GCSE Chemistry AQA C8 Chemical Analysis (Paper 2 - Triple)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
purity definition
a pure substance is something that only contains one compound or element throughout.
how to tell the purity of a substance
a pure substance will boil/melt at a specific temperature.
you can test the purity of a sample by measuring its melting and boiling point and comparing it with data from a book
the impurer a substance, the lower the melting point and higher the boiling point.
formulations definition
formulations are useful mixtures with a precise purpose that are made by a formula
the importance of formulations
formulations are used in cleaning products, metal alloys, cosmetics, fertilisers etc.
chromatography definition
chromatography is an analytical method used to separate the substances in a mixture.
mobile phase
where the molecules can move. this is always a liquid or gas.
stationary phase
where the molecules can't move. usually a solid or thick liquid.
chromatography experiment
during chromatography, the mobile phase(ink) moves up stationary phase(paper) and it separates the substance. the solvent is the liquid the paper is dipped into.
the amount of time the molecules spend in each phase depends on...
- how soluble they are in the water
- how attracted they are to the paper.
Rf value equation
Rf= distance travelled by substance/distance travelled by solvent
test for gases: chlorine
bleaches damp litmus paper, turning it white
tests for gases: oxygen
if you put a glowing splint inside a test tube containing, oxygen will relight the splint.
tests for gases: carbon dioxide
bubbling carbon dioxide through an aqueous solution of calcium hydroxide(limewater) causes it to go cloudy.
tests for gases: hydrogen
if you hold a lit splint at the end of a test tube containing hydrogen, you will hear a squeaky pop.
test for sulfates
add hydrochloric acid followed by barium chloride to get a WHITE PRECIPITATE of barium sulfate
test for halides
add dilute nitric acid and silver nitrate solution to the solution
test for halides: chloride
a white precipitate of silver chloride
result of tests for halides - bromide
cream precipitate of silver bromide
tests for halides: iodide
yellow precipitate of silver iodide.
flame tests
used to identify metal ions
flame tests: lithium
crimson/red flame
flame tests: sodium
yellow flame
flame tests: potassium
lilac flame
flame tests: calcium
orange/red flame
flame tests: copper
green flame
metal hydroxide test with NaOH
metal hydroxides are mixed with NaOH and produce a specific colour
metal hydroxide test: calcium
white precipitate formed
metal hydroxide test: copper(II)
a blue precipitate is formed
metal hydroxide test: iron (II)
a green precipitate is formed
metal hydroxide test: iron (III)
a brown precipitate is formed
metal hydroxide test: Aluminium
white precipitate that redissolves in excess NaOH to form a colourless solution.
metal hydroxide test: magnesium
a white precipitate is formed
flame emission spectroscopy
used to identify metal ions
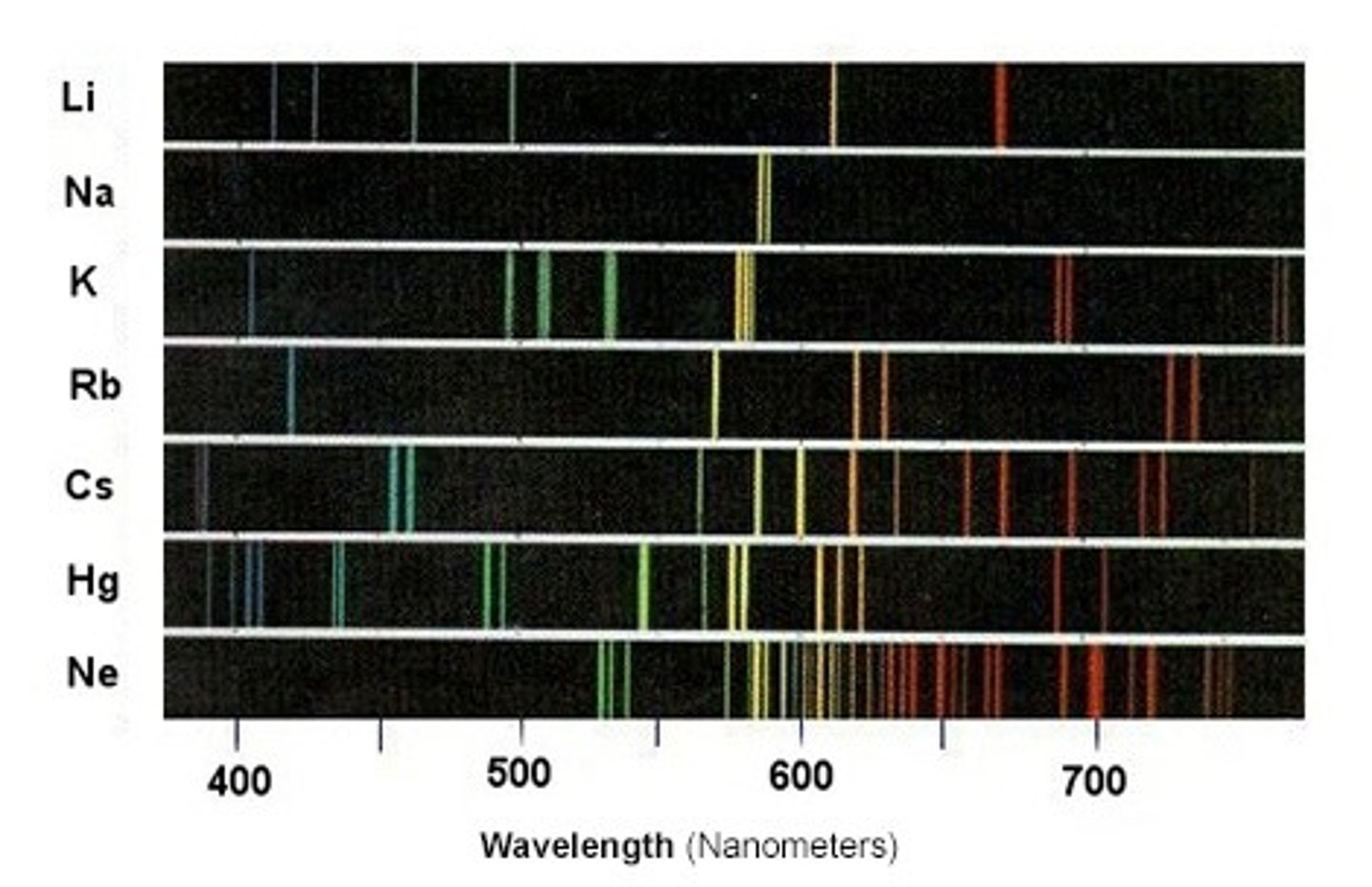
now flame emission spectroscopy works
1.) a sample is placed in a flame and the ions get excited and heat up.
2.) when the electrons drop back to their original energy levels, they transfer light energy
3.) the light passes through a spectroscope which detects different wave lengths of light to produce a line spectrum.
4.) the combination of wave lengths emitted depends on the ions charge and electron arrangement
5.) they give off certain colours for each ion which can be identified
flame emission spectroscopy works for mixtures
it can be used to identify different ions in mixtures. this makes it more useful than flame tests because they can only work for a single metal ion.
machine analysis
chemists often use instrumental analysis (tests that use machines) such as f.e.s instead of conducting tests
advantages of using machines
very sensitive whilst detecting things
very fast
tests can be automated
very accurate