BIOSCI 109 🎓Lecture 9 Ecosystems 1: Biotic networks
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
explain co exitance
Multiple species co-existing in complicated networks can result in indirect and often unexpected effects
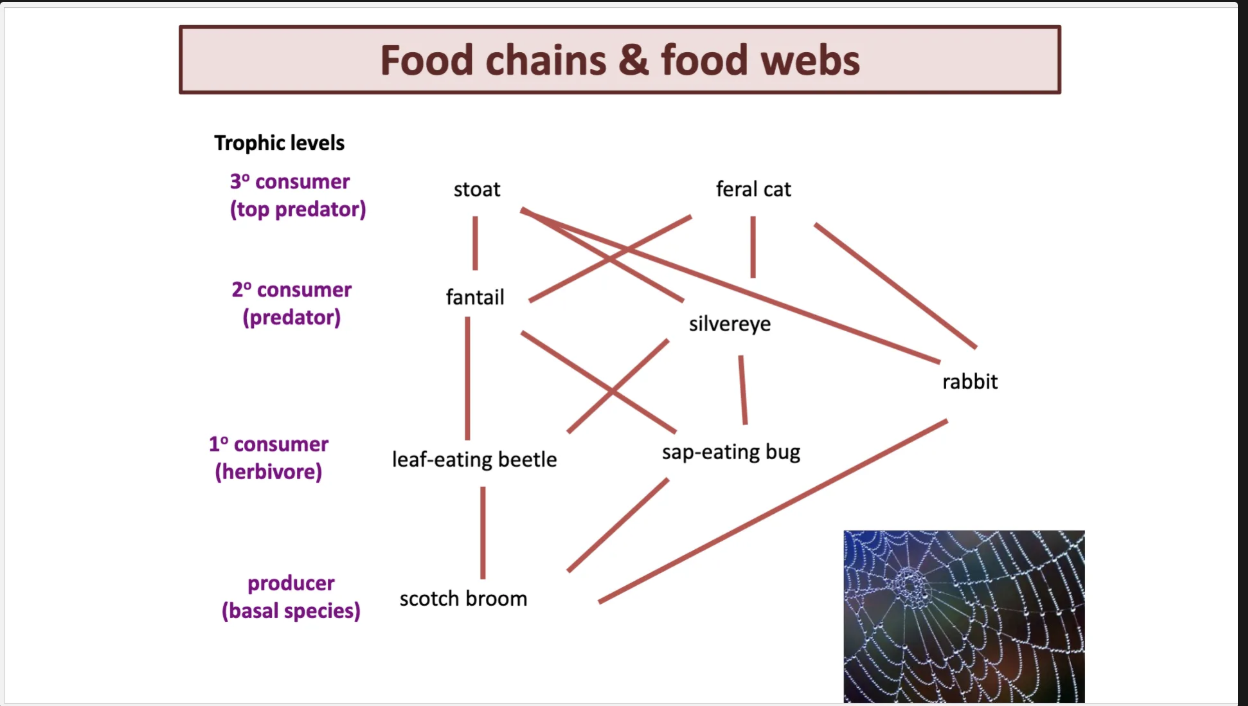
used to seeing food chains.
get past the knowledge of food webs.
primary producer is broom then leaf eating beatle is the primary consurmer ex.
limit to how many you can have in a chain.
food web is a series of chains
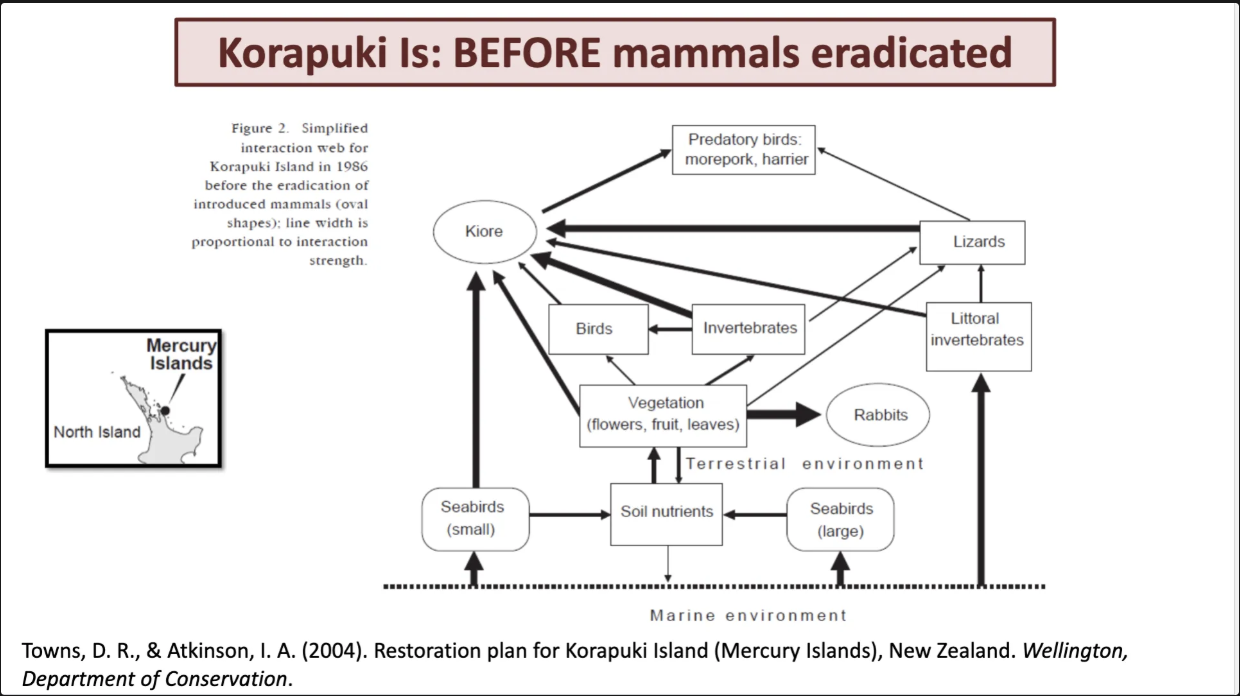
explain erradiation of animals benefits
this is in pukiisland. before animals eradicates most vegitation = rabbit. then kiore is eating the most animals.
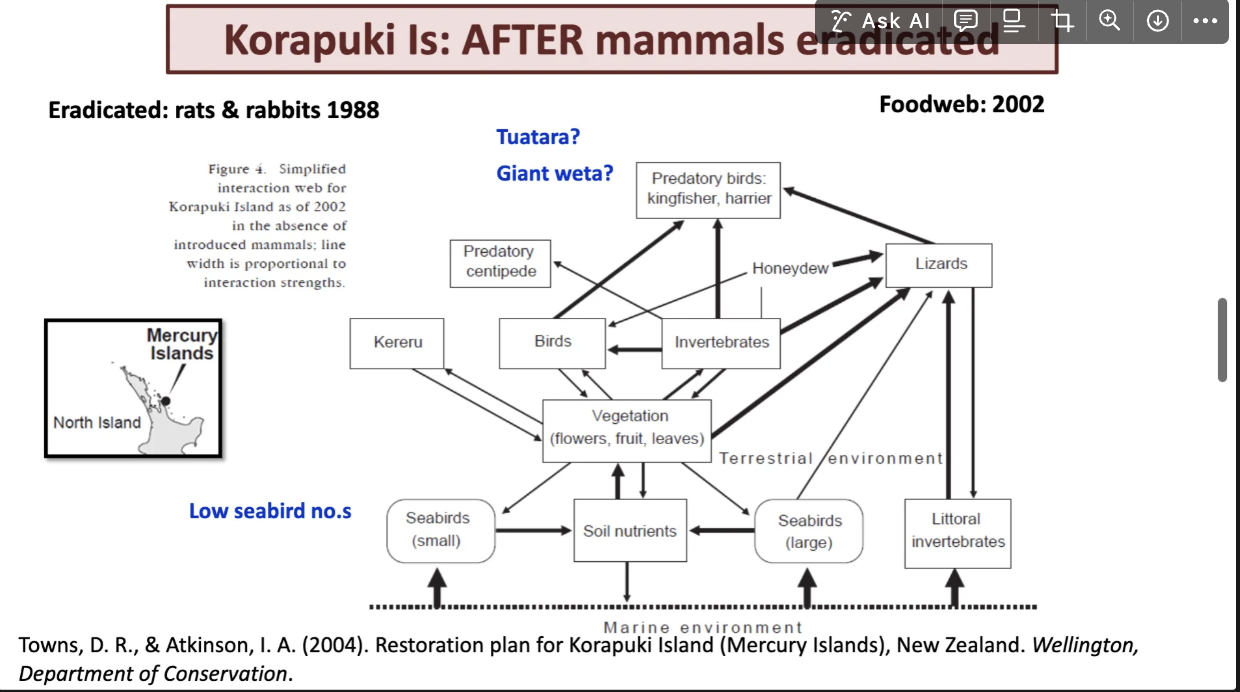
after mammals eradication we can see sudenlty lzards are comming into the ford. they have invertibrates kioara arnt taking. a
and vegitation fuirts flowers and hunnydue.
the preditory centapeded is also coming out of predotry and establishing ing the food web.
pre pirds comming more to the ford.
some recovery but not all recovery. sea bird recovry is very low. not recovered properly. not dependent on predory manmalls but fish aswell.
taking mammals back doesnt help all the time but other species must be established aswell.
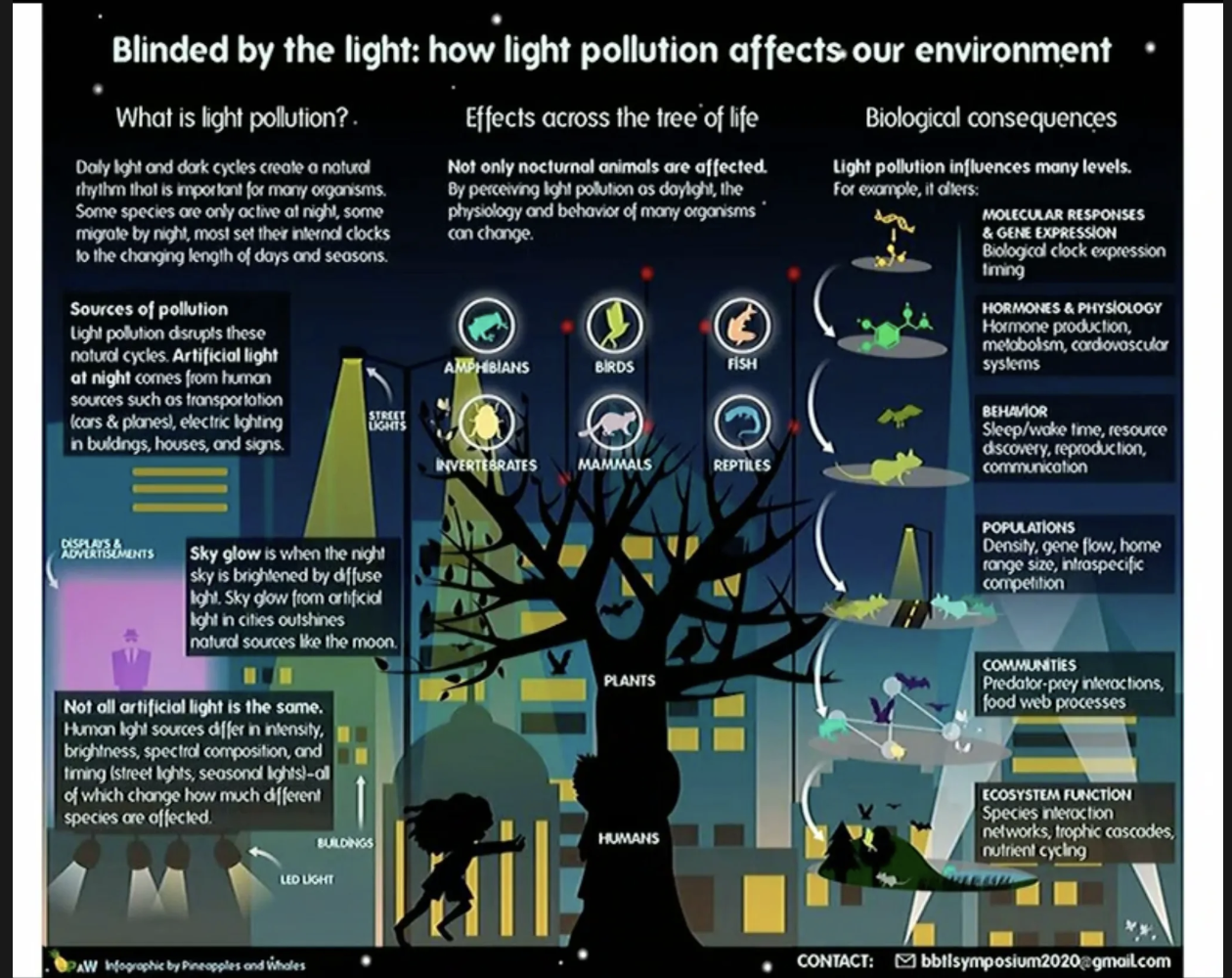
explain how light impacts the environment.
main idea that taxa are impacted. insects dont know what time of the day it is.
blue light impacts sleep.
pervasive throughout system.
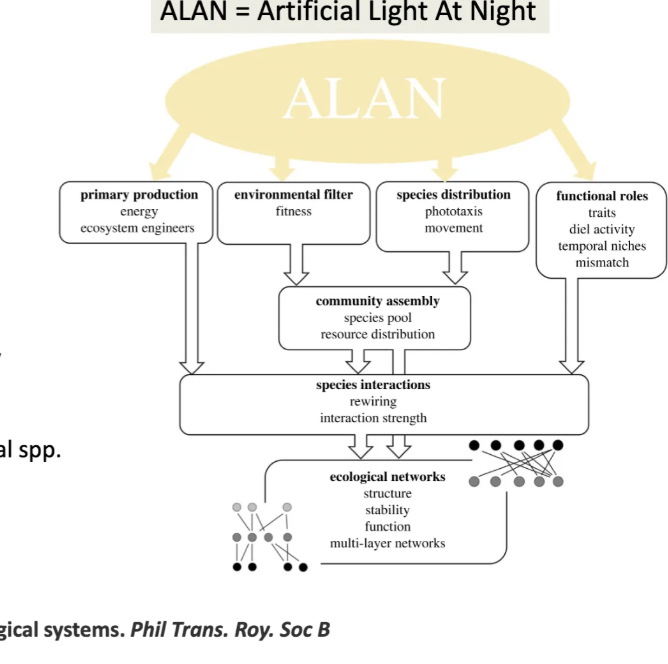
explain.
light impects how plants grow (flowering).
movment of aimals cant naviagte the time of day.
a change in species biology will have a knwockon eefct to the ecosystem.

mututalism

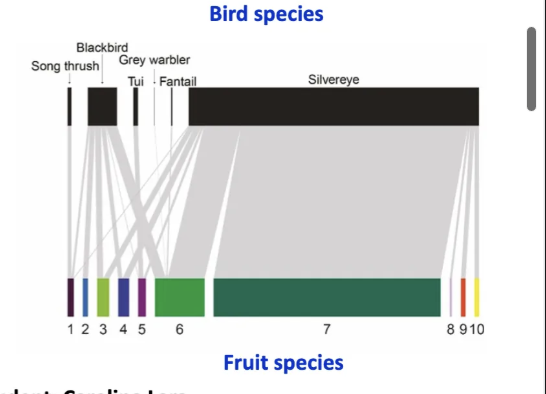
how does is mutualism more broader than just food.
mutualism is much broader than just food.
honey bees are goign to several plants.
same as fruits and birds.
silverey do a llot of fruit digesting and is dominating.
insectivours are also moving pollen around.
what are the 2 main parts in mututalsitic networks
plant seed disperers.
plant pollinators.
trophic cascade meaning.
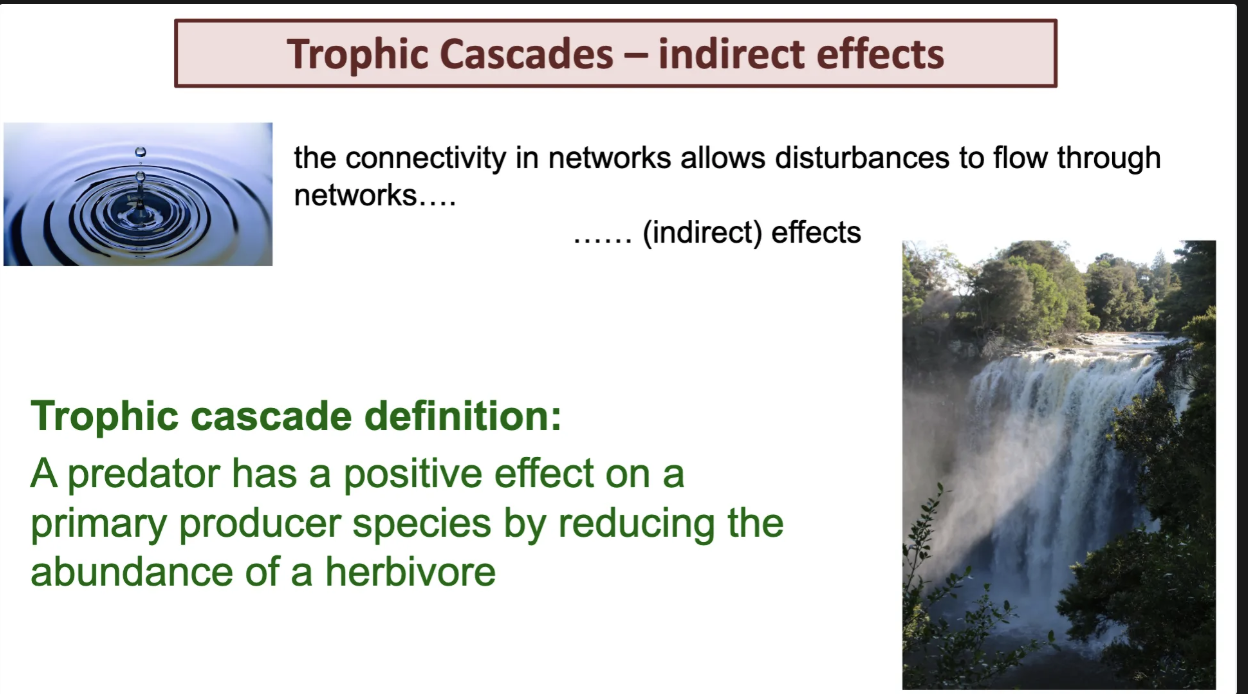
Give me on wolf and elf example
rophic cascade
classic exmaples is
treentroducing of wolds top preditros haivng an impact on primary producers by removing the herbior elk causing fewer elk. indirecly impacting the willow and asprin.
but now more beavers due to less competitions.

otter and kelp example
another example is the otter fern hunting.
humans the pred took out otters to low numbers and now stopepd killing kinna. now kelp are utterly distroyed.

what happens when we remove some species or interactions
not all sticks are the same. some sticks can cause the whole thing to calapse.
this is similer to biotic networs as some species being more important than others. mucking them around can colpse systems and is called KEYSTONE SPECIES

key stone species definition
A keystone species is a species whose removal produces a significant effect (extinction or large change in density) in 1 or more species.
explain key stones
removing a species causes the network to calapse.
in more than one species (diproportionate impact).
arch that if you remove
the keystone spcies doesnt have to be specici like only primary producers.

kereru example
Kereru are the only bird that can sawaly large fruited.
these 3 species are completely relian t on kireru to disperse seeds.
tui can b ut very rre.
low or no kereru mean no seedling regeneration and changing the forest composition. throse species arnt regeneration.

name another key stone species related to bugs.
second example ;scale insects.
sits under bakrk of trees.
and has a moutht that trys to get into phloem and nitrogen. it pumps allot of sugar. because amount for of energy for it pumps heaps of sugar out. because amount its trying to get though to try get little protein, the excess sugar is relased from kundi on kanuaka. allot of sugar on tree prodivde food for birds.

how can eradication of mammales be good nsect good and ecosystems.
the erradicationof mamals results in trees to be infested by scale insects which wasnt seen before.
now 30 geckos on trees and an important part in food webs.
scale insects are keystone species on main land but arnt seen in mmny impratnt places.
this si one that is an important part of our ecosystem. birds reptiles would of ate on it.
explain marine input
importnace of seebirds is they are brinding marine neutrient to land. by changing terrestial.
they discrupt soil.
regertigna dn pooing result in high nitrogen neutreints in these area. not much vegigtation due to tracks.
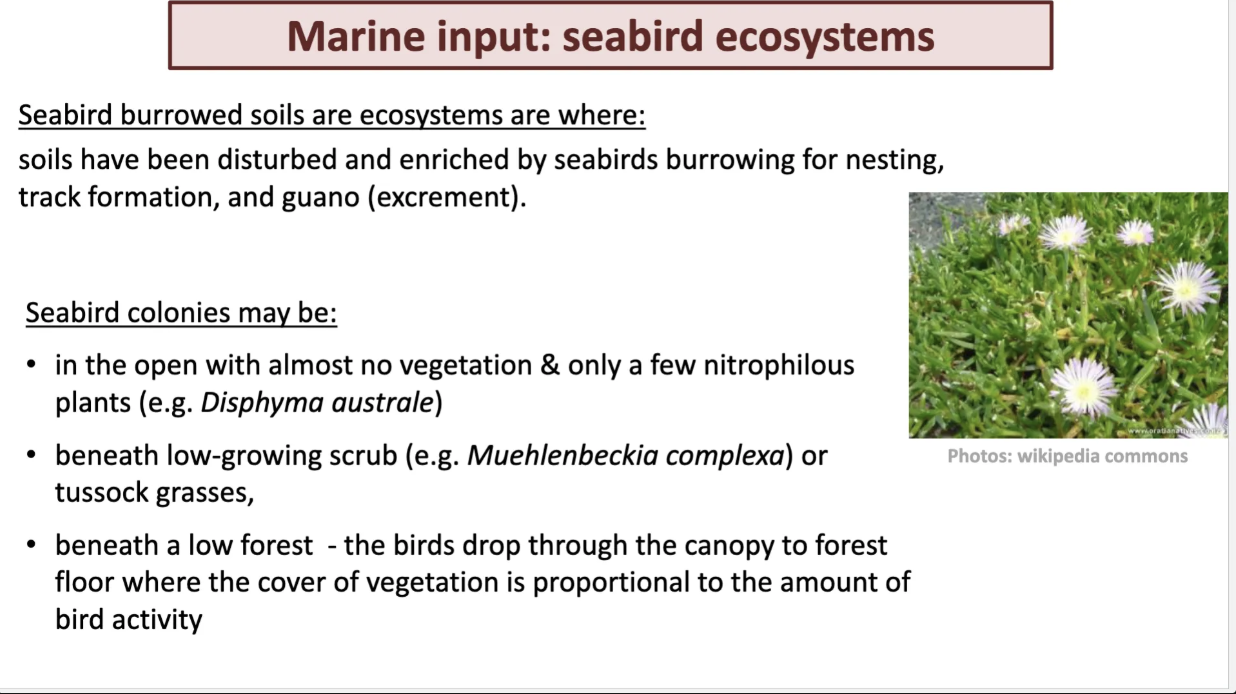
explain seabird burrow ecosystems and threats to sea birds.

marine input: seabird ecosystems
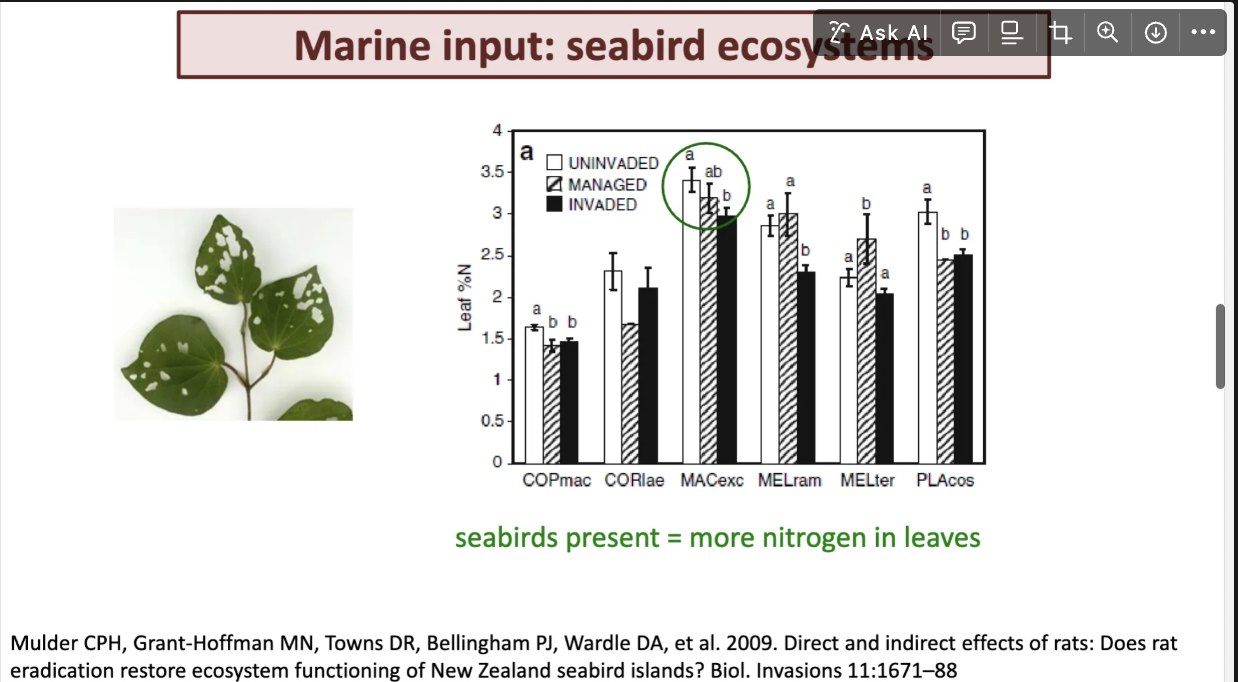
explain how seabirds inpact plants
mammals means really good population of seabid and allot o nitrogen in leaves. this is a common pattern for most plants.
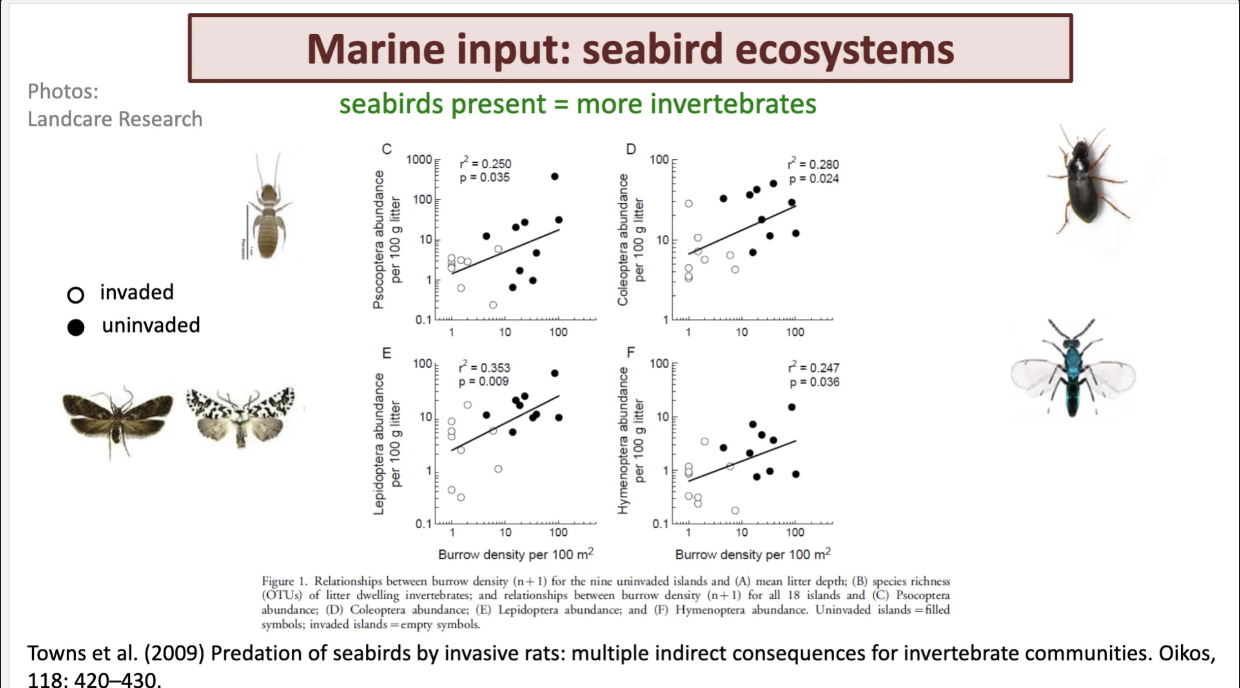
explain how seabirds impact insects.
what is mulispecies pest managment
Multispecies pest management is less likely to result in unexpected effects than removal of single species
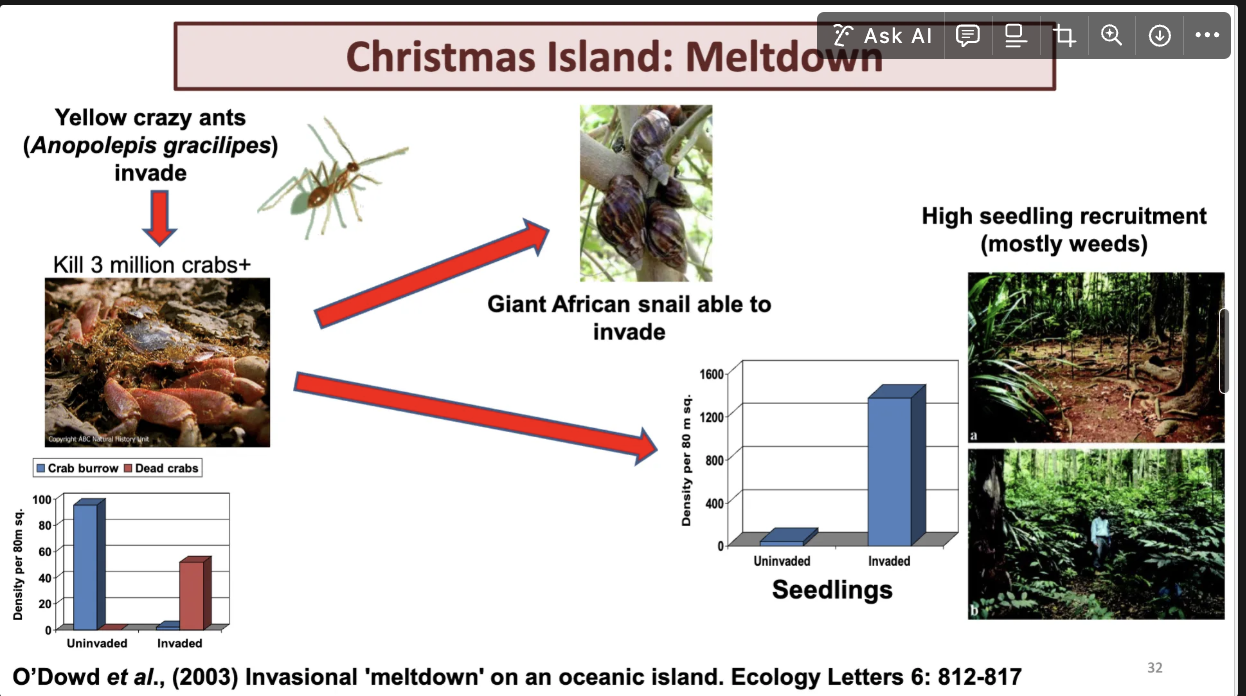
chrimas island has yelow crazy ants that killed allot of crabs (3 million)
the number of dead crabs and crab burrows have depleated.
gient african snail able to invade due to crabs the preditors for snails and casued massive damage to vegitation.
crabs created open forrest and ate seedling now we have heaps of seedlings that are weeds.
crzy ants making knockon effects of multitude of impacts.
pest managment equation

examples of these impacts

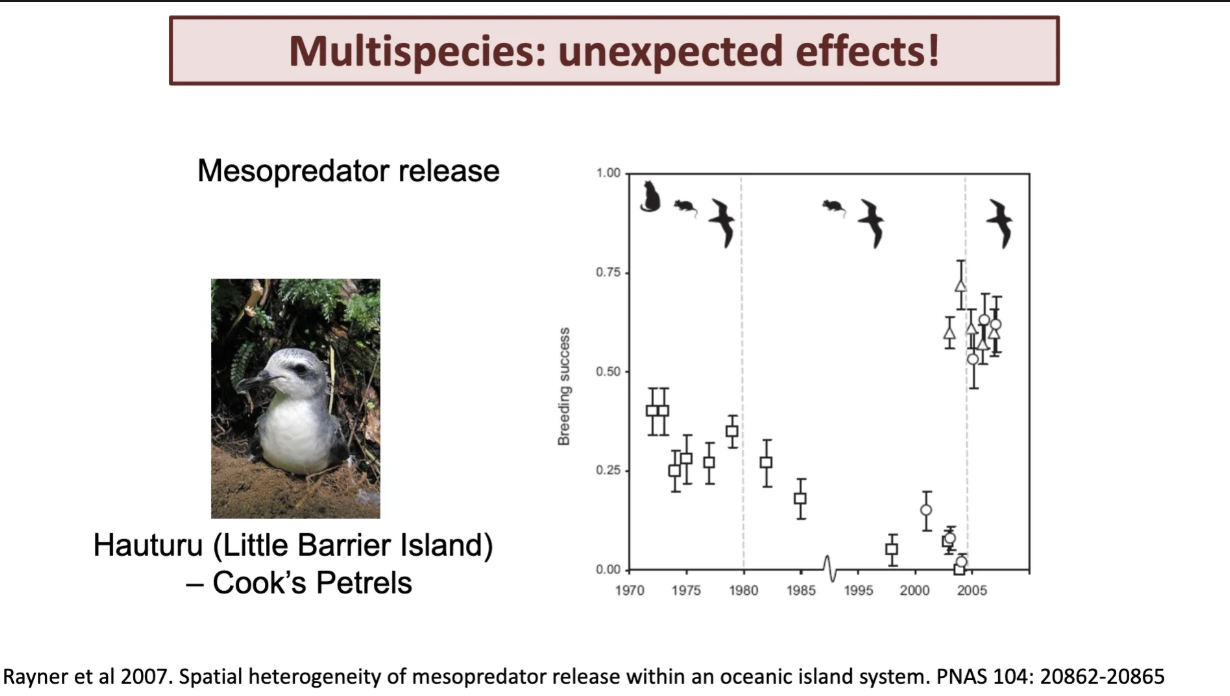
multispecies example for birds rats and cats.
had lad breading success intially.
but after killing rats meant that breeding crashed middle) due to cats killing the birds. the dire state of collony ment that removing cats also meant the opulation could stablisze.