A1.2 NUCLEIC ACIDS
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Draw a nucleotide.
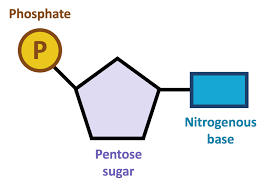
What is a condensation reaction?
Condensation reactions = two molecules are combined to form a single molecule (e.g. RNA) and water is also a product.
Purines:
Larger
Adenine
Guanine
Pyrimidines:
Smaller
Thymine
Cytosine
The antiparallel nature of DNA
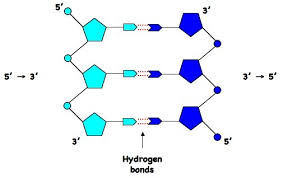
DNA VS RNA
The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose and the sugar in RNA is ribose. These contribute to the names of each molecule: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
RNA is single stranded and DNA is double stranded polymer molecule.
The four bases: DNA contains A, C, T and G. RNA contains A, C, G and U (Uracil).
Three types of RNA: rRNA, mRNA and tRNA.
Explain the Semi-Conservative Hypothesis
The DNA helix is unwound and unzipped by the enzyme HELICASE which breaks the weak “H” bonds between the base pairs.
The exposed, unpaired bases form a template.
Free nucleotides are specifically base paired to the exposed bases by the enzyme DNA POLYMERASE.
ATP is required as a source of energy.
Two identical DNA molecules are produced.
Since each new DNA molecule retains half an old one, this is known as the “SEMI-CONSERVATIVE HYPOTHESIS”.
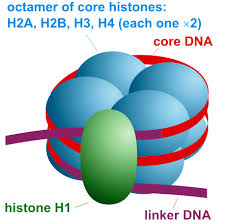
Nucleosome
Hershey - Chase experiment
Radioactive sulphur (35S) in protein coat.
Radioactive phosphorus (32P) in DNA.
Bacteria (T2 bacteriophage) infected by viruses separately. Viruses insert their DNA and the host cell replicates it.
Blend the bacterial culture.
Centrifuge the blend culture to concentrate the dense cells into a pellet.
ASSUMPTION: cells would contain the genetic material
Measured radioactivity of supernatant and pellet.
Sulphur radioactivity in the Supernatant,
Phosphorus radioactivity in the Pellet.