Properties and pharmacology of blood vessels
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What do the arteries do?
-they carry blood away from the heart towards organs and tissues. Arterial blood is normally oxygenated, with the exception of the pulmonary artery
What are the 3 layers of the blood vessels?
-tunica intima
-tunica media
-tunica adventitia
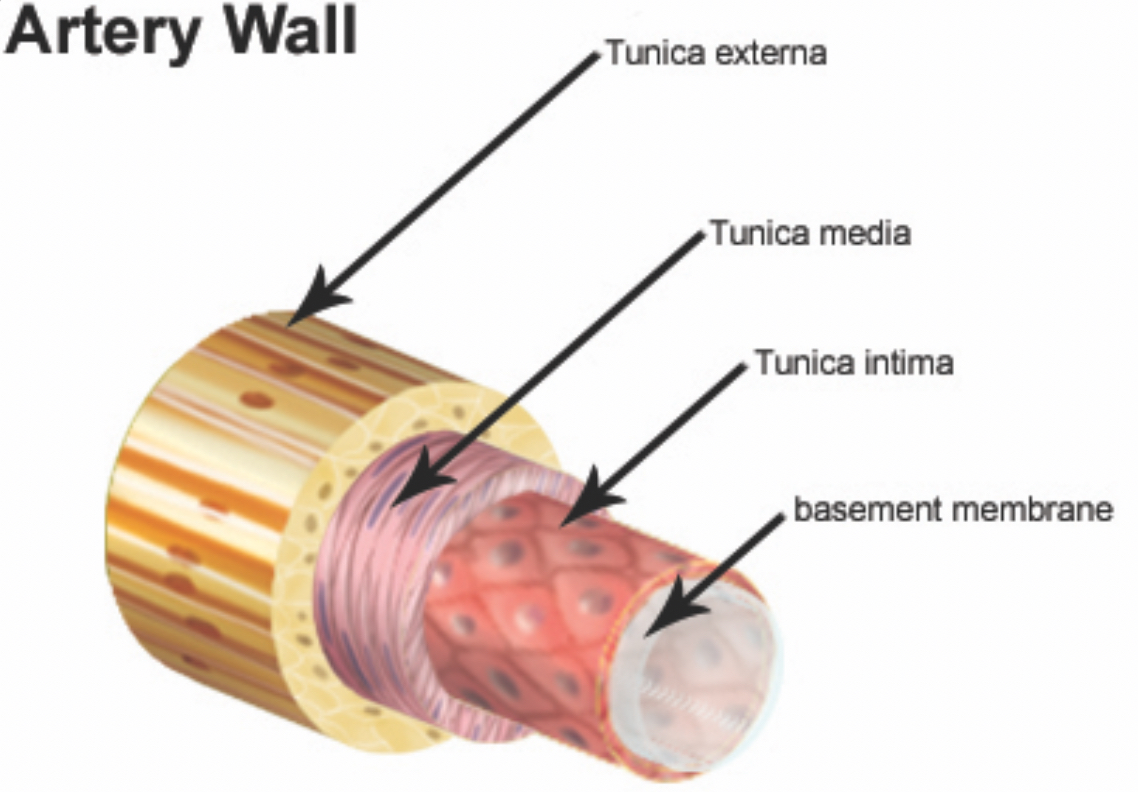
What is the tunica intima?
-an inner lining of endothelial cells in the blood vessel. It’s also made up of a thin layer of fine connective tissue dominated by elastic fibres
What is the tunica media?
-the middle layer
-larger elastic arteries e.g. the aorta have a high proportion of elastic tissue in the middle layer whereas the smaller muscular arteries have a large amount of smooth muscle in the middle layer.
What is the tunica adventitia?
-Last layer of blood vessels. It’s composed of mainly collagen fibres and elastic tissue. Nerves and lymphatic vessels are found within this layer.
What do elastic arteries branch into?
-they branch into smaller muscular arteries, then into arterioles before reaching the capillaries. The capillary bridges the arterial and venous systems.
What do the veins do?
-they carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues to the heart and lungs. The only exception is the pulmonary veins, which carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
State the order of the blood vessels
-artery, arteriole, capillary, venules, veins
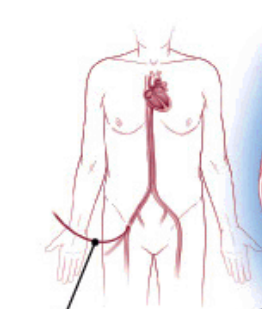
What is Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) used for and how is it performed?
-it treats arrhythmias by destroying part of the heart’s electrical conduction system or a dysfunctional area of cardiac muscle using heat from high-frequency alternating current (350–500 kHz).
A catheter is inserted through a vein into the heart
Performed in hospital under local anaesthesia or mild sedation
Lasts about 4 hours
Guided by real-time X-ray fluoroscopy
Usually very successful, especially if the abnormal focus is clearly identified beforehand