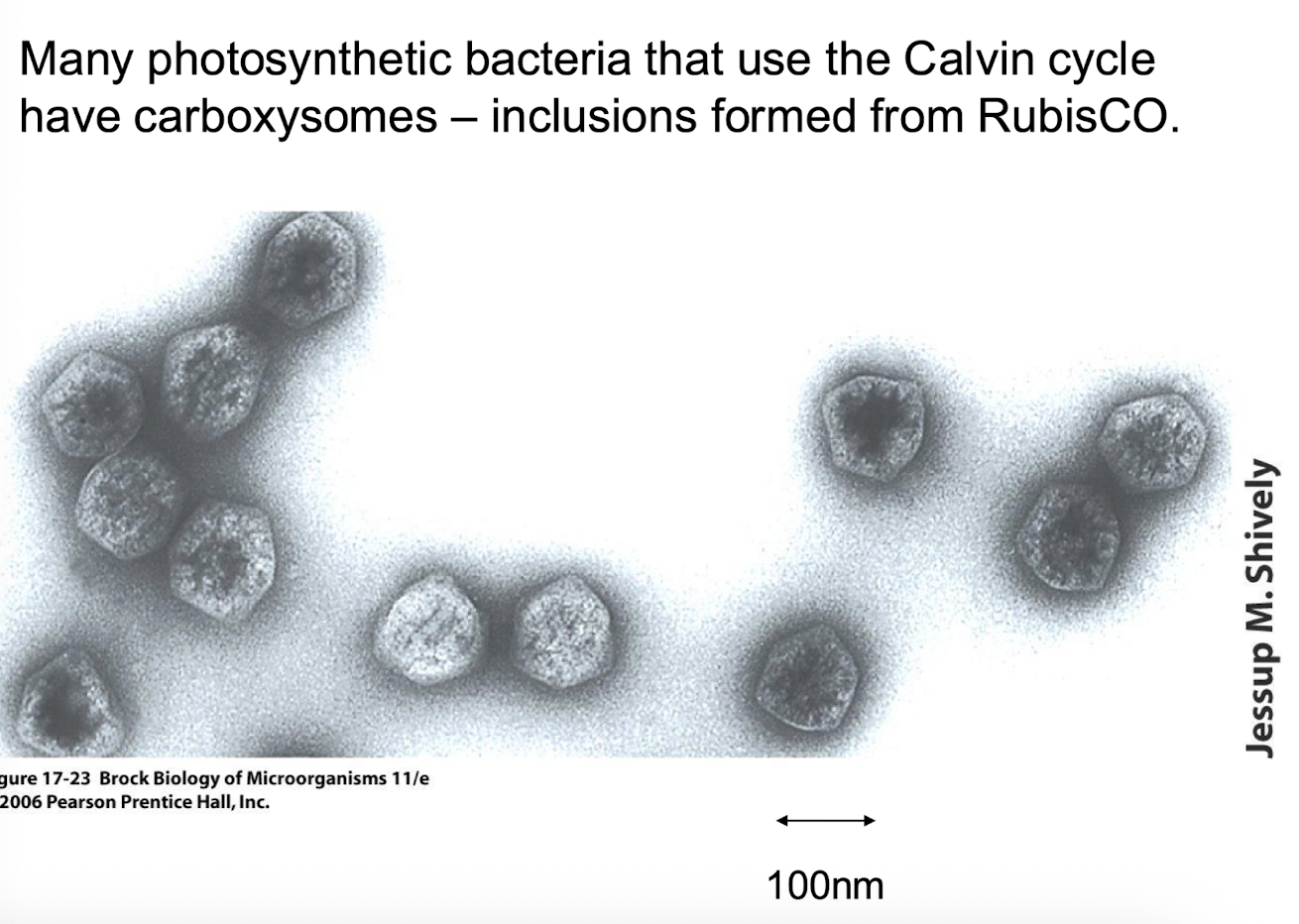
what are carboxysomes in photosynthetic bacteria?
Carboxysomes are specialized organelles found in photosynthetic bacteria that contain the enzyme Rubisco.
They facilitate the fixation of carbon dioxide by providing a localized environment for the Calvin cycle, enhancing the efficiency of carbon fixation.
Which organisms primarily use the Calvin cycle for CO2 fixation?
Green plants, most bacterial phototrophs, and lithotrophs.
In the initial stage of the Calvin cycle, what two molecules react with each other?
CO2 and ribulose-bisphosphate.
How does the Calvin cycle decrease the oxidation state of C?
It reduces CO2 (+4) to levels found in carbohydrates (i.e +2 in keto groups -(-CO=) to 0 in secondary alcohols (-CHOH-) using electrons from NADPH.
Hence also known as the reductive pentose phosphate cycle
What are the 4 main functions of the pentose phosphate pathway?
1. Generates pentoses for nucleotide biosynthesis.
2. Generates NADPH via oxidation for biosynthetic reductions
3. Enables pentoses to be used as a source of carbon and energy.
4. Provides precursors for aromatic amino acid biosynthesis i.e. Phe e.g. erythrose 4 phosphate (precursor in shikimate pathway)
Which enzyme catalyzes the initial reaction of CO2 with ribulose-bisphosphate in the Calvin cycle?
Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco).
What energy carriers are required to reduce 3-phosphoglycerate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate in the Calvin cycle?
ATP and NADPH
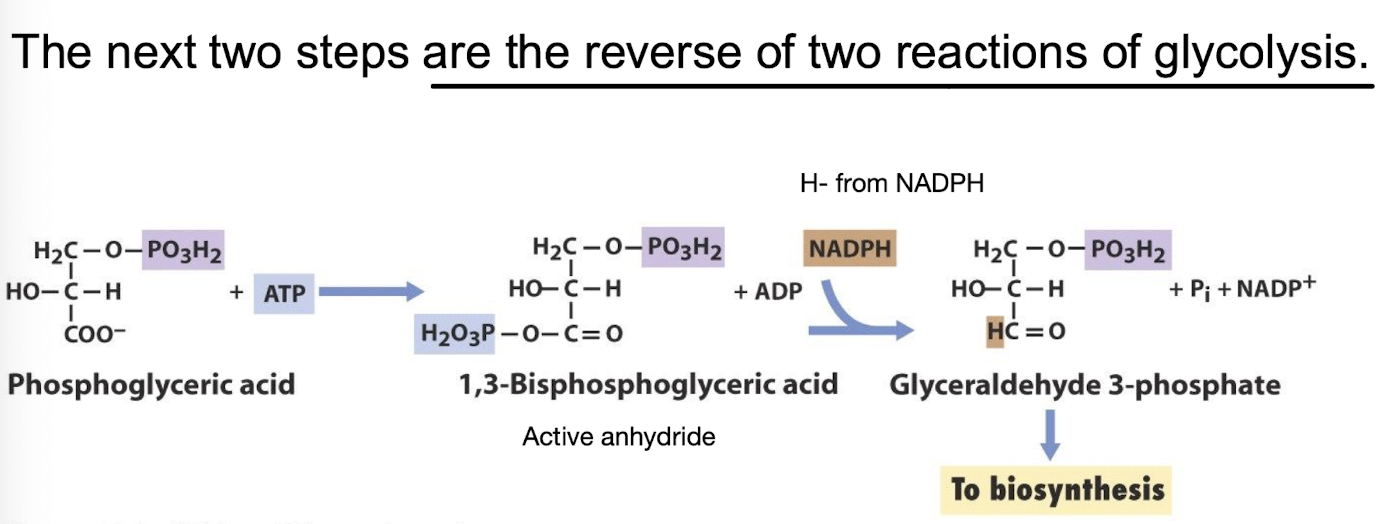
where does 3PGA go after the reduction step?
It can be converted into glucose i.e G3P + DHAP used to create starch or sucrose or used to regenerate RuBP in the Calvin cycle.
What reaction occurs in the calvin cycle that is similar to amino acid biosynthesis reactions?
Reduction of a carboxyl group to aldehyde consumes one ATP and one NADPH
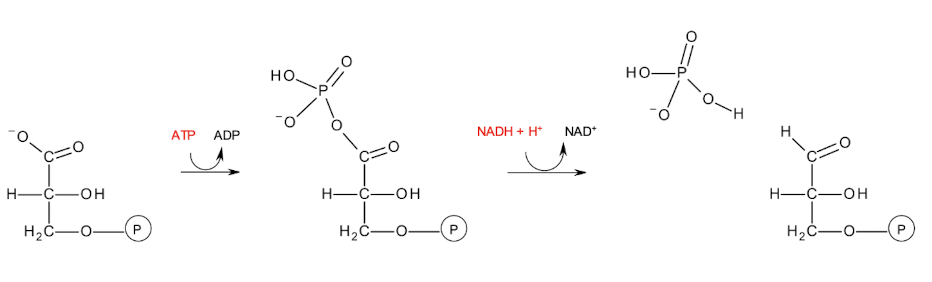
In AA biosynthesis, the side chain carboxyl groups of ASP and GLU are also reduced to aldehydes.
Reduction of a carboxyl group to a more reactive aldehyde facilitates further reactions.
Which part of the Calvin cycle is a reversal of a step in glycolysis?
Reduction of 3-PG → 1,3-BPG → GA3P (reverse of GAPDH + PGK steps)
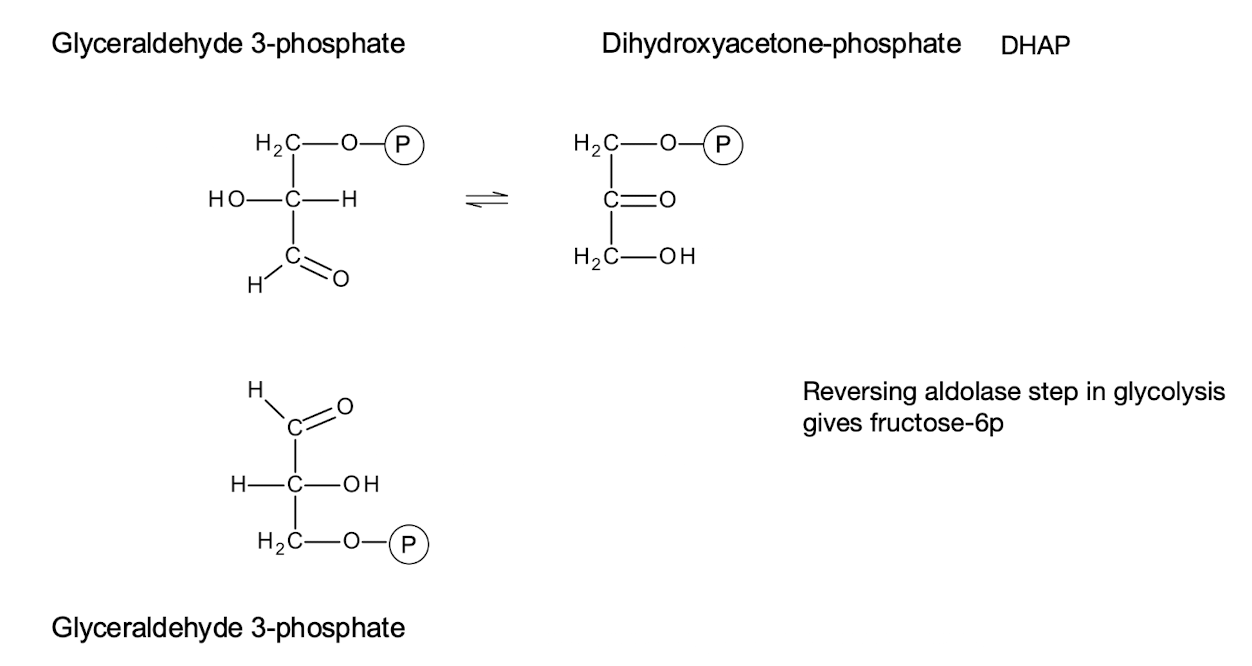
Condensation of GA3P + DHAP → F-1,6-BP (reverse of aldolase cleavage)
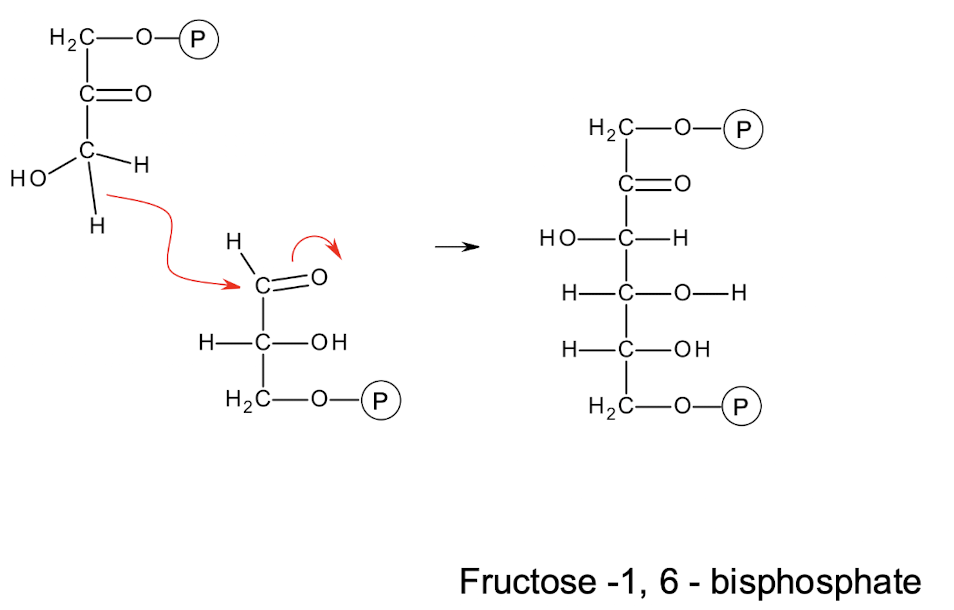
Hydrolysis of F-1,6-BP → F-6-P (reverse of PFK-1 step via FBPase)
How many ATP and NADH + H+ molecules are required in the Calvin cycle to generate one new hexose from six CO2 molecules?
18 ATP and 12 NADH + H+.

In some phototrophs and lithotrophs, what is the primary function of the reverse citric acid cycle?
To synthesise acetyl CoA from CO2
e.g. in the green sulphur phototroph Chlorobium limicola
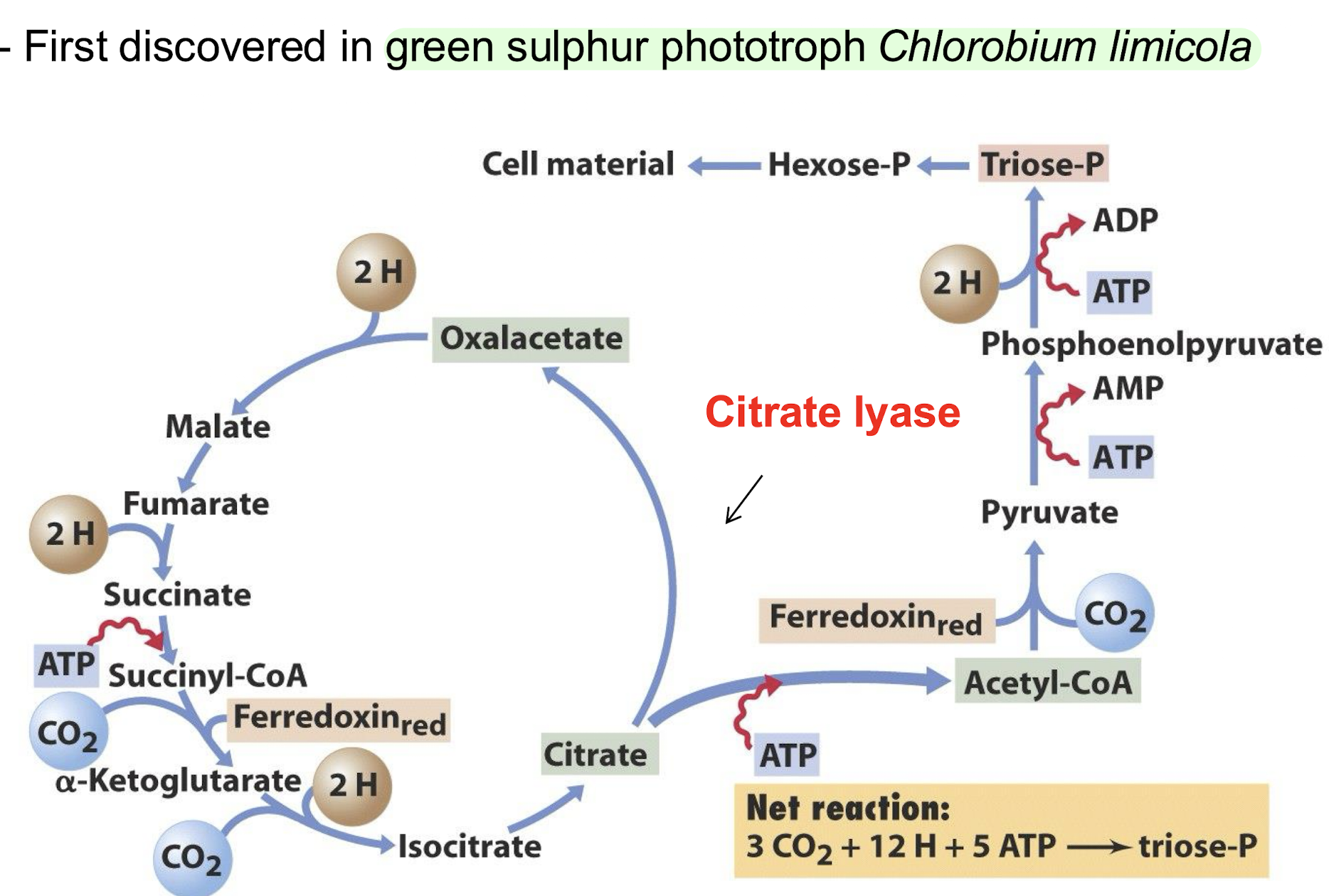
What does the reverse citric acid cycle consume to synthesize acetyl CoA from CO2?
ATP and reducing power.
Name additional enzymes required for the reverse citric acid cycle compared to the forward cycle.
Ferredoxin-dependent α-ketoglutarate synthase
Pyruvate synthases
ATP citrate lyase
Which photosynthetic bacterium was the hydroxypropionate pathway discovered in, and what is a key intermediate in this pathway?
Chloroflexus, with 3-hydroxypropionate as a key intermediate.
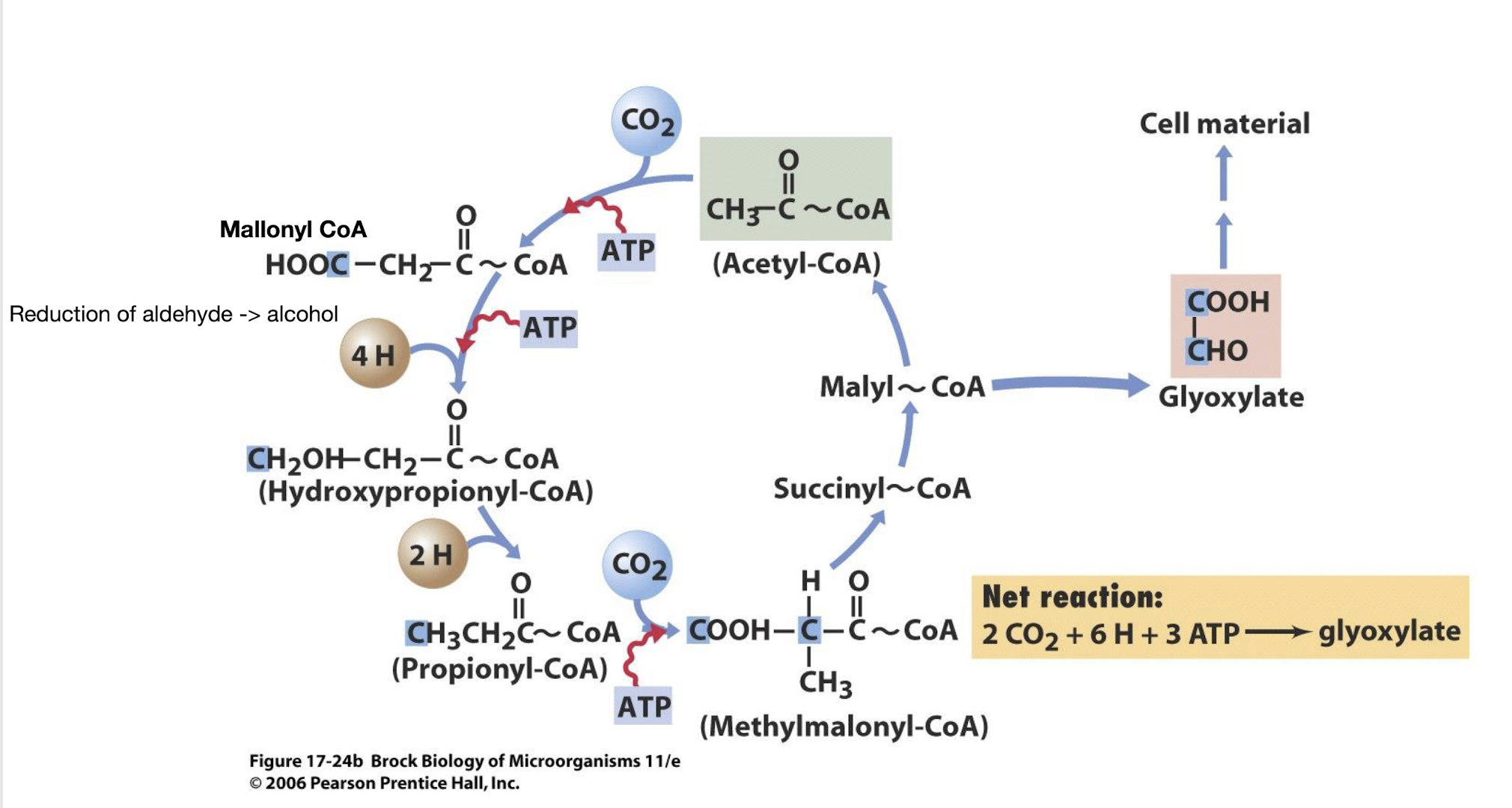
Which types of lithotrophs use the reductive acetyl CoA pathway (acetogenesis)?
Acetogens and methanogens.
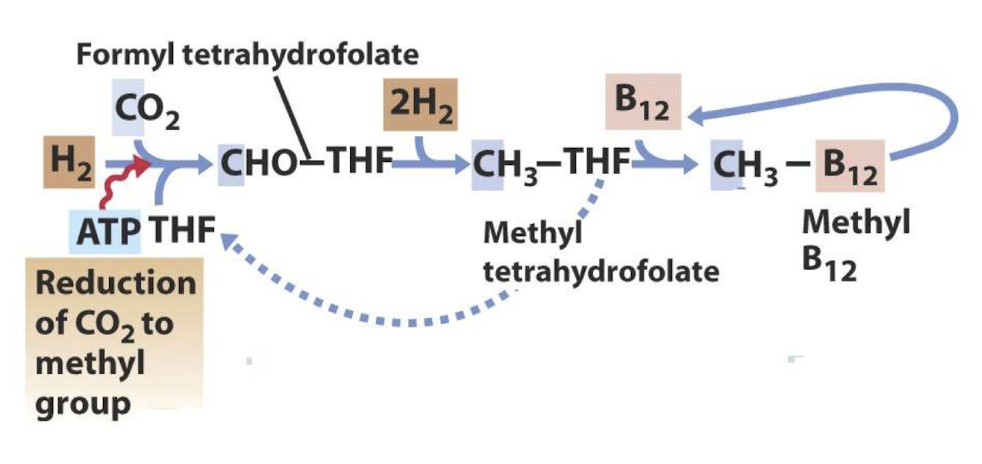
In the reductive acetyl CoA pathway, how are the two CO2 molecules processed to form acetyl CoA?
One CO2 is reduced to a methyl group (via formic acid and THF), and the other CO2 is reduced to carbon monoxide.
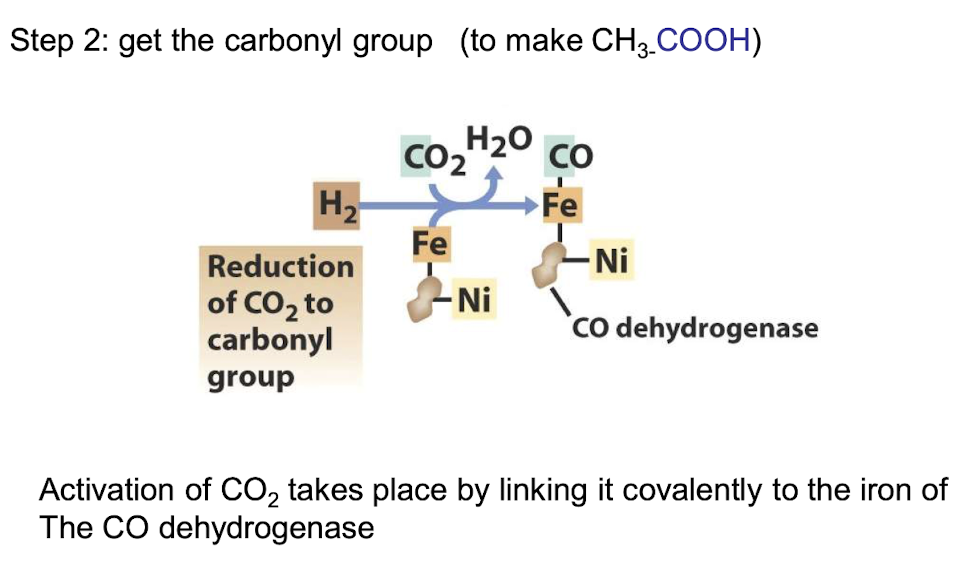
What bifunctional enzyme is involved in the reductive acetyl CoA pathway?
CO dyhydrogenase
Activation of CO2 takes place by linking it covalently to the Fe of this enzyme
How does the reductive acetyl CoA pathway generate ATP directly from the energy released during its steps?
Energy released generates a transmembrane sodium gradient that can drive ATP synthesis.
What is the biochemical function of tetrahydrofolate (THF)?
To act as a carrier of one-carbon units in different oxidation states (e.g., formyl, methenyl, methylene, and methyl groups).
What are 3 important functions of fatty acids in organisms?
They are components of membrane lipids, serve as an energy store, and function in post-translational modifications of proteins.
What key product of glucose breakdown serves as the building block for fatty acids?
Acetyl CoA.
What kind of process is fatty acid biosynthesis, in terms of adding carbon units?
A cyclic process involving repeated additions of two carbon units.
What are the two main precursors for fatty acid biosynthesis?
Acetyl CoA (the starter) and malonyl CoA (the extender).
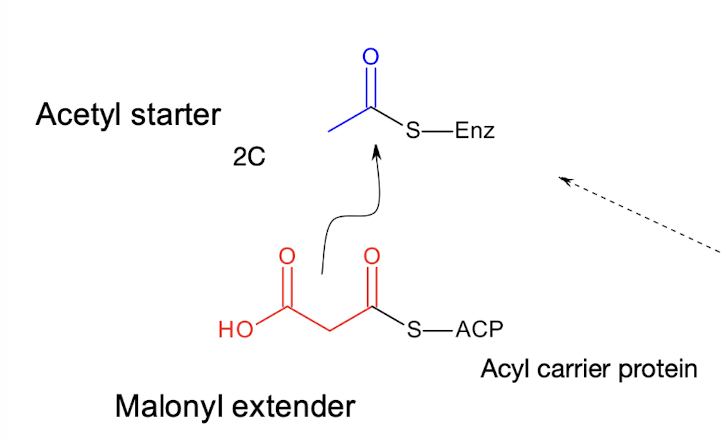
How is malonyl CoA formed during fatty acid biosynthesis?
By carboxylation of acetyl CoA in an ATP-requiring reaction.
Besides ATP for malonyl CoA formation, what other energy carrier is required for the chain-building process in fatty acid biosynthesis?
NADPH.
What protein plays a crucial role in coordinating the six enzymes involved in fatty acid chain assembly?
Acyl carrier protein (ACP).
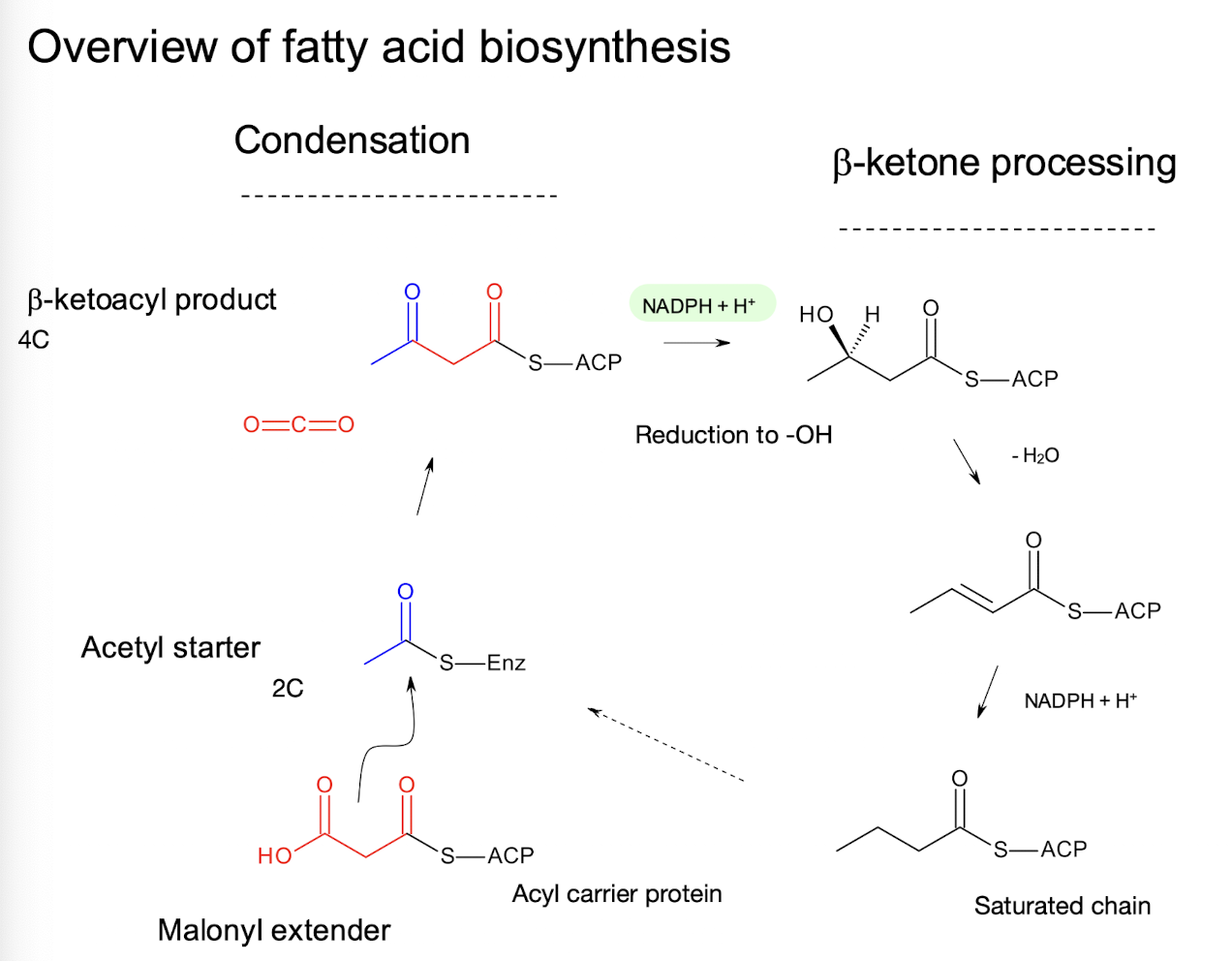
What special prosthetic group does ACP have, and what is its role?
Phosphopantetheine, which has a thiol group where carboxylic acid chains are attached as thioesters.
What is the major final product of fatty acid biosynthesis, typically a 16-carbon chain?
Palmitic acid.
What is the overall process of fatty acid breakdown known as?
Beta-oxidation of fatty acids.
What energy-carrying molecules and carbon units are yielded during fatty acid breakdown?
FADH, NADH, and acetyl CoA.
Before degradation, what molecule is the fatty acyl chain loaded onto?
CoA.
During fatty acid breakdown, what molecule is reduced to FADH during the dehydrogenation step?
Dehydrogenation gives an α-β unsaturated chain and reduces FAD to FADH..
Which enzyme splits the β-ketoacyl chain to release acetyl CoA and a shortened acyl chain?
Thiolase.
What pathway do the acetyl CoA molecules generated from fatty acid breakdown feed into to yield energy?
The citric acid cycle.