4.1- Features of the Animal Kingdom
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Animals common ancestor
similar to choanoflagellate protist
Features used to classify animals
true tissues
body plan: symmetry
developmental pathway:
1. number of tissue layers
2. Origin of mouth and anus
3. Presence of a body cavity
Complex Tissue structure
lack cell walls
unique intracellular communication-gap junctions
differentiation/ specialization of tissues
Specialization tissues
connective tissues
epithelial tissues
nervous tissue
muscle tissue
Asymetrial
no symmetry (sponges)

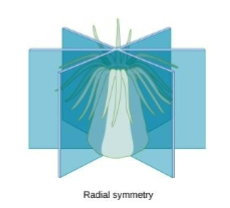
Radial symmetry
arranged around central axis with parts radiating outward
can encounter environment from any direction
jellyfish, comb jellies
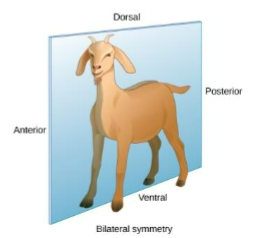
Bilateral symmetry
divides body along right and left halfs
allows for cephalization, (anterior vs. posterior)
suited for moving forward
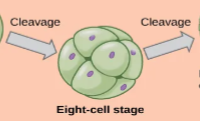
Embryonic Development- 1. Cleavage
series of mitotic cells with no cell growth
after three divisions→
cell continues to divides and or rearrange
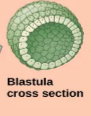
Embryonic Development- 2. Blastulation
forms blastula
migration of cells
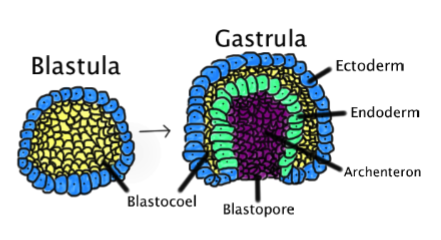
Embryonic development 3. gastrulation
forms gastrula
forms blastopore and archenteron
sets up formation of outer and inner germ layers
organogenesis gives rise to tissue, organs and organ systems
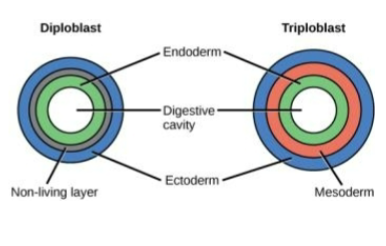
Diplolasts
two germ layers: ectoderm and endoderm
radial symmetry
Cnidarians
Ctenophores
Triploblasts
three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
bilateral symmetry
all other animals
Coelom
body cavity
derived mesoderm germ layer
lies between body wall and visceral organs
fluid filled
improved mobility
organs can move within
aceolomates
pseudocoelomate
coelomates
Acoelomates- coelom
mesoderm filled with tissue
plathyhelminthes (flatworms)
Pseudocolelomates- coelom
false body cavity
derived from both
still functional
nematodes
Coelomates- coelom
body cavity and internal organs lines with epithelial membrane
tissue holds organs in place, allowing motion
most other animals
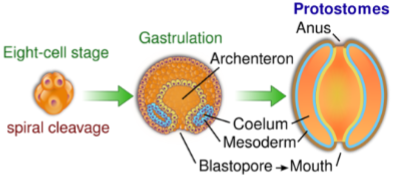
Protostomes
blastopore becomes the mouth, anus second opening
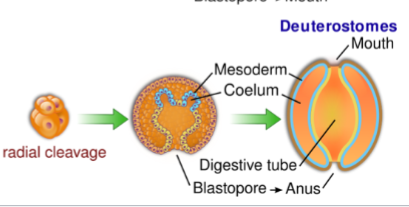
Deuterostomes
blastopore becomes anus, mouth forms a second opening
Cleavage patterns- protostomes
spiral cleavage
determinate cleavage: fate of cells determined
Cleavage patterns- Deuterostomes
radial cleavage
indeterminate cleavage: fate of cells determined somewhat
Digestive system: incomplete
sac like cavity with one opening that serves as both mouth and anus (gastrovascular cavity)
Complete digestive system
separate mouth and anus
Nervous System- Cephalization
concentration of nerves and sense organs at anterior end of body, forming a head a brain
Body Patterns- segmentation
organism is divided into a linear series of repeating, similar units along its anterior-posterior (head-to-tail) axis
Animal Reproduction
most animals diploids
reproduce sexually
Direct Development
grows without larvae stage
Indirect Development
larvae stage
Incomplete metamorphosis
young resemble small adult
Complete metamorphosis
organism looks different in each stage
Hox Genes
master regulatory genes that control embryonic development (code for transcription factors)
determines body plant, segmentation, number and placement of appendages, embryonic polarity
Cambrian period
542-488 MYA
most of todays phyla originated'
explosion of animal life
Post Cambrian
global and regional climate change
lead to mass extinctions
loss of diversity
Permian Triassic Boundary
greatest extinction event due to climate change from impact events and/or volcanic activity
extinction of 95% species