BIO 101 Lab Midterm UNC
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
objective observation
observations can be verified, often involve counting or measuring
subjective observation
observer-specific observations, qualitative
hypothesis
tentative explanation of cause and effect based on underlying observed phenomena, must be testable
independent variable
the cause
dependent variable
the effect
control variable
all the factors are the same as the test group, except this one factor being tested is left in its normal, unmanipulated state
protocol
description of steps in a scientific investigation
occam's razor
if there are several explanations that might fit an observation, the simplest is most probable and therefore best
prokaryotes
unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus; most abundant organisms in the world and found in virtually every known habitat; reproduce mostly asexually
eukaryotes
cells with true nuclei and membrane-bound organelles
domain Bacteria
bacteria and cyanobacteria/blue-green algae
nitrogen fixation
bacteria converts nitrogen into forms that can be used by plants
decomposers
bacteria break down dead plants and animals, and thereby return the organic materials to the system to be used by other organisms
photosynthetic bacteria
use light as their energy source in a process similar to photosynthesis in plants, however, they do not use water, pigments are different in structure, and lack chloroplasts
chemosynthetic bacteria
obtain their energy from the oxidation of inorganic substances
bacilli
rod-shaped bacteria
cocci
small spheres bacteria
spirilla
corkscrew-shaped bacteria
Lactobacillus
the bacterium that uses milk sugar (lactose) and converts milk to yogurt
cyanobacteria/blue-green algae
photosynthetic bacteria, possess the pigment chlorophyll a and use water in their photosynthetic process
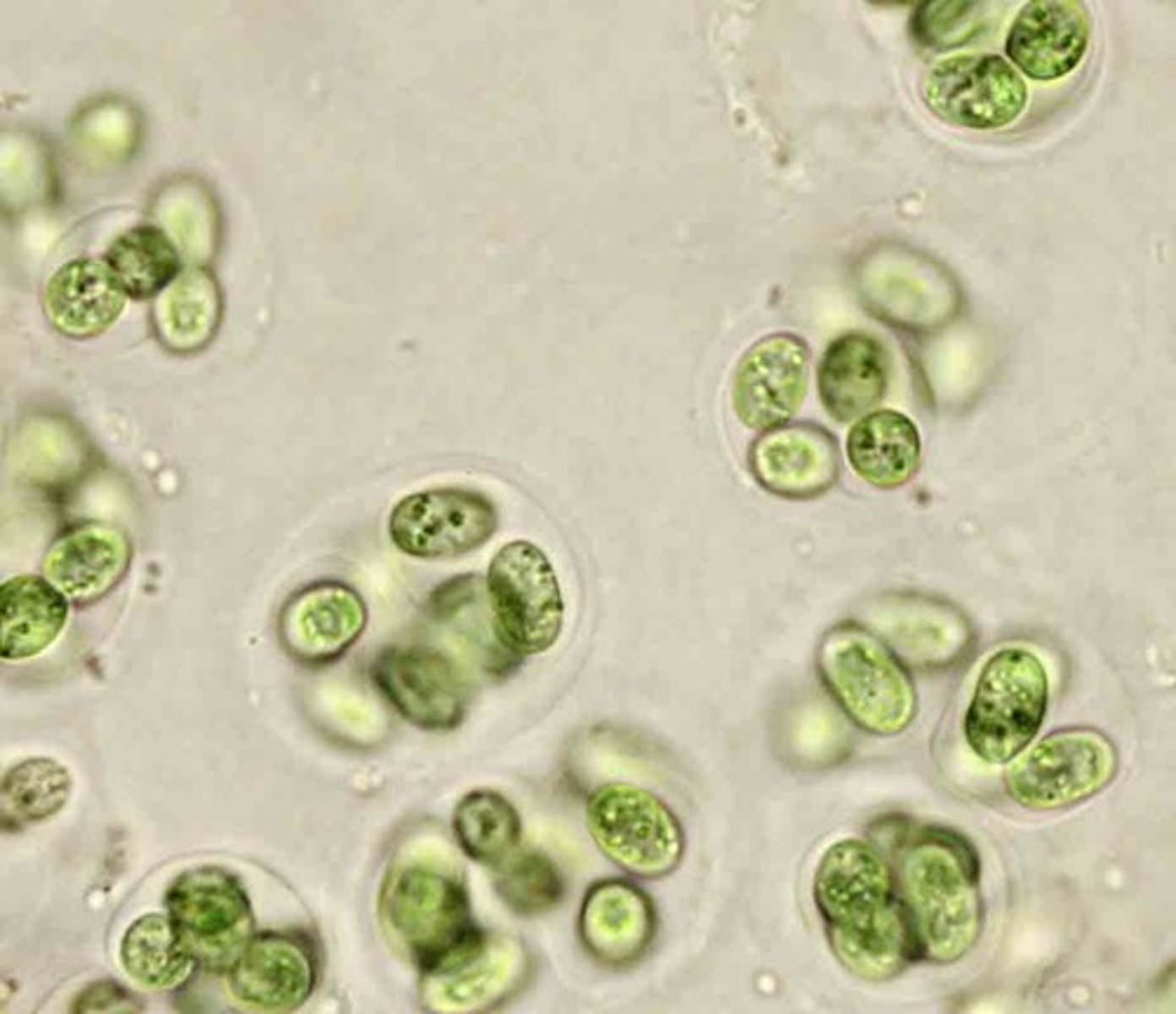
gloeocapsa
unicellular form of cyanobacteria, gelatinous sheath surrounds the cell, clustered together, green color
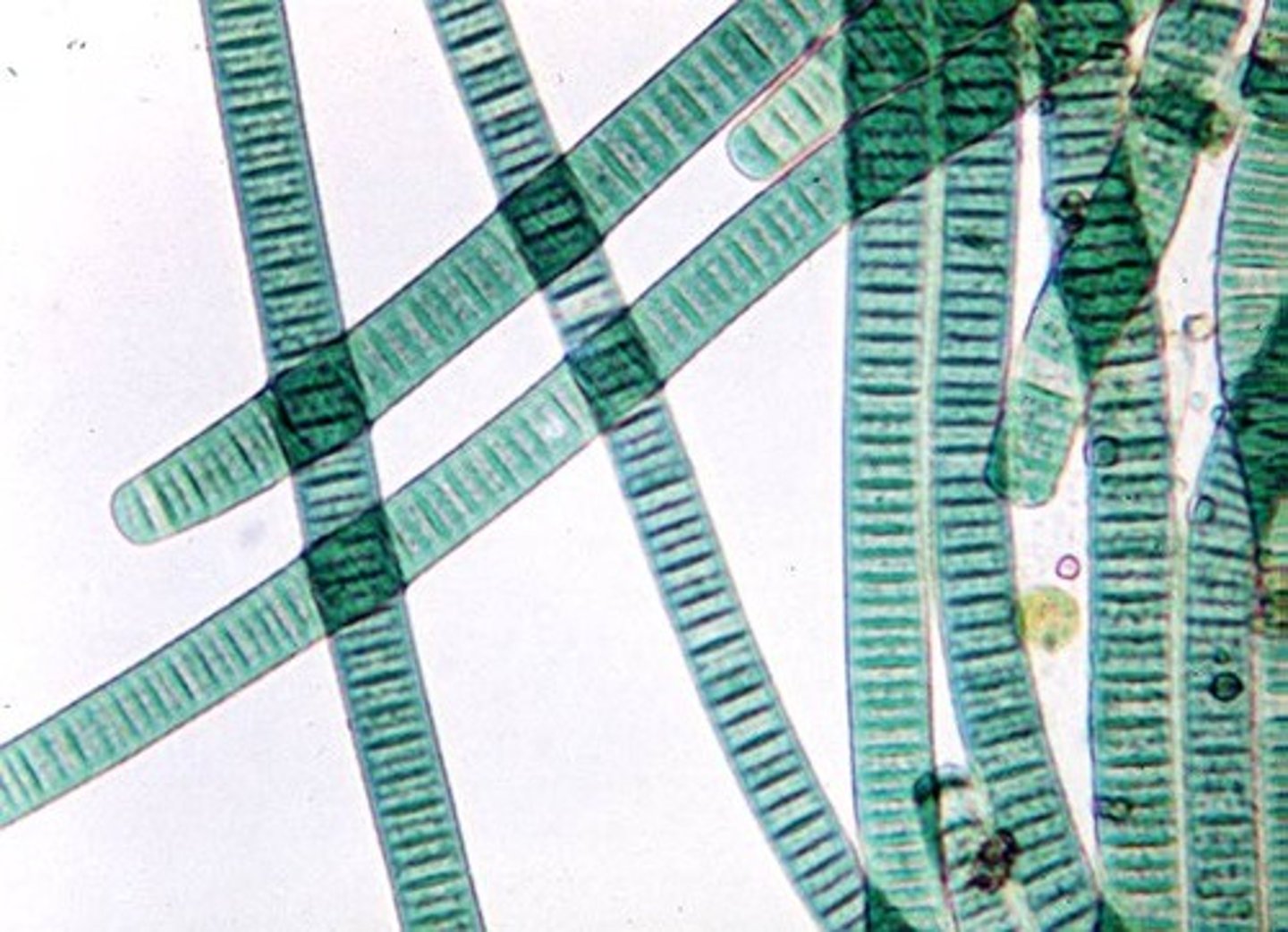
oscillatoria
colonial form of cyanobacteria, may occur as filaments, plates, or spheres
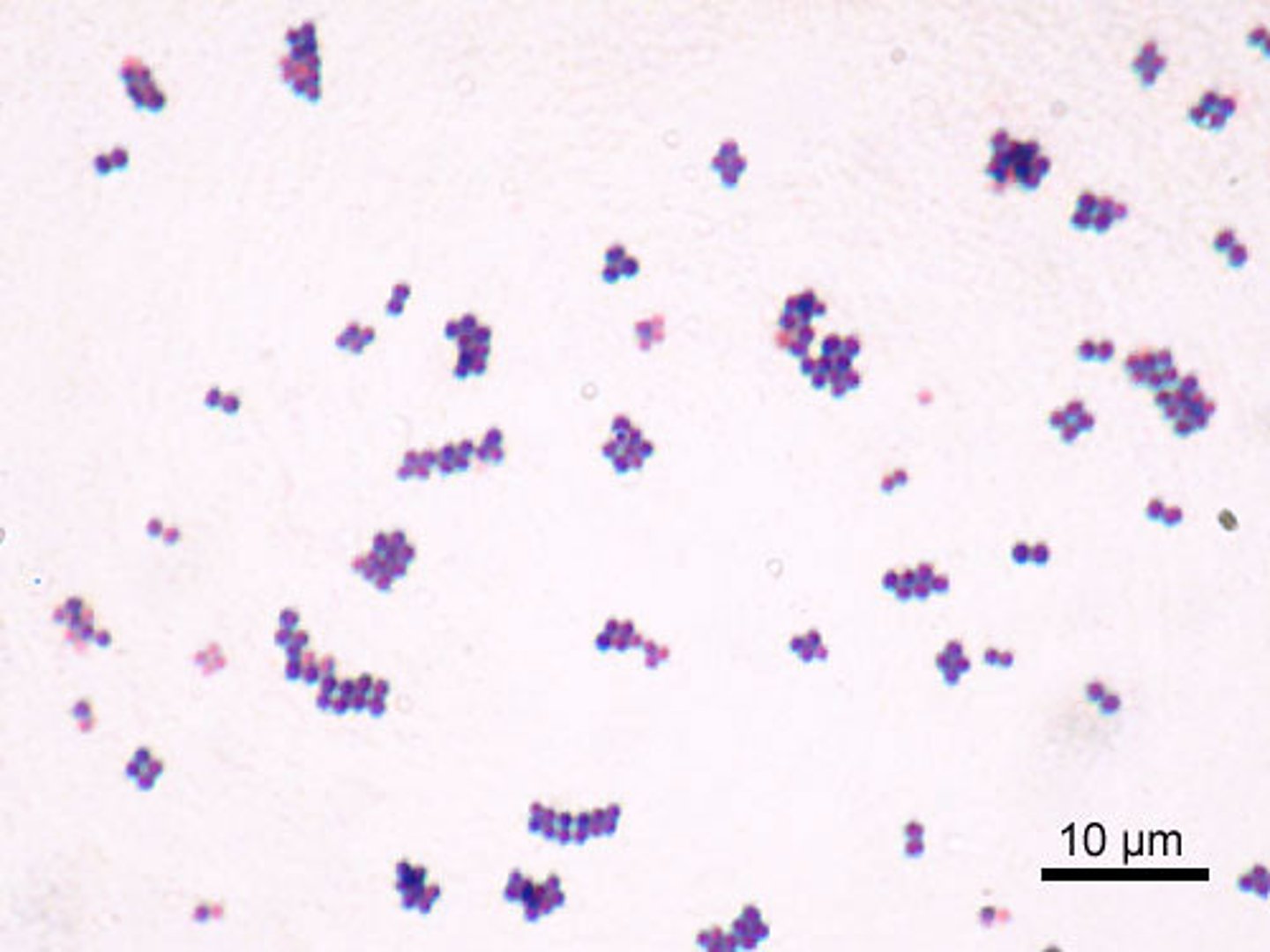
staphylococcus
moist-looking colonies, gram-positive cocci
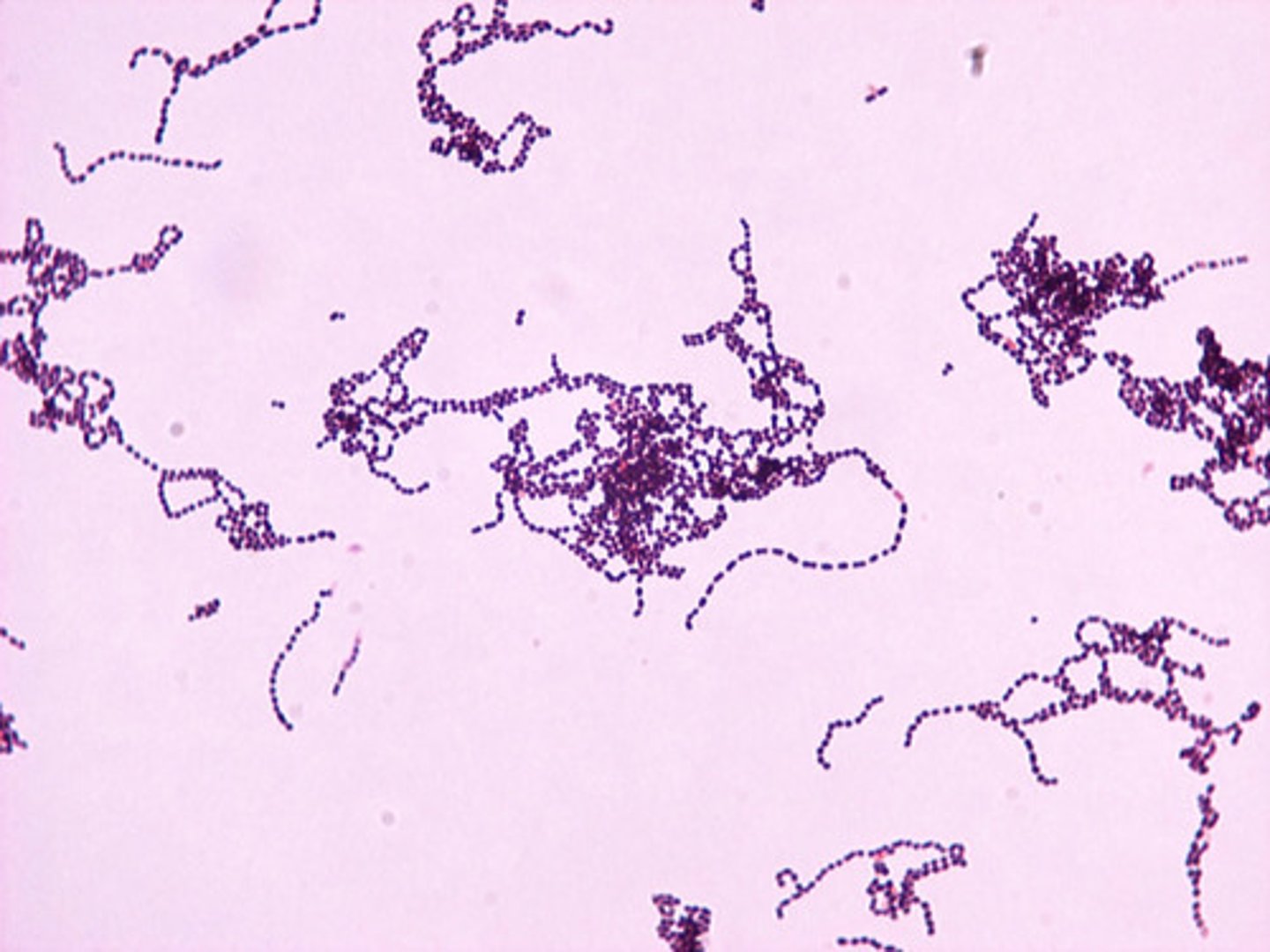
streptococcus
gram-positive coccus, common in nose and mouth, cause of "strep throat"
bacillus
waxy-looking, gram-positive bacillus, spores may be visible as poorly stained oval swellings, genera of decomposers
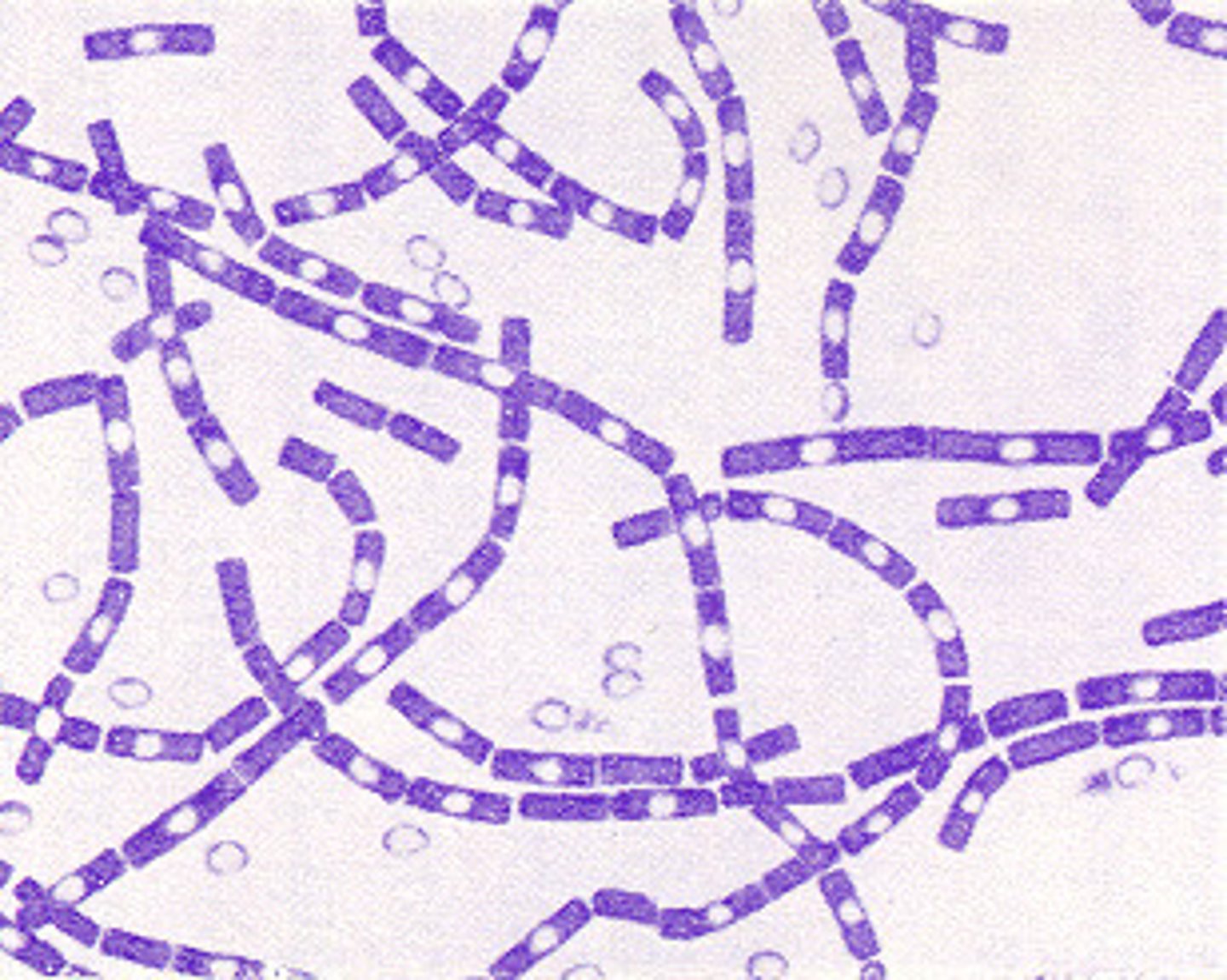
coliform
frequently foul-smelling colonies, wet-looking, gram-negative rods, common in intestines, and consequently in sewage and sewage-contaminated things, ability to ferment lactose
pseudomonas
diffuses into the medium, produce severe infections, especially in burn patients
yeasts
fungi that form very large colonies, strikingly white and glistening, very raised
molds
fungi is hairy-looking colonies, stains show hyphae (broken ends)
paramecium
animal-like protists, single-celled organism, cilia along cell membrane over body used for locomotion and food capture
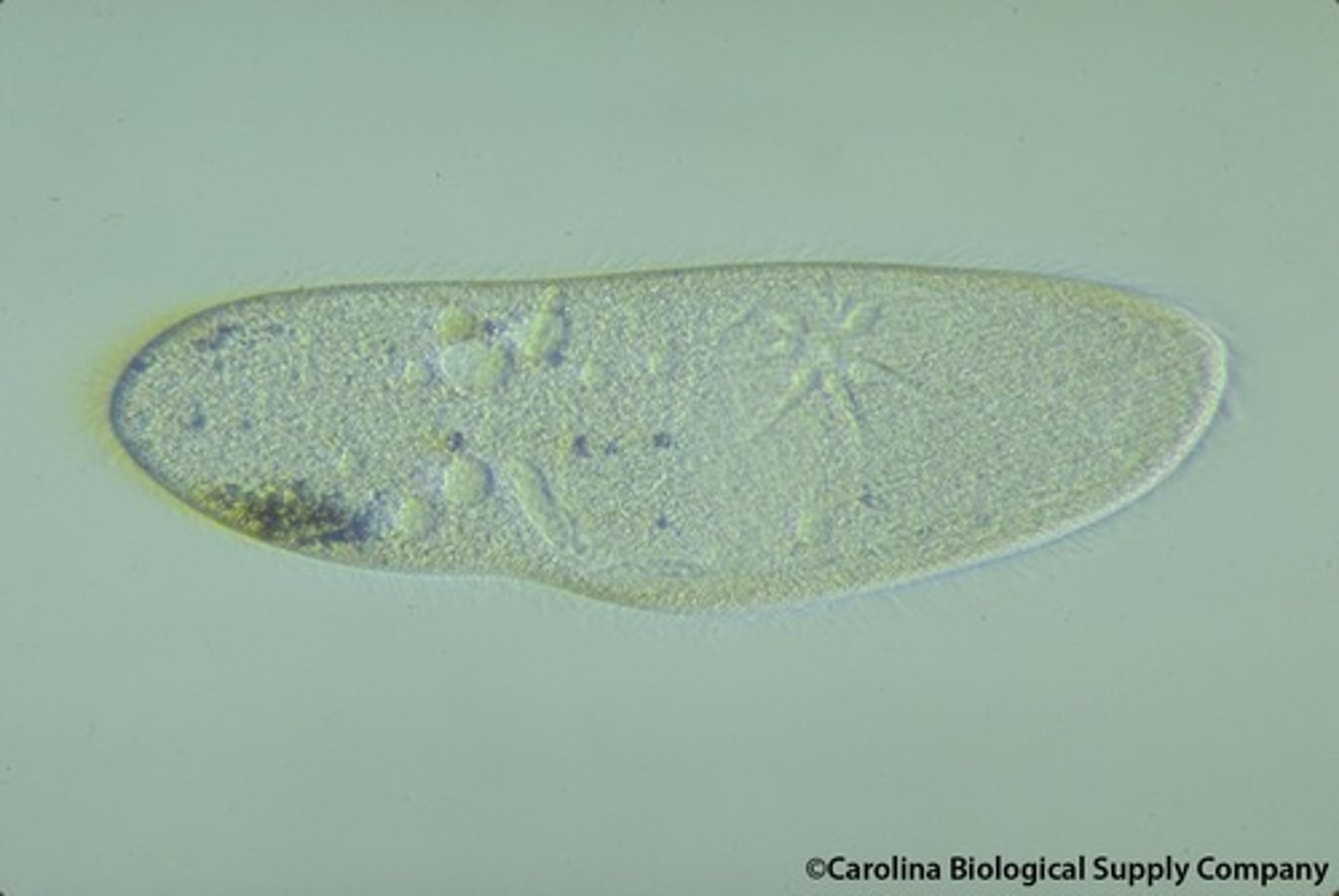
Phylum Ciliophora
phylum contains the largest single-celled organisms and most complex protozoans, all members are heterotrophic and most live in freshwater environments
oral groove
in paramecium, rapid movement of cilia creates water currents outside the cell that force fluids and food particles into this, which appears as a fold on one long side of the cell
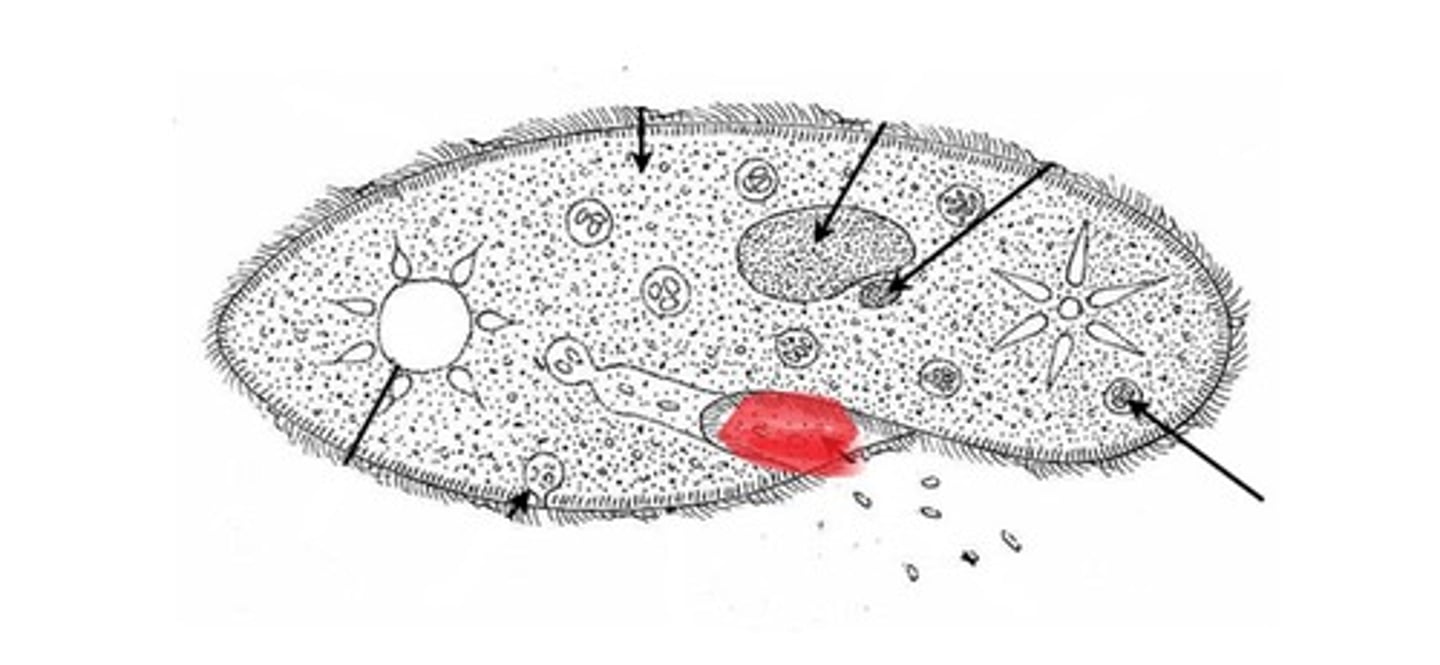
cytopharynx
region of lower end of the oral groove where food particles accumulate in paramecium
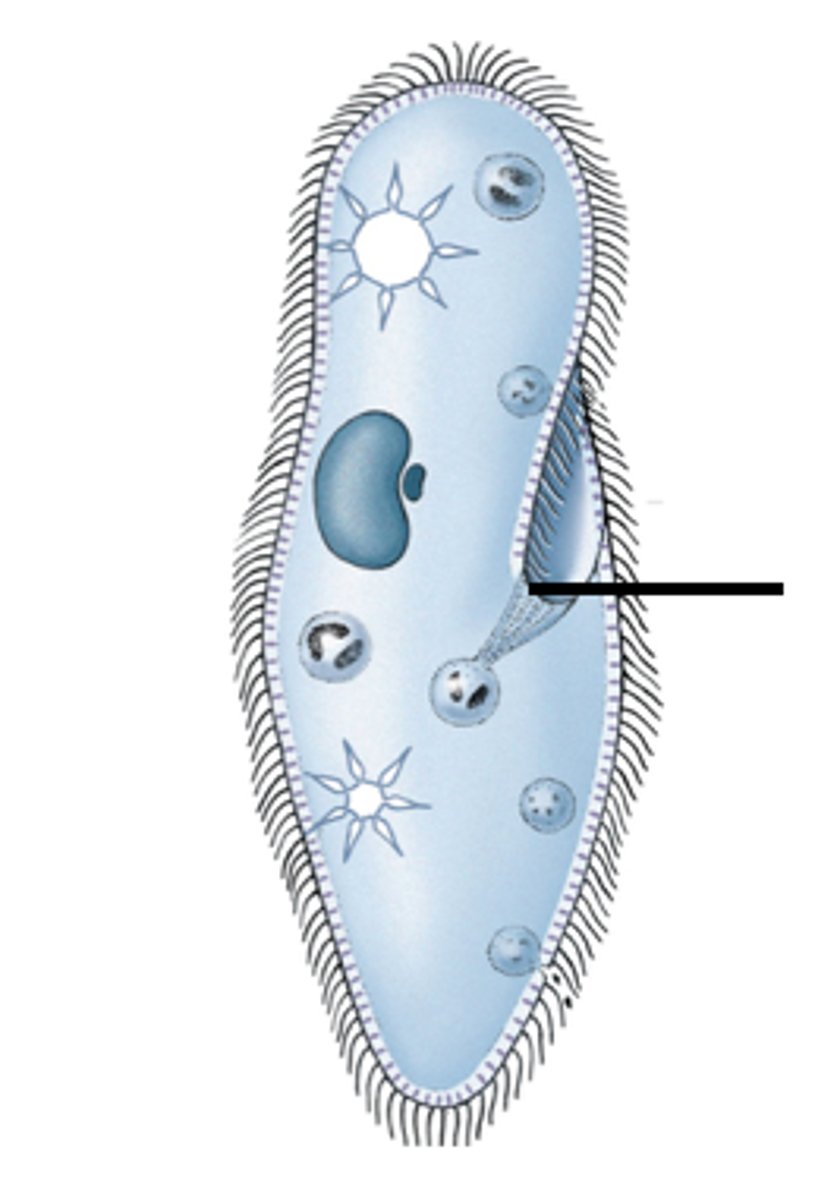
food vacuole
in paramecium, forms enveloping the food particles and migrates to an opening
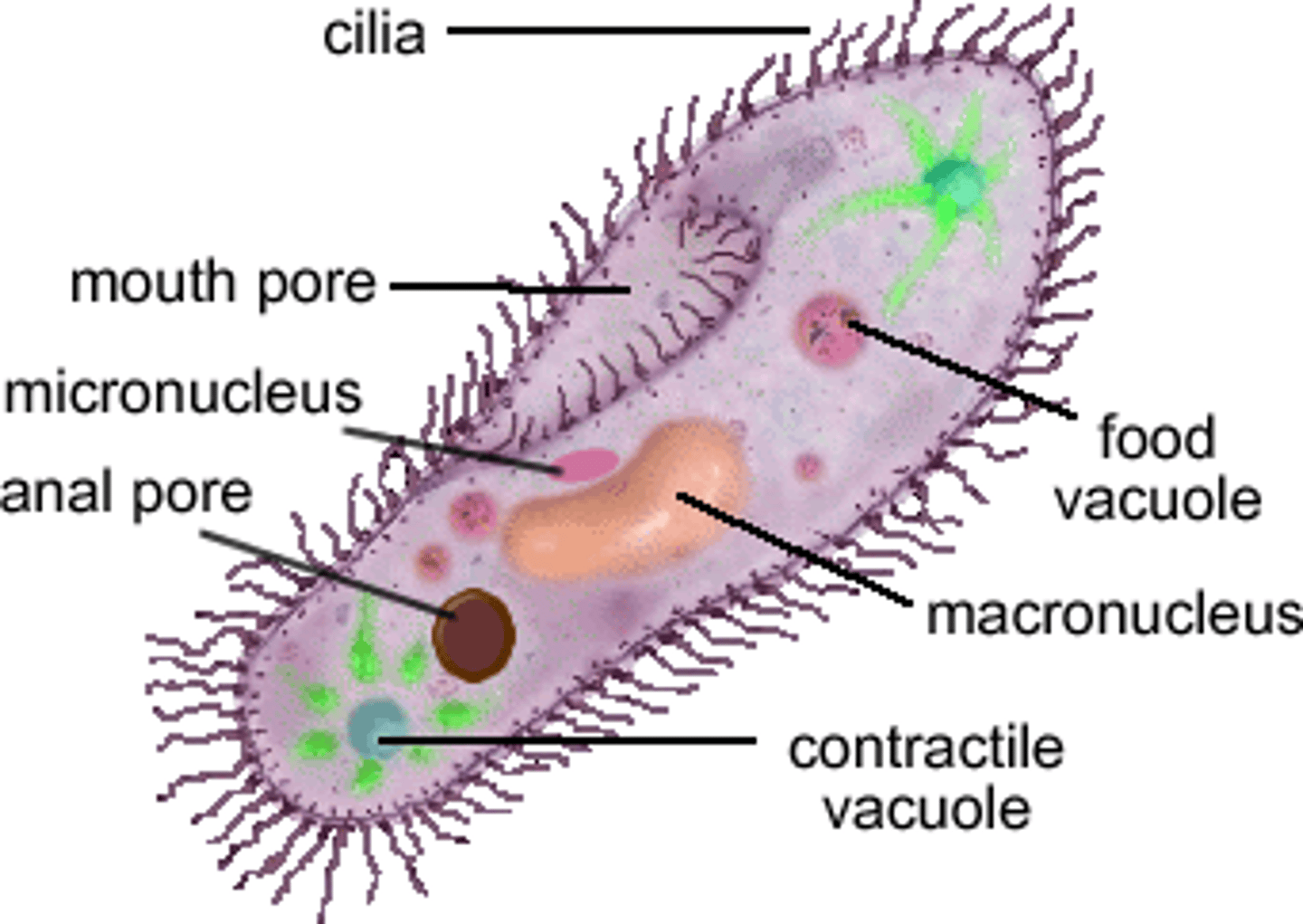
anal pore
in paramecium, opening where food vacuole attaches and empties its contents, releasing indigestible food particles outside the cell
contractile vacuoles
paramecium has 2 of these and euglena has 1; removes excess fluids from the cell
macronucleus
large nuclei in ciliates that controls cell maintenance functions
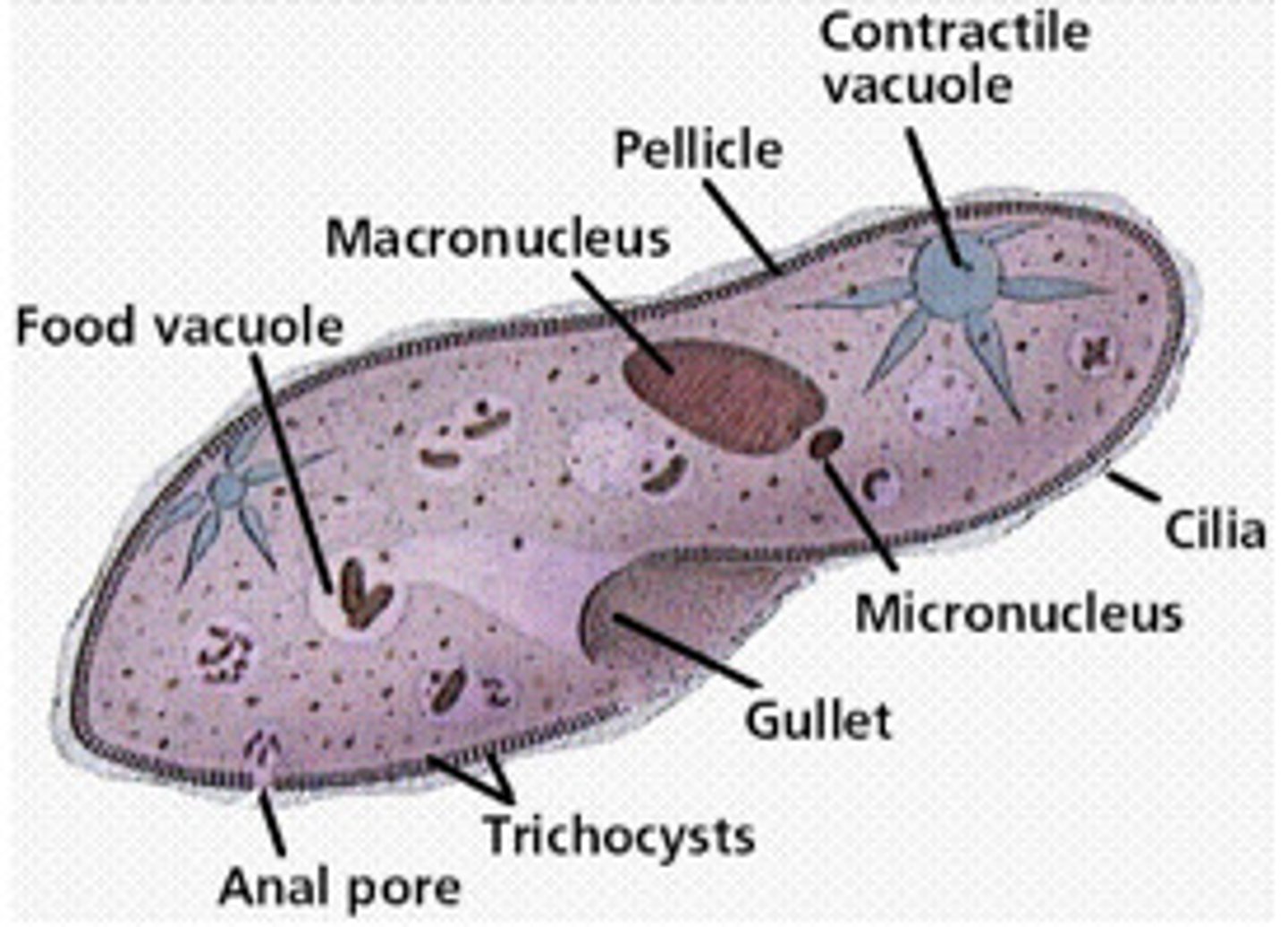
micronucleus
small nuclei in ciliates that is responsible for genetic and reproductive functions, including producing the macronucleus
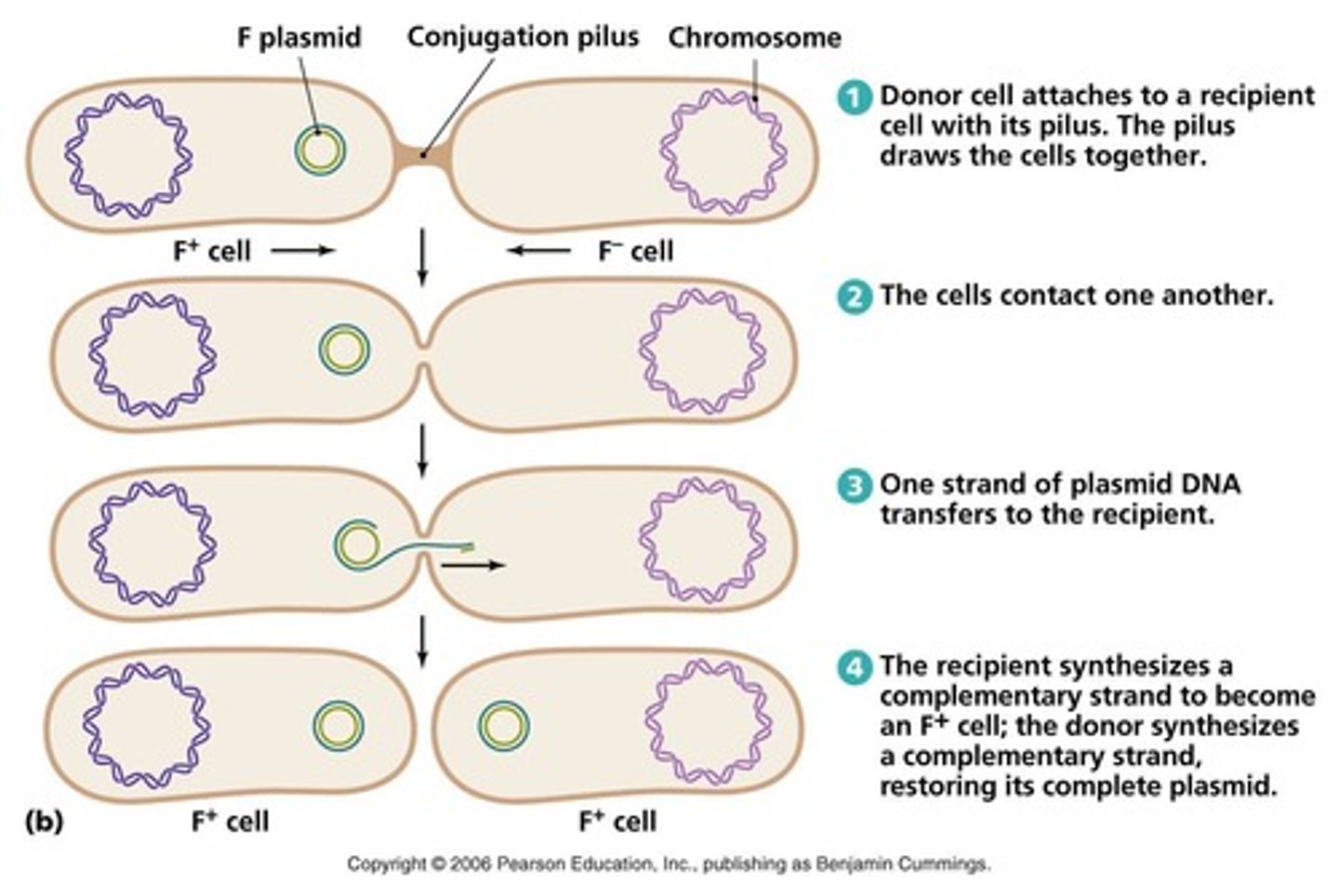
conjugation
reproduction in ciliates may be asexual or sexual, in this form, two cells exchange micronuclei and thus genetic material; each cell acts as both "donor" and "recipient"
euglena
unicellular organism with plant and animal characteristics; it is photosynthetic and contains chlorophyll a and b, yet not entirely autotrophic, Division Euglenophyta, freshwater organisms; reproduces asexually
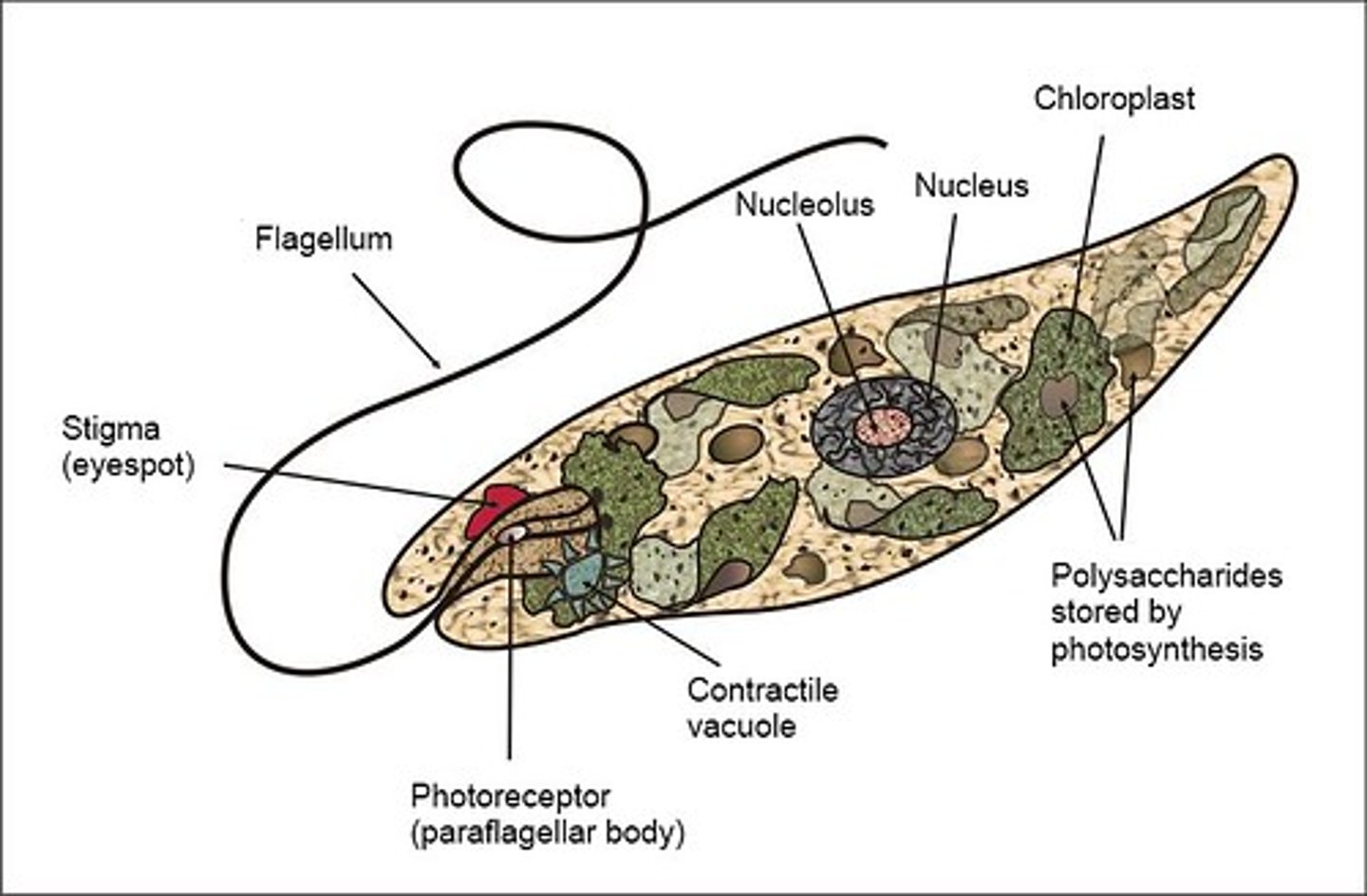
phagocytosis
how euglena ingest food particles
pellicle
euglena does not have a cell wall, but retains rigid shape due to this, a layer of elastic proteins just inside the cell membrane
flagellum
how euglena moves, whiplike structure
stigma
eyespot, a light-sensitive structure containing carotenoids in euglena
pyrenoids
organelles in euglena that store sugars
pseudopodia
form of motility for amoeba where false feet extend from body and pull the rest of the cell along
plastids
the unique double membrane-bound organelles in plants
Endosymbiont Theory
implies chloroplasts and mitochondria were prokaryotic cells that were engulfed and developed a symbiotic relationship with their host cells
elodea
common pond weed found in NC, contains cell wall, chloroplasts, nucleus, vacuoles
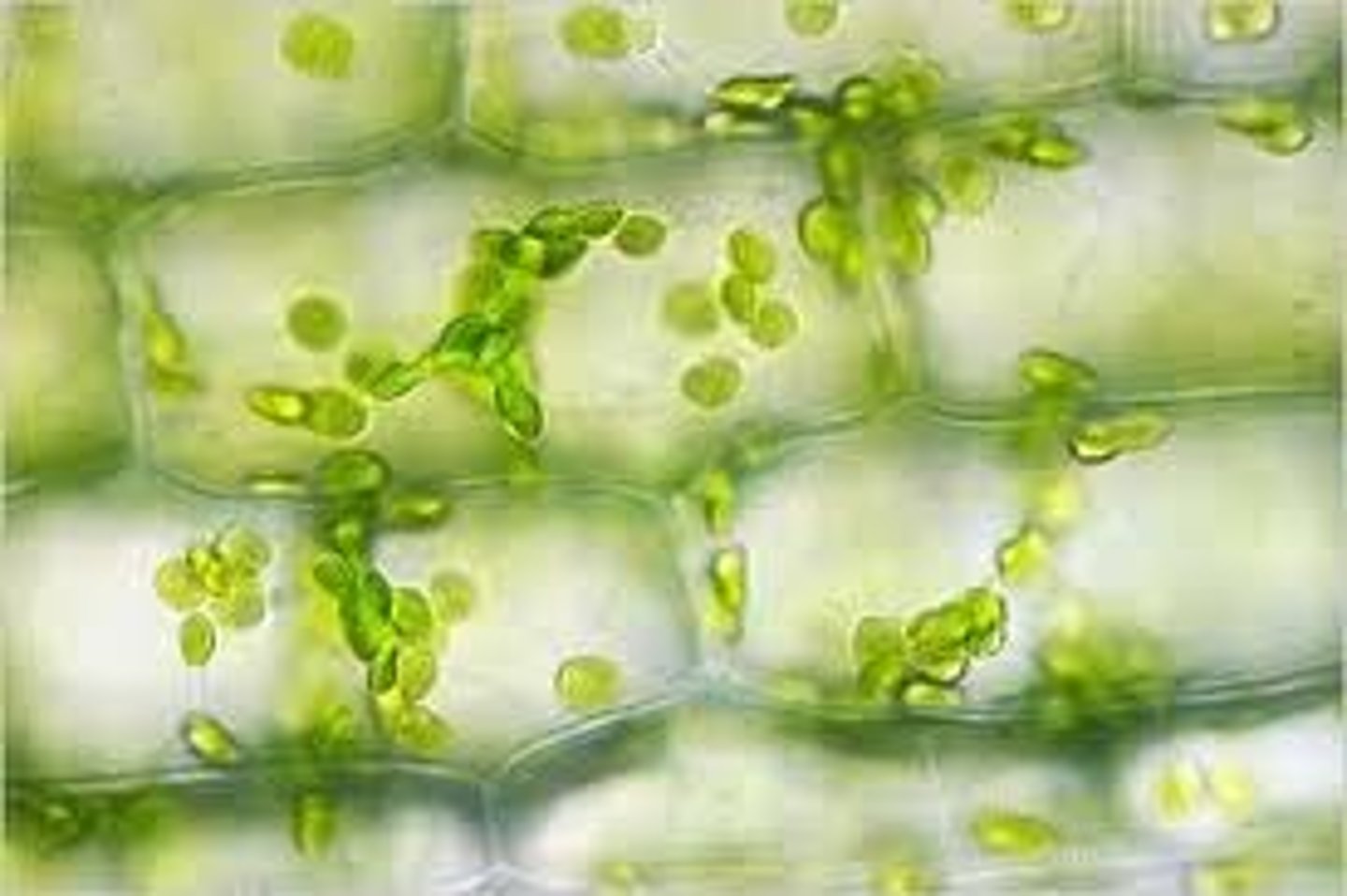
cytoplasmic streaming
in elodea, chloroplasts are suspended in the cytoplasm and moving throughout the cell
volvox
belongs to the Division Chlorophyta, colony contains 500-50,000 cells, biflagellate, colony surrounded by a thin mucilaginous layer, reproduce sexually or asexually by reproductive cells produce daughter colonies inside the parent which are released when parent colony bursts
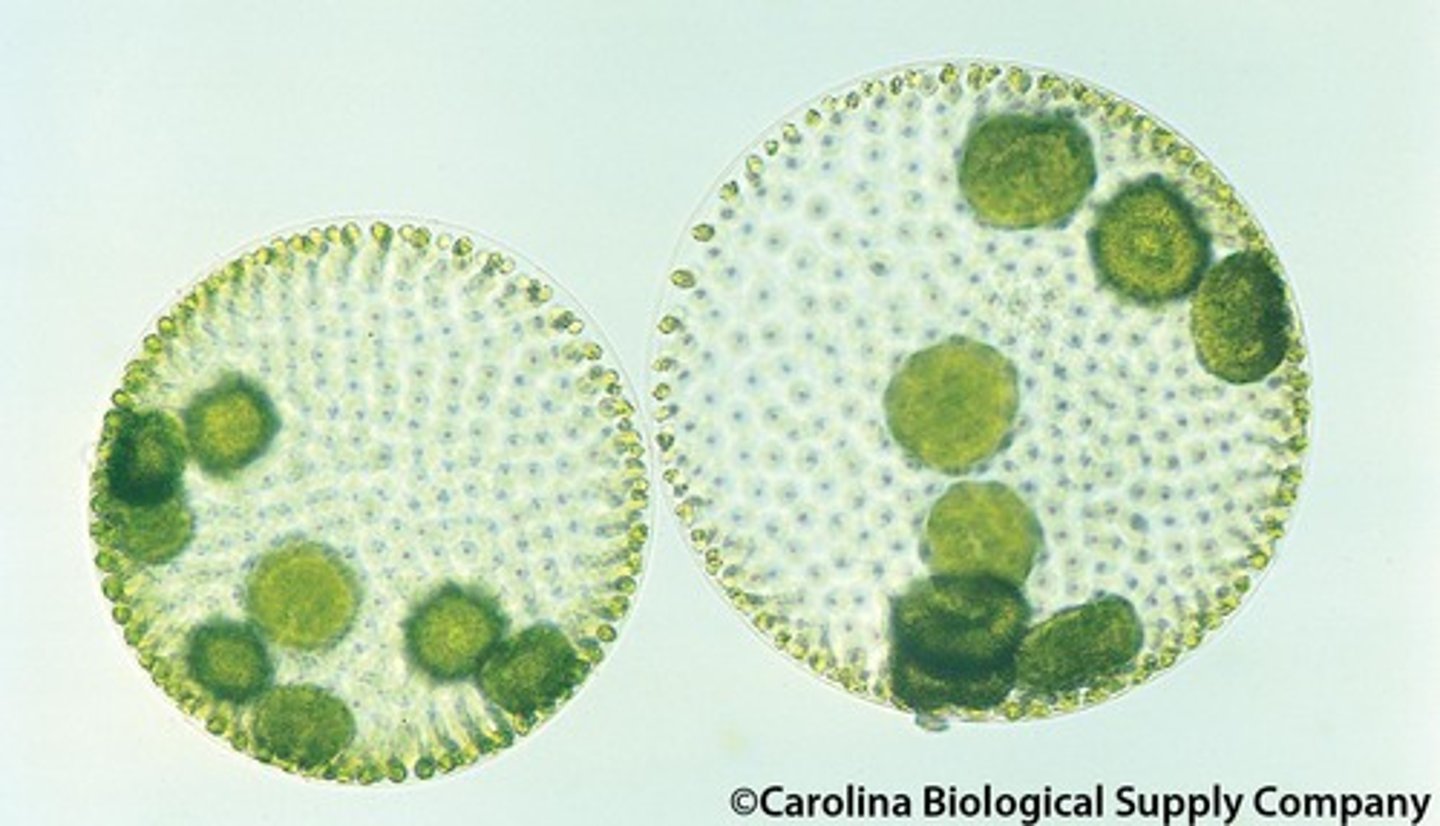
cytoplasmic strands
volvox outer cells are connected to one another by this
plasmolysis
cellular shrinkage occurring as a result of a cell being exposed to a hypertonic solution (examined in elodea)
human epithelial cells
consume food through ingestion rather than absorption, feature prominent nuclei, and form a protective layer so there is little extracellular material between cells (cells are tightly packed)
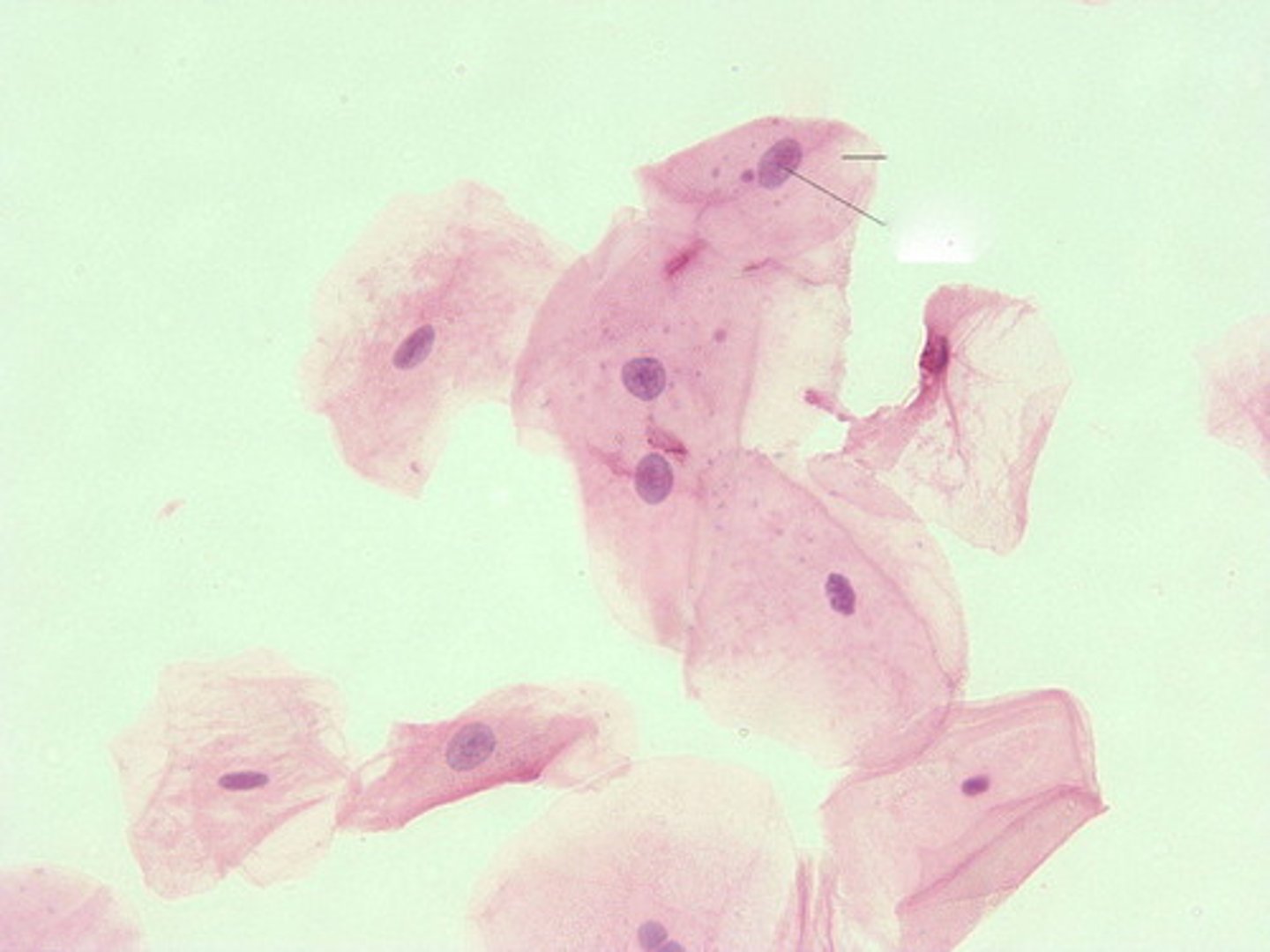
photoreceptors
pigments that trap light energy
chlorophyll a
blue-green pigment and occurs in all photosynthetic eukaryotes and cyanobacteria; essential photosynthetic pigment
chlorophyll b
olive-green pigment in most plants and is an accessory pigment (capture additional light energy which is then transferred to chlorophyll a)
chlorophyll c
pigment is found in certain kinds of algae
carotenoids
other class of yellow, orange, or red pigments; functions as accessory pigments and as coloring in reproductive parts to enhance pollination and fruit dispersal; can be divided in 2 groups: carotenes and xanthophylls
beta-carotene
yellow-orange pigment, essential dietary supplement in animals; chemically modified by splitting and adding water to form vitamin A
xanthophylls
yellow pigments
paper chromatography
method used to analyze pigments; pigments are separated at different rates (reference front value); polar molecules absorb to the polar chromatography paper and do not move whereas non polar molecules travel with the solvent
order from origin to solvent front
chlorophyll b, chlorophyll a, 2 xanthophylls, and beta-carotene
Hill Reaction
shows that chloroplasts in water can operate in the present of light and an electron acceptor to release oxygen (no CO2 was present so O2 came from water)
DPIP
replaced some of the NADP+ molecules to be reduced and change color from blue to colorless
parts of microscope
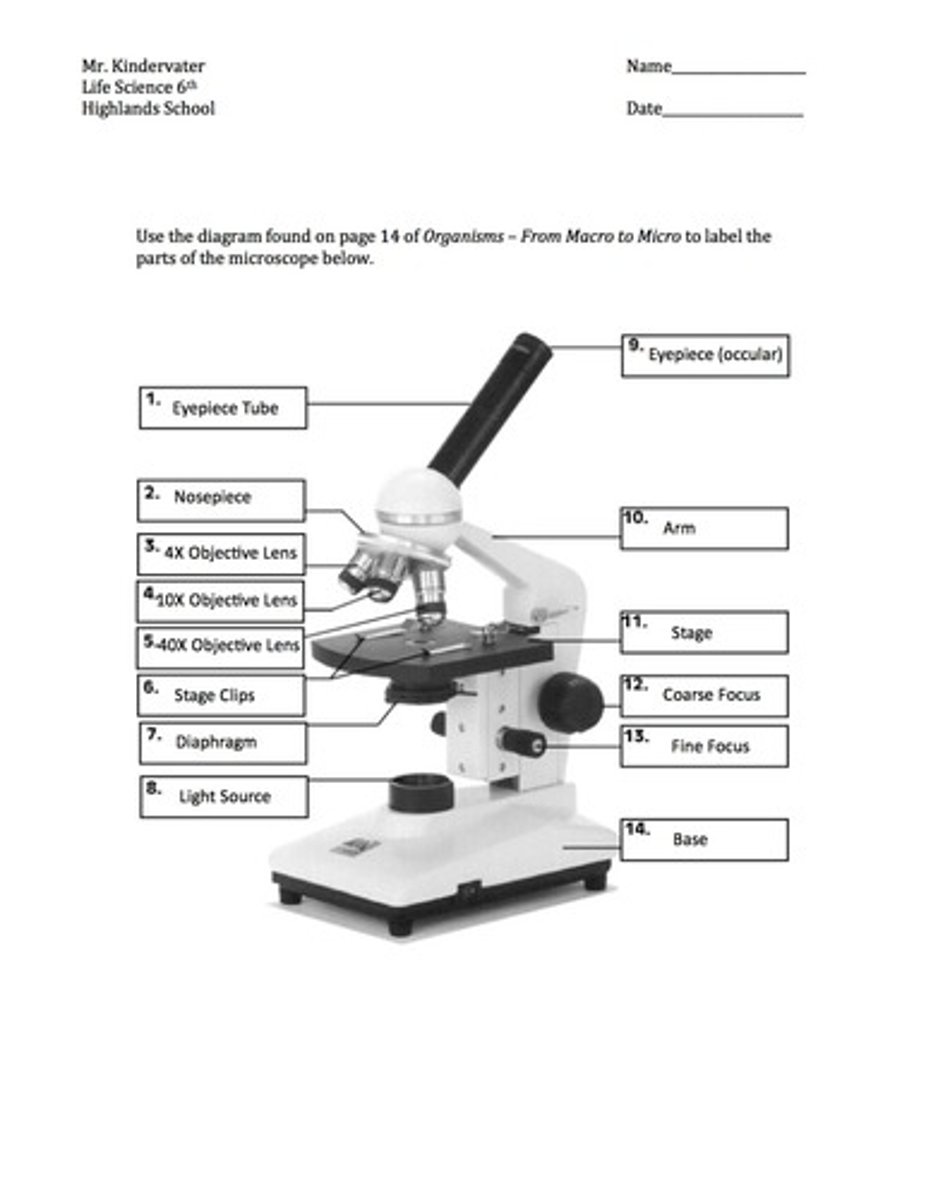
iris diaphragm
light passes through this before it goes through the slide which controls the amount of light passing through the slide
condenser
focuses all light on the specimen and should be close to the slide
objectives
first set of lenses; after light strikes the specimen, it goes up these which magnifies the image of the specimen
ocular lens
last set of lenses that the beam of light passes through
course and fine focus knobs
allow you to bring the specimen into focus by bringing the objectives as close to the stage as possible
gram stain
technique to identify bacteria; bacteria have strong cell walls that surround the cell membrane and provide protection made up of disaccharide sugars; gram-positive cell is thick and stain purple while gram-negative cell wall is thinner and partially dissolved so does not retain stain
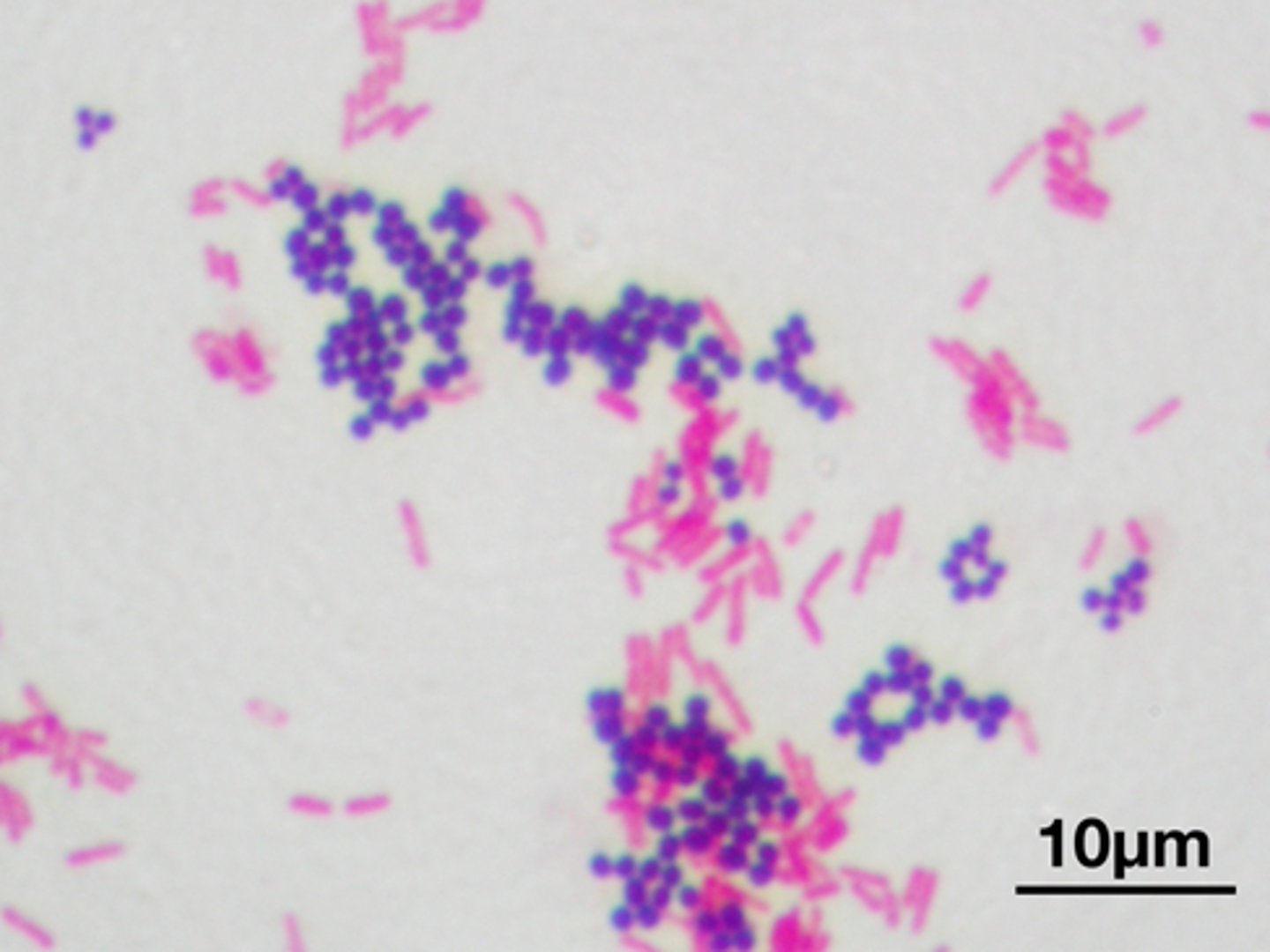
gram stain procedure
crystal violet, gram's iodine, safranin