Working Scientifically Keywords for CIE Checkpoint
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Hypothesis
An answer to a scientific question that we can test with an experiment. It should be a statement include the independent and dependent variable.
Example: The larger the animal the larger mass of food eaten.
Variable
Something that can change in an experiment.
Independent Variable
The variable you choose to change in an investigation.
Dependent Variable
The variable you measure or observe in the investigation.
Control or standardised variable
Variables that you must keep the same in the investigation to ensure the investigation was fair.
Investigation
An experiment carried out to support or refute a hypothesis.
Prediction
A guess as to what will happen in an experiment using your scientific knowledge.
Fair Test
A type of experiment where only one variable is changed, and others are controlled or kept the same. If variables are not controlled.
Precision
The number of significant figures a measurement is taken to or the smallest unit an instrument can take a measurement to.
Example: Measuring in centimeters is more precise than measuring in meters. Measuring temperature every minute is more precise than measuring every 10 minutes.
Control experiment
An experiment that is used for comparison.
For example: if you asked which fertiliser helps plants grow the tallest, the control would have no fertiliser.
Anomaly
A result that is very different from the pattern of other results.
An anomaly could be caused by a mistake by the experimenter or a change in an uncontrolled variable.
Risk assessment
Stating the hazards, risks and safety measures for an experiment.
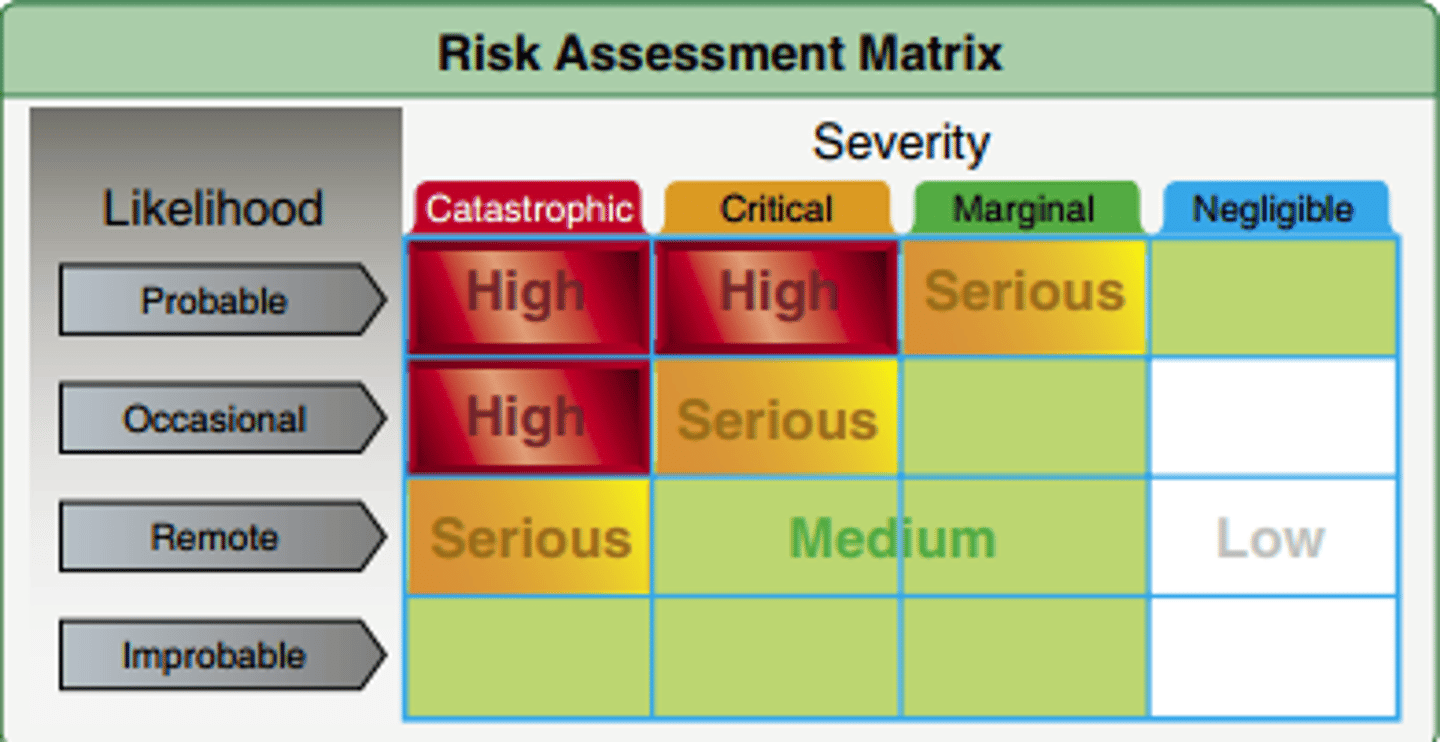
Conclusion
An answer to the scientific question that the experiment answers. This should be supported by data from the experiment.
Example: Animals with a larger mass eat a greater mass of food. For example: the 15kg dog ate an average of 350g of food per day and the 45kg dog ate an average of 910g of food per day.
Error
A difference between the true, accurate value and what you measured.
This could be a mistake in your method, for example starting a stop clock late or putting in too much of one reactant. You can reduce error by using better ways of measuring, for example: use a measuring cylinder or syringe to measure volume.
Reliable data
When data is repeatable and you have collected enough data so you know it is repeatable; data was collected as a fair test; and measurements were taken accurately to avoid any error.
Trend or Pattern of results
As (the independent variable) increases (the dependent variable) increases/decreases/stays the same.
Example: As the mass of the dog increases, the mass of food it eats increases.
Accuracy
How close a measurement or observation is to the true value.
Use a different term to this, such as 'not a fair test' or 'not repeatable' or give a specific example of how to measure more accurately e.g. Use a syringe to increase accuracy.
Repeatable
If you perform the same experiment multiple times you get the same or very similar results each time.
If it is not the there will be many anomalies or a wide range in the repeats.
If you only repeat the experiment once you will not know.
Model or analogy
A representation of objects, systems or processes that helps scientists explain and think about ideas that are abstract or not visible.
Scientists use these to make sense of things we can't see (like atoms) and communicate scientific ideas clearly
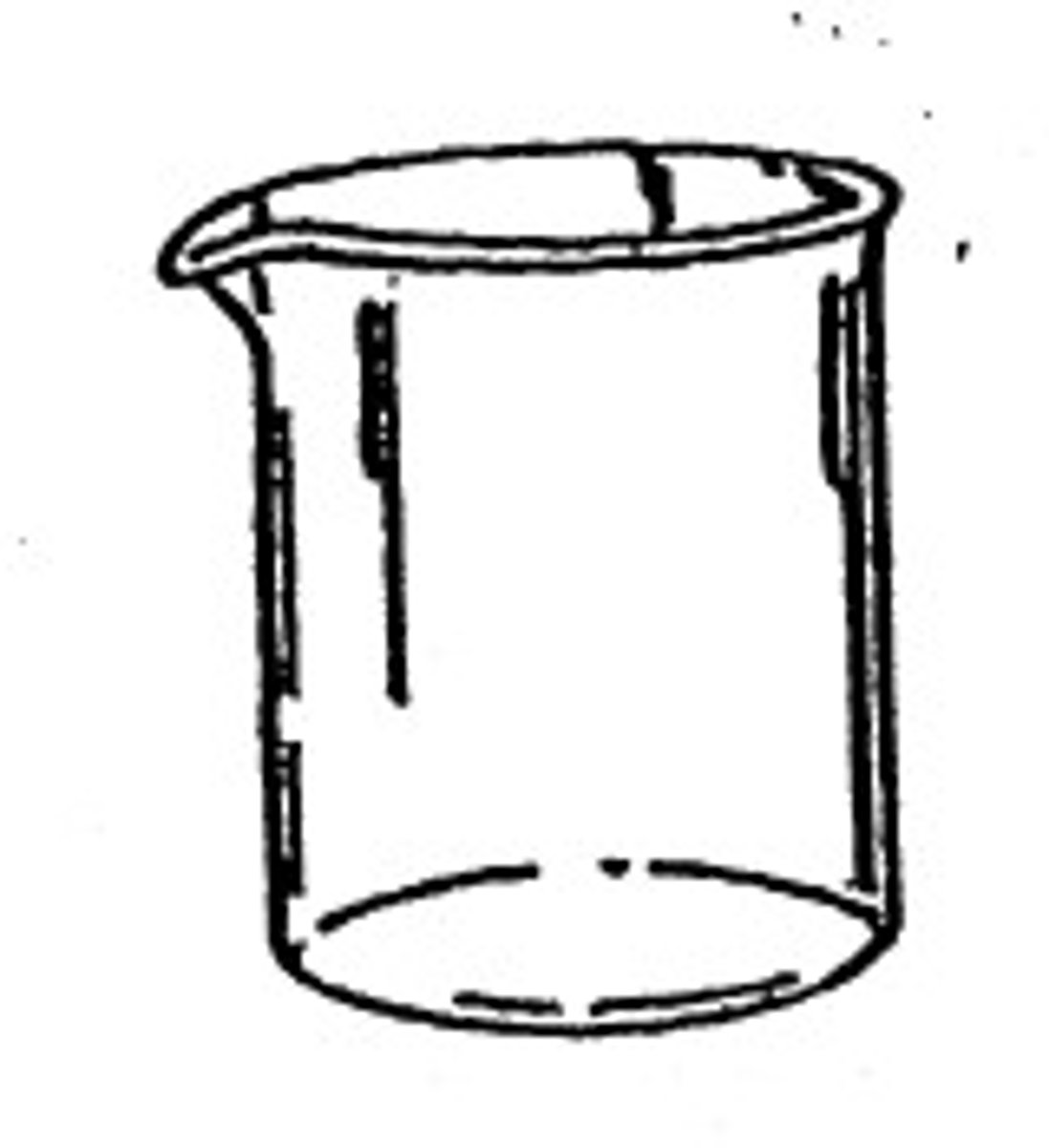
Beaker
Used to hold, mix, and heat liquids. Not an accurate for measuring volumes.
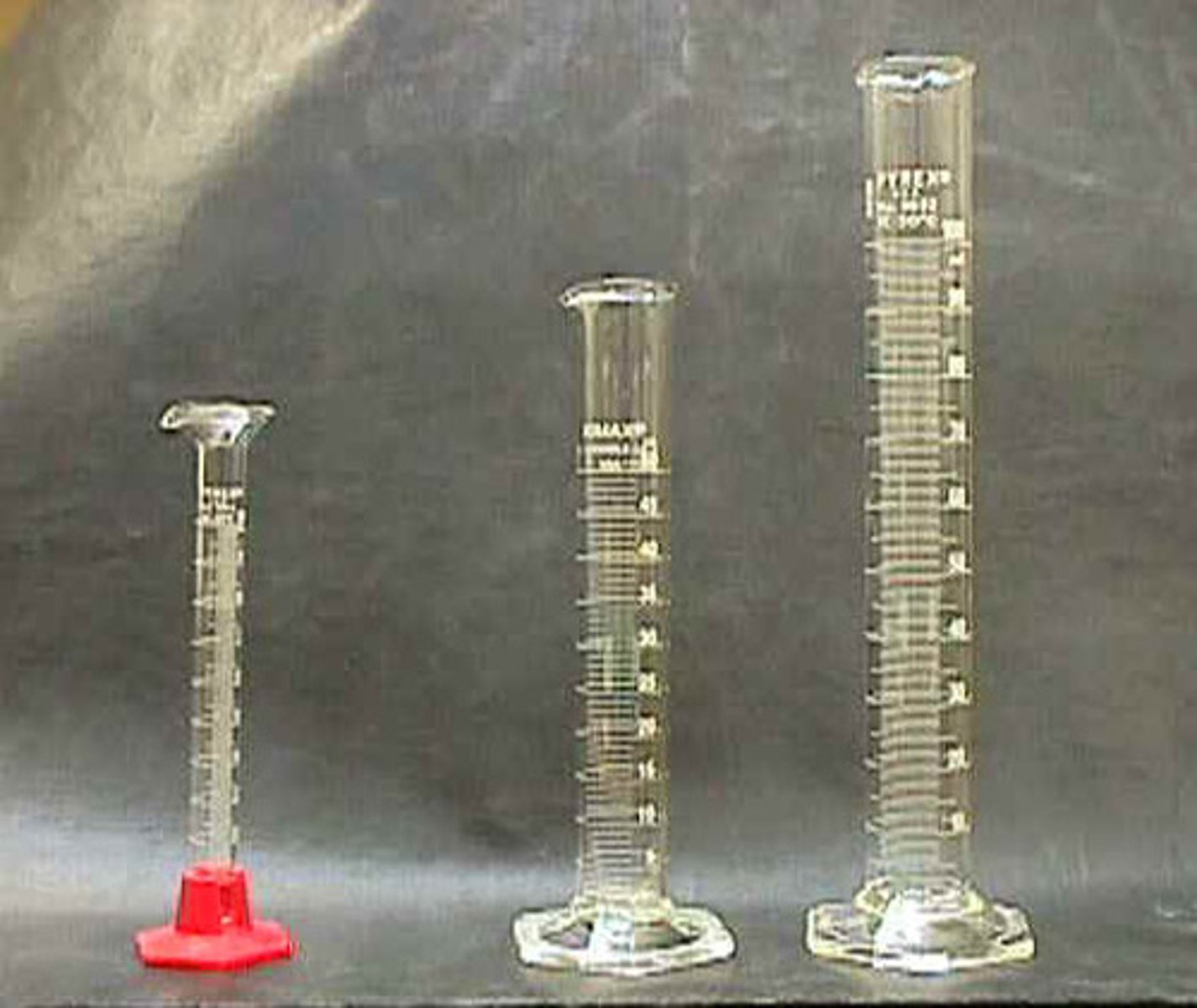
Measuring Cylinder
Use to accurately measure volumes of liquids.

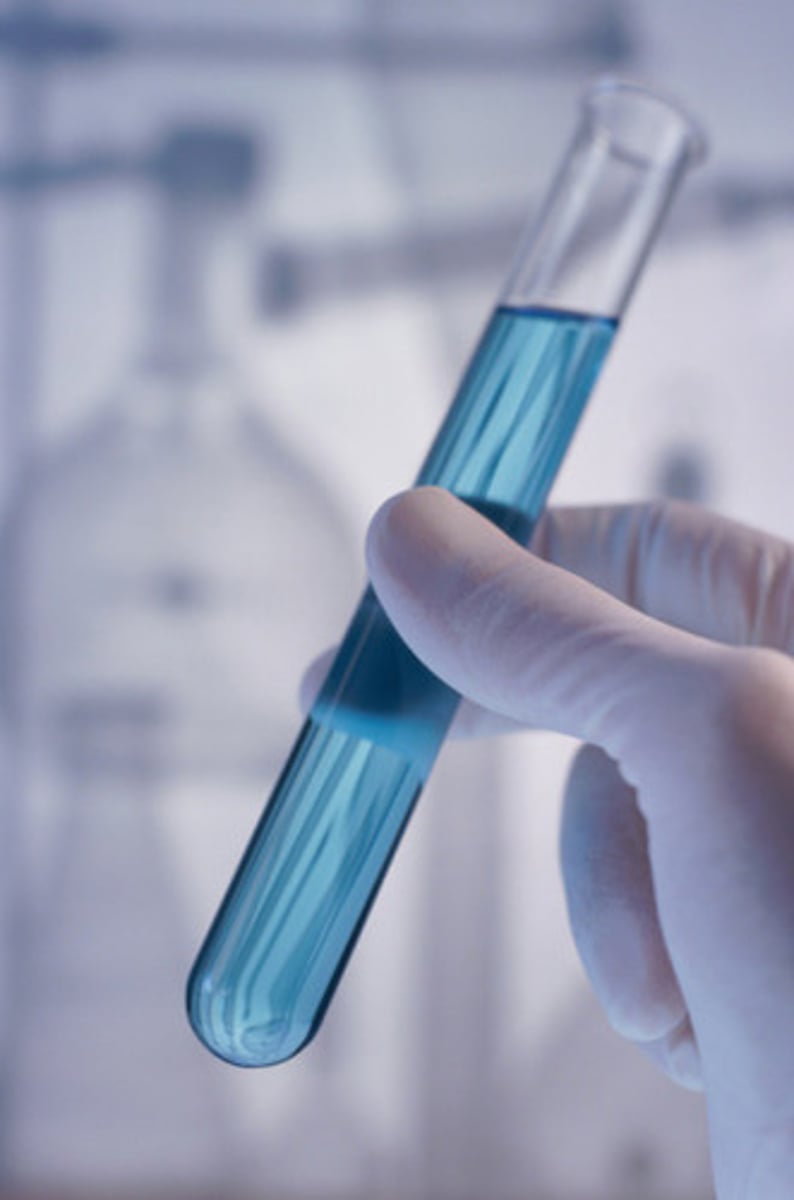
Test Tube
Small glass tube used for experiments with small amounts of substances.

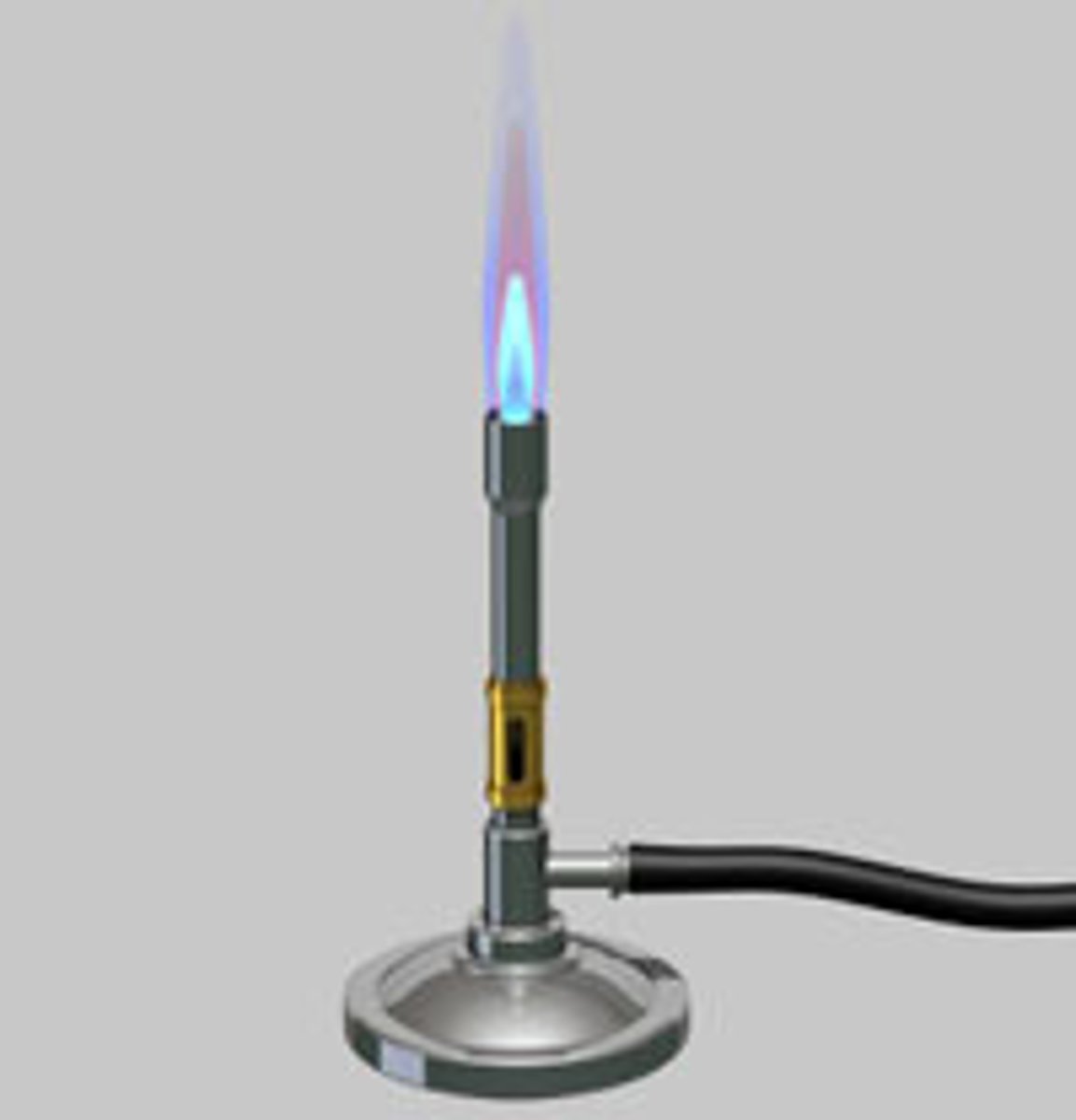
Bunsen Burner
Heats substances using a gas flame.

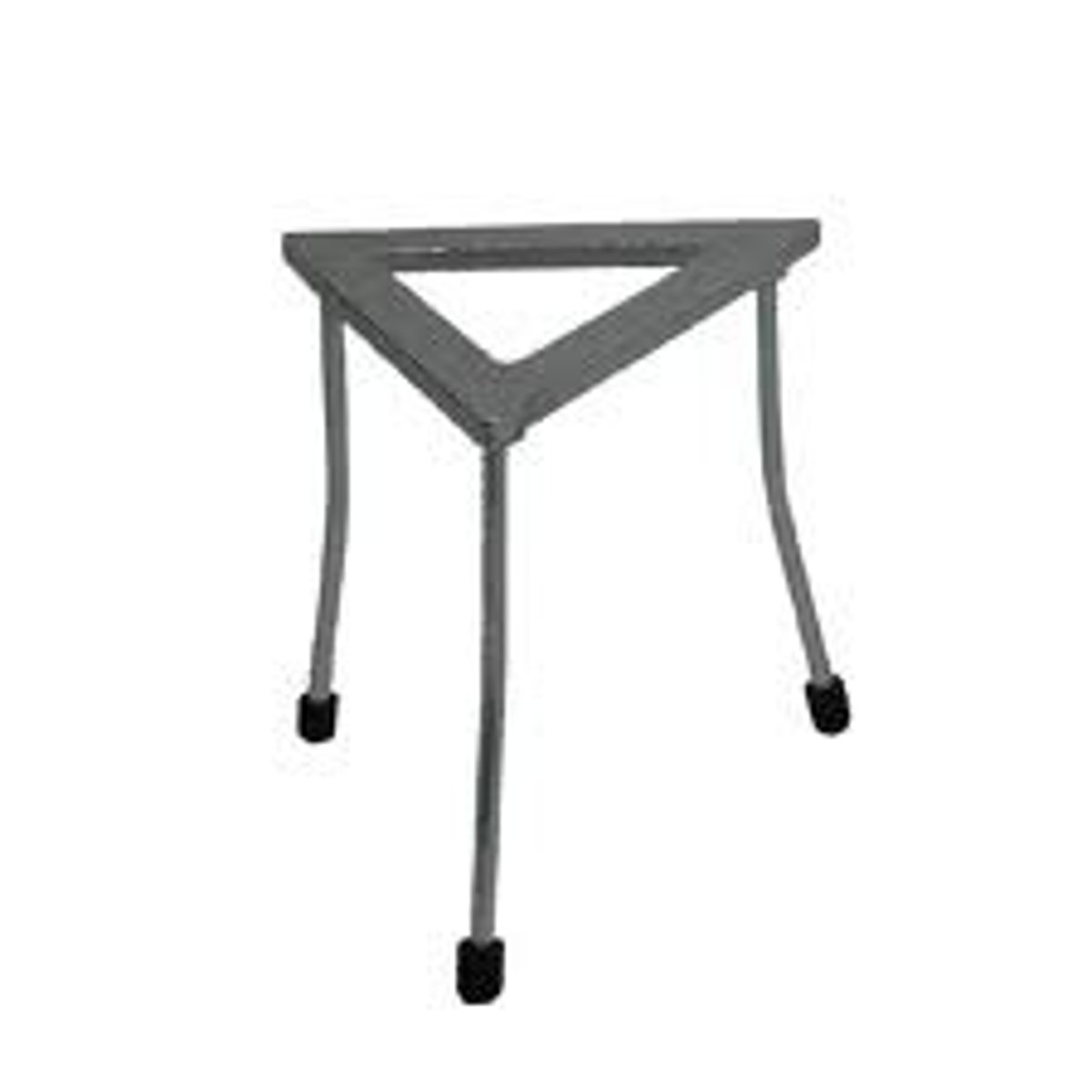
Tripod
Supports equipment above a Bunsen burner.

Gauze
Placed on a tripod to support beakers during heating.

Conical Flask
Used for mixing and heating liquids; has a narrow neck to prevent spills.

Evaporating dish
A small, heatproof bowl used in science to heat liquids so they evaporate, leaving behind any solid substances.

Clamp stand
Holds equipment in place, like test tubes or flasks.

Balance
Used to measure the mass of a substance

Stopwatch
Used to measure time

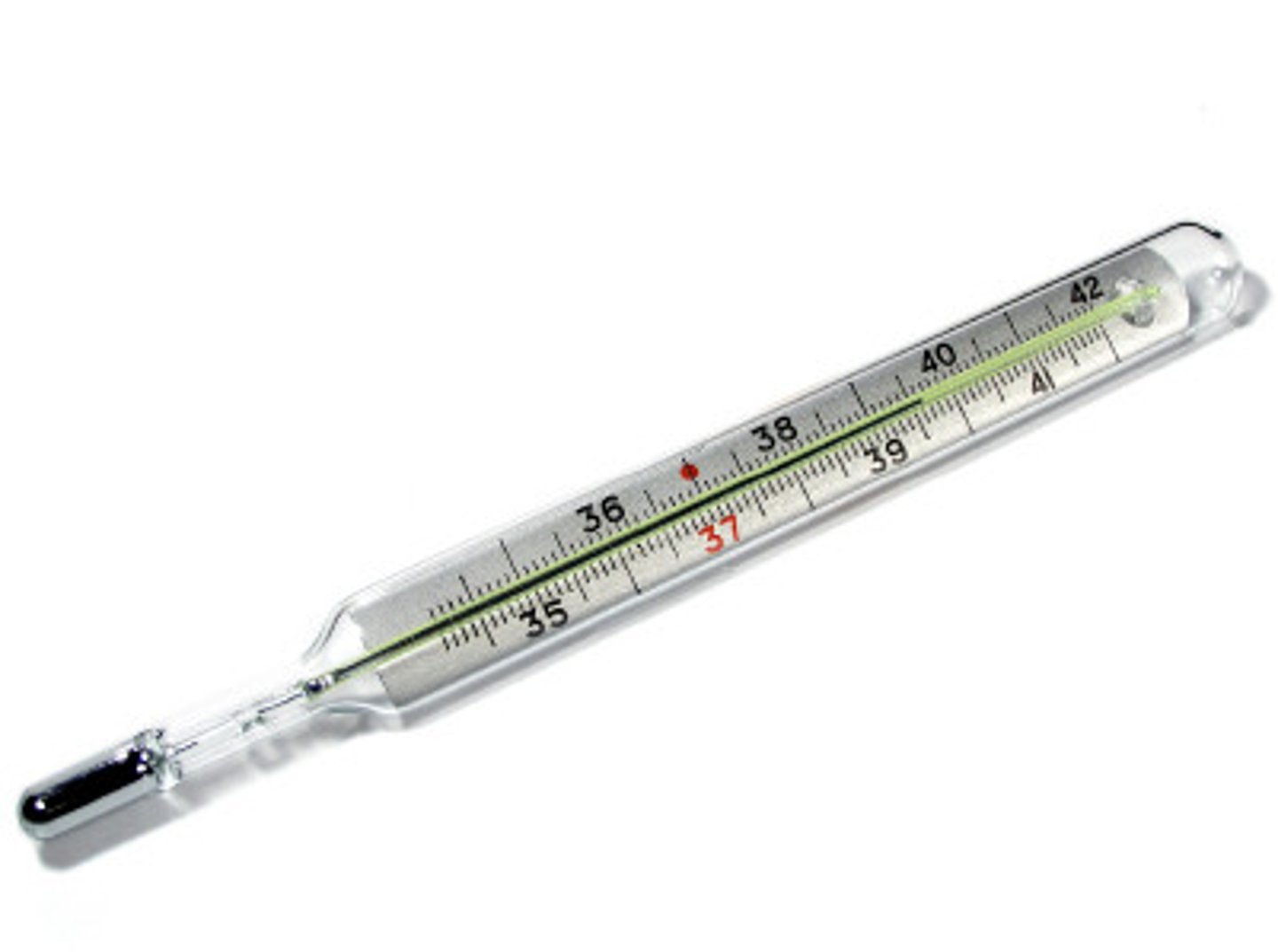
Thermometer
Used to measure temperature
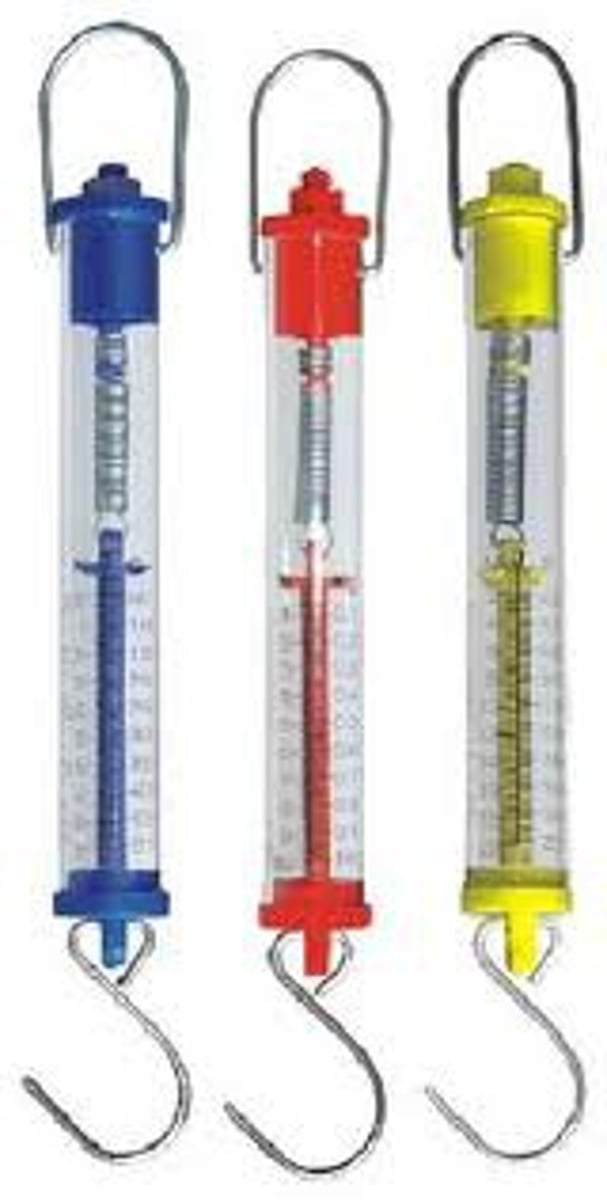
Newton meter
Used to measure force
Ruler
Used to measure distance

Safety Goggles
Protects eyes during experiments

Lab coat
Protects clothing and skin

Gloves
Protects skin on hands
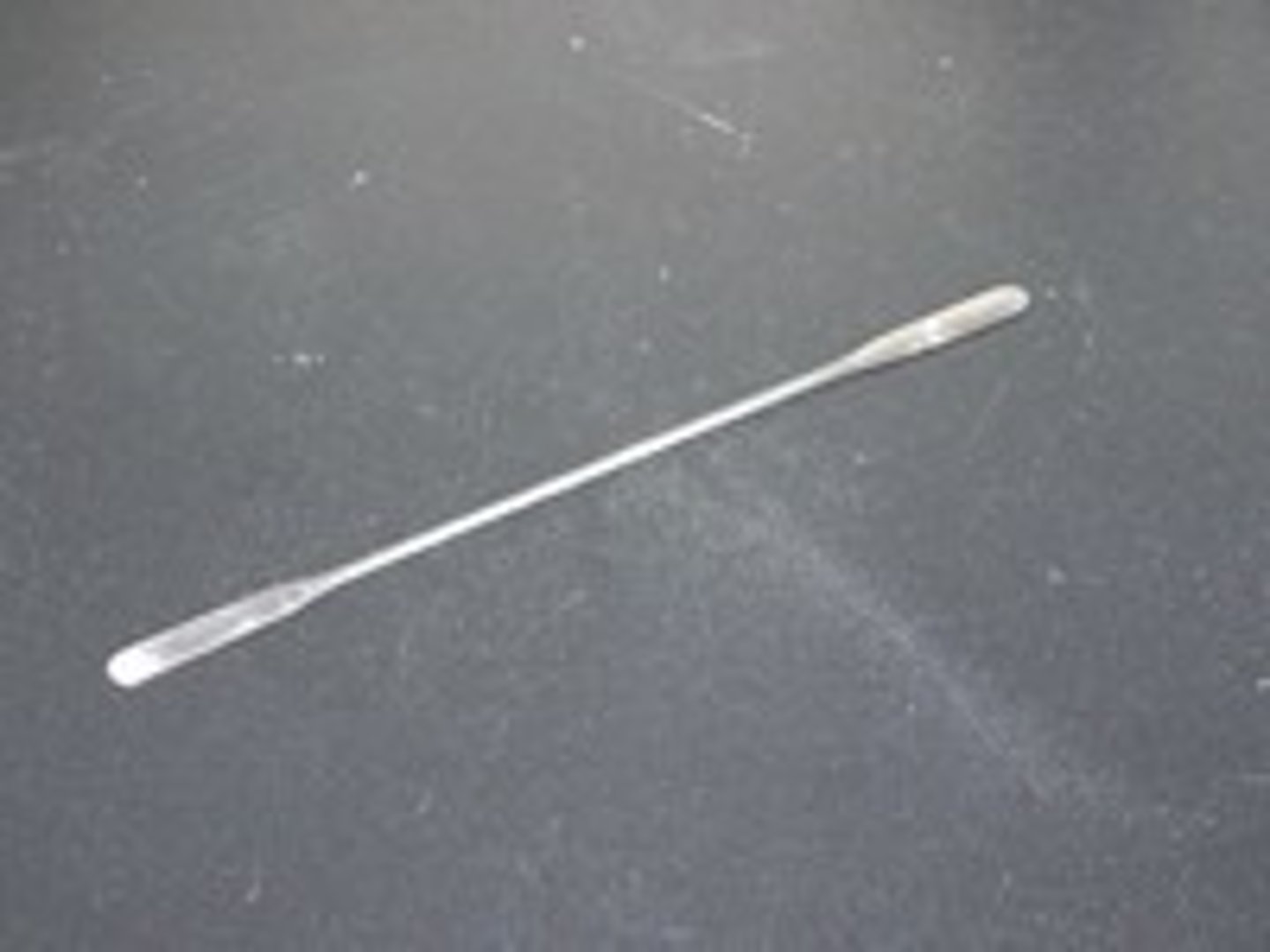
Stirring rod
Glass rod used to stir liquids

Spatula
Transferring solid chemicals from larger containers to smaller
