BIO 221 - Nervous System Histology
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
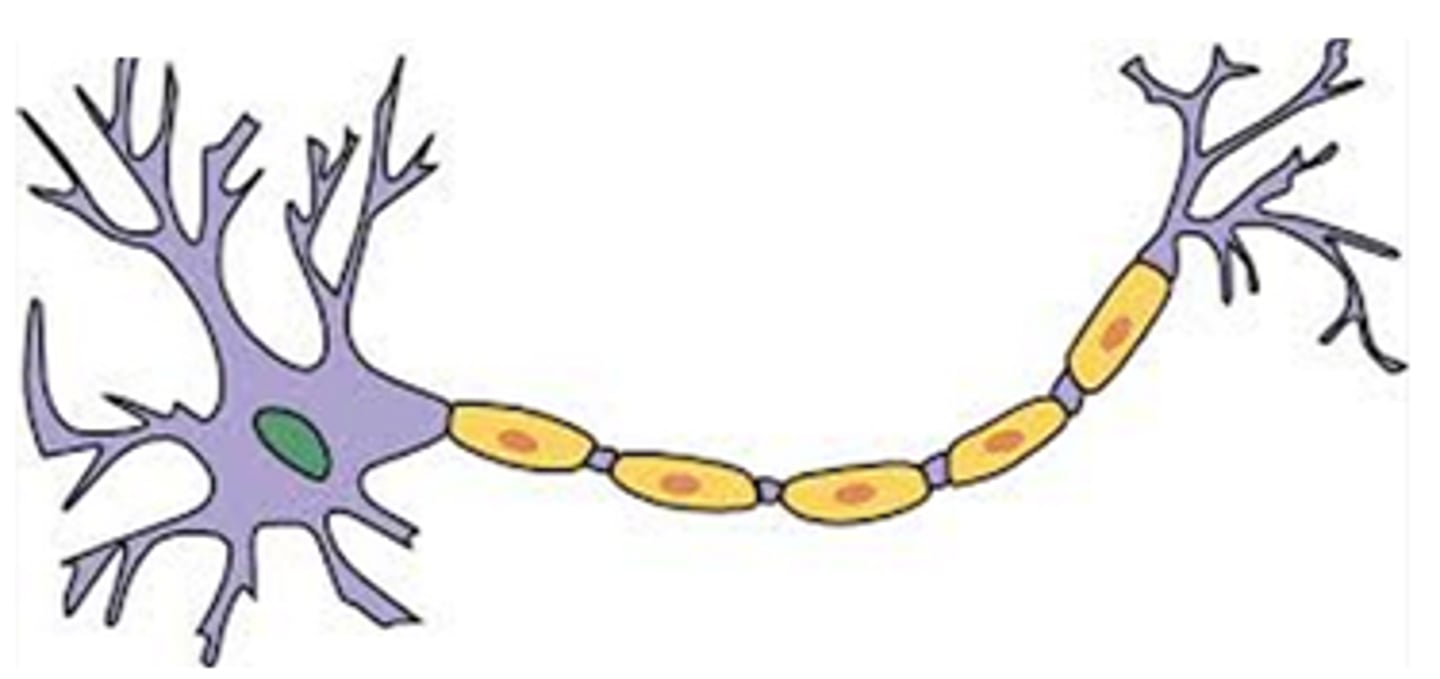
Neuron
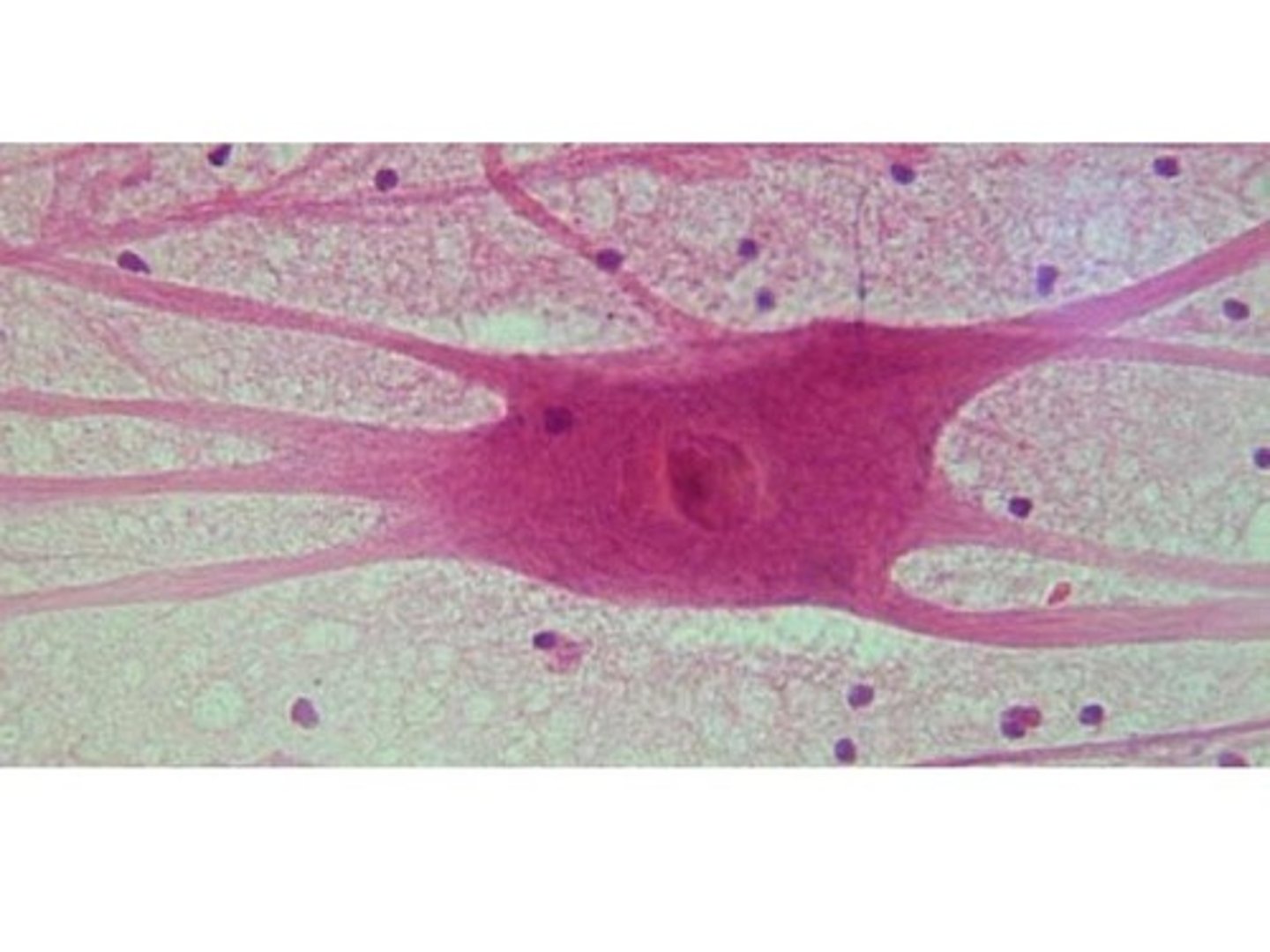
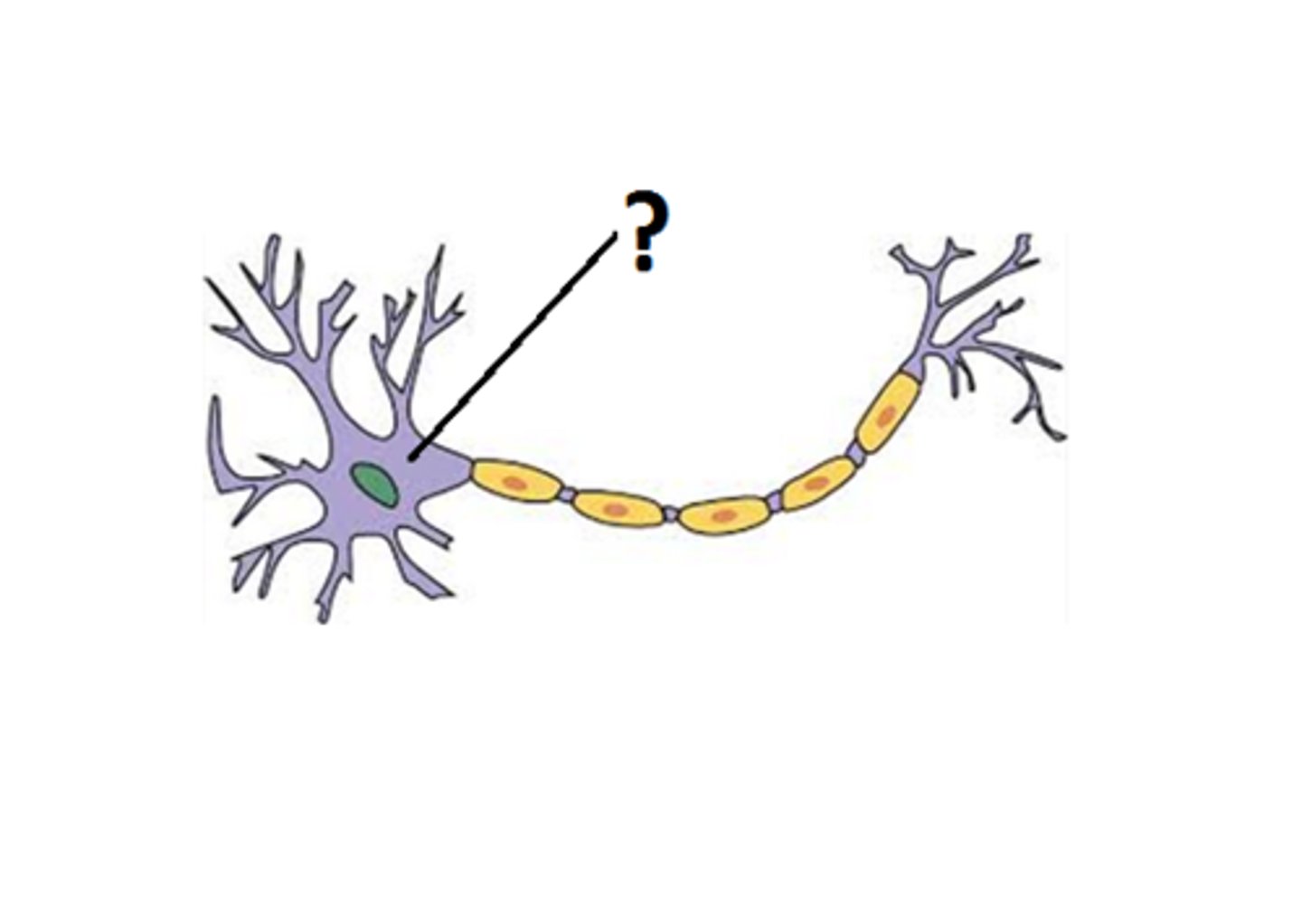
Neuron Nucleus
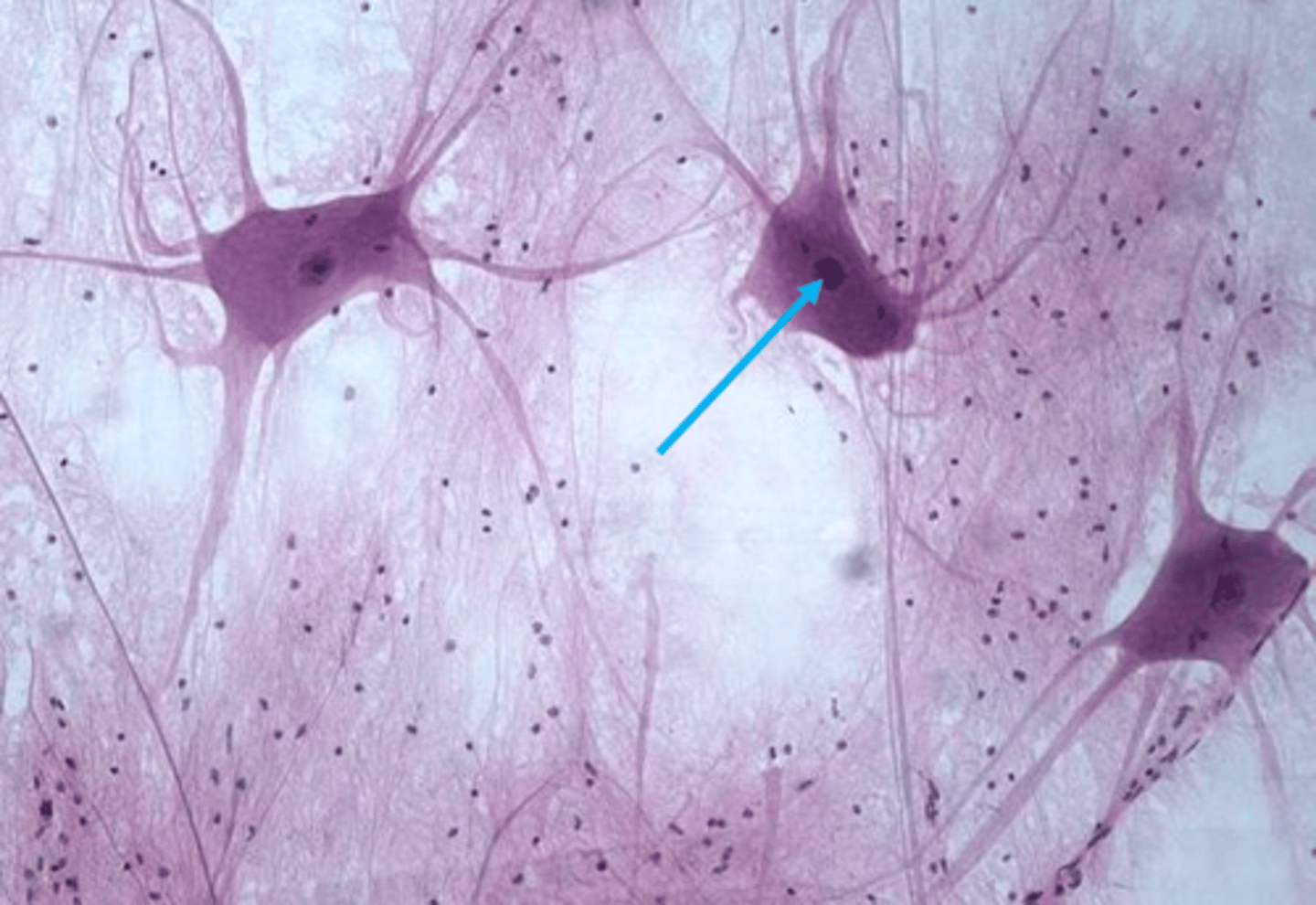
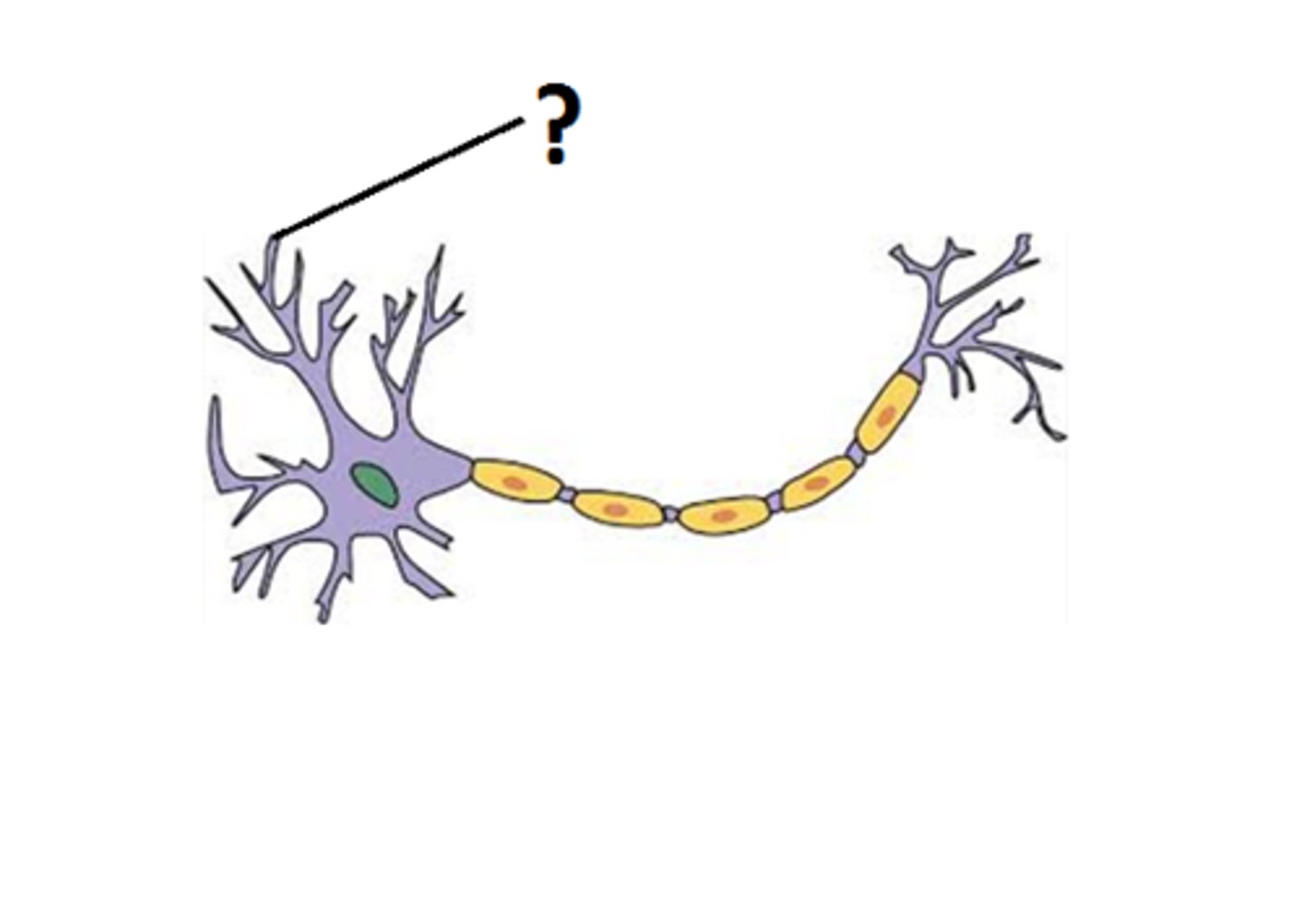
Neuron Dendrites
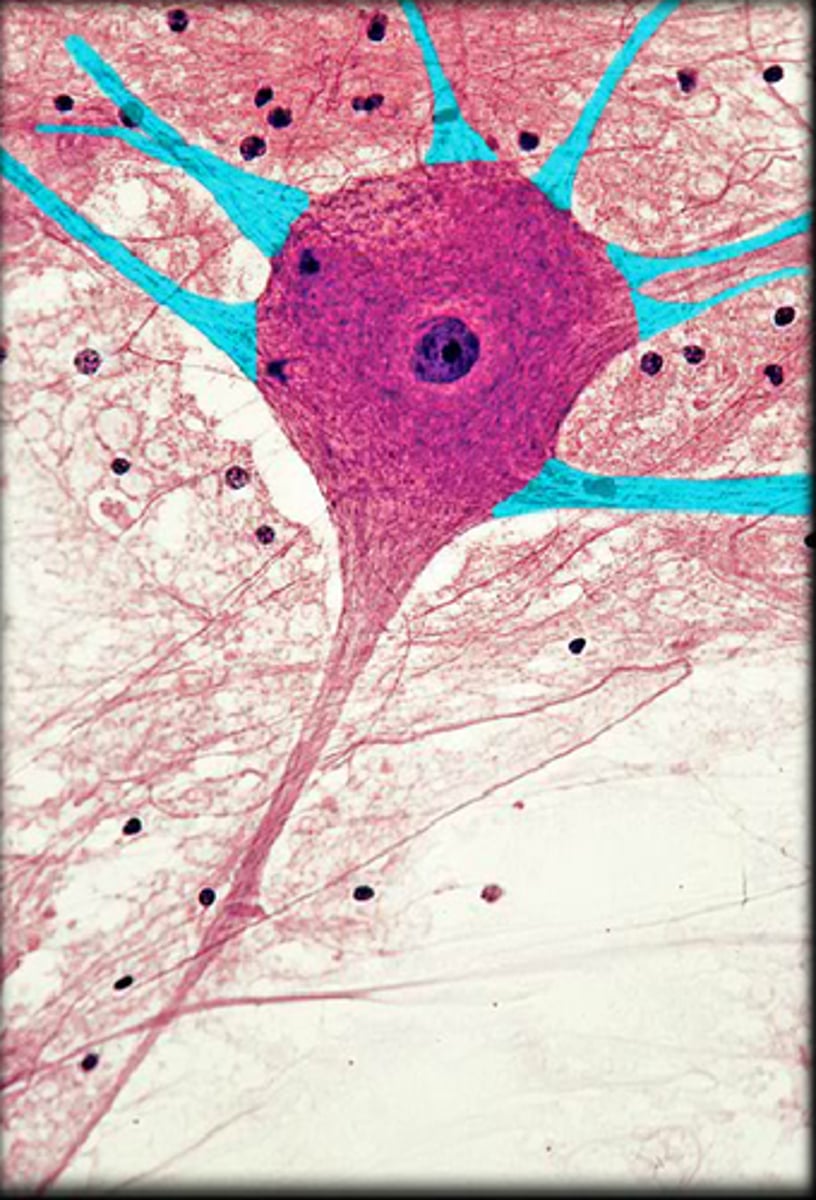
Neuron Soma
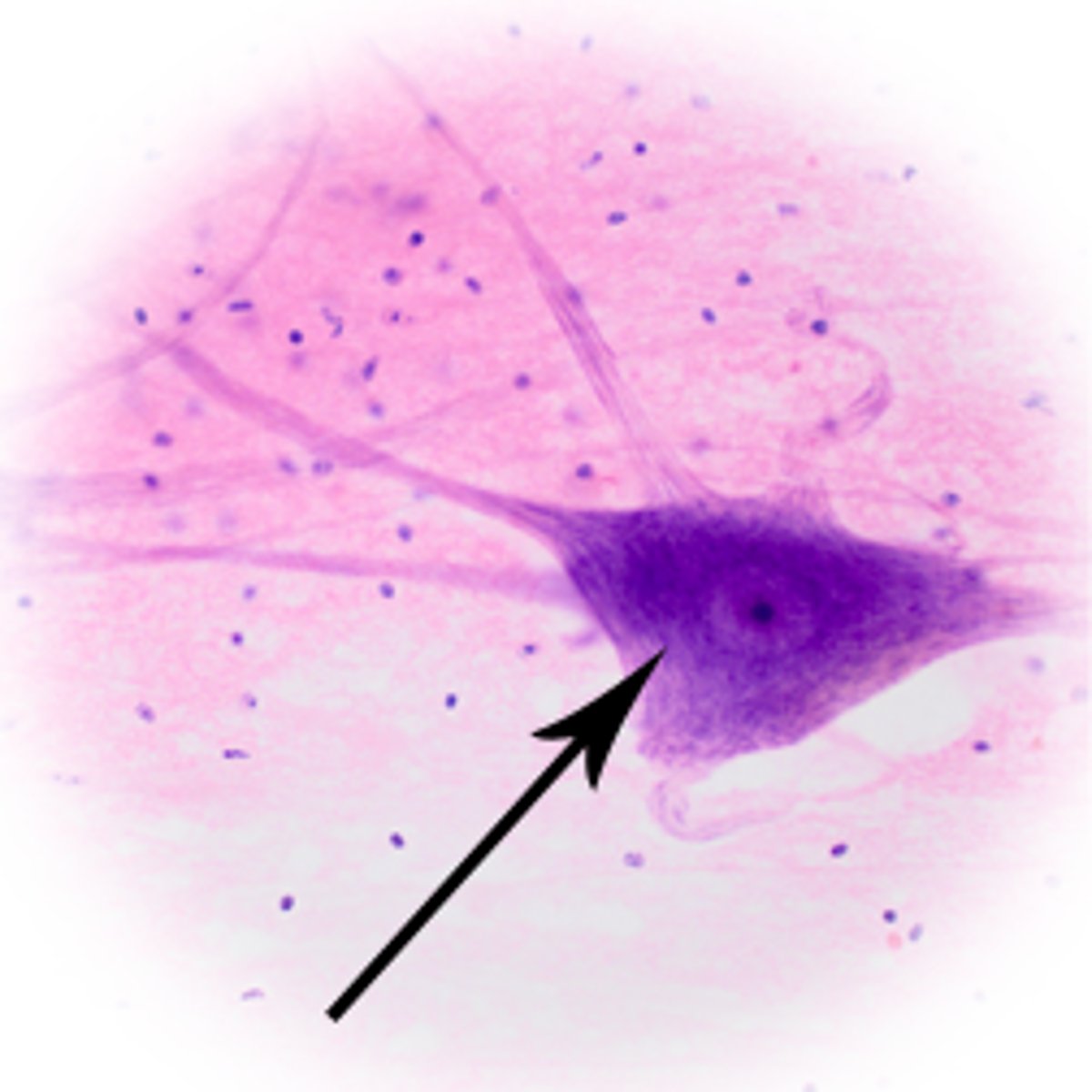
Neuron Axon
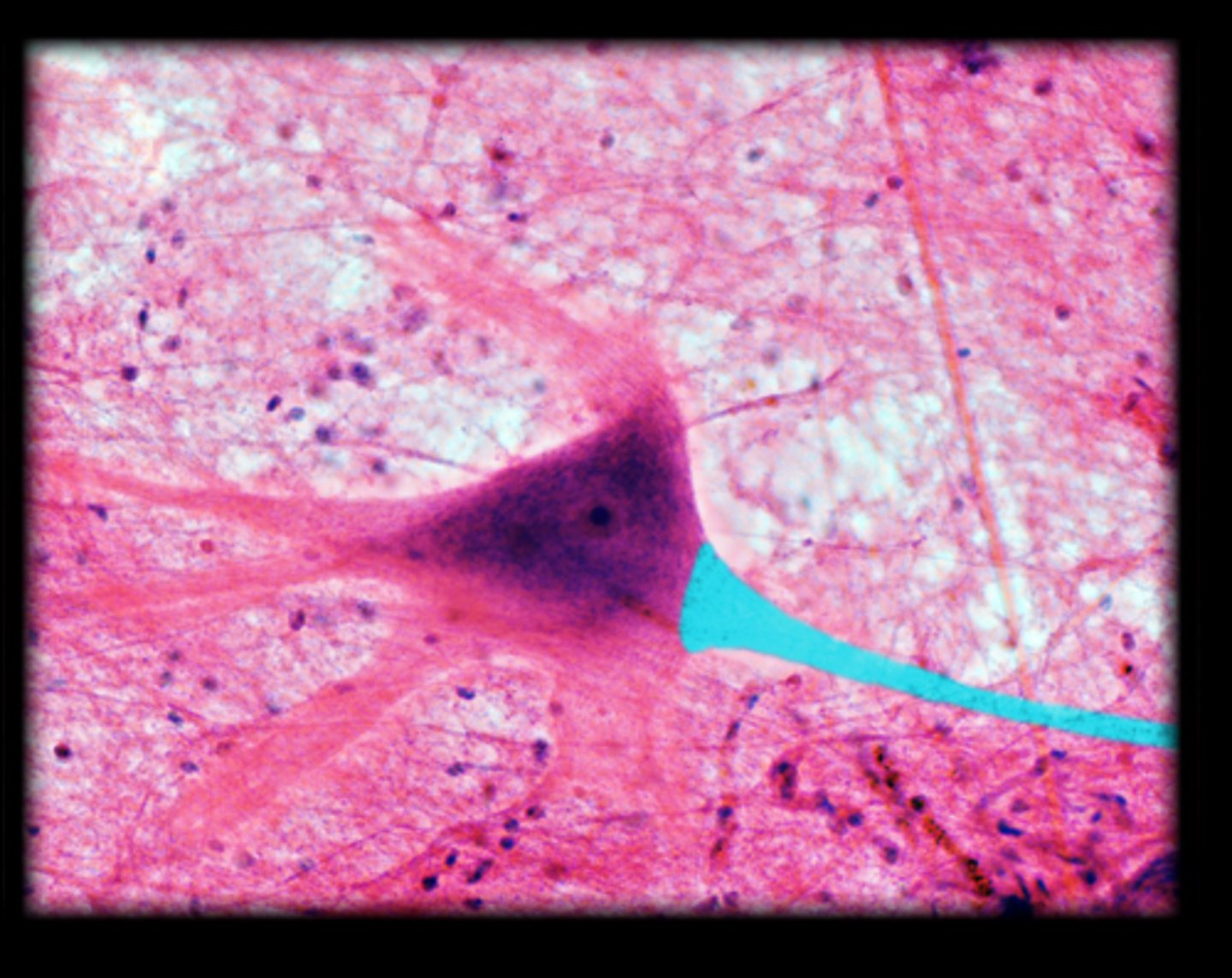
Neuron
Neuron Dendrites
Neuron Soma
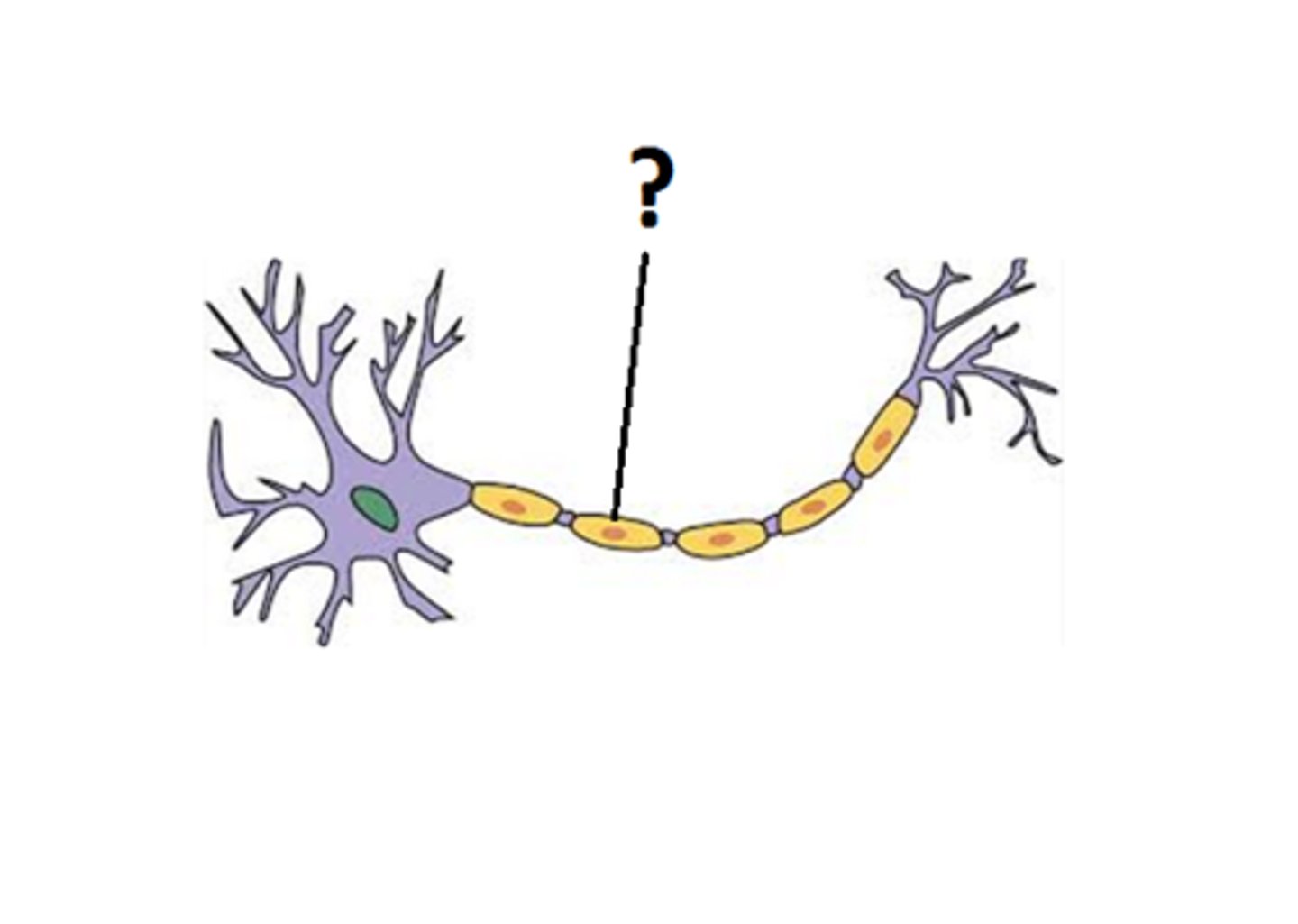
Myelin
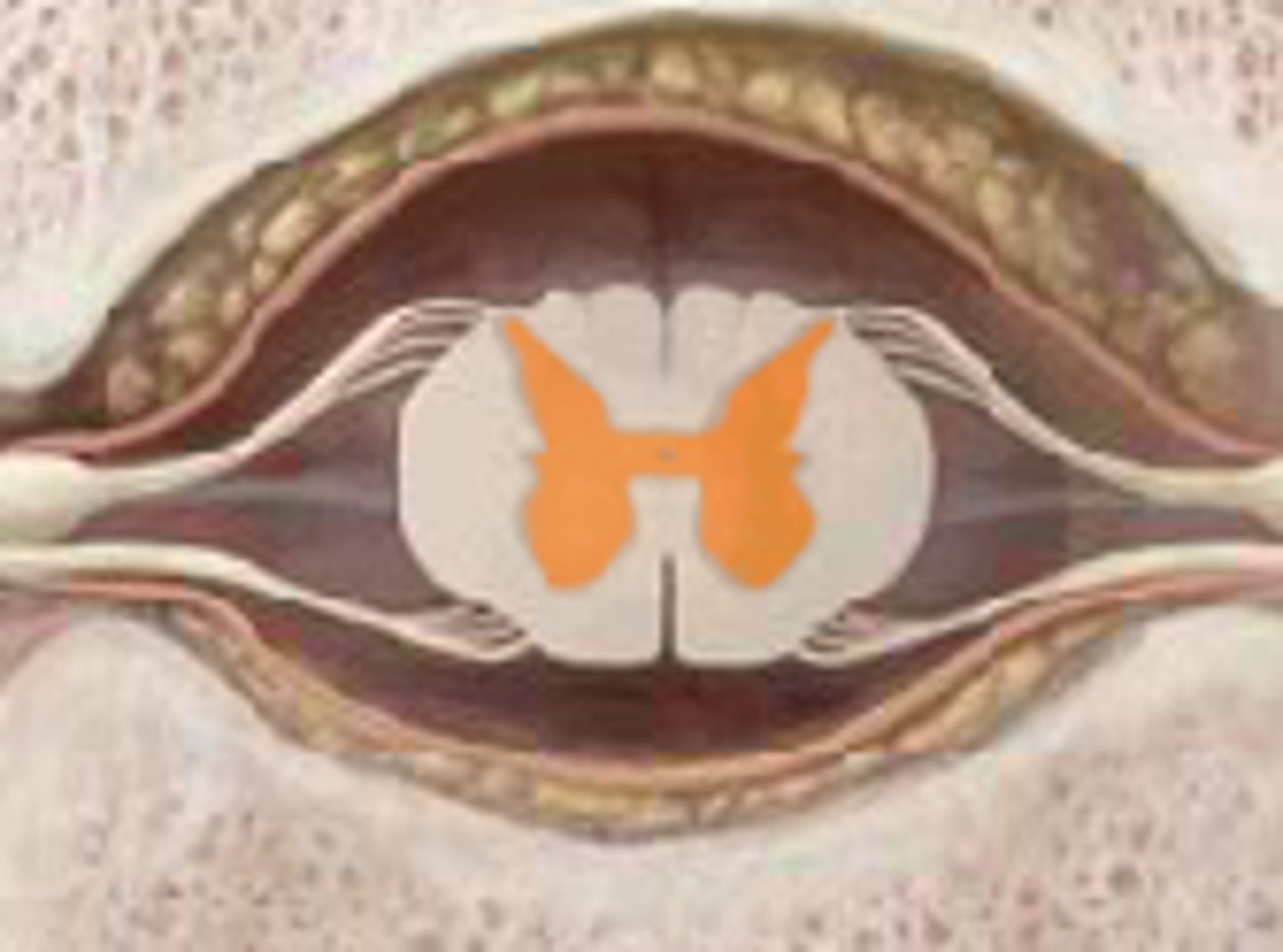
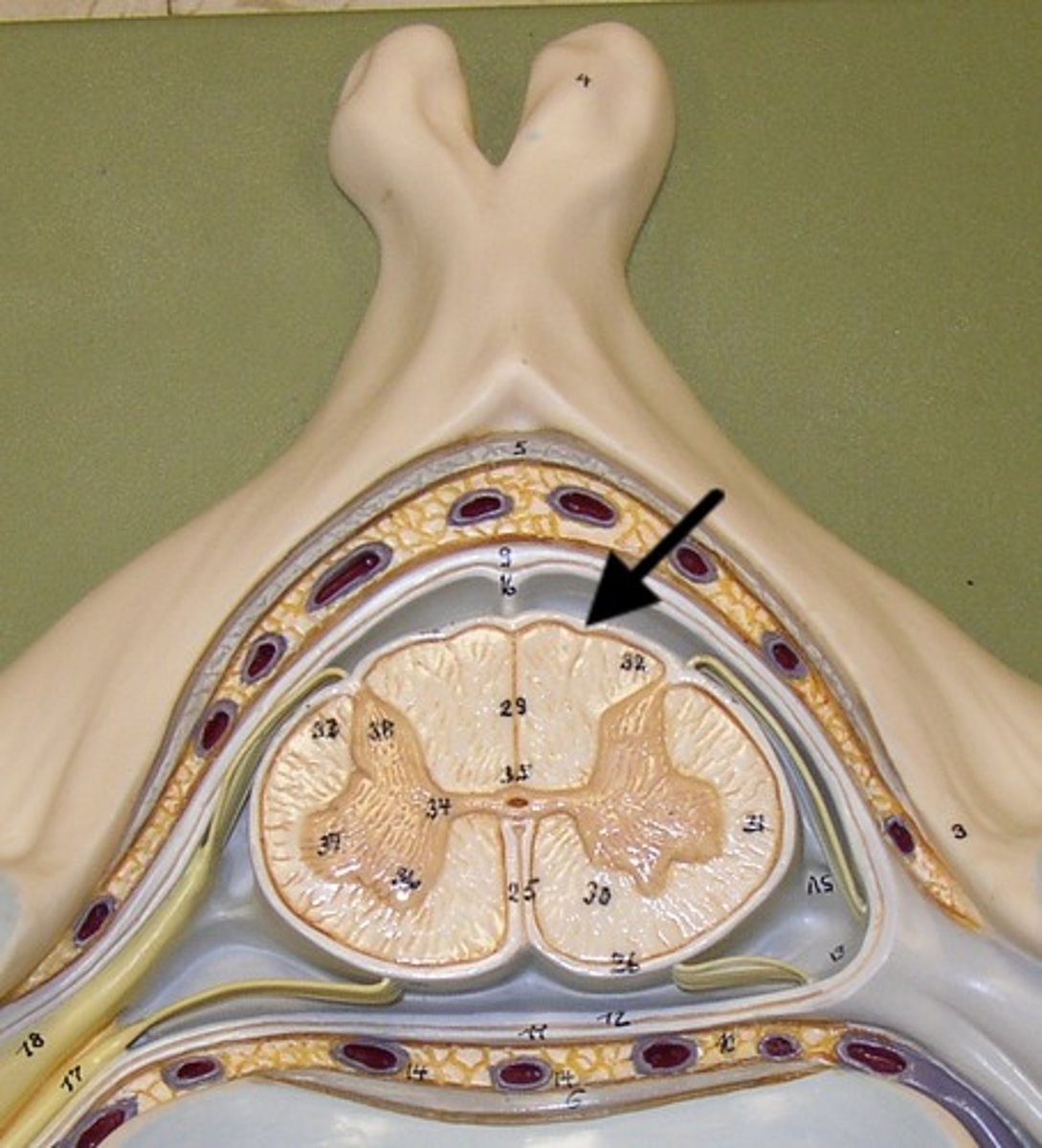
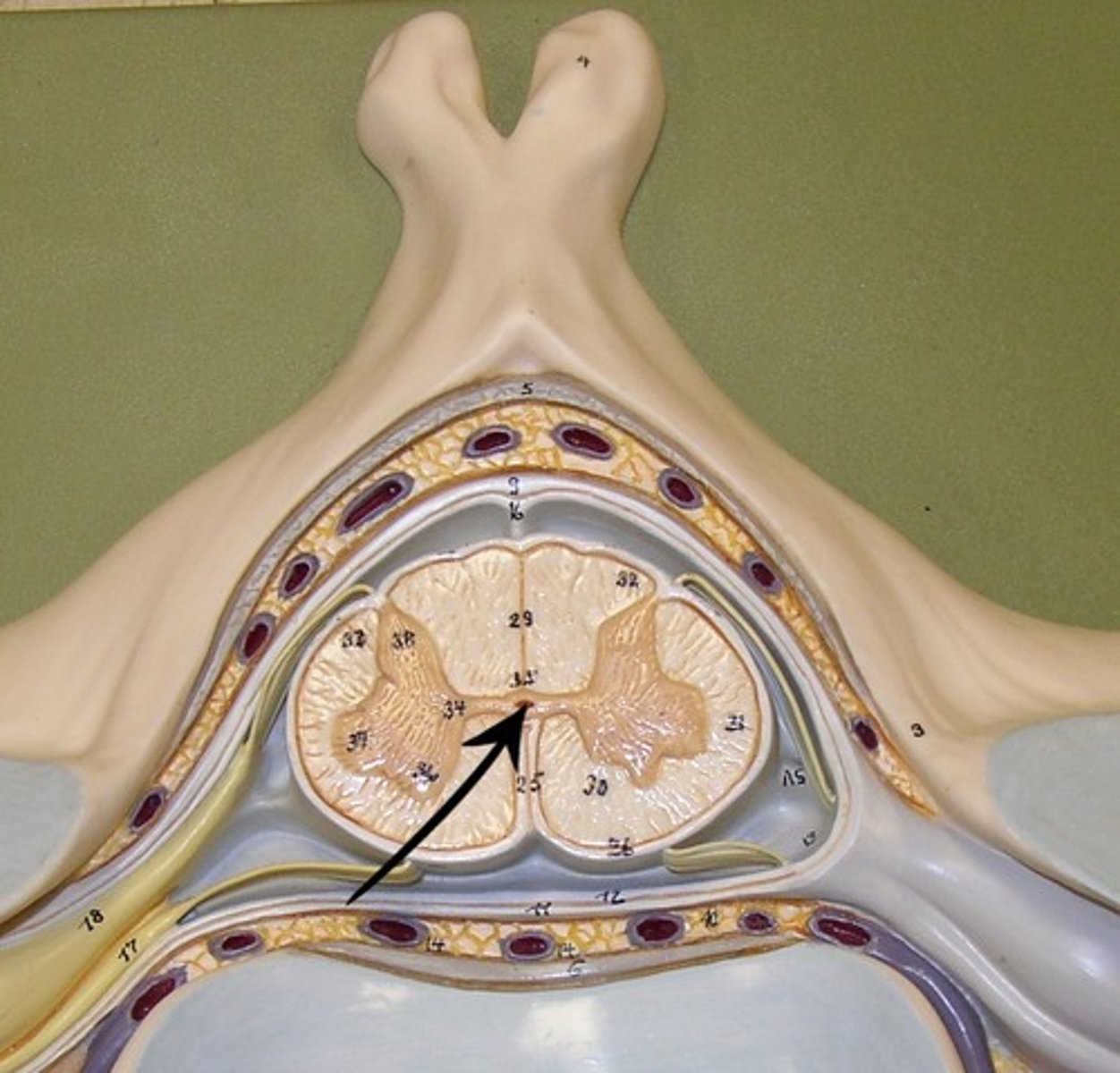
Dorsal Horn
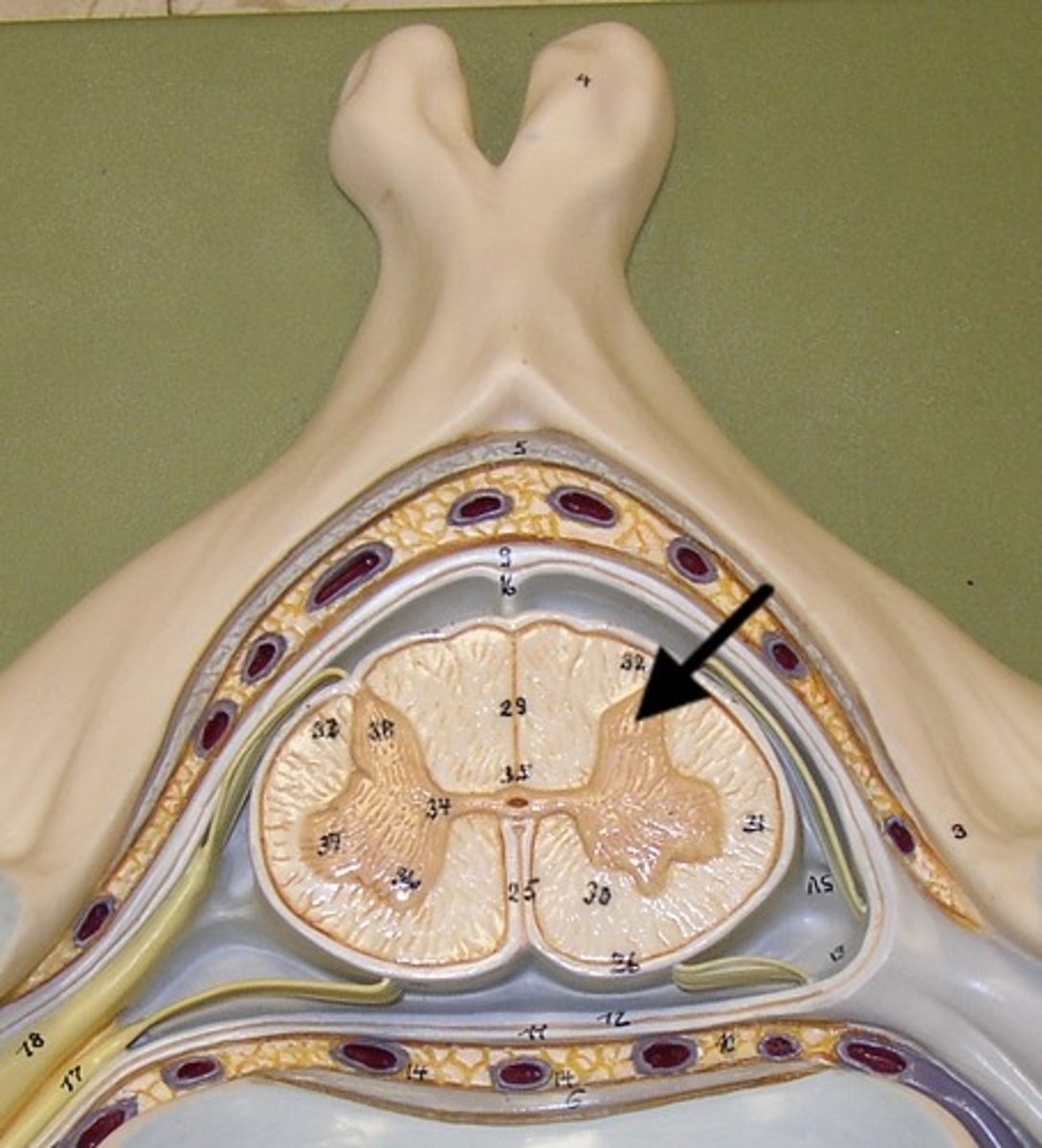
Ventral Horn
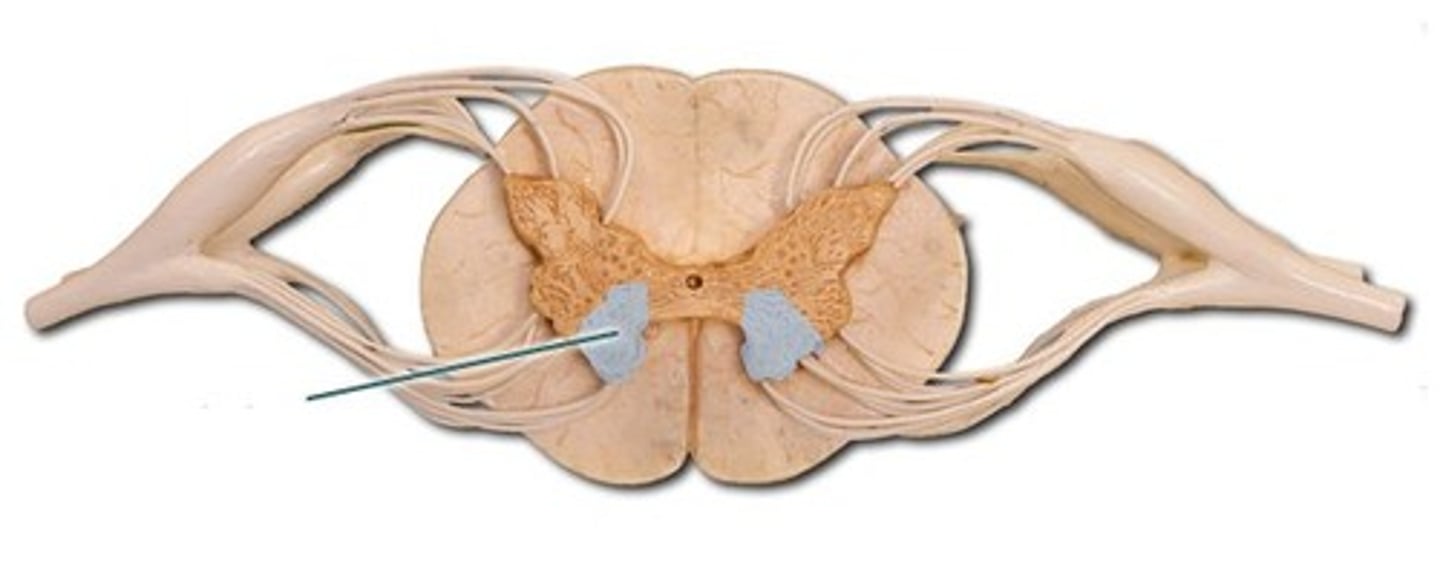
White Matter
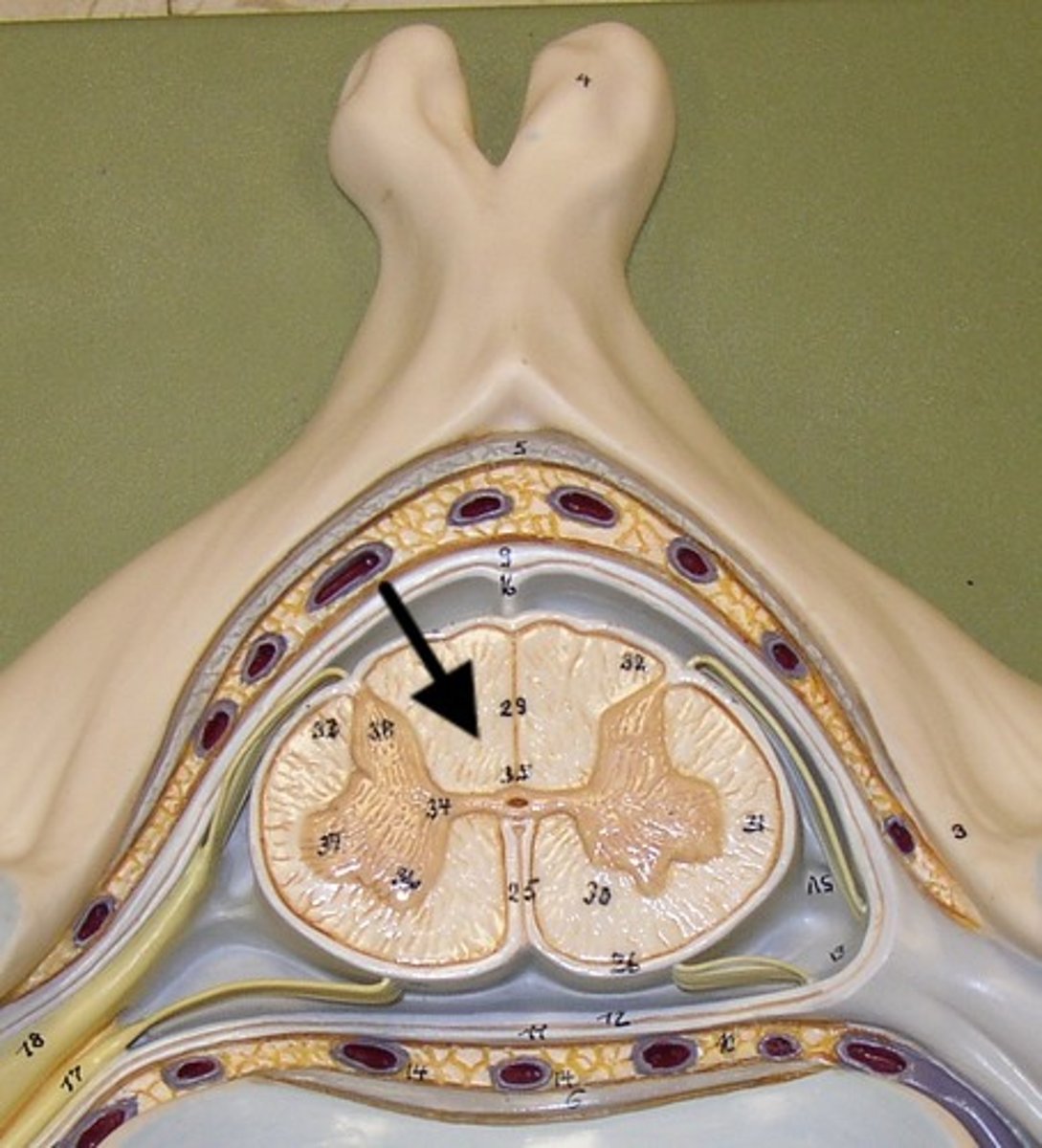
Gray Matter
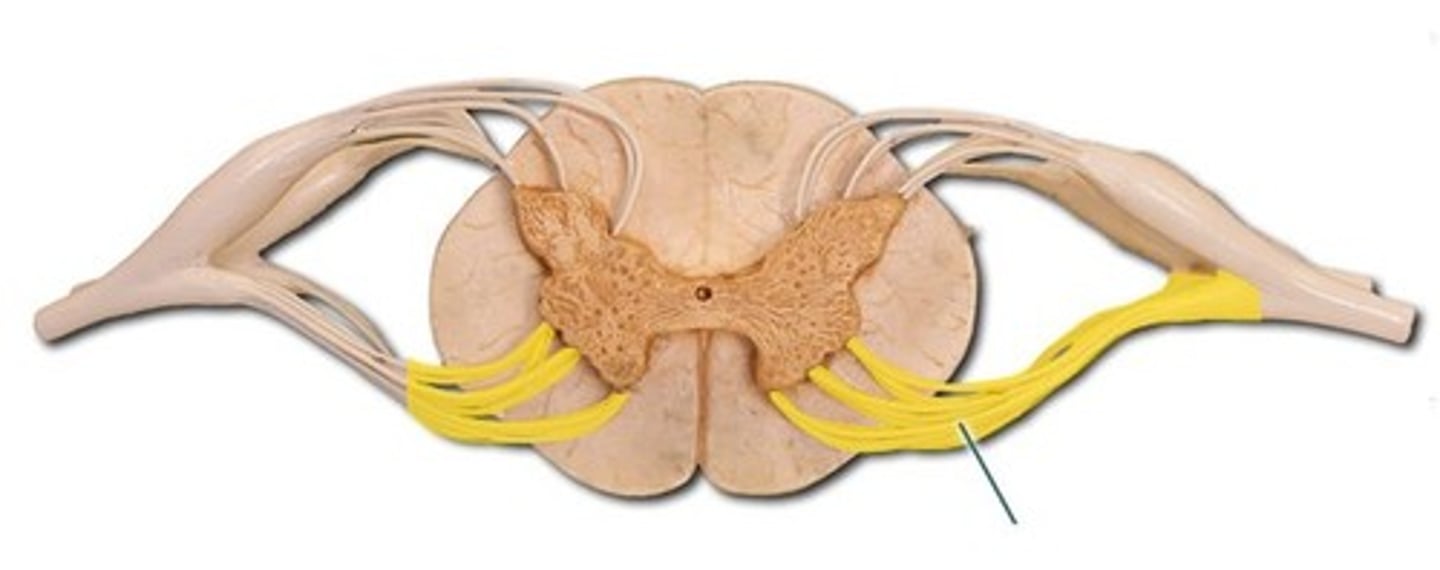
Dorsal Root
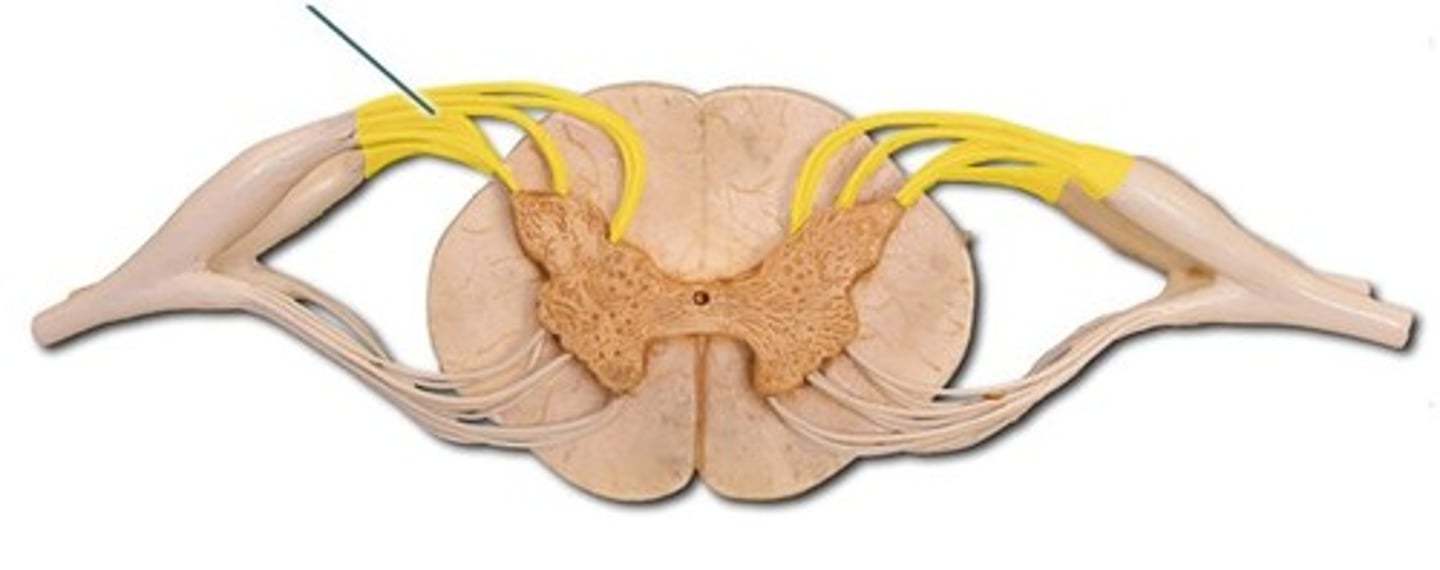
Ventral Root
Dorsal Root Ganglion
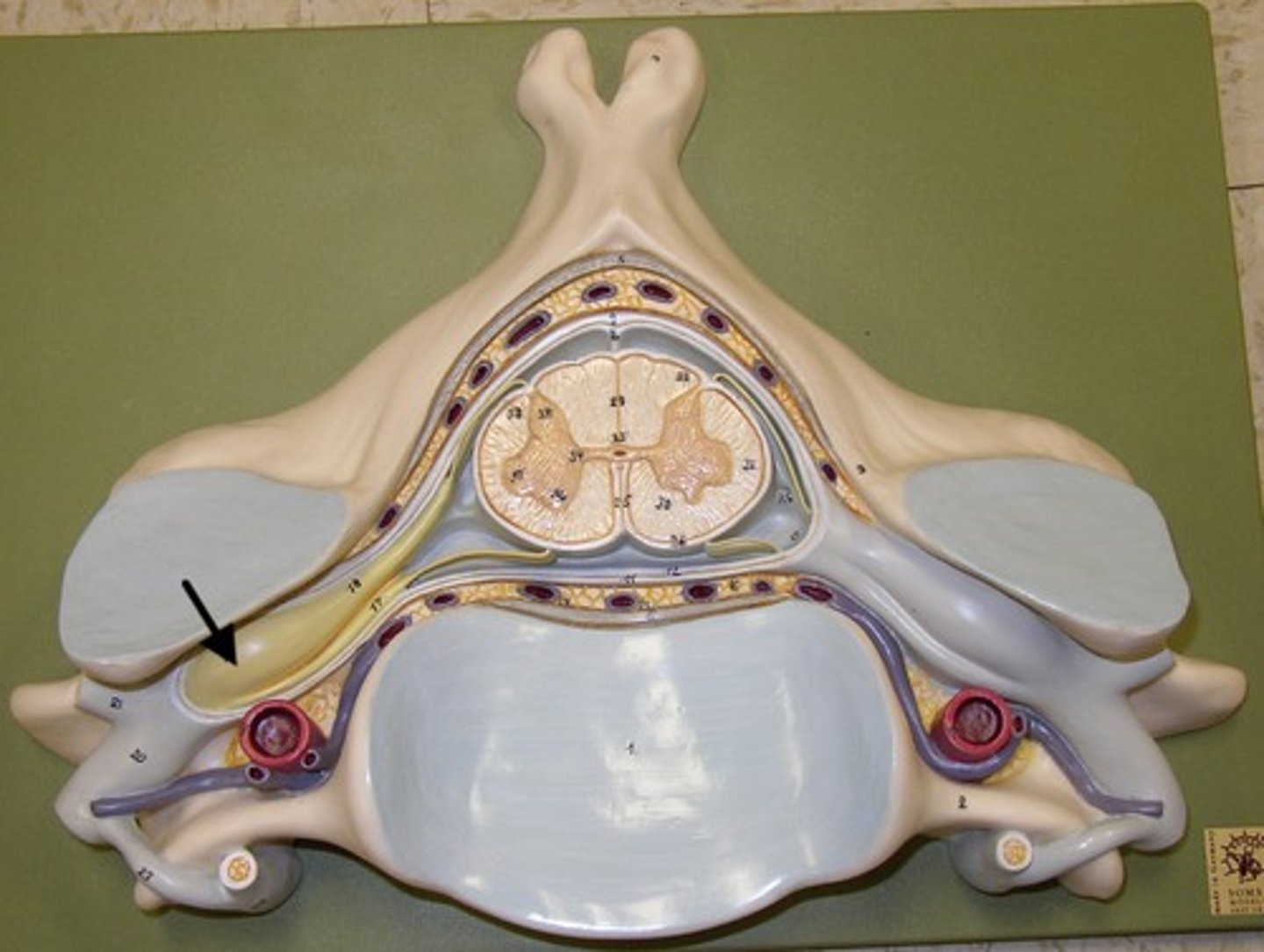
epidural space
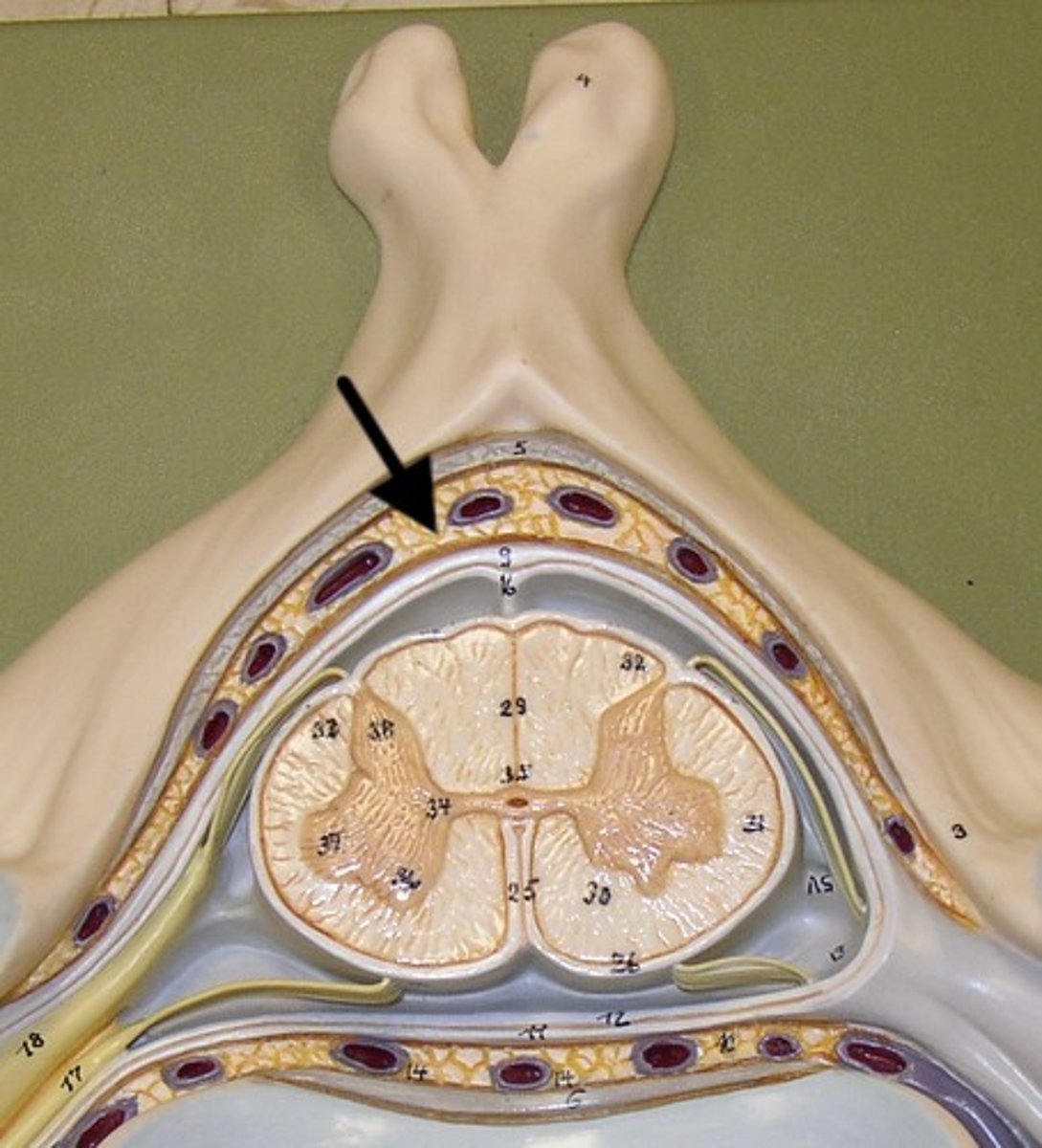
Dura Mater
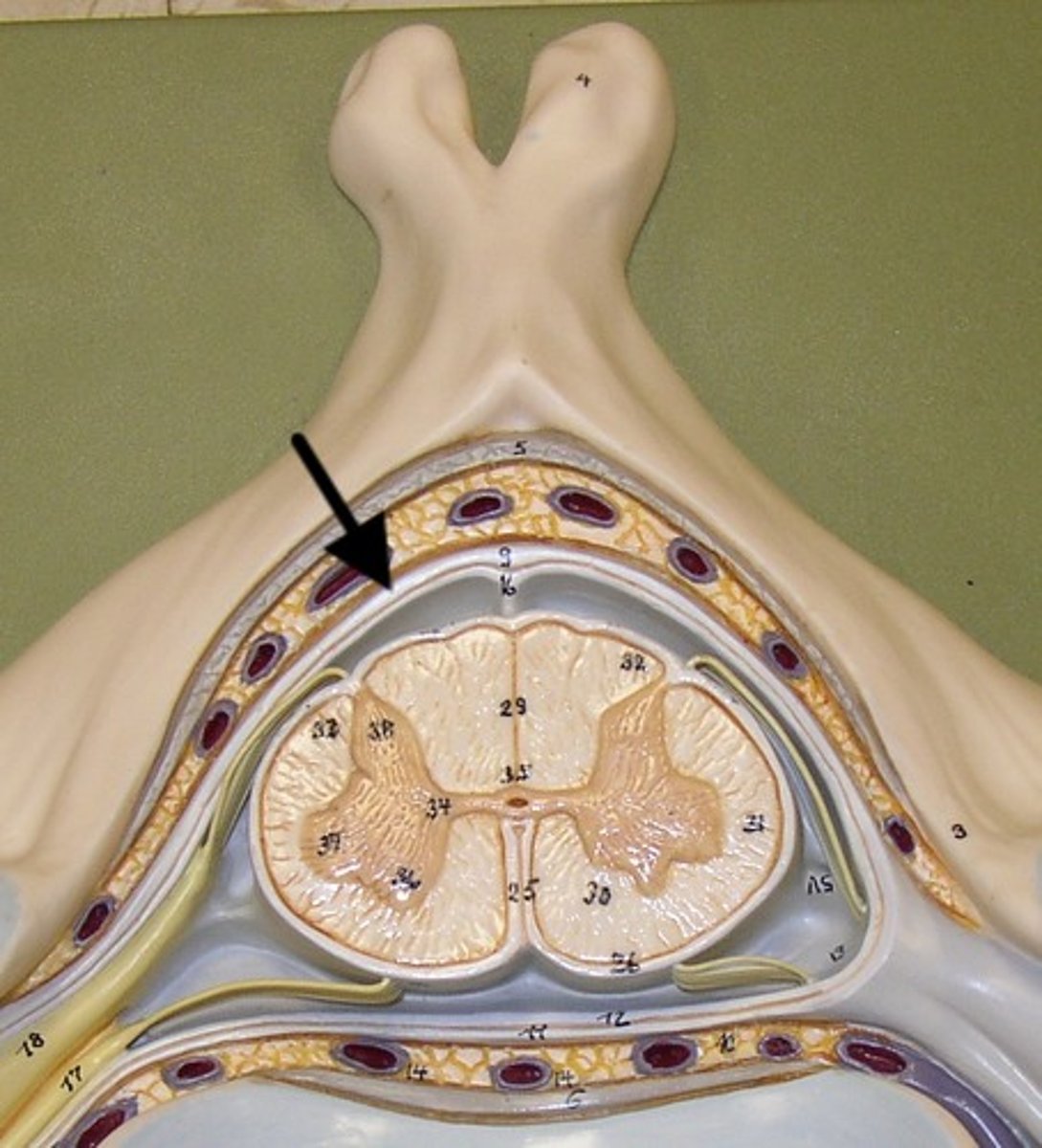
arachnoid matter (3)
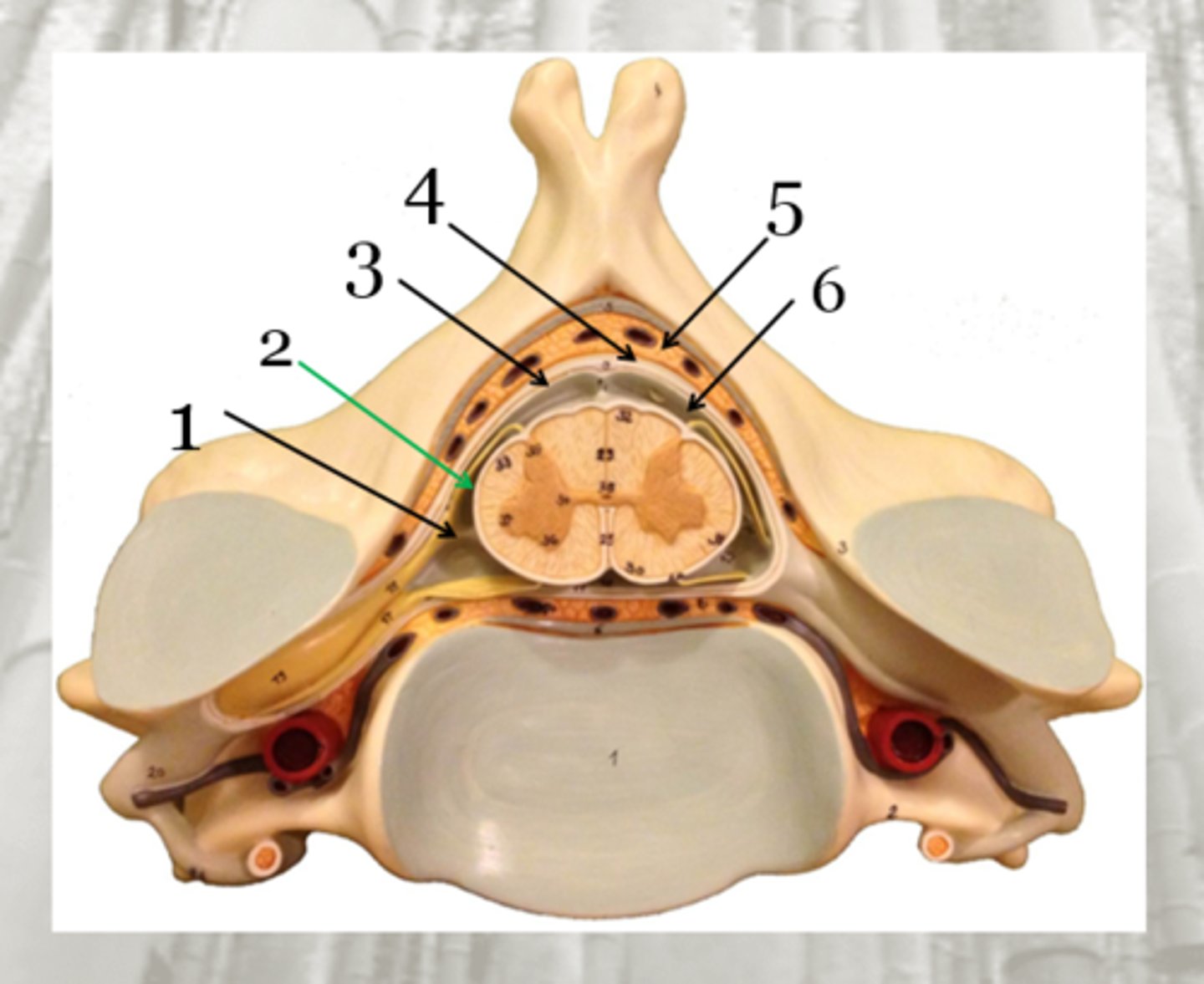
subarachnoid space
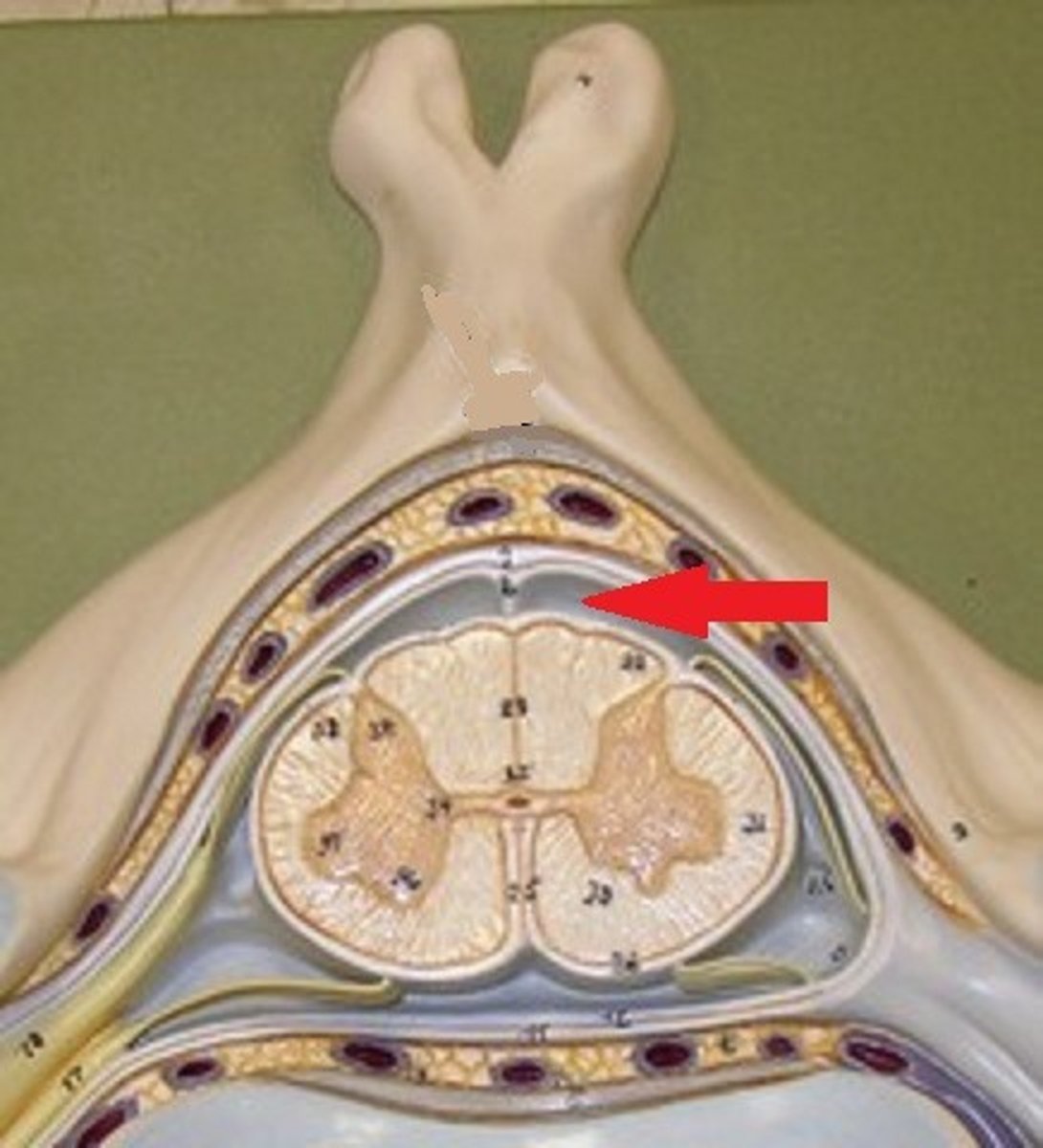
Pia Mater
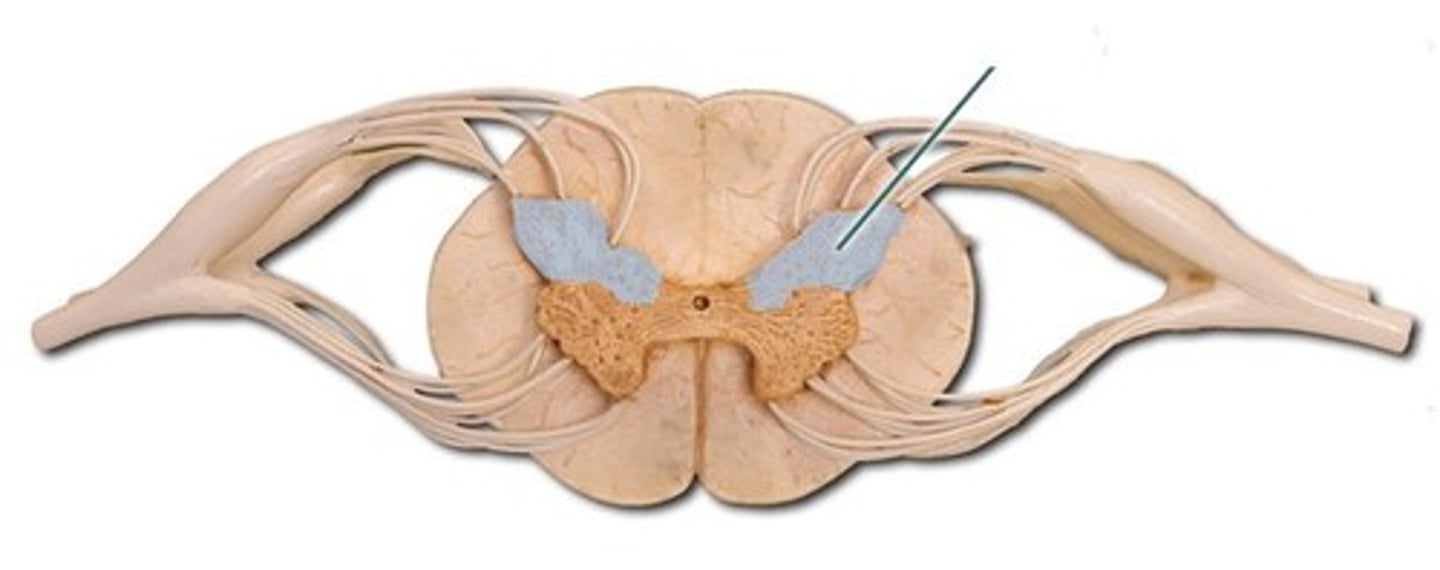
posterior horn
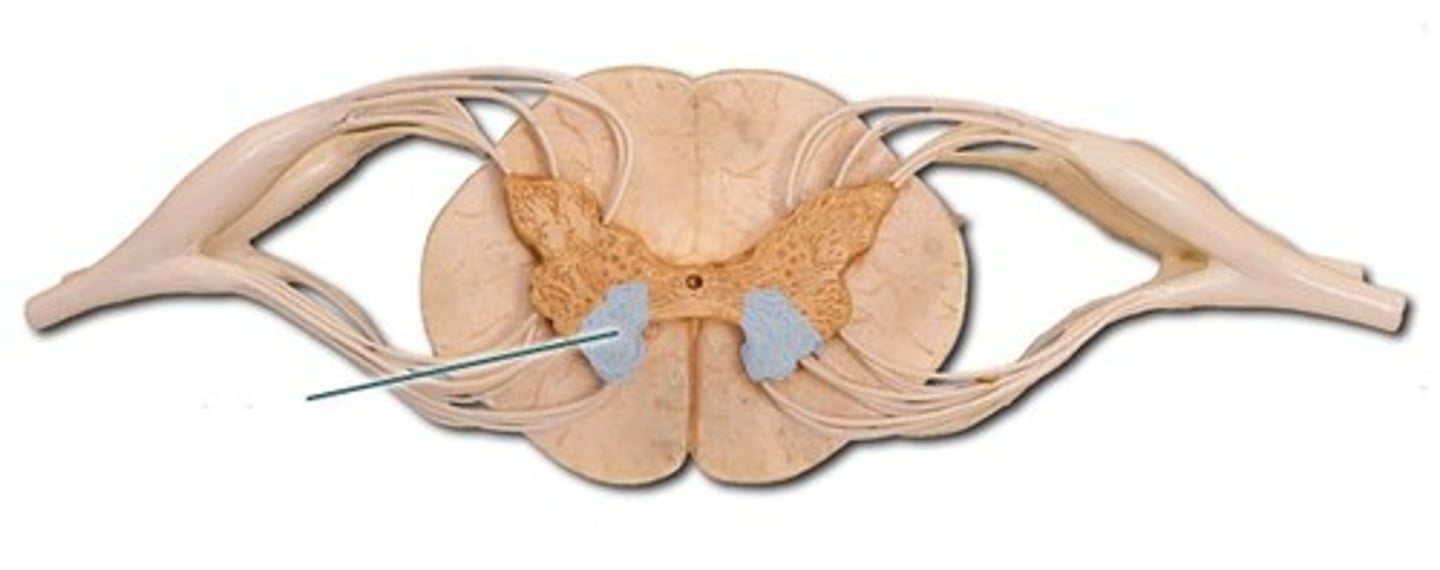
anterior horn
gray commissure
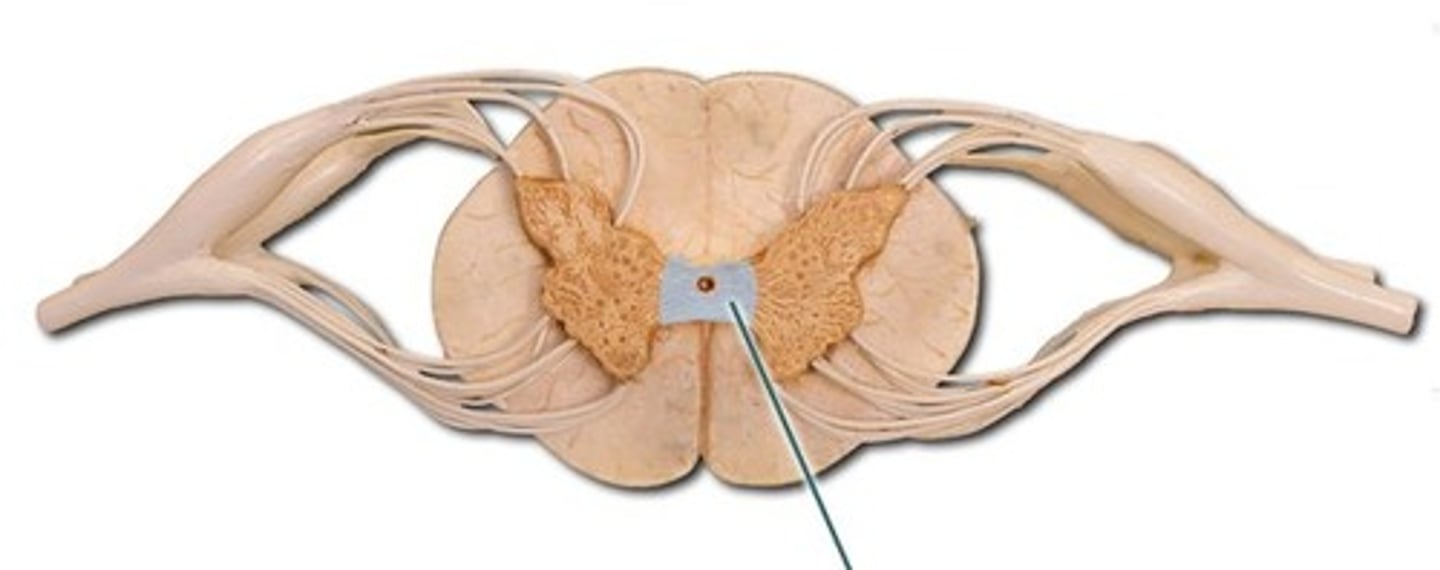
central canal
Monosynaptic reflexes
Reflexes that involve one synapse between the afferent and efferent neuron.
Polysynaptic reflexes
Reflexes that involve more than one synapse, usually including interneurons.
Stretch reflex
A monosynaptic spinal reflex in which a muscle contracts in response to being stretched; example shown in the document includes the quadriceps contracting when the patellar tendon is tapped.
Flexion withdrawal reflex
A polysynaptic reflex that pulls a limb away from a painful stimulus (e.g., stepping on something sharp), involving nociceptors and multiple muscles (often paired with a cross-extensor response).
Somatic reflexes
Reflexes in which signals go to skeletal muscles through somatic motor neurons.
Patellar reflex
A somatic stretch reflex where tapping the patellar tendon causes contraction of the quadriceps and leg extension.
Calcaneal reflex
A somatic reflex tested by tapping the calcaneal (Achilles) tendon, causing plantar flexion of the foot.
Pupillary light reflex
An autonomic reflex where light entering the eye causes the pupils to constrict.
Plantar reflex
A somatic reflex in which the sole of the foot is stroked to observe toe movement.
Babinski sign
An abnormal plantar reflex response in which the toes fan upward, indicating a neurological issue (normal only in infants).
Autonomic reflex
A reflex that sends signals to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, or glands through the autonomic nervous system.
Action-reaction times
The measured time it takes to perceive and voluntarily respond to a sensory stimulus. The document notes that reaction (not reflex) is voluntary, involves thought, and is affected by factors such as synaptic delay, nerve conduction velocity, receptor sensitivity, number of synapses, distraction, fatigue, age, arousal, drugs, practice, warnings, and punishment.
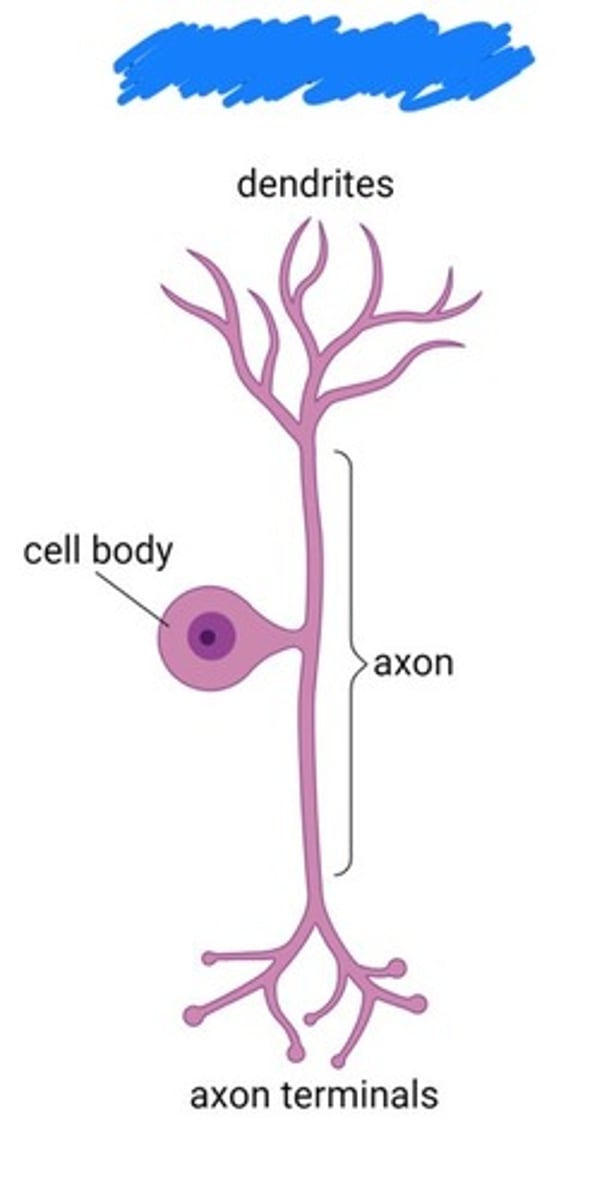
Unipolar neuron
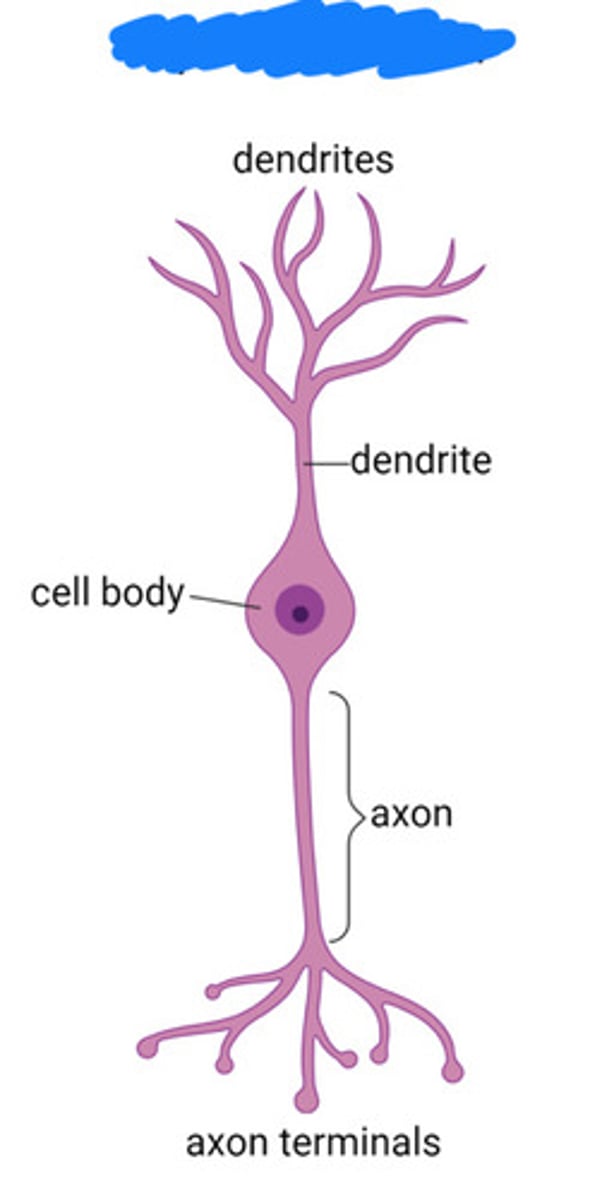
bipolar neuron
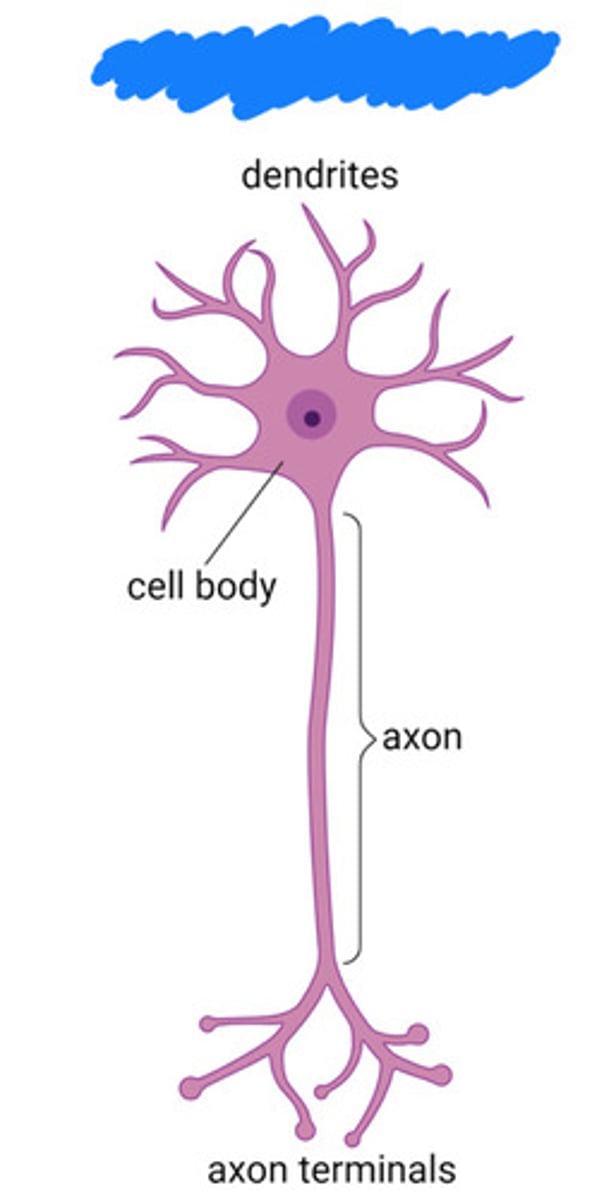
multipolar neuron
reflex classification
Spinal/cranial, somatic/autonomic, innate/conditioned,
ipsilateral/contralateral, monosynaptic/polysynaptic
reflex arc
the neural path for a reflex, made up of 5 components
Reflex arc component 1
sensory receptors
Reflex arc component 2
afferent neuron
Reflex arc component 3
integration center at the CNS
Reflex arc component 4
efferent neuron
Reflex arc component 5
efferent organ (visceral or somatic)