
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Nomenclature
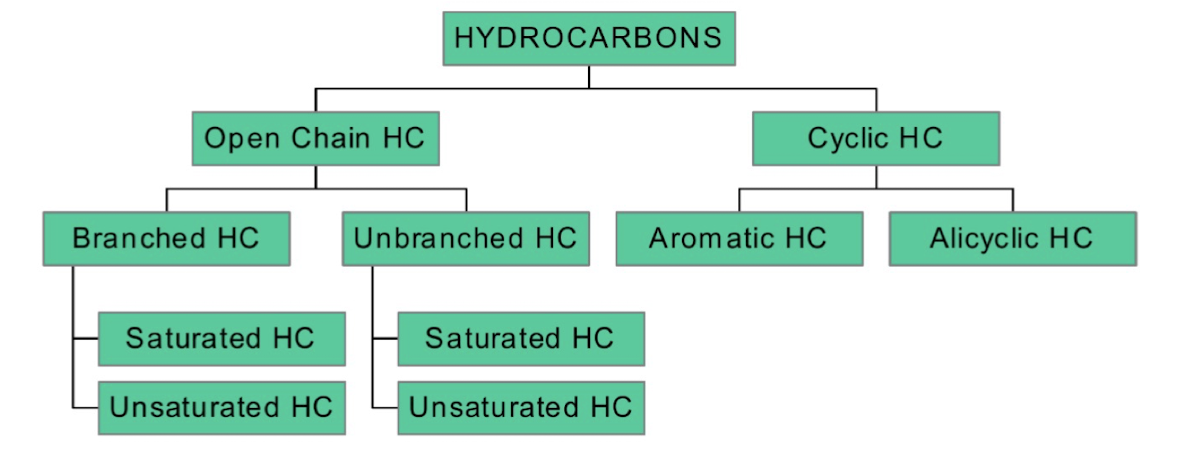
Hydrocarbons are classified into:
Open Chain HC (Aliphatic)
• Branched HC
• Saturated HC (Alkanes)
• Unsaturated HC (Alkenes, Alkynes)
• Unbranched HC
• Saturated HC
• Unsaturated HC
Cyclic HC
• Aromatic HC (Benzene & derivatives)
• Alicyclic HC (Cycloalkanes, Cycloalkenes)
What is the naming convention for unbranched, saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes)?
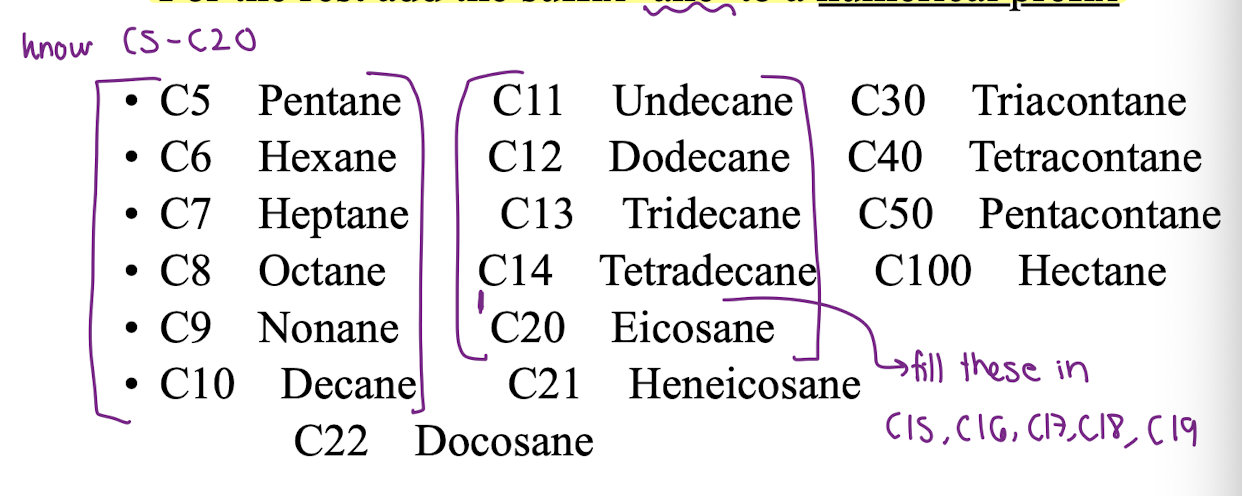
KNOW C5-C20
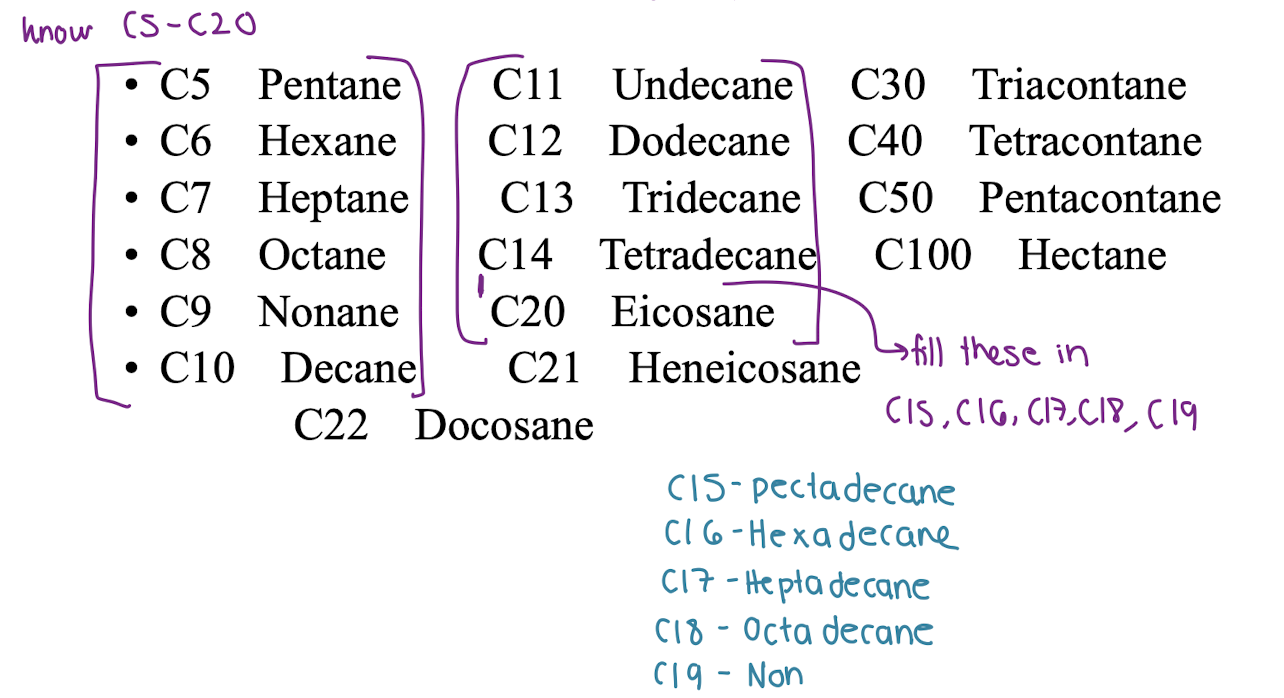
Their names end in -ANE
first four members: methane, ethane, propane, and butane
Suffix: ‘ane’ to a numerical prefix
Their names end in ”-ane” and follow a numerical prefix system for longer chains (e.g., Pentane (C5), Hexane (C6), Heptane (C7), etc.). The first four members are Methane, Ethane, Propane, and Butane.
KNOW C5-C20?
How are unbranched alkenes with multiple double bonds named?
Double bonds- ending is ‘-ENE’
Generic name: alkene
• ”-adiene” for two double bonds (e.g., 1,3-Butadiene)
• ”-atriene” for three double bonds (e.g., Allatriene)
Trivial names exist, such as Ethylene (systematic name: Ethene) and Allene (CH₂=C=CH₂).
How do you name compounds with both double and triple bonds? How would you draw 1, 4-Pentadiyne vs 1-Penten-4-yne??
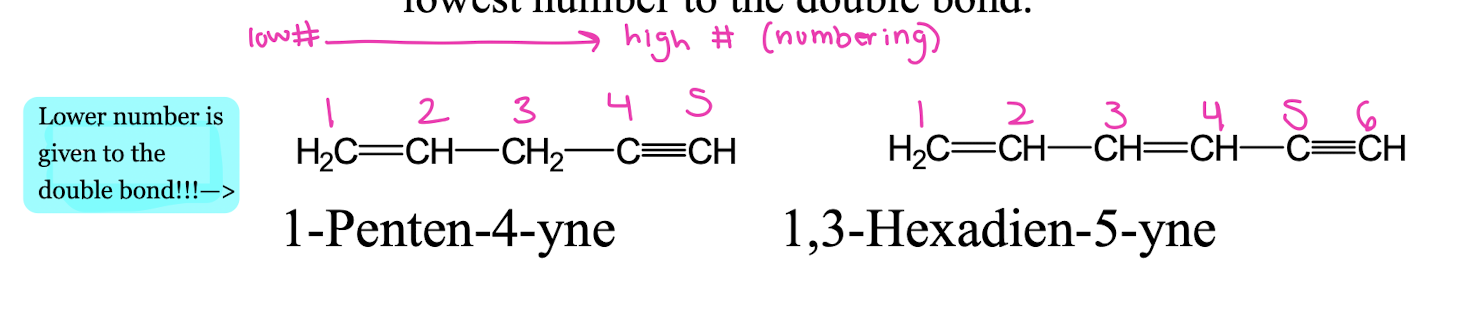
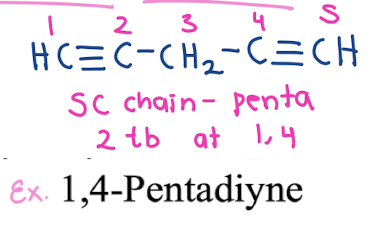
• The suffix “-enyne” is used for molecules with both double (-ene) and triple (-yne) bonds.
Endings:
-yne
-adiyne
-atriyne
-generic -alkyne
• Numbering rules:
Assign the lowest possible number to any unsaturation (double or triple bond).
If a double bond (db) and triple bond (tb) are equally positioned, give the lower number to the double bond.
• Examples:
How would u draw:
• 1-Penten-4-yne → Double bond at C1, triple bond at C4.
• 1, 4-Pentadiyne —> 2 triple bonds at C1, and another tripe bond at C4
5C chain -penta
• 1,3-Hexadien-5-yne → Double bonds at C1 and C3, triple bond at C5.
How do you name a branched alkane?
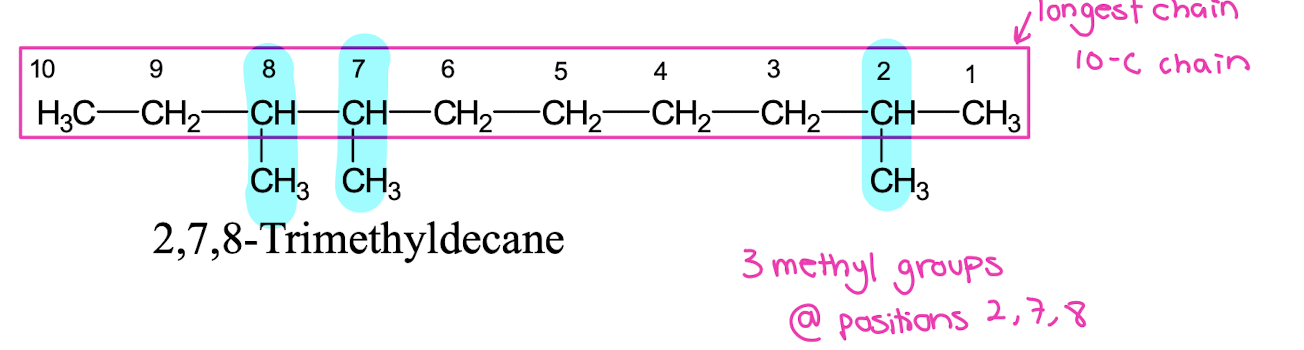
1. Select the longest carbon chain (parent chain).
2. Number the chain from the end closest to the first substituent.
3. Identify and name the substituents (e.g., methyl, ethyl).
4. Assign numbers to substituents based on their position in the chain.
5. List substituents in alphabetical order and use prefixes (di-, tri-) for multiple identical groups.
Example:
• 2,7,8-Trimethyldecane
• Parent chain: Decane (10 carbons)
• Substituents: Three methyl (-CH₃) groups at positions 2, 7, and 8.
What are the systematic names for common branched alkanes with trivial names?
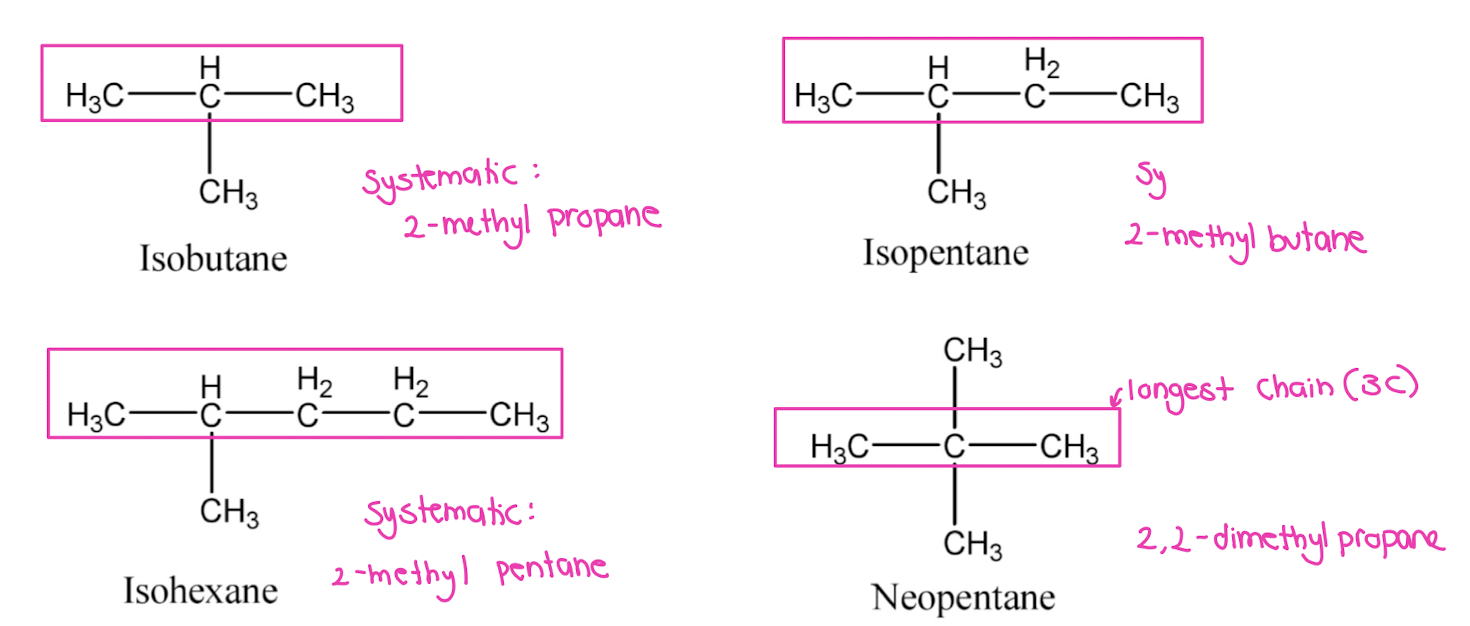
• Isobutane → 2-Methylpropane
• Isopentane → 2-Methylbutane
• Isohexane → 2-Methylpentane
• Neopentane → 2,2-Dimethylpropane
Key Naming Rules:
1. Identify the longest carbon chain (parent chain).
2. Number the chain so that substituents get the lowest possible numbers.
3. Name and position substituents as prefixes (e.g., methyl, dimethyl).
What are the rules for selecting the parent chain in branched unsaturated hydrocarbons?