KIN 224 Chapter 15: Homework
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
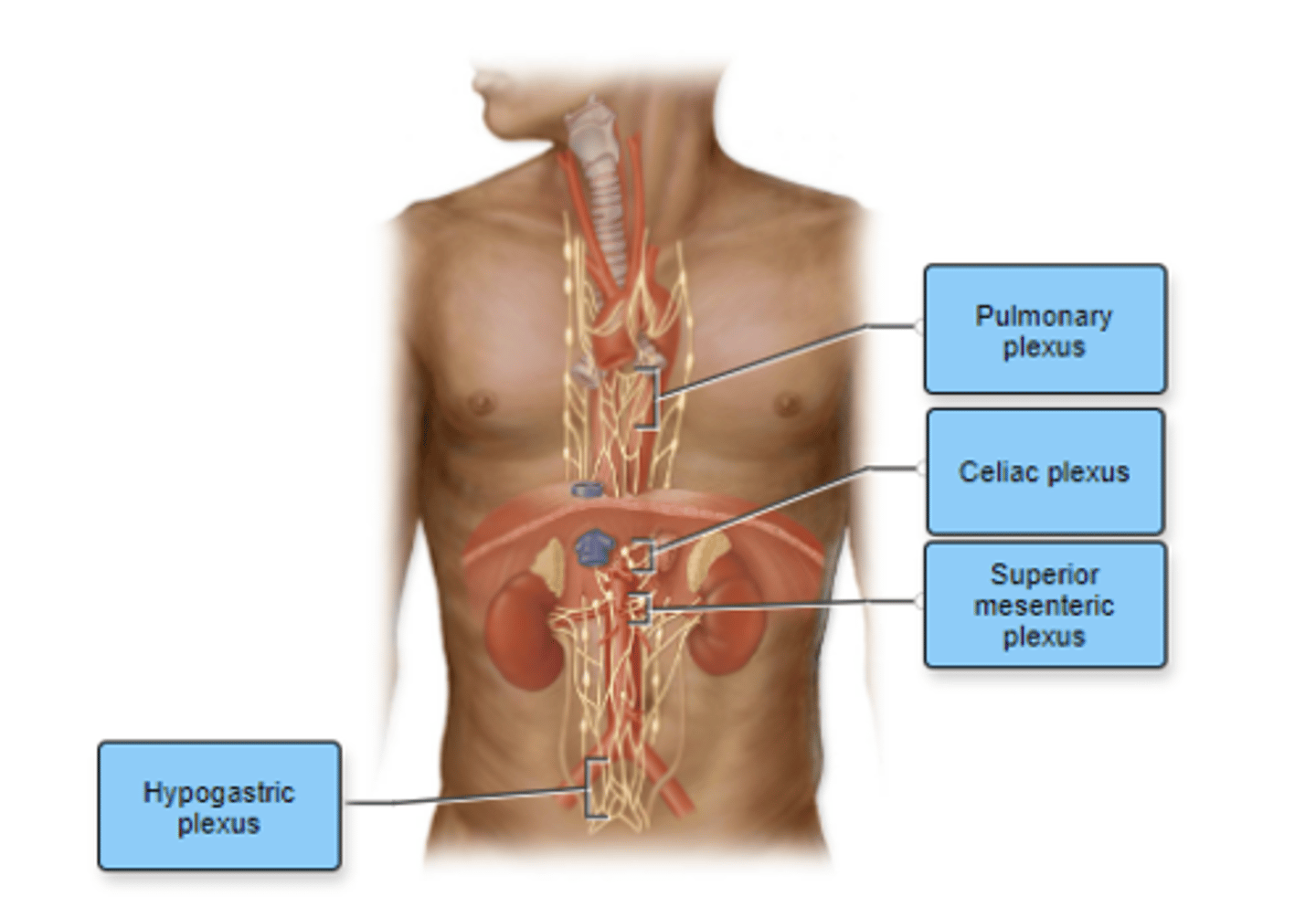
Label the autonomic plexuses in the figure.
Also known as the ______ division, the sympathetic nervous system exits the CNS via many spinal nerves T1—L2.
thoracolumbar
Action potentials travel along the preganglionic nerve fiber and enter the ______.
sympathetic chain ganglion
Fibers exiting the sympathetic chain ganglia take one of three routes: 1) the spinal nerve route, 2) the sympathetic nerve route, or 3) the ______ nerve route.
splanchnic
Arriving at target cells, ______ nerve fibers release acetylcholine or norepinephrine into the synaptic cleft.
postganglionic
The effect of norepinephrine binding to _______ receptors stimulates cardiac muscle cells.
adrenergic
Match the four pathways of sympathetic neurons with the region of the body having effector organs innervated by each pathway.
A: neck, torso, and limbs - spinal nerve pathway
B: head/eye - postganglionic sympathetic nerve pathway
C: abdomen/pelvis - splanchnic nerve pathway
D: adrenal gland - adrenal medulla pathway
Which neurotransmitters are considered catecholamines?
dopamine, norepinephrine, acetylcholine, epinephrine
Which of the following is an example of a system or function only controlled by the sympathetic nervous system?
the adrenal medulla
The sympathetic division is also called what?
thoracolumbar division
Esophogeal plexus:
carries signals that control swallowing correct
Hypogastric plexus:
carries signals to pelvic region correct
Pulmonary plexus:
passes signals to bronchi correct
Abdominal aortic plexus:
composed of celiac and mesenteric plexuses correct
Which of the following statements is true regarding the adrenal gland's relationship with the autonomic nervous system?
parasympathetic postganglionic neurons synapse with cells of the adrenal cortex