Lecture 15 Key Concepts/Terms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
1
New cards
megaspore
spore that develops into a female gametophyte and is produced by a conifer's female cone
2
New cards
microspore
small haploid spore formed by some plants that develops into a male gametophyte
3
New cards
megasporangium
A plant structure in which megaspores are formed, such as those of the female cones of pines.
4
New cards
microsporangium
a plant structure that produces microspores
5
New cards
integument/seed coat
outer protective layer of a seed
6
New cards
micropyle
minute opening in the wall of an ovule through which the pollen tube enters
7
New cards
what are the three ways that seeds are adaptive?
embyrophytic
dispersal
dormancy
dispersal
dormancy
8
New cards
how is dispersal beneficial for seeds?
the hardness of seeds allows them to move farther
9
New cards
what is seed dormancy?
a delay between developing and dispersal or dispersal and developing
10
New cards
homospory
the production of one type of spore
11
New cards
microspore mother cell
a diploid cell that undergoes meiosis to yield a haploid microspore
12
New cards
heterospory
production of different types of spores
13
New cards
pollen
the tiny granules that contain the male gametophyte of seed plants
14
New cards
sperm (plant structure)
seed
15
New cards
ovules
A structure that develops within the ovary of a seed plant and contains the female gametophyte.
16
New cards
megaspore mother cell
a diploid cell that undergoes meiosis to yield a haploid megaspore
17
New cards
female gametophyte
embryo sac; archegonia
18
New cards
male gametophyte
pollen grain; antheridium
19
New cards
egg (plant structure)
develop in ovules, tiny structures embedded in the ovary
20
New cards
naked seeds
Seeds not enclosed in layers of tissue from an ovary, usually lying naked on a scale (as in a pine cone).
21
New cards
pollen tube
A tube that forms after germination of the pollen grain and that functions in the delivery of sperm to the ovule.
22
New cards
Why aren't seed plants dependent on water?
the evolution of seeds, coupled with the evolution of pollen grains with sperm that no longer require water to swim through for fertilization (they have the pollen tube) allows for seed plants to be able to reproduce without water present
23
New cards
features of seed plants
seeds allow for dispersal
seeds allow for dormancy
all heterosporous
dramatic reduction of gametophytic stage
sporophyte is the dominant form
seeds allow for dormancy
all heterosporous
dramatic reduction of gametophytic stage
sporophyte is the dominant form
24
New cards
gymnosperms
cycads, ginkgos, gnetophytes and conifers
25
New cards
cycads
ancient (been around since the dinos)
can become very large
slow growing
motile sperm
can become very large
slow growing
motile sperm
26
New cards
ginkgos
only one extant species
dioecious
motile sperm
dioecious
motile sperm
27
New cards
female ginkgos
has fruit on it that smells very very bad lol
28
New cards
male ginkgos
has cones
29
New cards
Gnetophytes
Welwitschia, Ephedra
have vessel cells (like angiosperms) that are homoplasious
have vessel cells (like angiosperms) that are homoplasious
30
New cards
Welsitschia
gnetophyte
only two leaves
dioecious
only two leaves
dioecious
31
New cards
Ephedra
most gnetophytes are these
many medical uses
many medical uses
32
New cards
conifers
gymnosperm; cone-bearing plants; most are evergreen
33
New cards
vessel cells in gnetophytes
vascular tissue that are much more efficient at transporting water than tracheids
34
New cards
vessel cells in angiosperms
most species have tracheids
characterized by primary and secondary cell walls
water conducting cells
characterized by primary and secondary cell walls
water conducting cells
35
New cards
key trait of angiosperms
develop flowers
36
New cards
sepal
A leaflike structure that encloses the bud of a flower.
37
New cards
petal
A colorful, leaflike structure of some flowers.
38
New cards
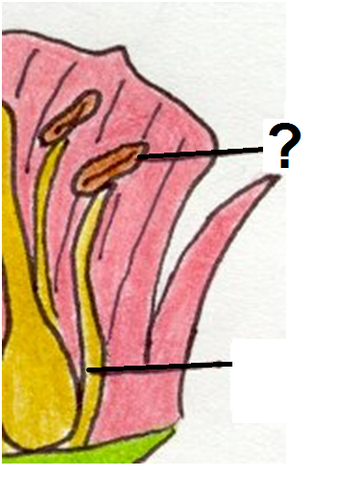
anther
the part of a stamen that contains the pollen (male)
39
New cards
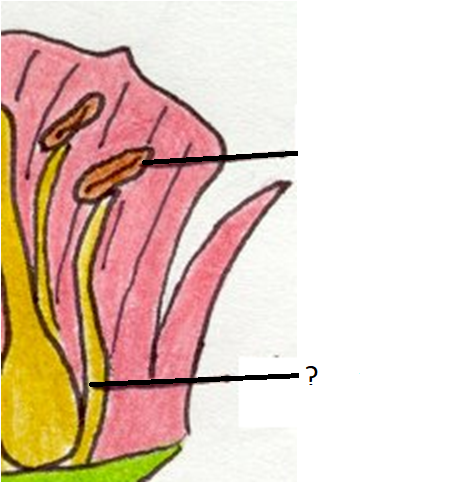
filaments
a slender threadlike object or fiber, especially one found in animal or plant structures (male)
40
New cards
stamen
the male reproductive organ of a flower (anther and filament)

41
New cards
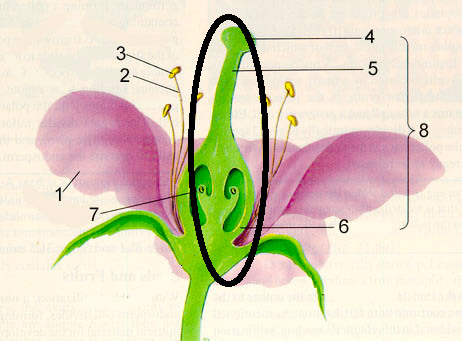
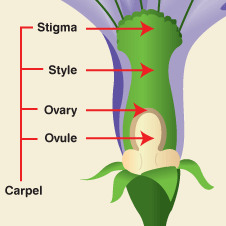
Ovary
Swollen part of pistil that contains the ovule where the ova are produced
42
New cards
Ovules
The female reproductive part of the seed plants that contains the female germ cell and after fertilization becomes the seed.

43
New cards
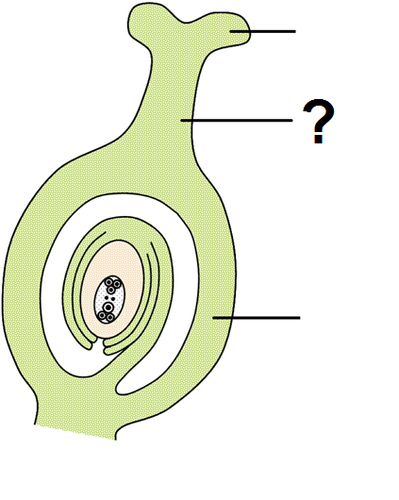
style
Connects the stigma to the ovary of a flower
44
New cards
stigma
The tip of the female reproductive structure of a flower where the pollen lands

45
New cards
carpel
The female reproductive organ of a flower, consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary.
46
New cards
types of fruits
simple, aggregate, multiple, accessory
47
New cards
apple
single carpel with interior seeds
48
New cards
tomato
true berry with two fused carpels
49
New cards
legume
each seed has a sugary coat, bean is the ovary
50
New cards
peach
drupe, seed is inside a hard pit
51
New cards
aggregate fruits
result from a single flower with multiple separate carpels
52
New cards
multiple fruits
develop from a group of flowers called an inflorescence
53
New cards
egg cell in angiosperms
inside the ovule
54
New cards
synergids
part of the egg apparatus and are thought to help the pollen nucleus reach the egg cell for fertilization
55
New cards
antipodals
Three cells of the mature embryo sac, located at the end opposite the micropyle.
56
New cards
polar nuclei
in anthophytes, the two nuclei in the center of a megaspore
57
New cards
tube cell
produces pollen tube
58
New cards
generative cell
in a pollen grain, the cell that divides mitotically and forms two sperm cells
59
New cards
double fertilization
A mechanism of fertilization in angiosperms, in which two sperm cells unite with two cells in the embryo sac to form the zygote and endosperm.
60
New cards
2N zygote
One sperm nucleus unites with the egg nucleus
61
New cards
3n endosperm
supplies nutrients to the developing embryo as the seed germinates, or as the embryo develops
62
New cards
how is the angiosperm life cycle different than the gymnosperm life cycle?
reduced cell number in female gametophytes
double fertilization
triploid endosperm
double fertilization
triploid endosperm
63
New cards
What makes angiosperms so successful?
Vessel cells, rapid maturation, pollinators, fruits
64
New cards
Ginkgo biloba
female ginkgo tree, very strong smelling fruit
65
New cards
You hear the familiar jingle "most have cones for seeds, move have needles for leaves" and you automatically think...
A) this song is about the most common group of gymnosperms, the ginkgos!
B) Ephedra is the plant mentioned in this catchy tune
C) that song was written by someone who hasn't take BIO200! It SHOULD go "most have cones for leaves, most have needles for seeds".
D) I'm thinking of that song because stores already have Christmas trees out even though it's not even Thanksgiving!
E) Cycads are really cool!
A) this song is about the most common group of gymnosperms, the ginkgos!
B) Ephedra is the plant mentioned in this catchy tune
C) that song was written by someone who hasn't take BIO200! It SHOULD go "most have cones for leaves, most have needles for seeds".
D) I'm thinking of that song because stores already have Christmas trees out even though it's not even Thanksgiving!
E) Cycads are really cool!
D) I'm thinking of that song because stores already have Christmas trees out even though it's not even Thanksgiving!