Lophotrochozoa- Phylum Mollusca
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
how many species does this phylum have
90,000 existing species; 70,000 extinct species (550 mya)
what are the characteristics of phylum Mollusca
spiral cleavage; trochophore larva; coelomate; protostomes
what are the four body plans that make up a mollusc
head-foot, visceral mass, mantle, radula
head-foot region purpose
feeding, sensory and locomotor organs
visceral mass
digestive, circulatory, respiratory, and reproductive organs
mantle
secretes a shell (valve) over the visceral mass
mantle cavity
space between mantle and body wall
Radula
protruding, rasping, tounge-like organ
what is the shell secreted by
the mantle
periostracum
outer organic layer composed of conchiolin; protective
middle prismatic layer
biggest layer made of calcium carbonate
inner nacreous layer
next to the mantle; used to capture unwanted items that may harm clam
nervous system of a mollusc
pairs of ganglia with connecting nerve cords
veglier
intermediate larval stage; has the beginning of a foot, mantle and shell ( changes shape; whole trochophore changes size)
What are the five classes of Mollusca
Caudofoveata, Solenogastor, Polyplacophora, Monoplacophora, Schapoda, Gastropoda
Class Caudofoveata and Solenogastres
marine worm-like, shell-less; reduced head, radula and other molluscan anatomy; calcareous spicules give it a shiny look
Kulindroplax (genus)
first mollusc with worm-like body and valves; suggests aplacophora may have evolved rom a shelled ancestor and are monophyletic
Class Polyplacophora
flattened body with eight dorsal calcareous plates; marine, intertidal zone or deep water ( chitons)
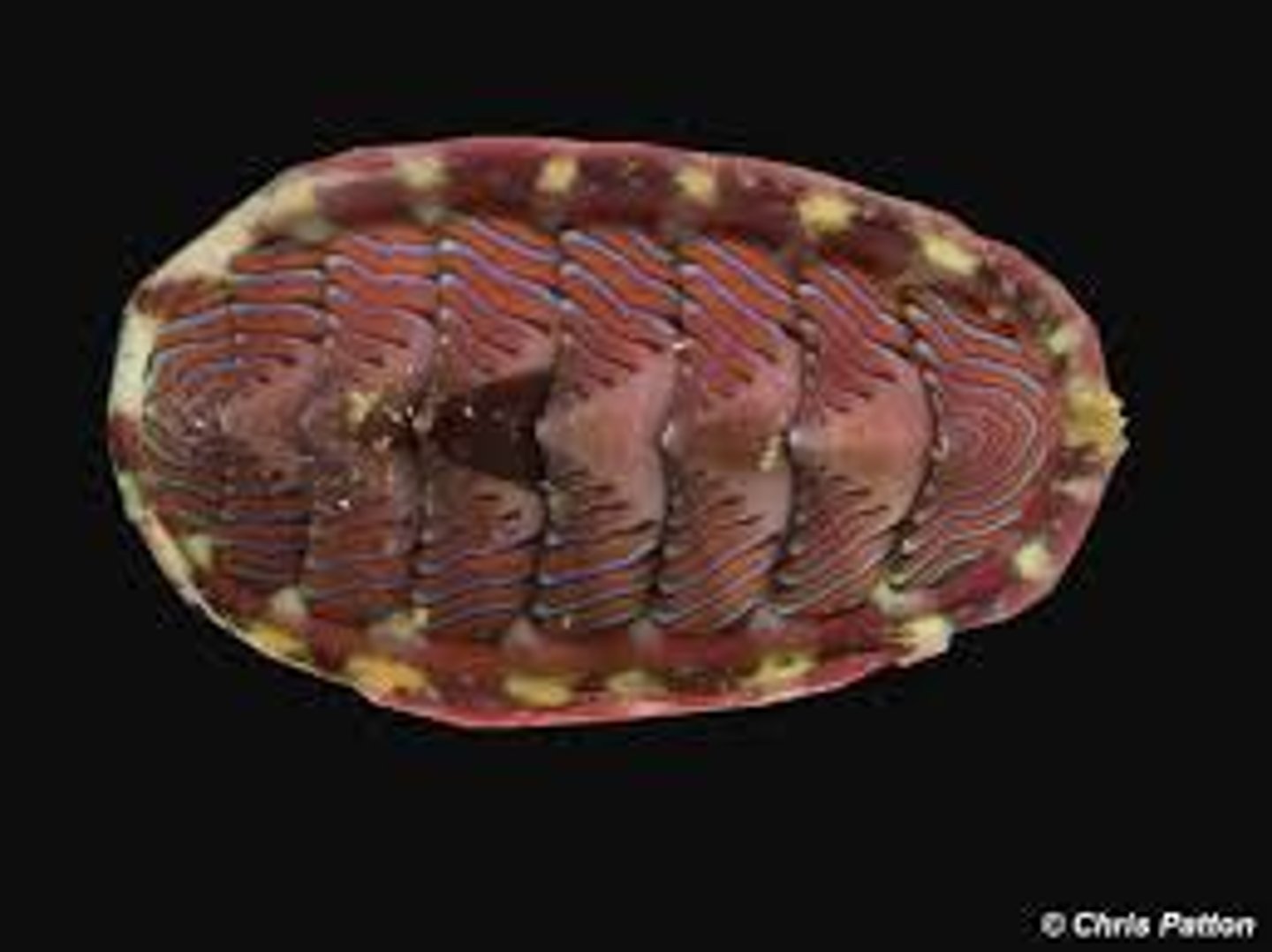

Biomineralization
teeth of the radula are composed of magnetic crystalline magnetite
Conchifera clade
univalve shell with periostracum, prismatic, and nacreous layers
Class Monoplacophora
(one-plate) previously considered extinct; rediscovered in 1952; single rounded shell; serially repeated organs: gills, metanephridia, gonads
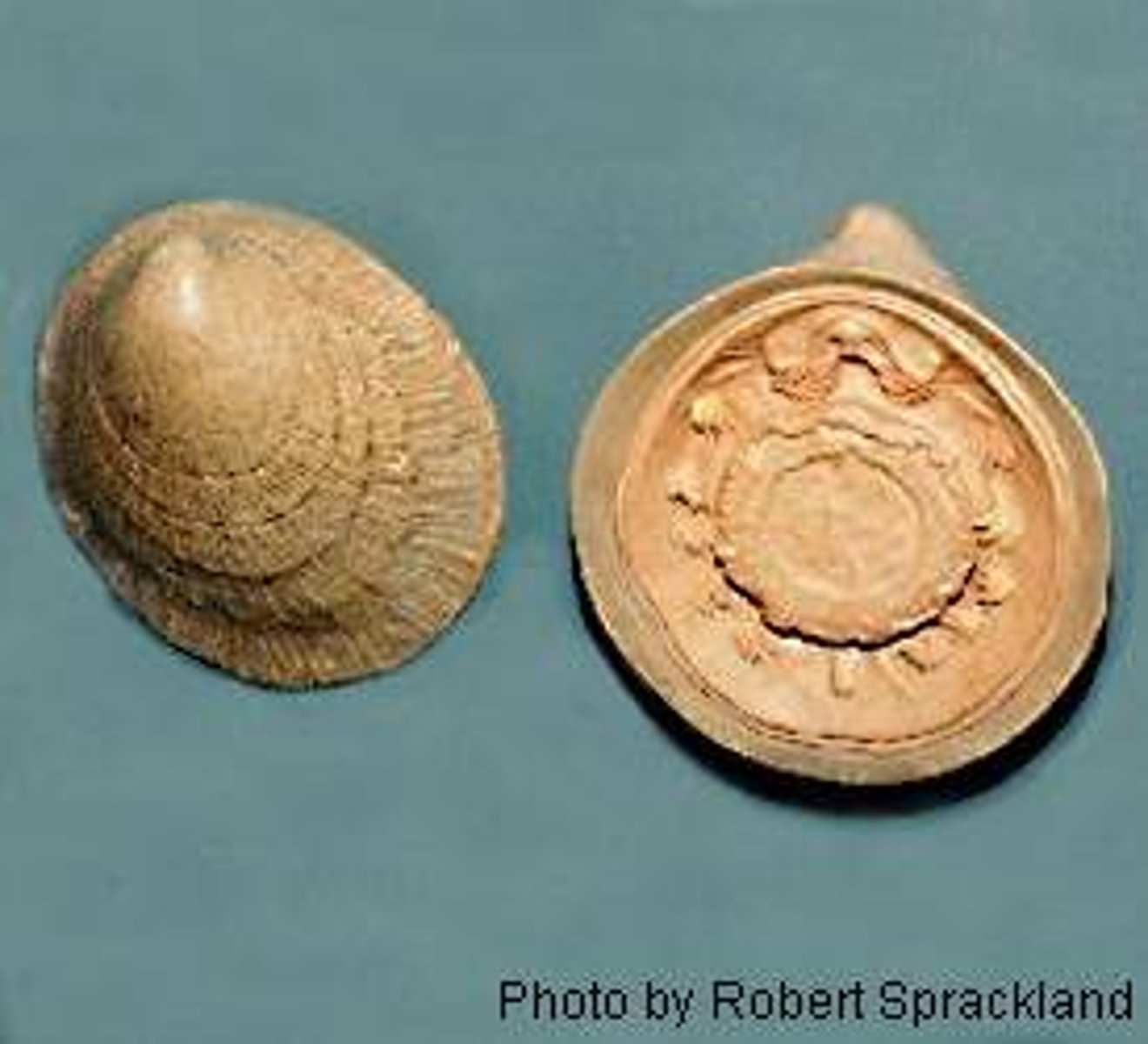

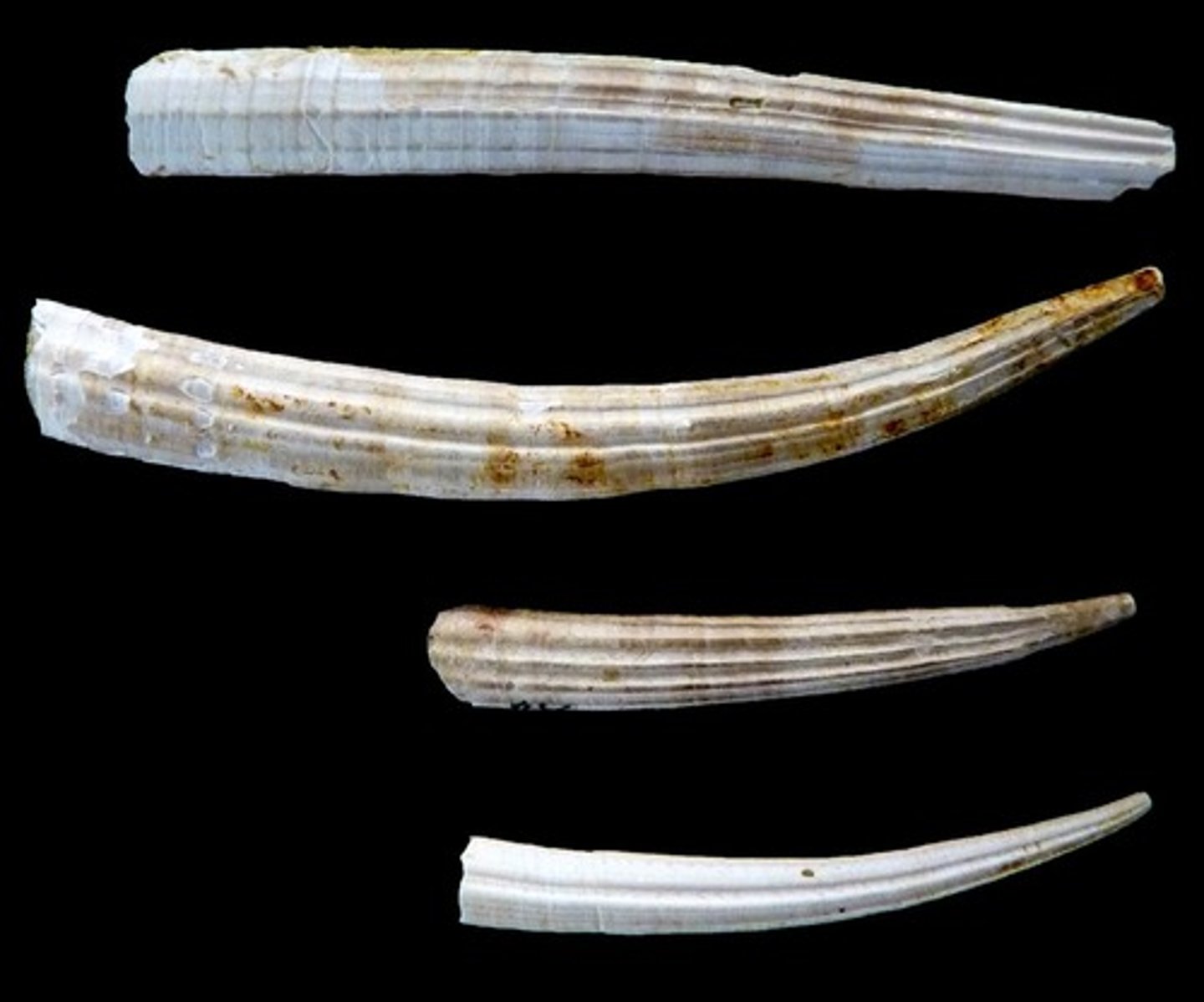
Class Schaphoda
(tusk shells) Benthic; marine/off-shore; burrow head down in substrate; tube shaped mantle; no gills

Class Gastropods
most diverse molluscan class; univalve shell; coiled or uncoiled; body undergoes torsion or coiling
How many species does class Gastropoda have
Over 70,000 living and 15,000 fossil species
torsion
twisting of body into new form
Coiling
curl of the shell and the visceral mass contained within the shell.
sinistral
left hand coil
Dextral
right hand coiled
What are the Molluscs feeding habits
herbivorous, scavengers, and a few carnivores
what are consequences of torsion
organs in visceral mass switch; loss of organs on one side (bilateral asymmetry); posterior anus and mantle cavity sit on top of the head
Fouling
Waste is washed back over the gills or mouth
What are the three subclasses of Class Gastropoda
prosobranchia, Opisthobranchia, Pulmonta.
Prosobranchia
subphylum that has a operculum(door); heart is location in front of the gill
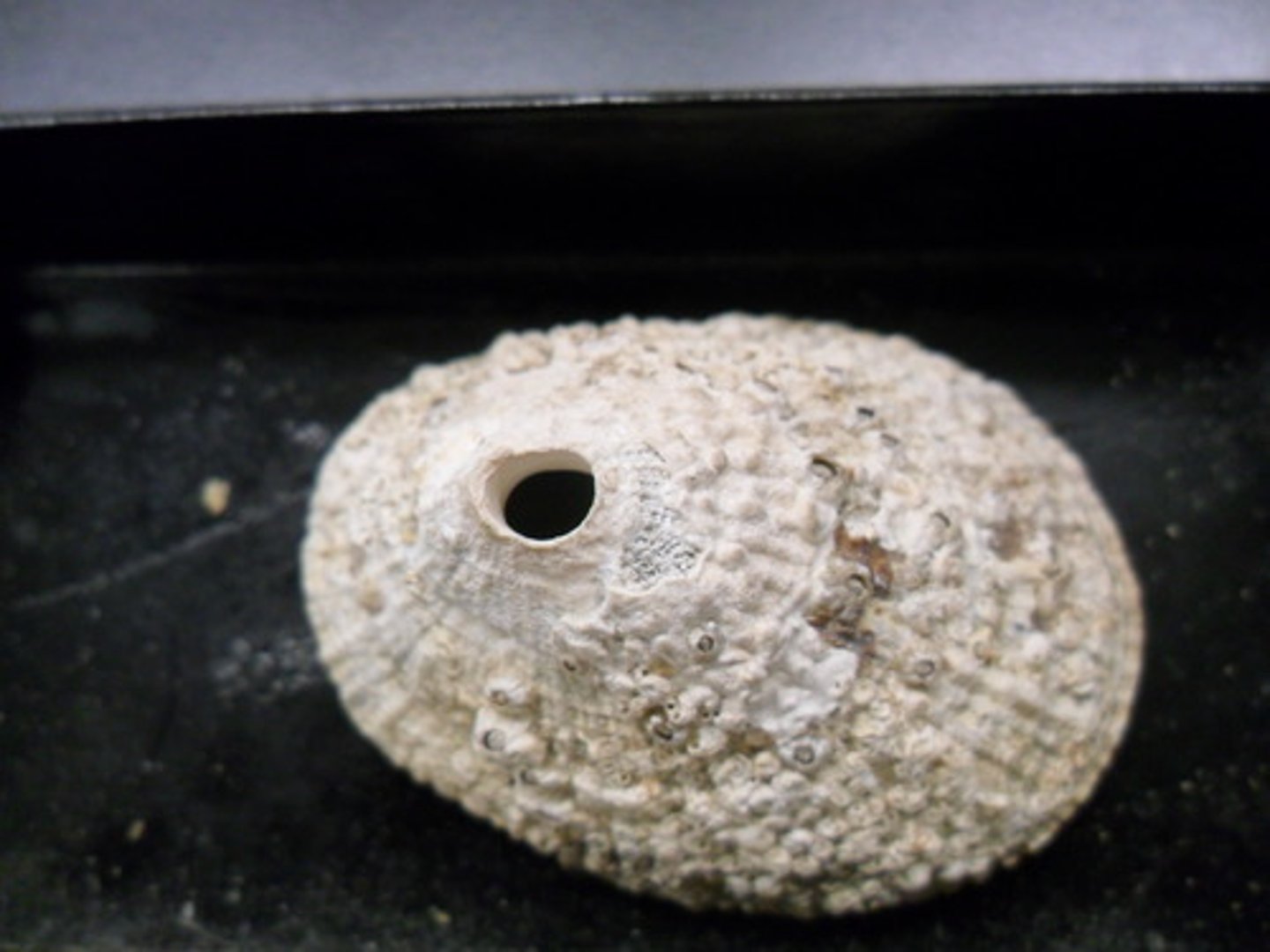

Opisthobranchia
subphylum where organisms heart located behind the gill
Pulmonta
subphylum that has lost their and breath by a lung; contain penises at the top of had that attach to each other when transferring gametes.
in mollusca, the coelom is most easily seen around what structure
the heart
which process or action resulted in the loss of the right gill in most modern gastrpods
torsion
what is the correct order (outside to inside) of their three shell layers
periostracum, prismatic, nacreous
The pulmonata are a subphylum group of gastropods that...
have lungs instead of gills in most members
Class Bivalvia
laterally compresses, with left and right valves, dorsal hinge
how does Class Bivalvia eat
sedentary suspension feeders; use ciliary currents tin gills to collect food
how does class Bivalvia reproduce
Dioecious; external fertilization in marine bivalves; internal fertilization in freshwater bivalves
what are the larval stages in Class Bivalvia
trochophore, velgier, and spat stages
Glochidia
velgier larvae stage of freshwater clams
Class Cephalopoda
Active Marine Predators; strong-beak like jaws to grasp prey
What is the system class cephalopods have
closed circulatory system with three hearts
umbo
closest to anterior and dorsal side
what feature is the most complex in Cephalopods
the eyes
syphon
tube on the posterior side of cephalopods