DNA Replication Part II
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
1
New cards
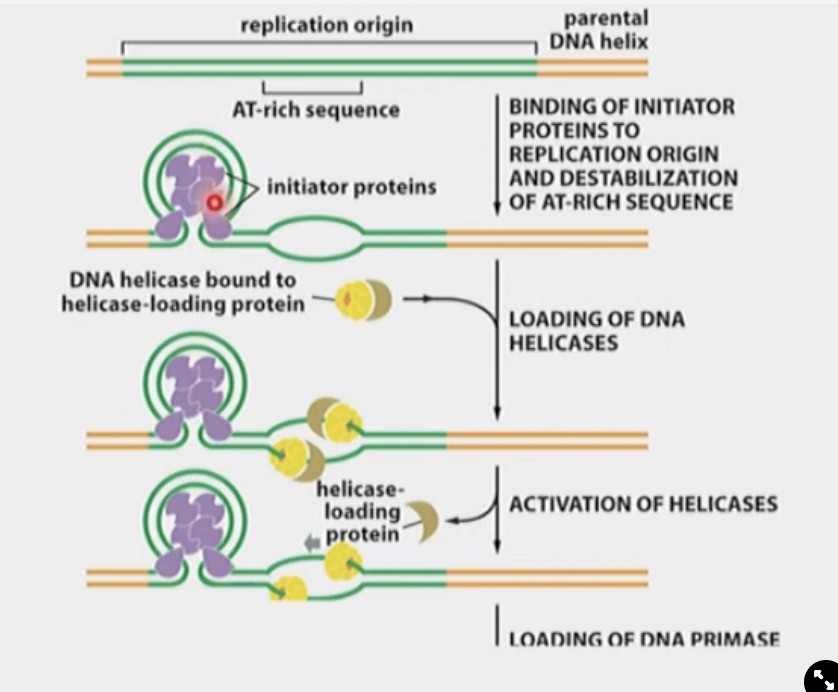
Initiator Proteins
Require ATP to wrap themselves in and melt some H-bonds, which attracts Helicase protein. They also help helicase bind.
2
New cards
How many helicase proteins are there? Which one is predominant?
Two helicase proteins, predominant helicase moves in the 5’ → 3’ direction along lagging strand template.
3
New cards
What does helicase require to function?
ATP, in order to break into ADP + Pi when separating base pairs
4
New cards
What level of organization is the helicase protein?
Quaternary
5
New cards
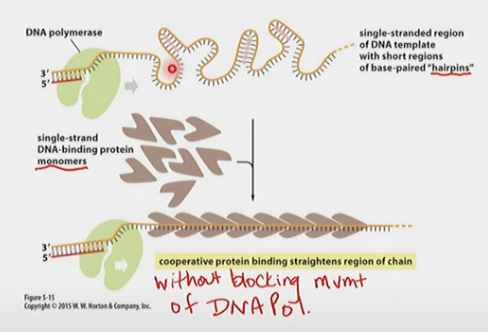
Single-strand binding proteins
Are monomers. Prevents re-annealing double-stranded templates (forming H-bonds) without blocking DNA Polymerase
* Partial H-bonds can cause hairpin loops
* Partial H-bonds can cause hairpin loops
6
New cards
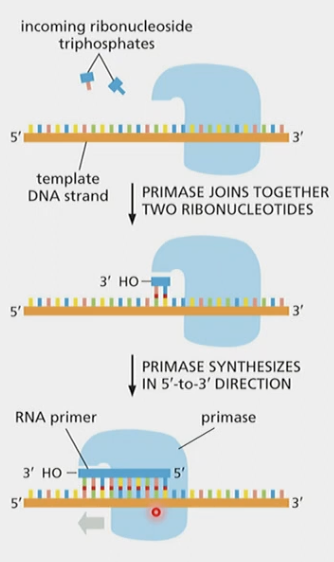
What are RNA primers
* Short sequences of nucleotides with a free 3’ OH base-paired to template - required by DNA polymerase to start replication
7
New cards
Purpose of primase in DNA replication
* Synthesize an RNA primer with free 3’ OH that DNA pol. can use. i.e., 5’ → 3’
8
New cards
Primase proceeds in which direction?
* reads 3’ → 5’ along template strand, same as DNA pol.
9
New cards
5 Steps of bacterial DNA Replication
1. Origin of replication.
2. Binding of initiator proteins.
3. Unwinding by helicase.
4. Binding of single-strand binding protein.
5. RNA primers made by primase.
10
New cards
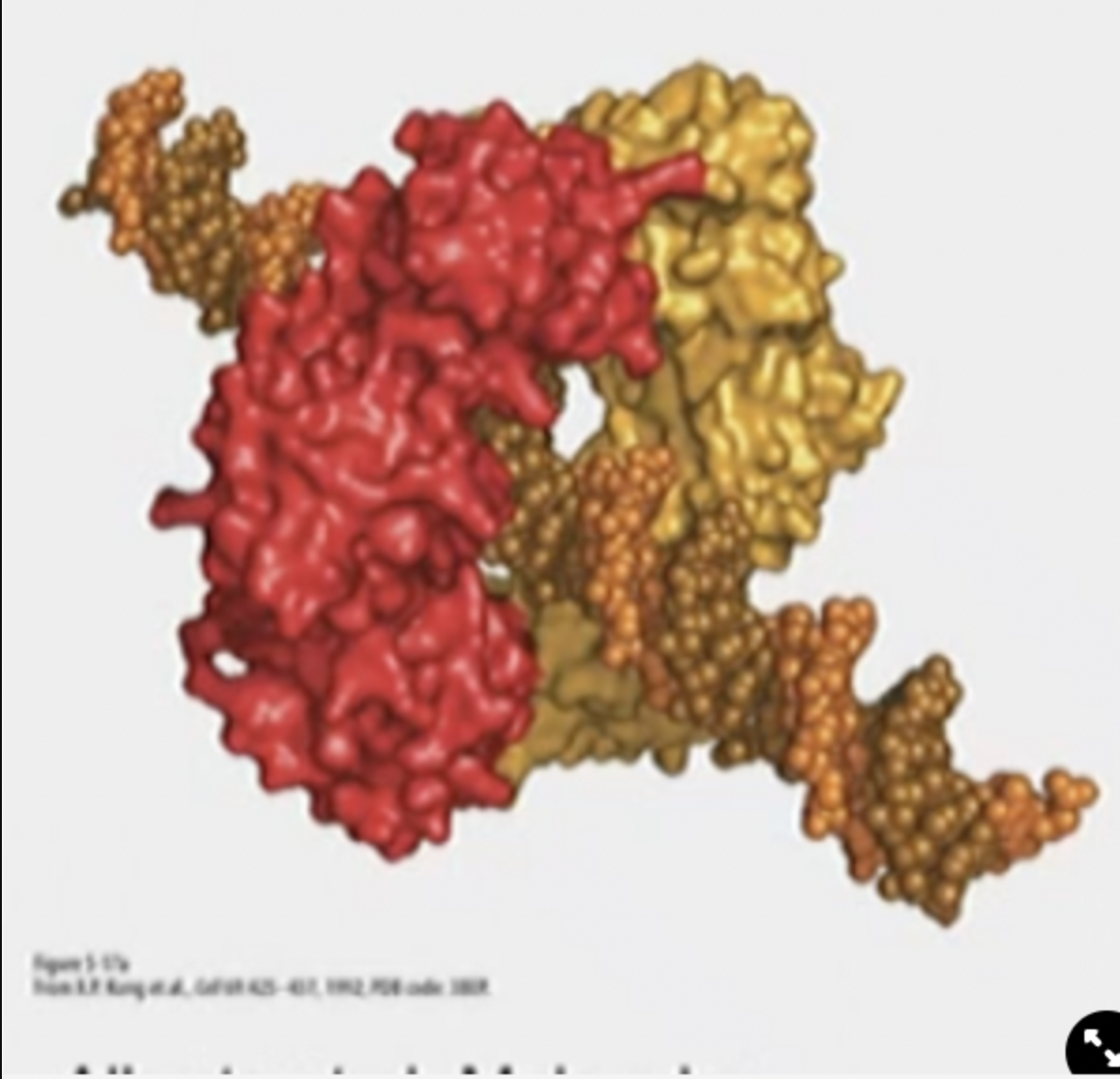
Sliding clamp function
* Holds onto DNA pol. from behind to prevent it from falling off.
* Ring shaped
* Ring shaped
11
New cards
@@Describe and label a replication fork@@
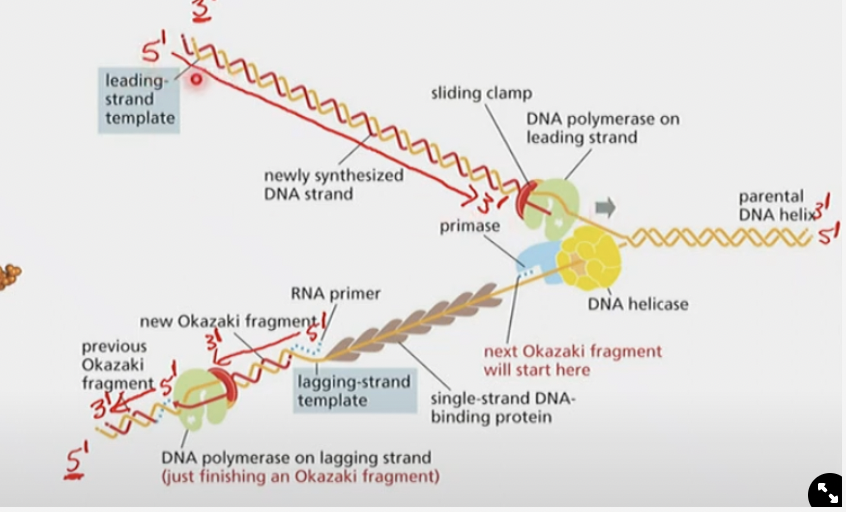
12
New cards
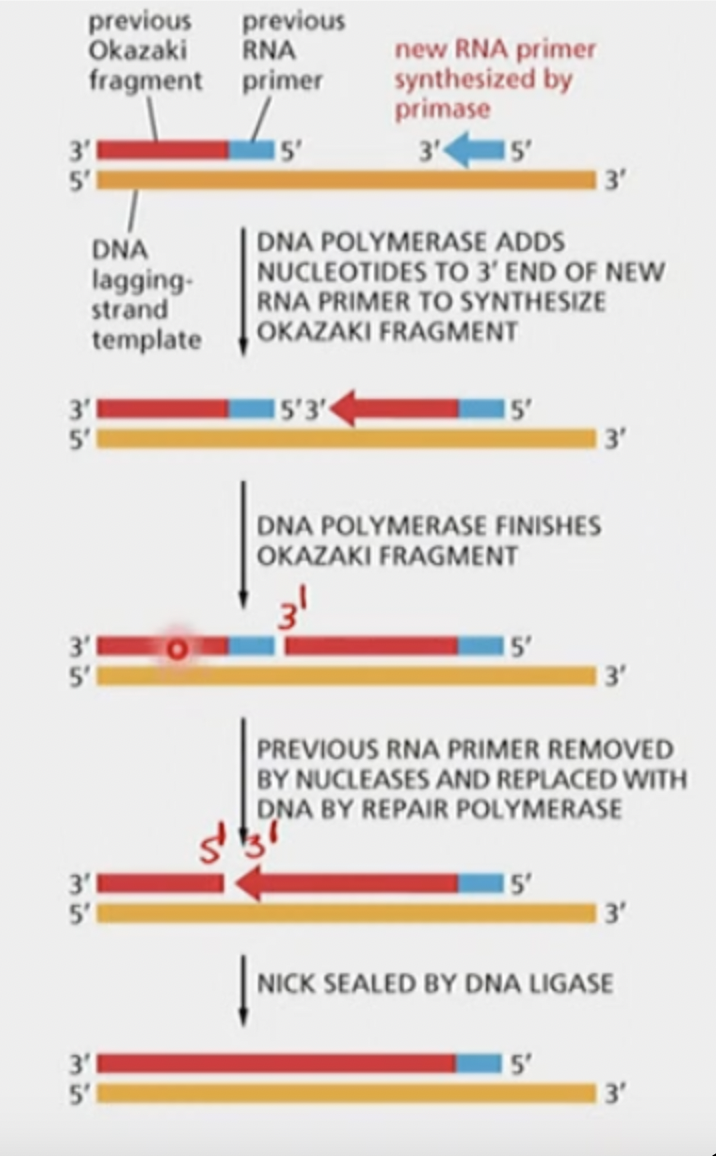
How are Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand linked together?
* A special DNA repair system is responsible for removal of the RNA primer and replacing it with a correctly matched DNA sequence
* repair pol. uses og template DNA to guide replacement of RNA primer with DNA
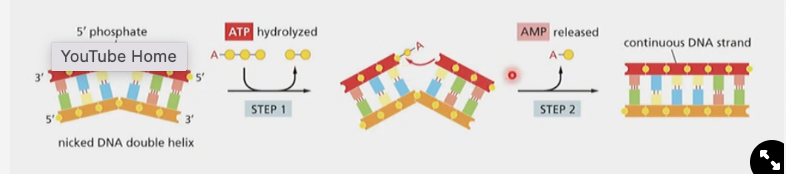
* DNA ligase seals the nick by
* hydrolyzing an ATP, to attach to the backbone, then an AMP is released to provide the energy for the nick to be sealed:
* THIS IS A DIFFERENT REACTION THAN WHAT DNA POLYMERASE DOES
* repair pol. uses og template DNA to guide replacement of RNA primer with DNA
* DNA ligase seals the nick by
* hydrolyzing an ATP, to attach to the backbone, then an AMP is released to provide the energy for the nick to be sealed:
* THIS IS A DIFFERENT REACTION THAN WHAT DNA POLYMERASE DOES
13
New cards
Summary of bacterial DNA Replication
14
New cards
Primosome
helicase + primase
15
New cards
Predominant helicase is on which strand?
The lagging strand
16
New cards
How is the leading strand synthesized? How about the lagging strand?
Synthesized continuously from single RNA Primer. Lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously from multiple primers.
17
New cards
Okazaki fragments
RNA primer + DNA
18
New cards
DNA synthesis proceeds (nucleotides are added) in which direction?
5’ → 3’