Section 36 Viral Classification, Structure, Replication
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
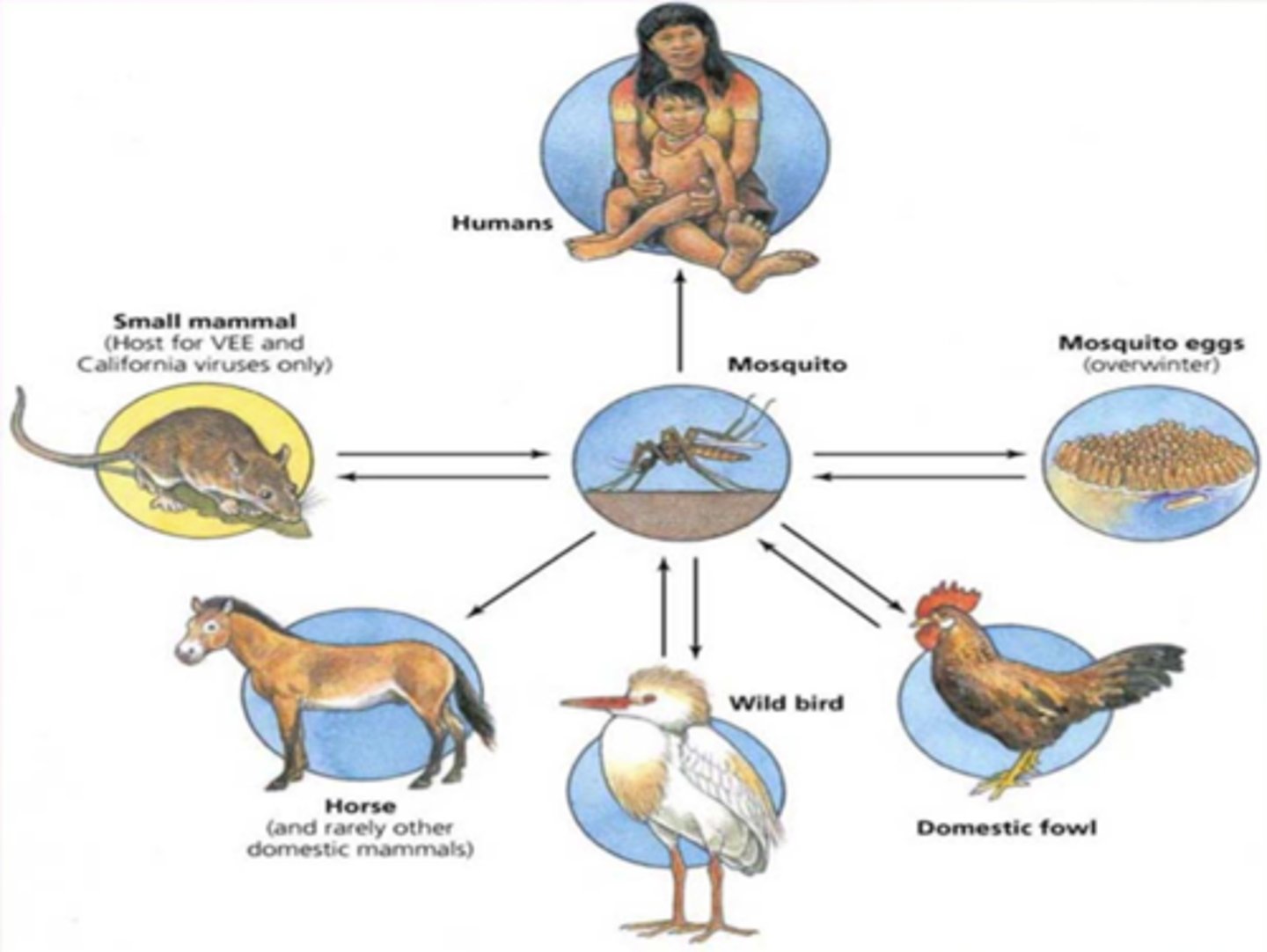
Arboviruses
arthropod-borne viruses that belong to several different viral groups - grouped together based on their vector (arthropod)
3 multiple choice options
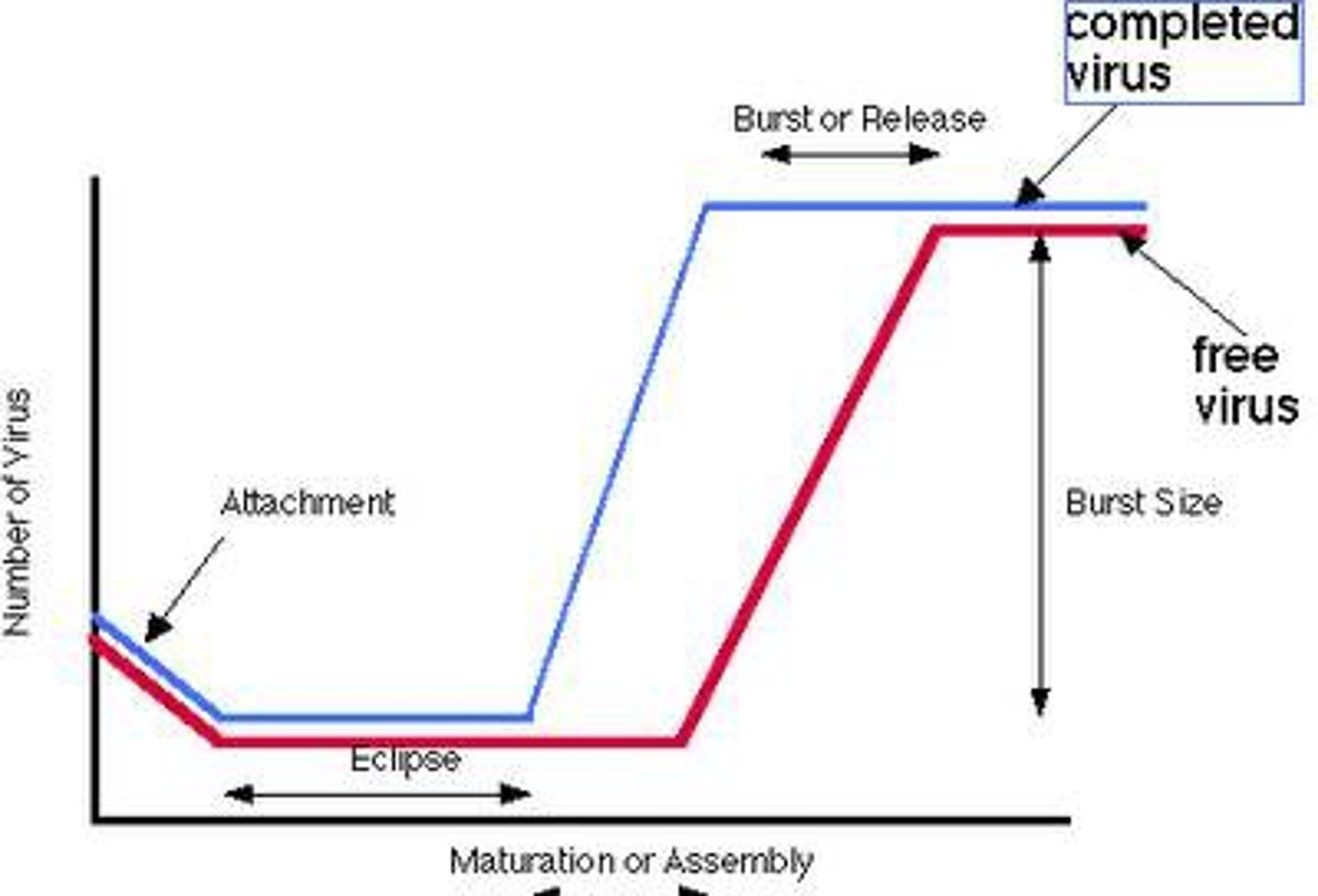
burst size
The number of virus particles released from each lysed host cell.
3 multiple choice options
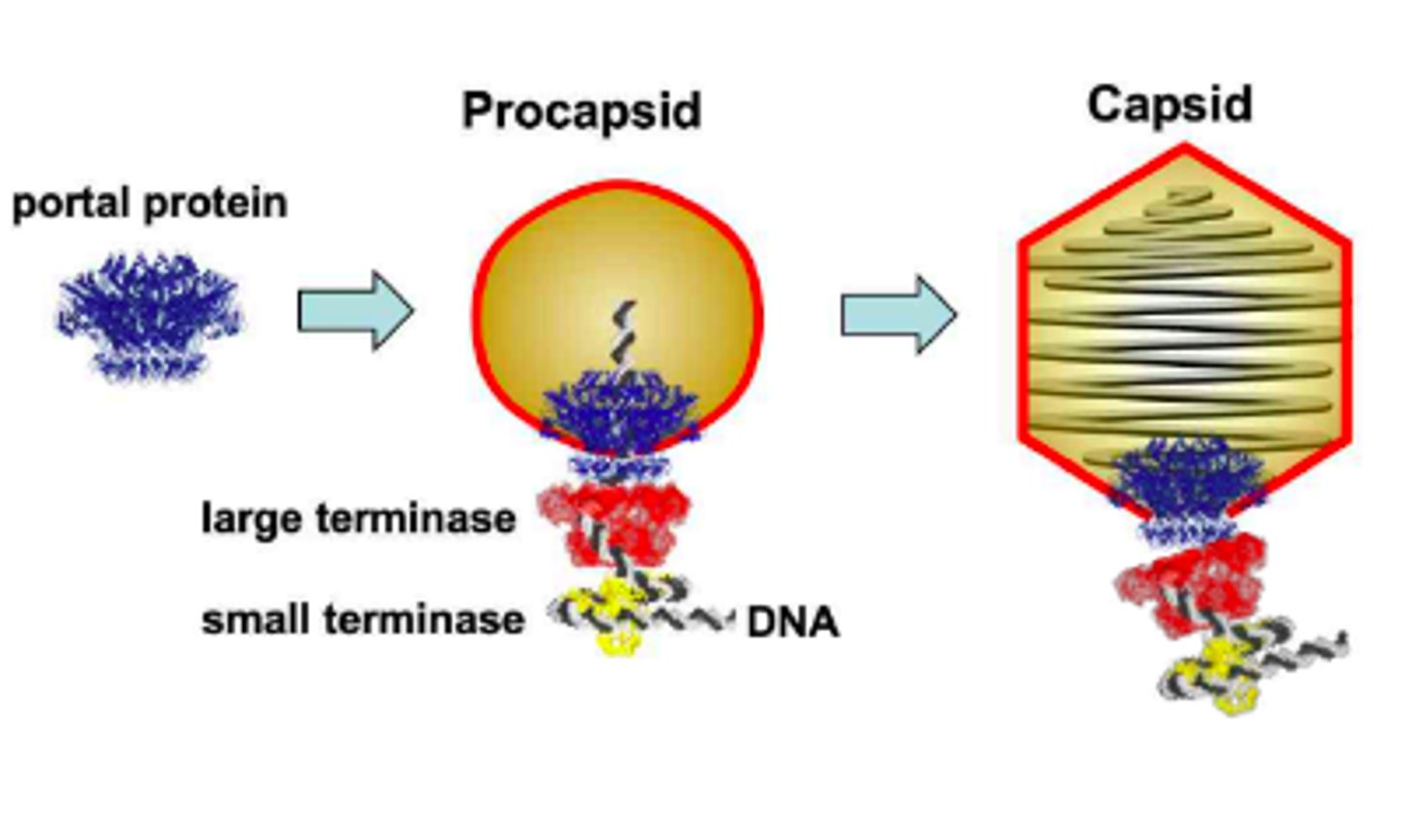
assembly
new virions are put together inside a host using "parts" manufactured during the synthesis process
3 multiple choice options
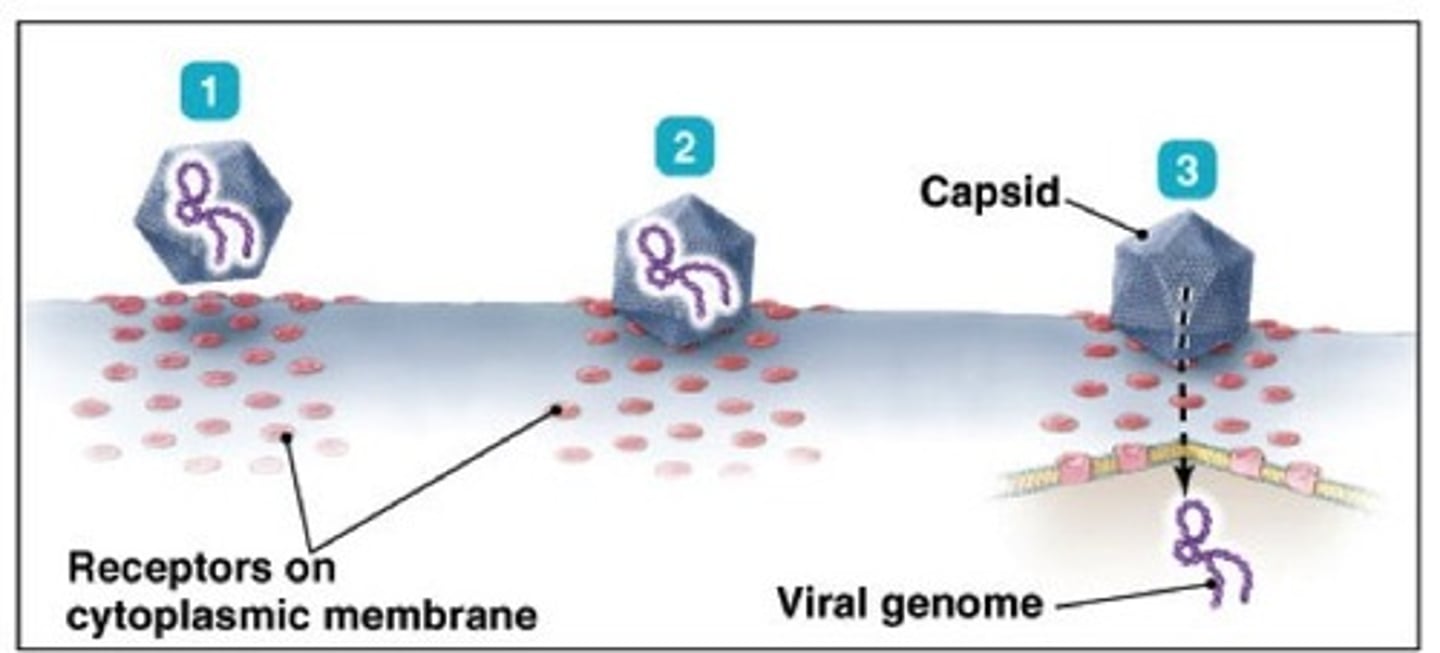
attachment
proteins on virions bind to specific host cell structures (aka receptors)
3 multiple choice options
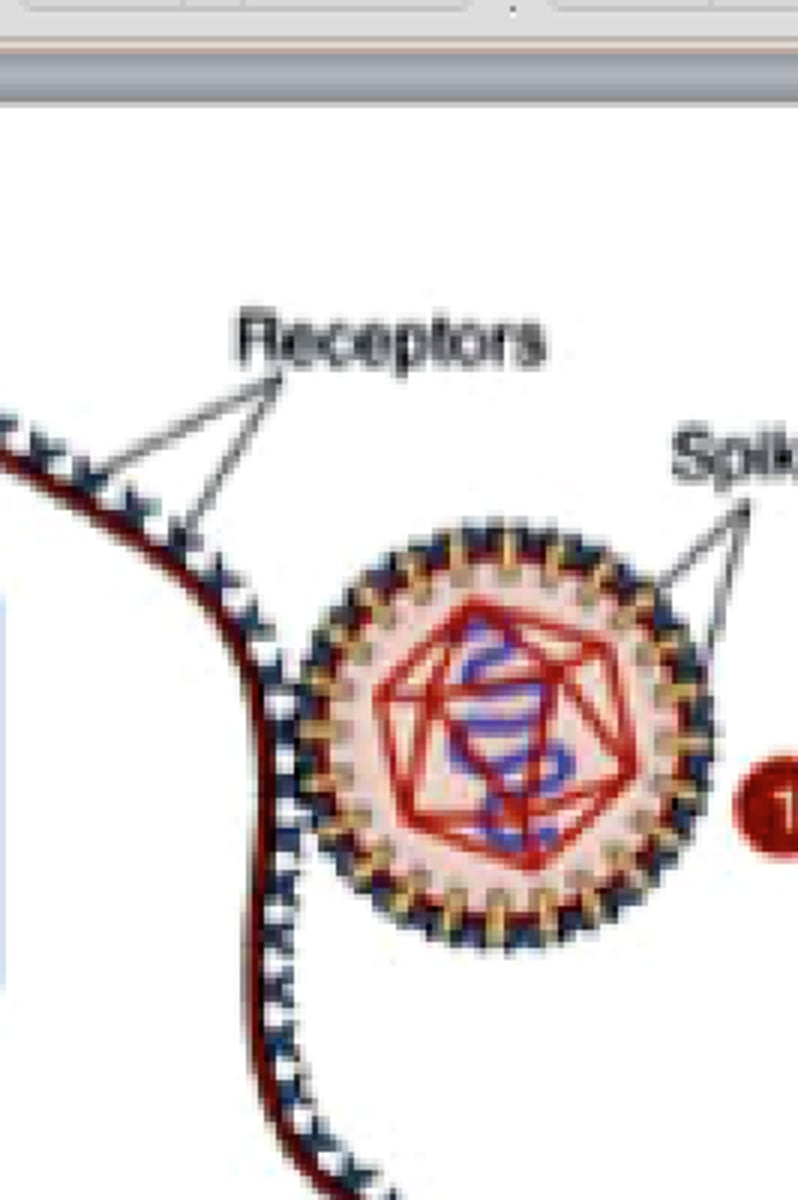
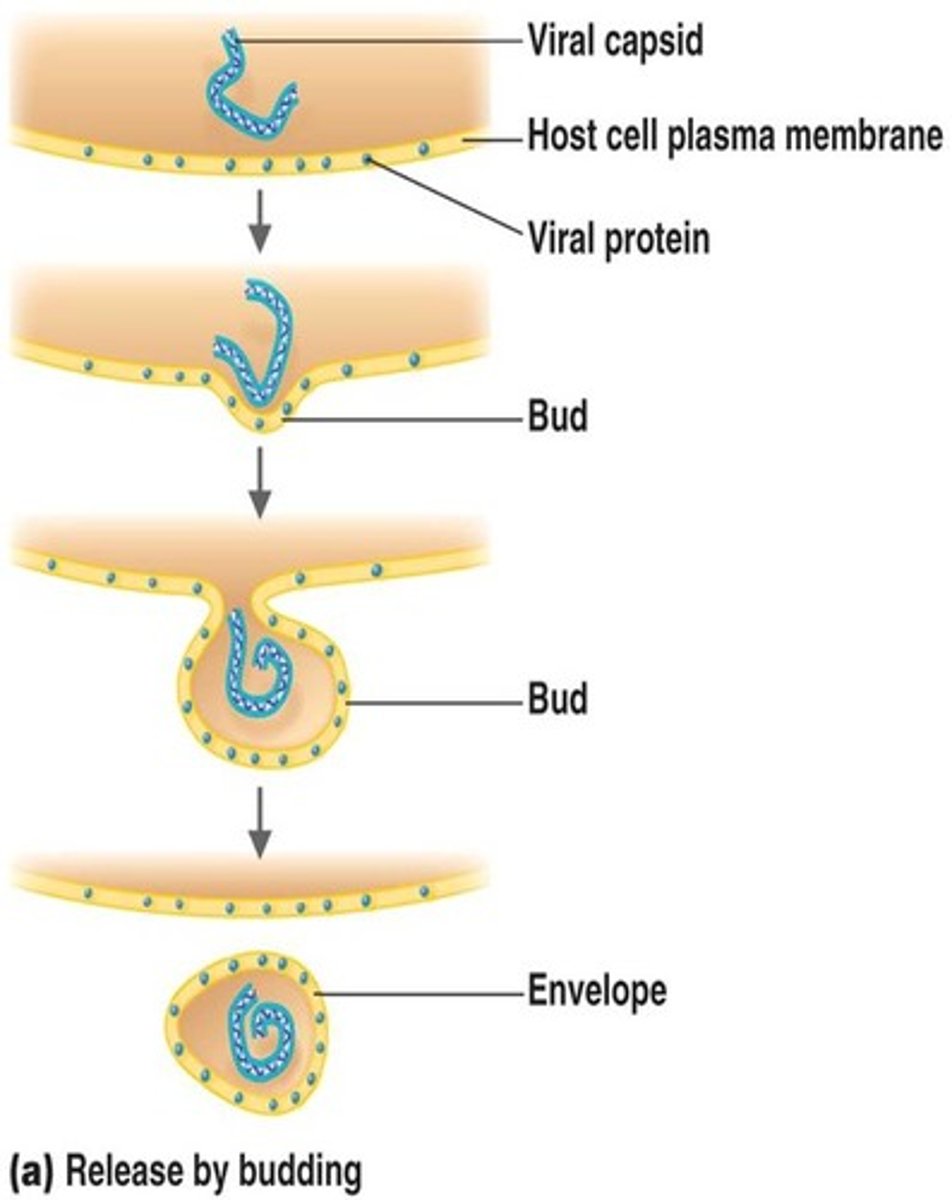
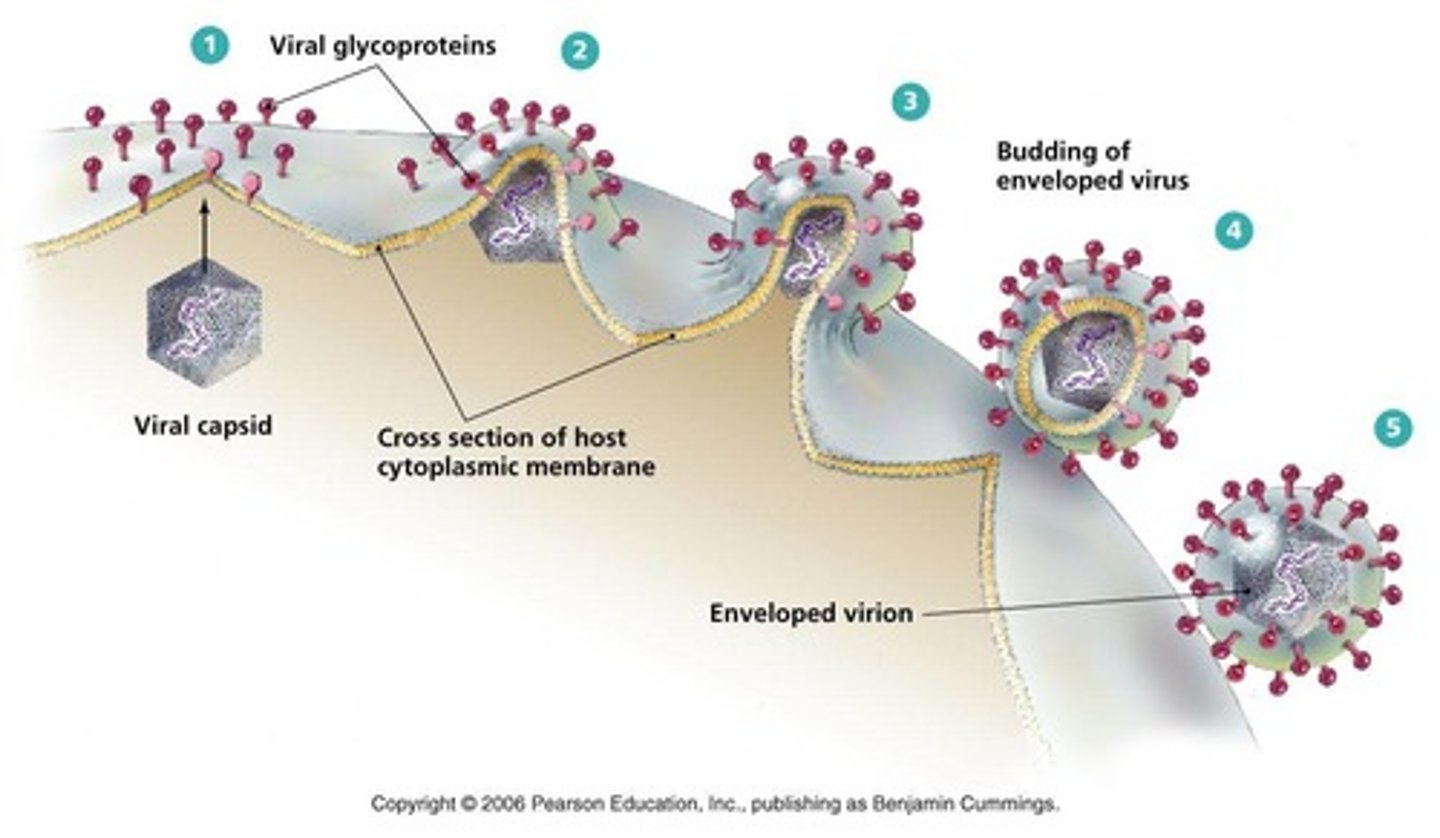
budding
release of an enveloped virus through the plasma membrane of an animal cell
3 multiple choice options
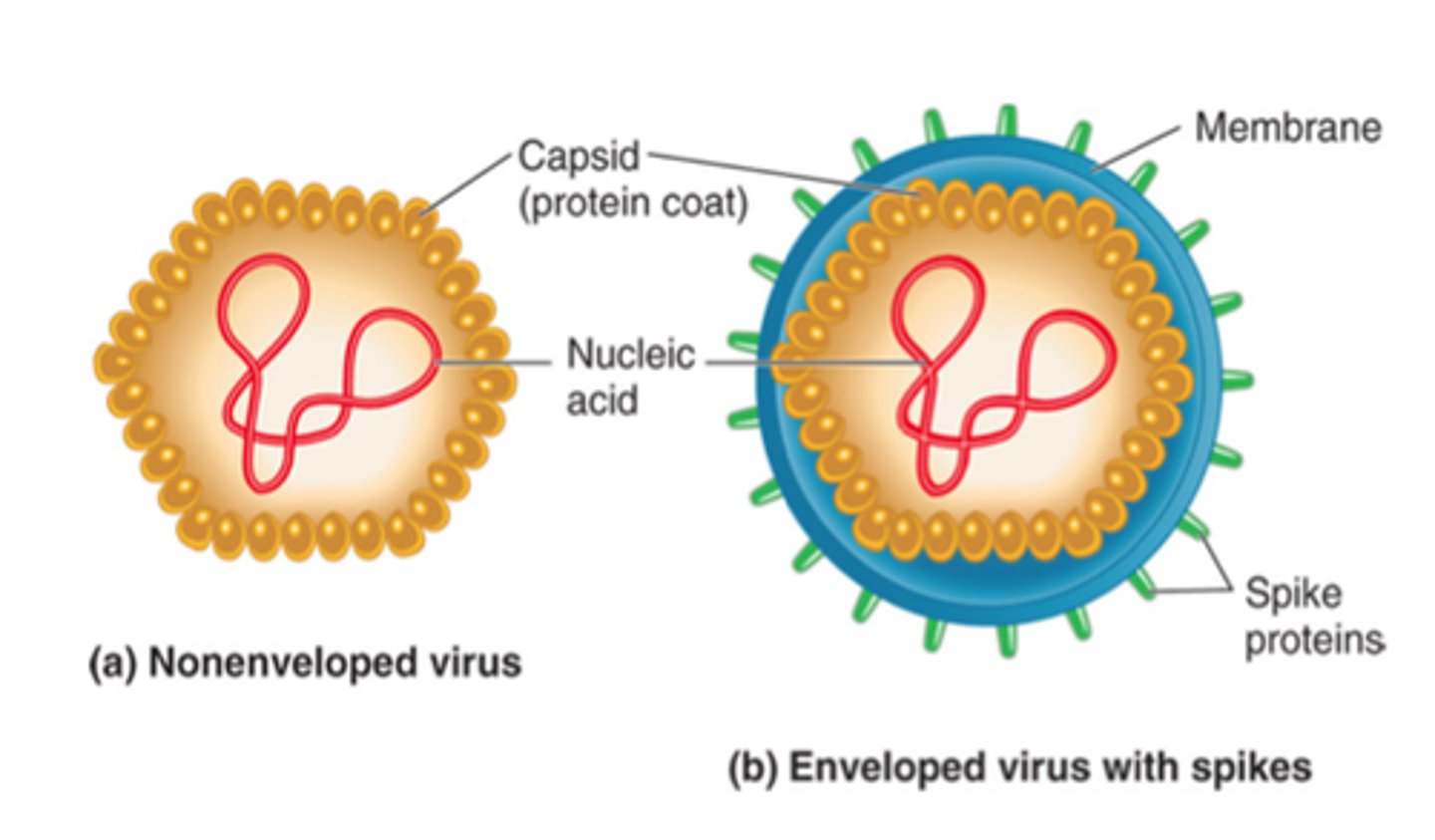
capsid
protein coat surrounding viral genome
3 multiple choice options
mutant
progeny that are genetically different from "parent" (original)
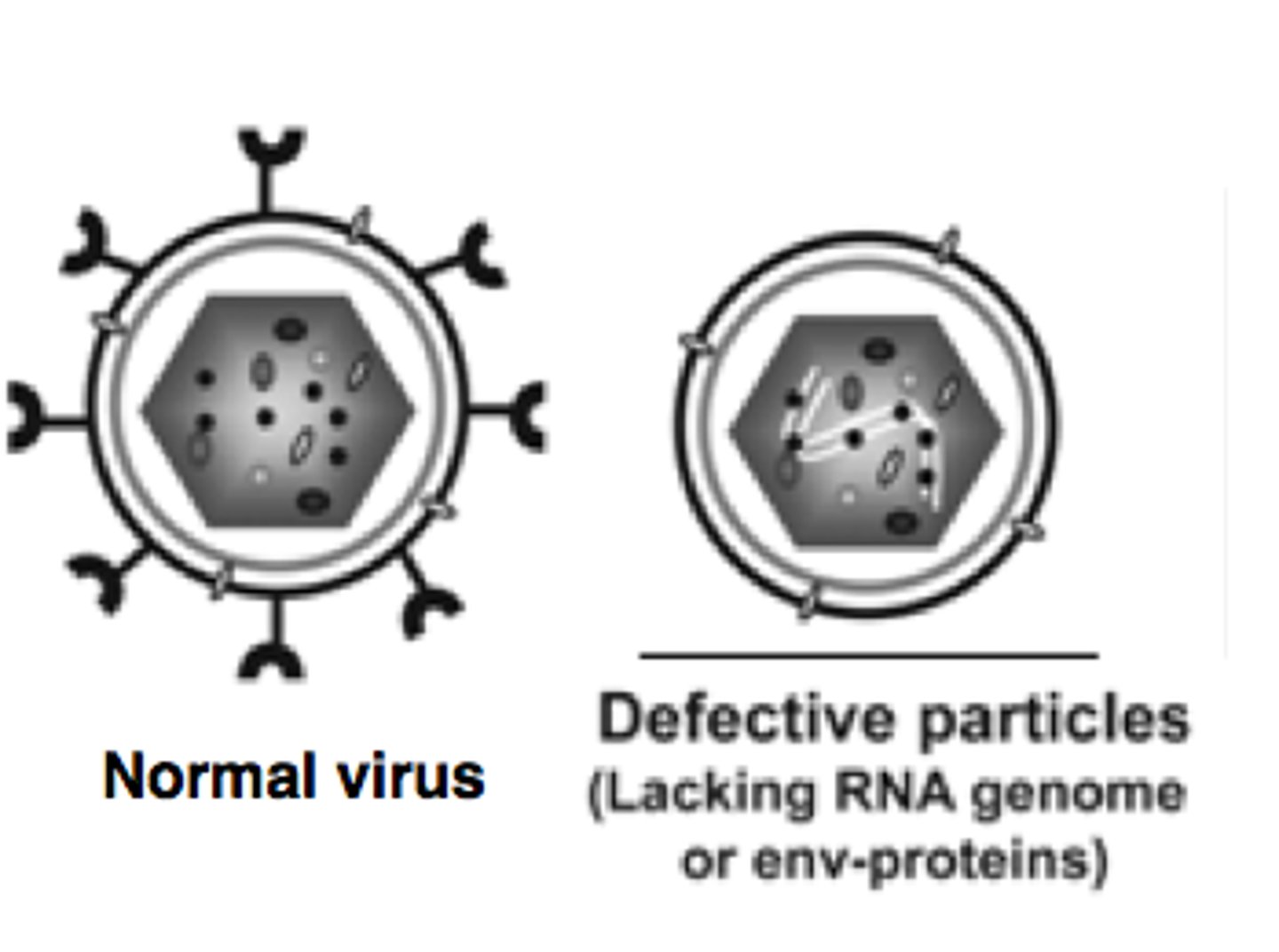
defective particles
mutant virions produced that cannot infect a new host cell
3 multiple choice options
dNTPs and rNTPs
host nucleotides all viruses need to replicate
3 multiple choice options
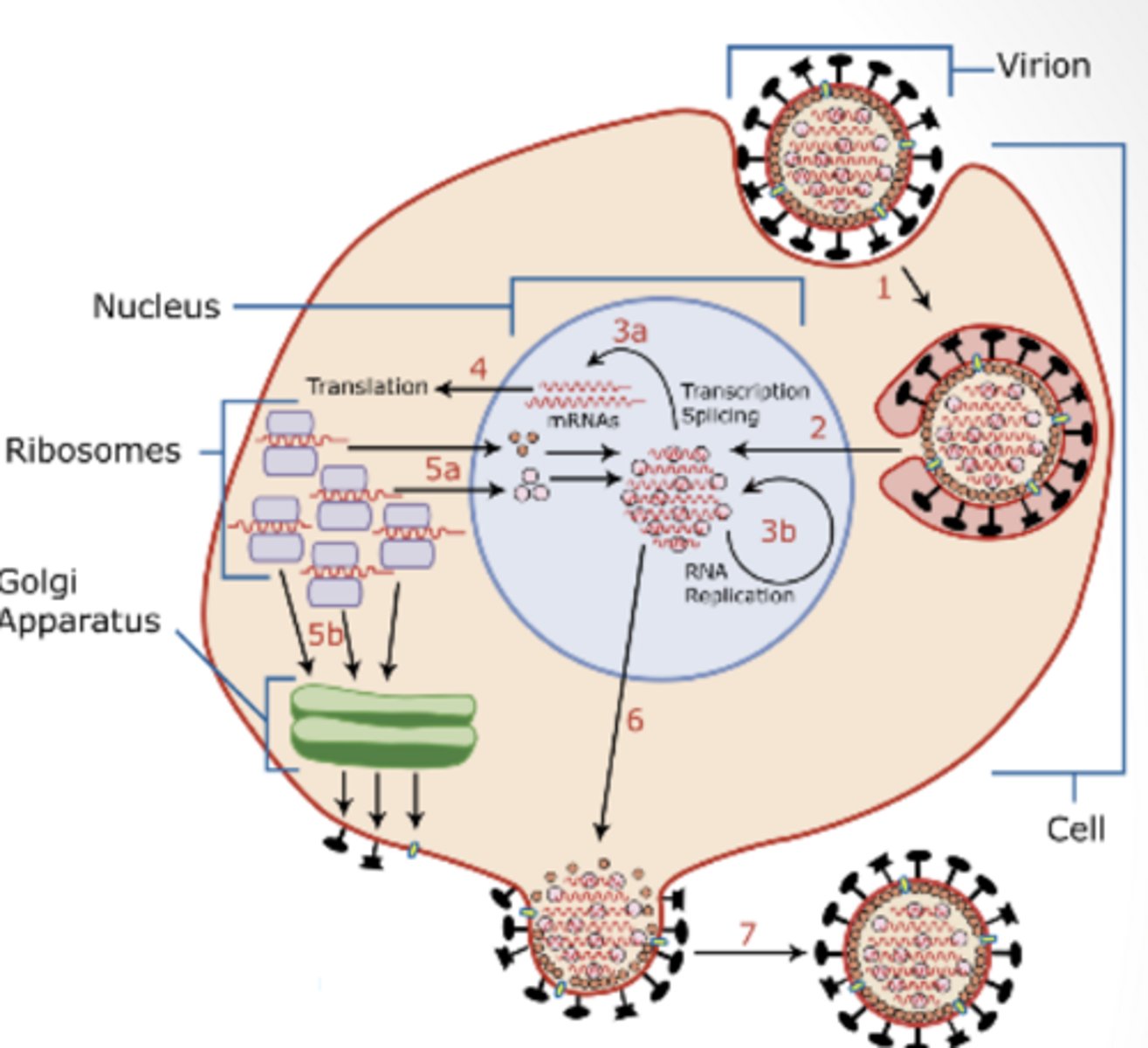
early phase
viral attachment, penetration, uncoating, stealing host genetic machinery
3 multiple choice options
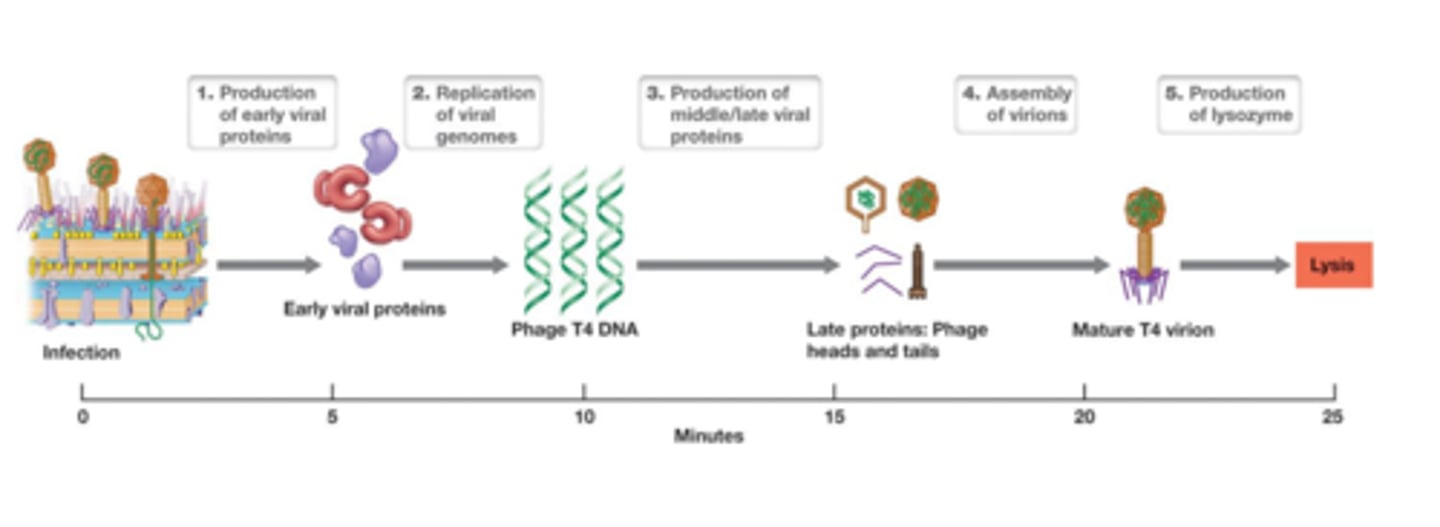
eclipse period
period between uncoating of infecting virus and production of new virions (lysing host cells during this period = no infective virions detected)
3 multiple choice options
morphology
shape of a virus
3 multiple choice options
antigenic drift
a mechanism for variation in viruses that involves the accumulation of mutations within the genes that code for antibody-binding sites.
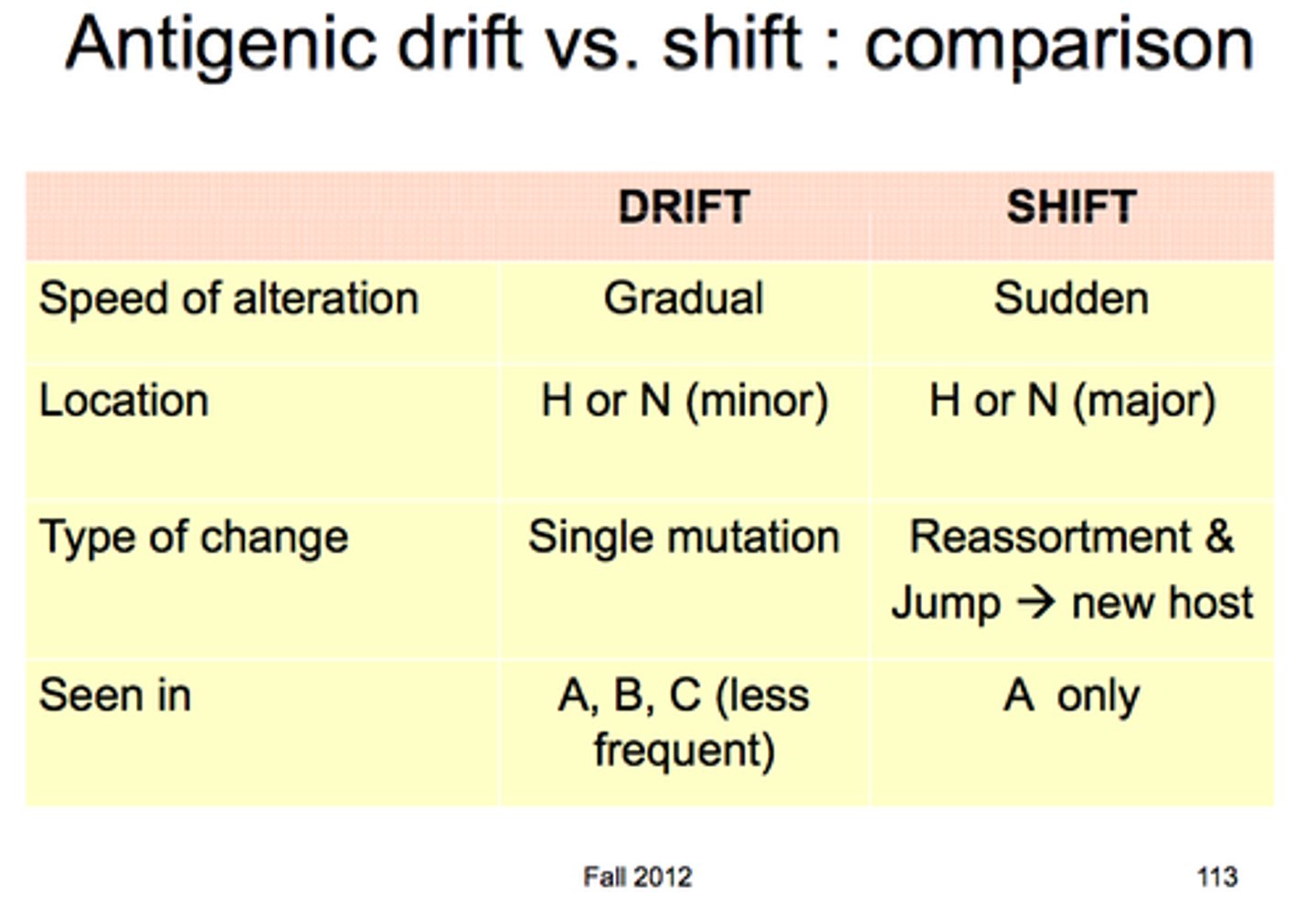
antigenic shift
the process by which two or more different strains of a virus, or strains of two or more different viruses, combine to form a new subtype having a mixture of the surface antigens of the two or more original strains.
late phase
synthesis of structural proteins, assembly and release of progeny virions
3 multiple choice options
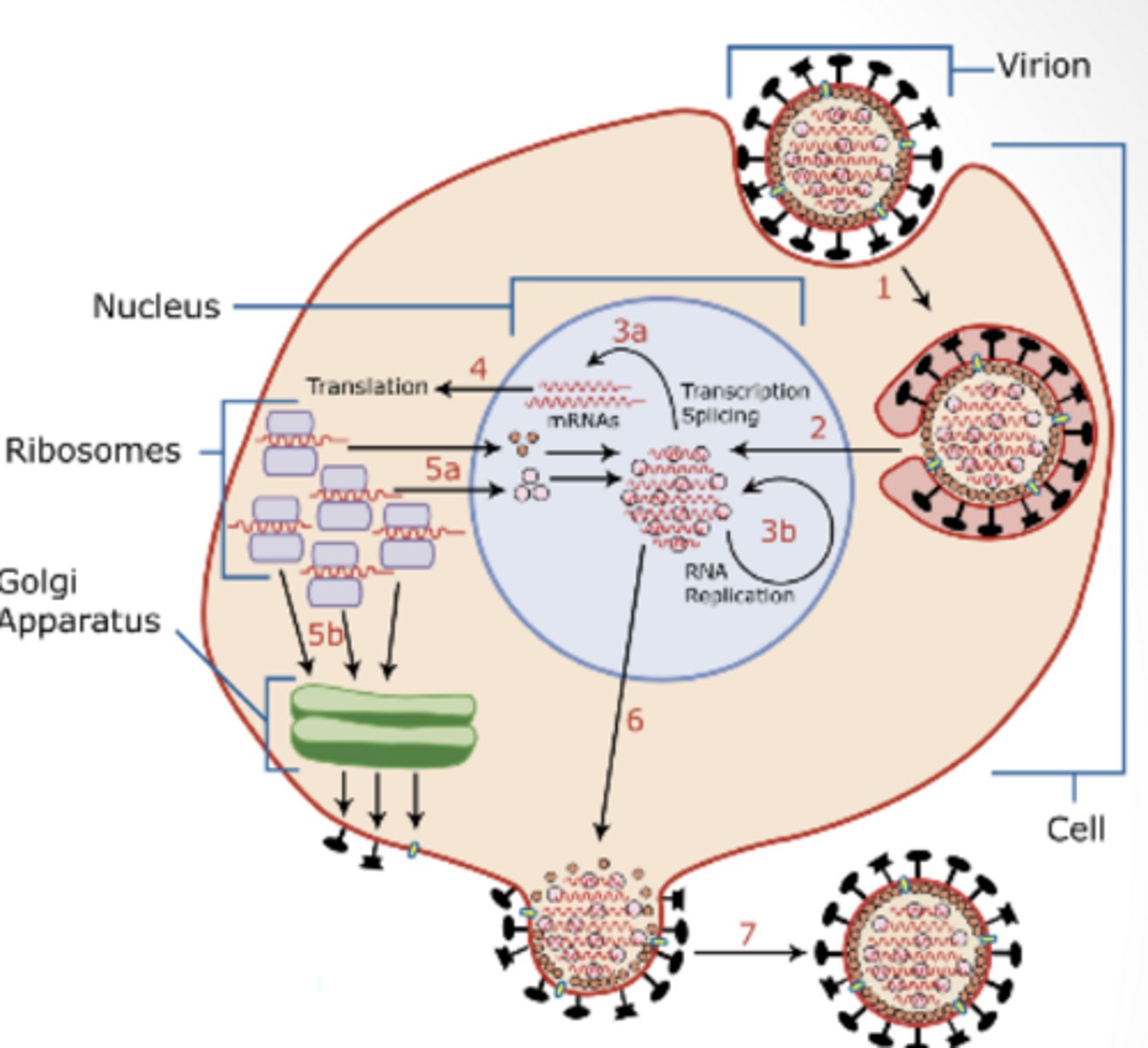
latent period
eclipse period + release of new viruses
3 multiple choice options
selective pressure
environmental conditions that select for certain characteristics of individuals and select against other characteristics - this is the basis of regularly passing stock pathogen cultures thru animals to maintain pathogenicity
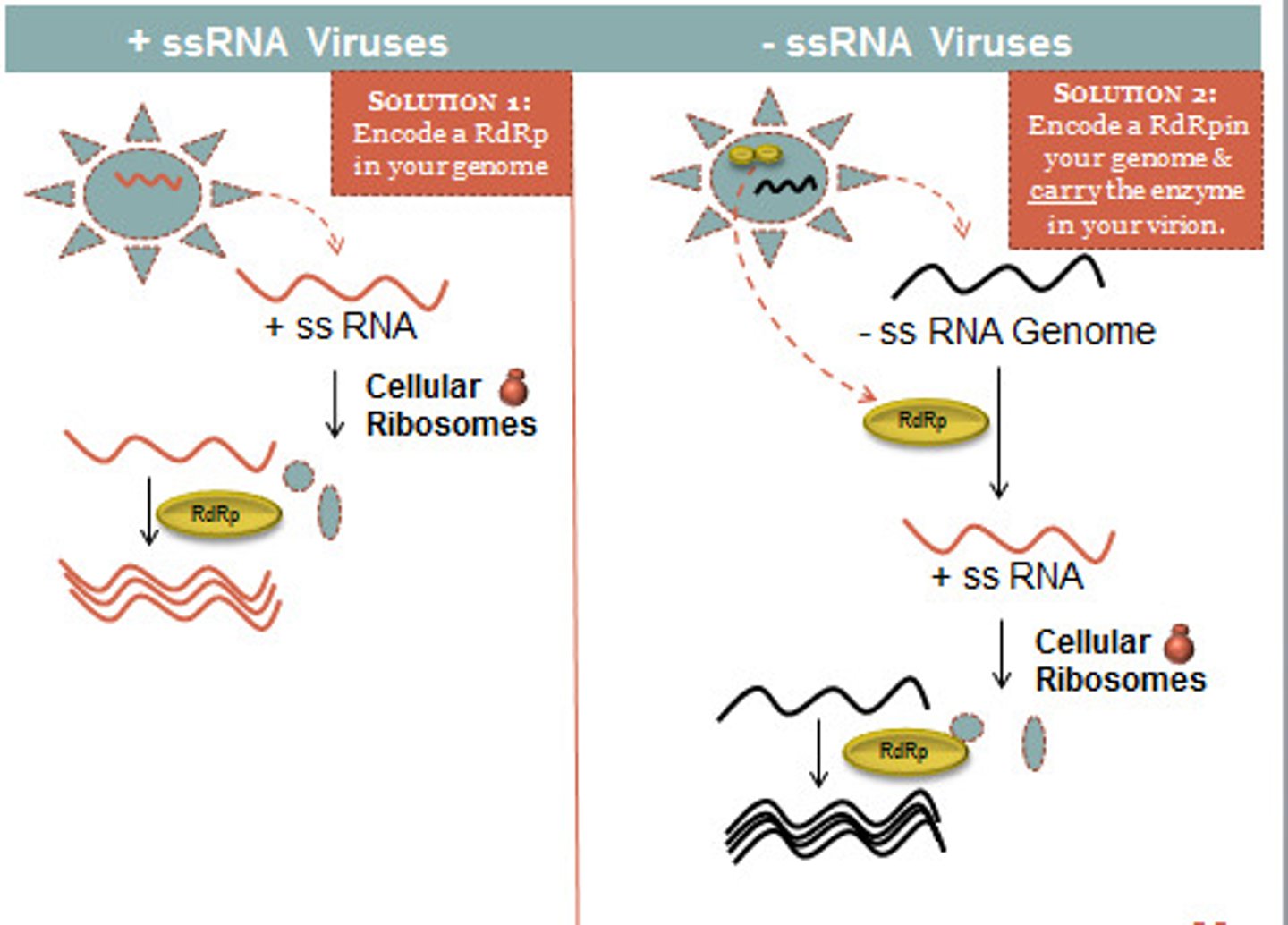
negative strand
a nucleic acid strand that has the opposite sense to (is complementary to) the mRNA
3 multiple choice options
penetration
The second step in viral infection, the injection of the viral genome into the host cell.
3 multiple choice options
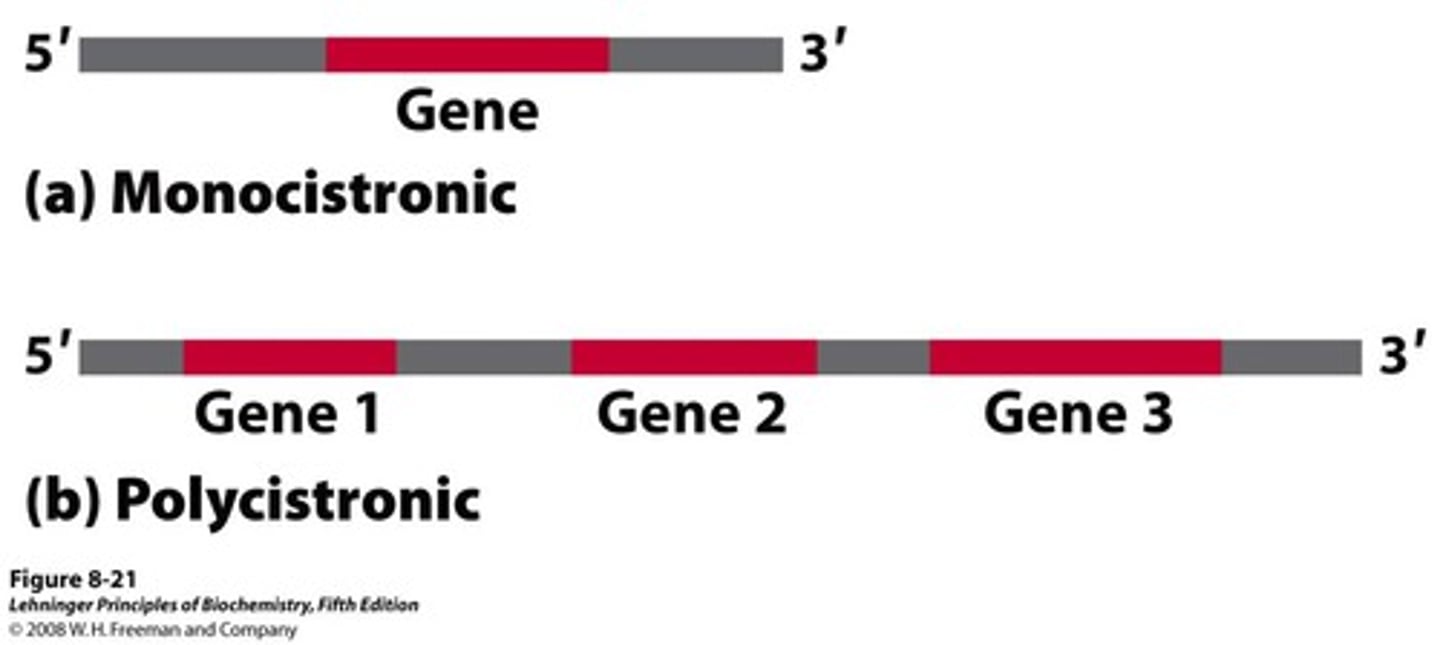
polycistronic
The coding pattern of prokaryotes, in which one mRNA may code for multiple proteins.
polypeptides
viral proteins are made as one long string of amino acids (encoding multiple proteins) that are then cut into separate functional proteins
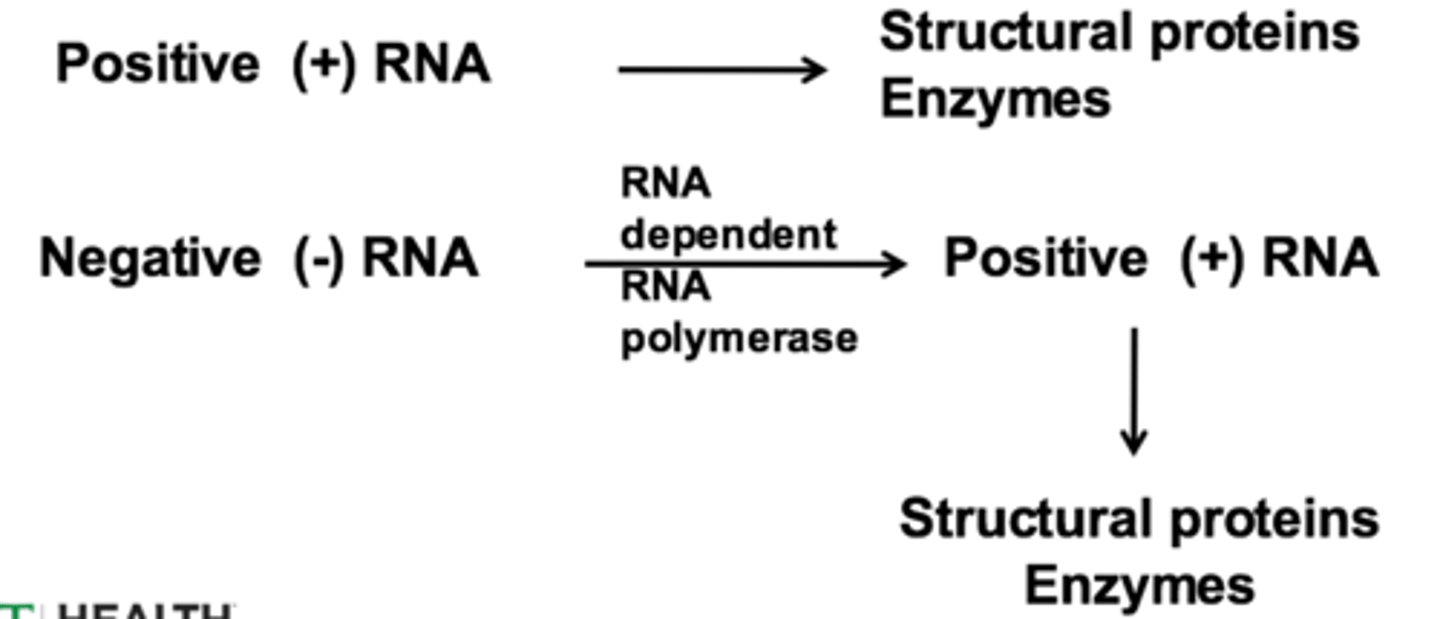
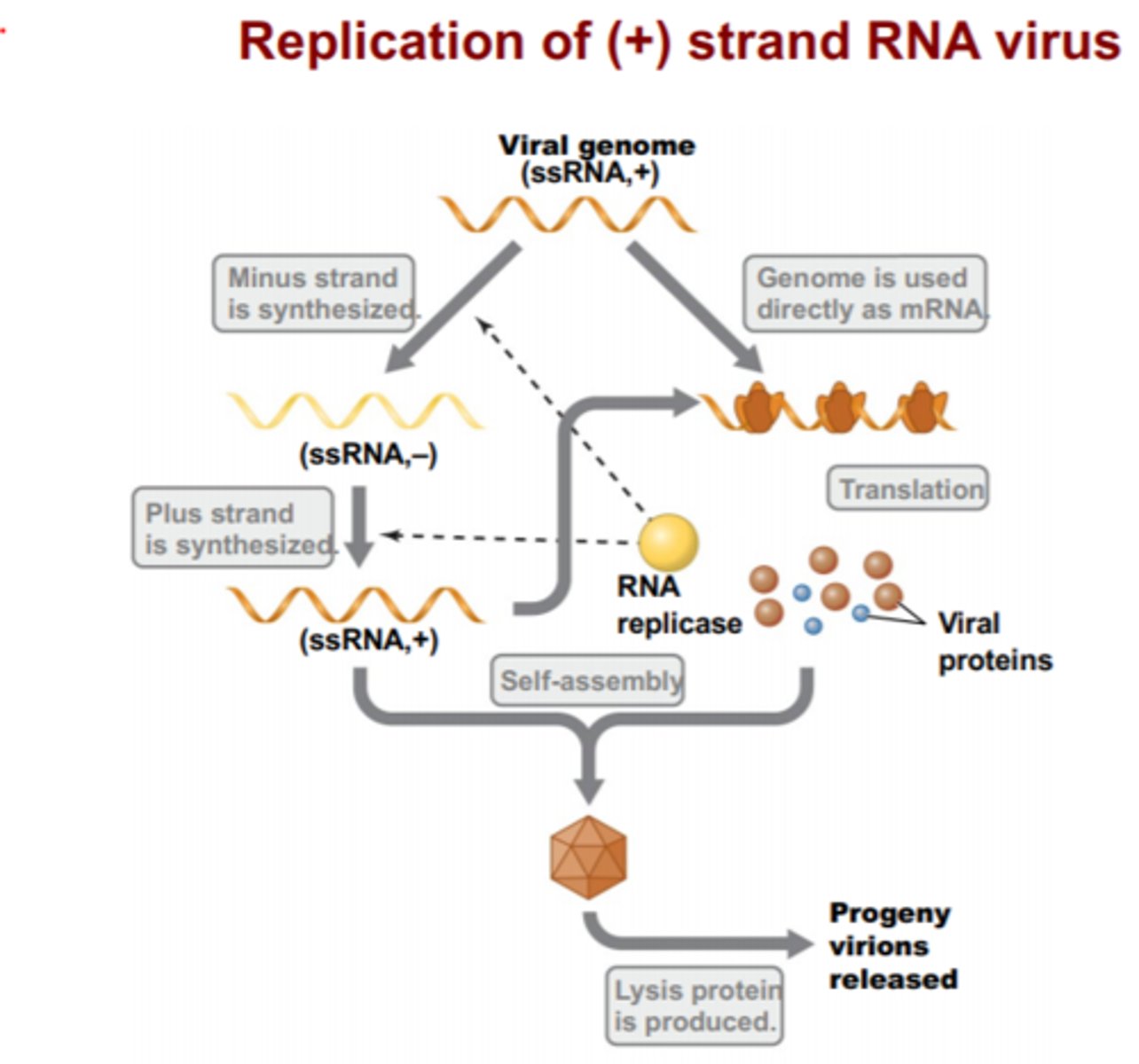
positive strand
means RNA is like mRNA and can move right into translation to turn into protein. These types of viruses can replicate much faster than (-) strand viruses.
attenuation
the decrease or loss of virulence in a pathogen - strains with this are frequently used for vaccines
release
stage in viral infection where new viral particles (virions) leave a host cell
lethal mutation
a mutation that causes death
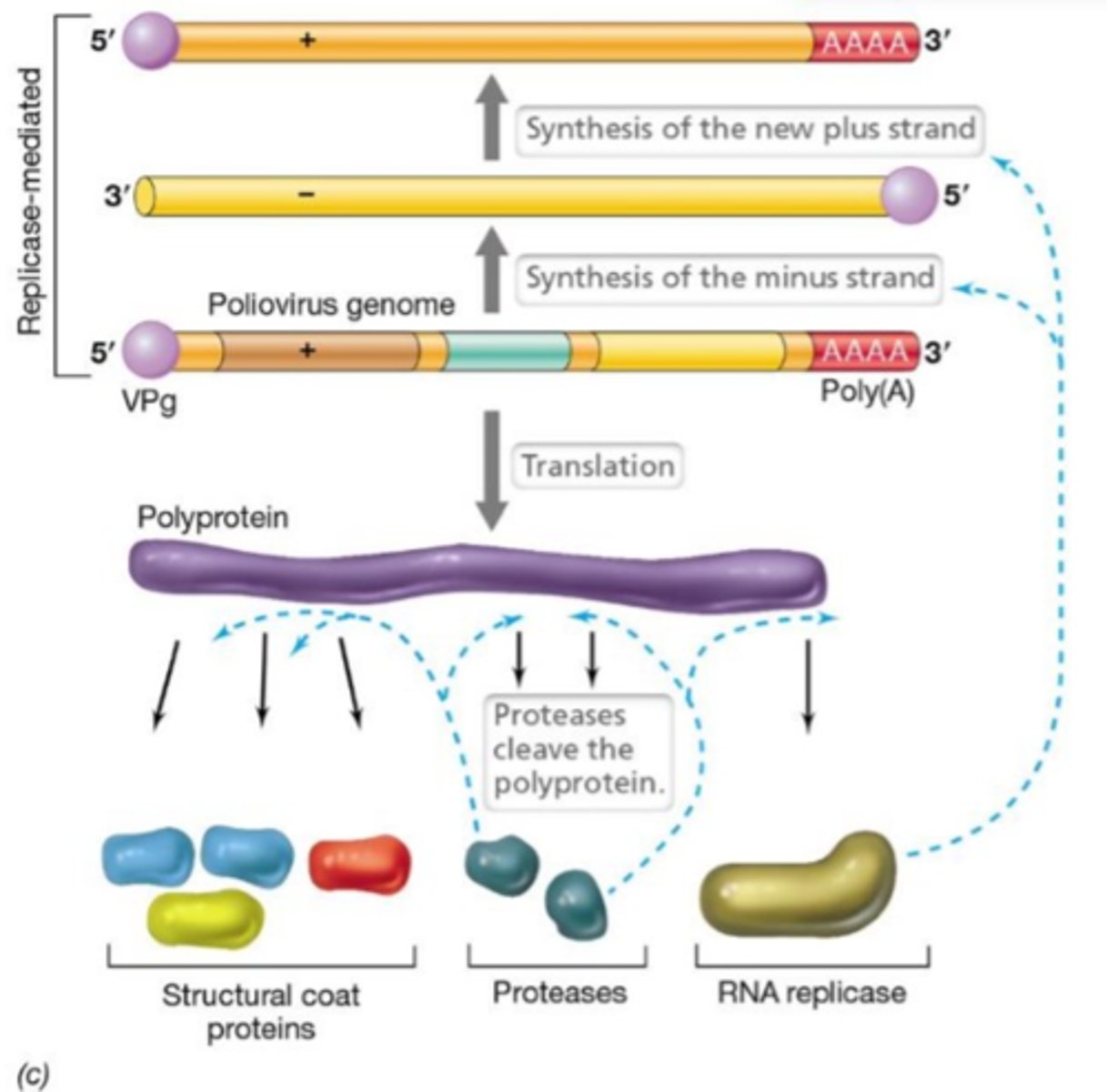
Replicase
Viral enzyme catalyzes the replication of RNA from an RNA template (RNA dependent RNA polymerase)
3 multiple choice options
retroviruses
An RNA virus that reproduces by transcribing its RNA into DNA and then inserting the DNA into a cellular chromosome; an important class of cancer-causing viruses.
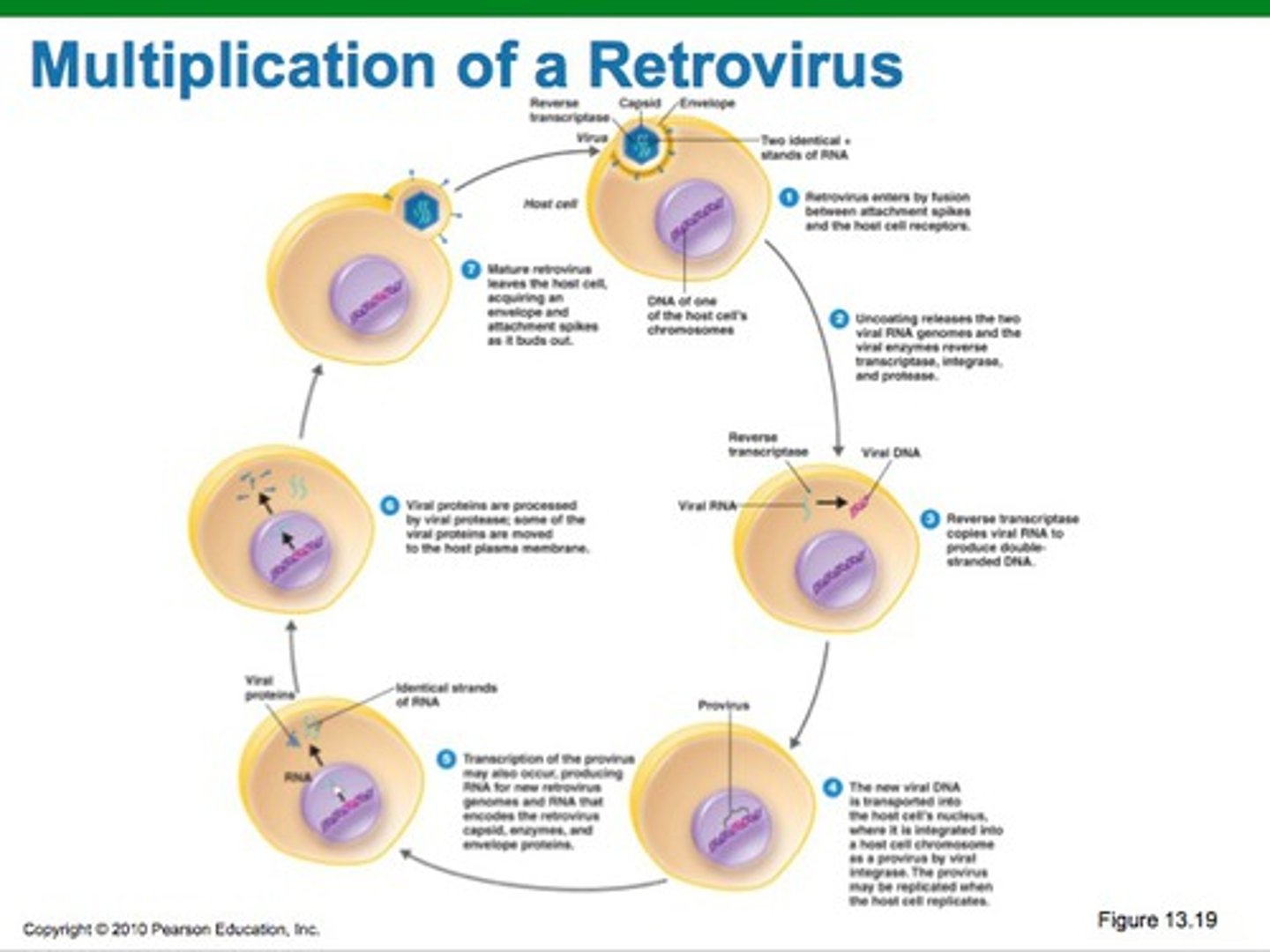
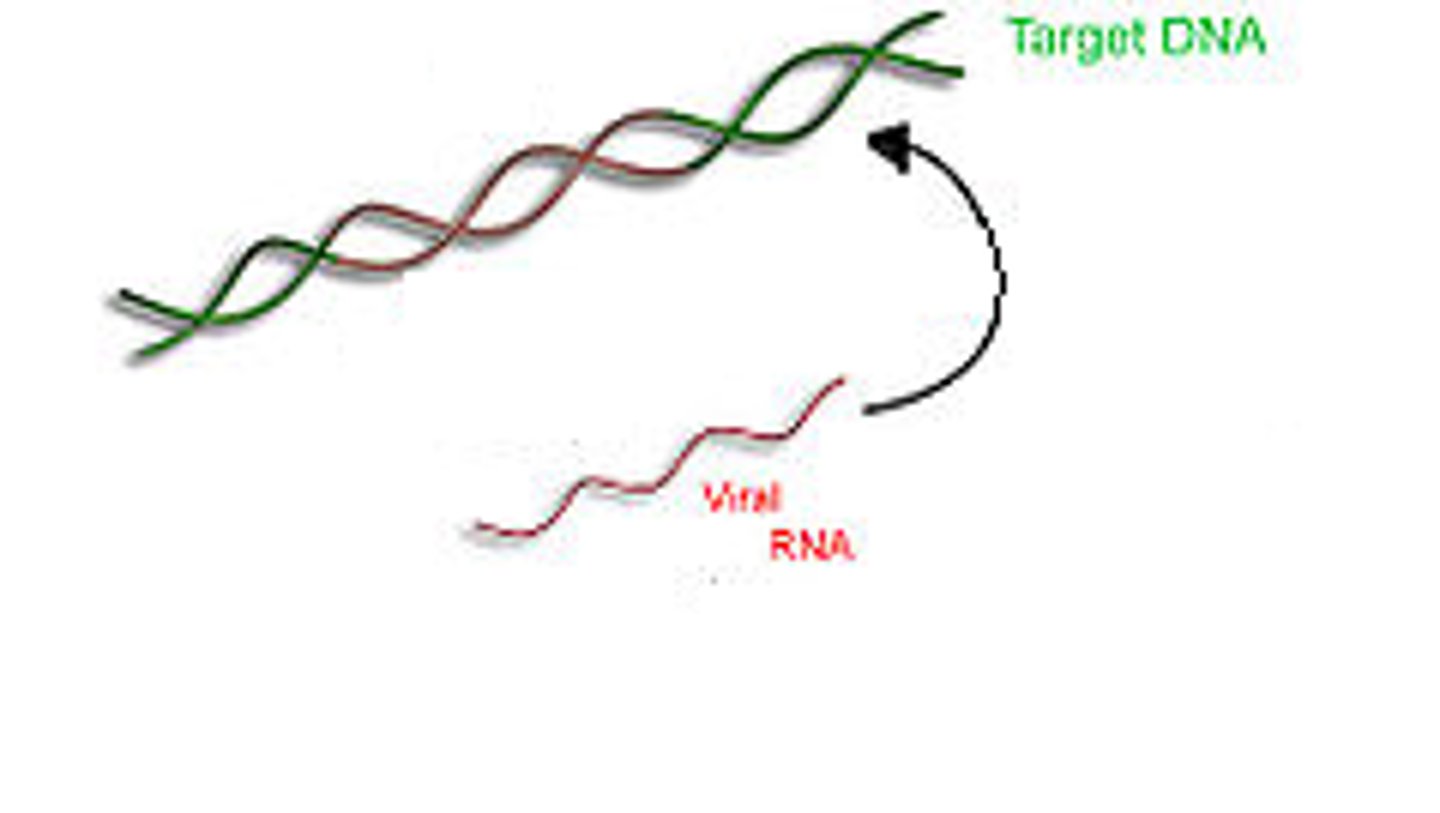
reverse transcriptase
An enzyme encoded by certain viruses (retroviruses) that uses RNA as a template for DNA synthesis.
RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP)
A viral enzyme that makes a strand of RNA by reading a strand of RNA . All prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases are DNA dependent
segmented genome
A viral genome that is divided into several fragments, each usually coding for a single polypeptide (influenza, looking at you here)
synthesis
viral stage where the virus uses host to replicate genome and make proteins
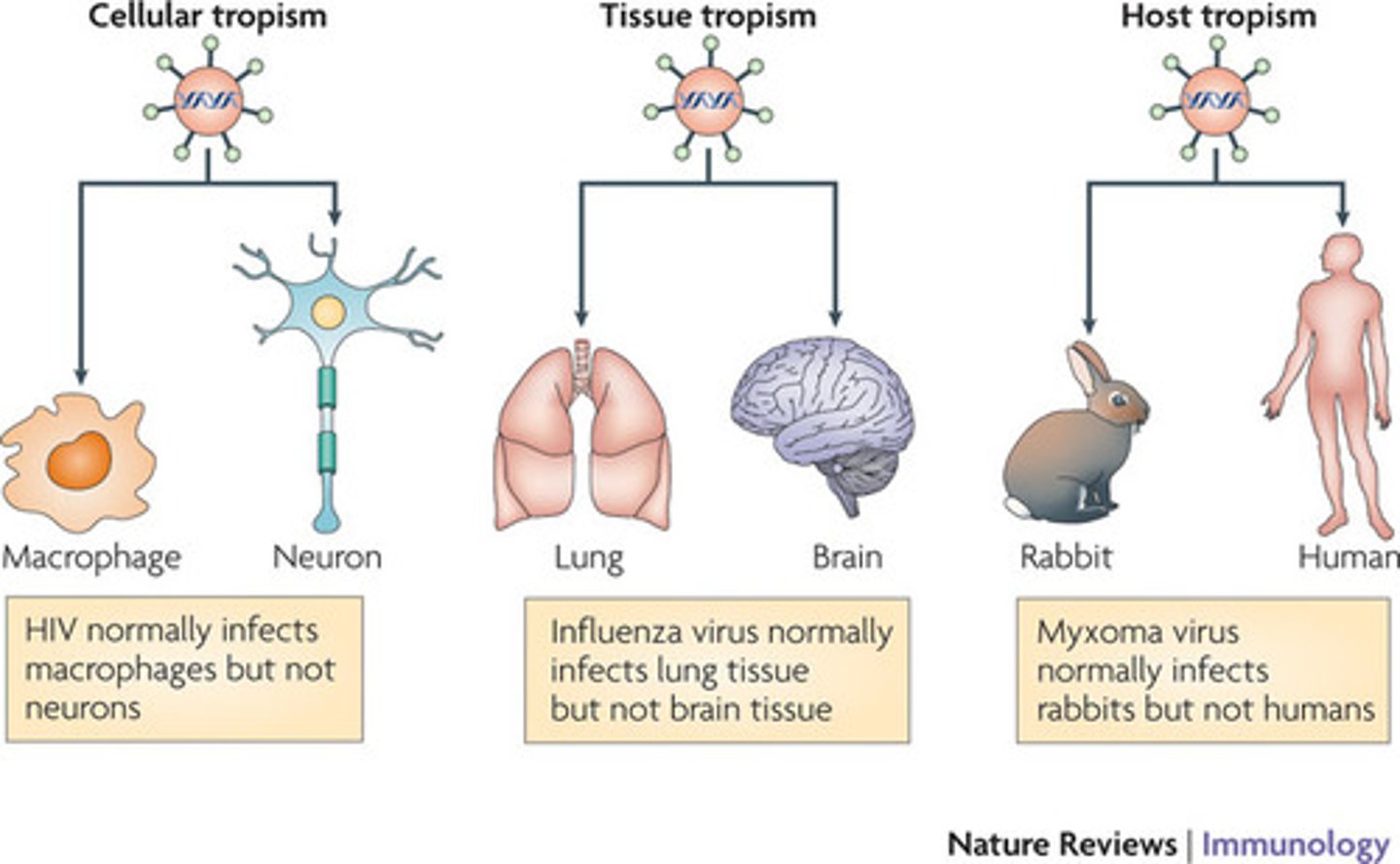
tissue tropism
the range of tissue types that a virus can infect - determined by specific protein-protein interactions needed at attachment
naked virus
virus without an envelope (has a genome (DNA or RNA) and a protein capsid
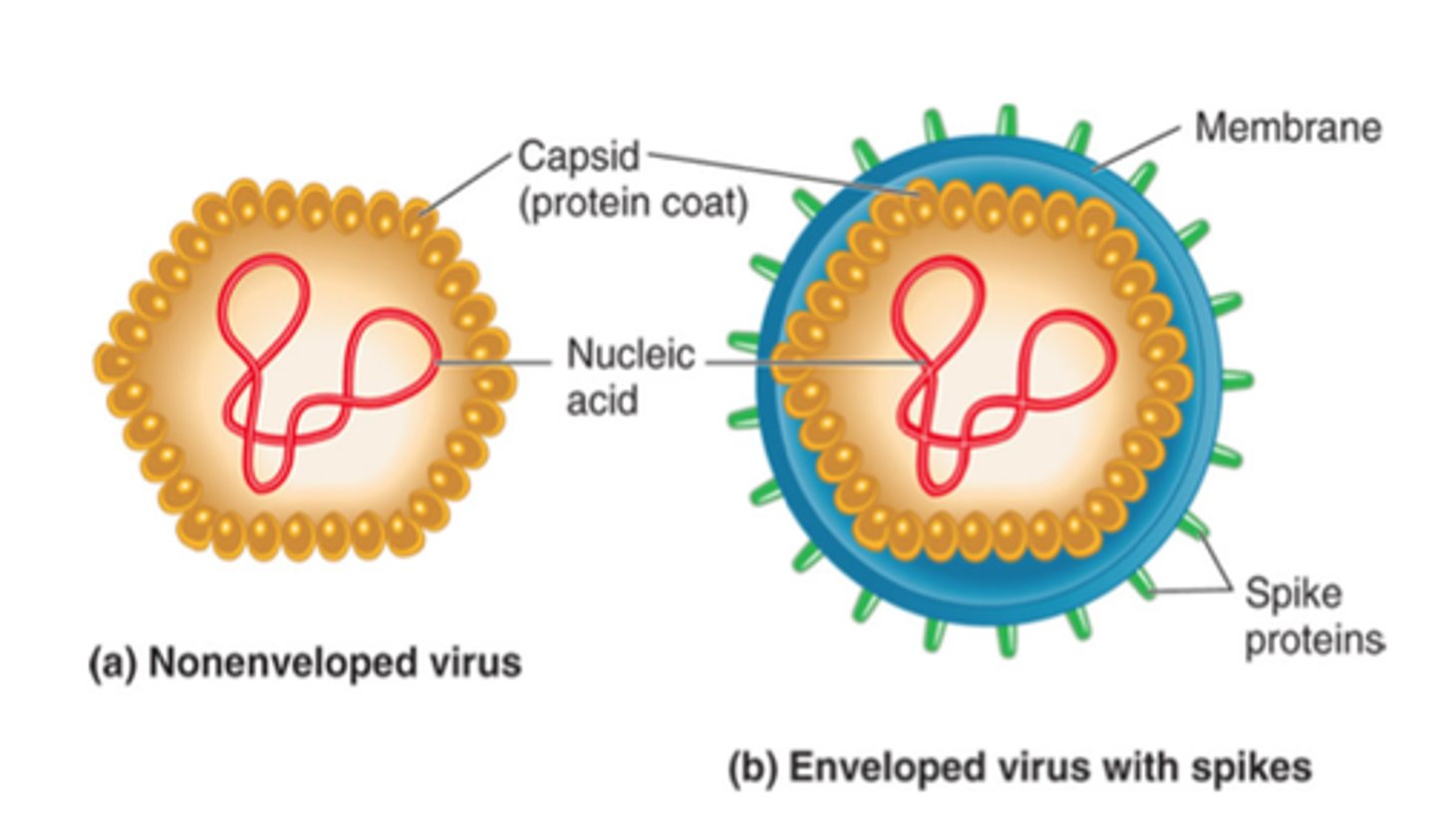
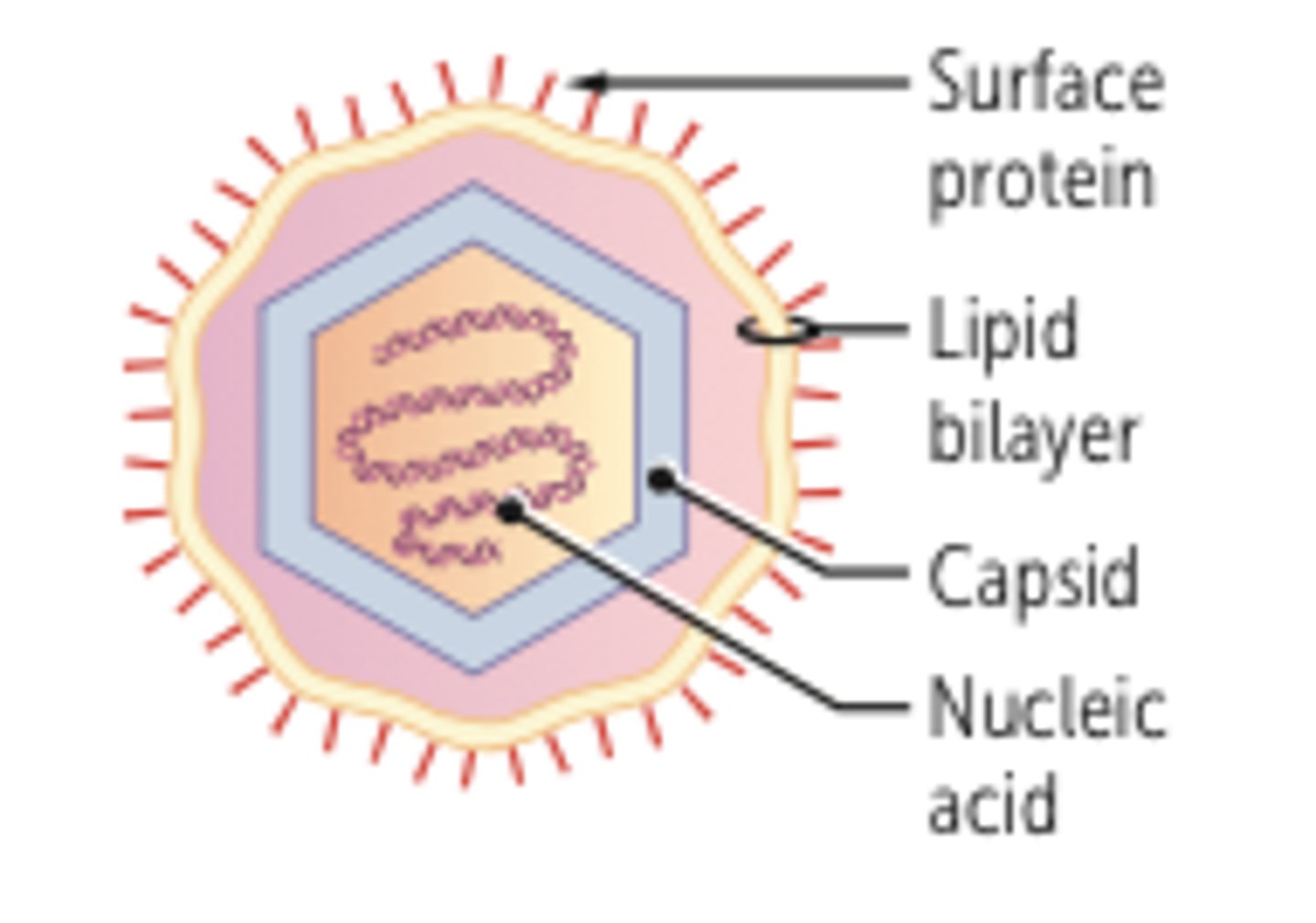
enveloped virus
A virus enclosed within a phospholipid membrane derived from its host cell (typically the host cell's plasma membrane)
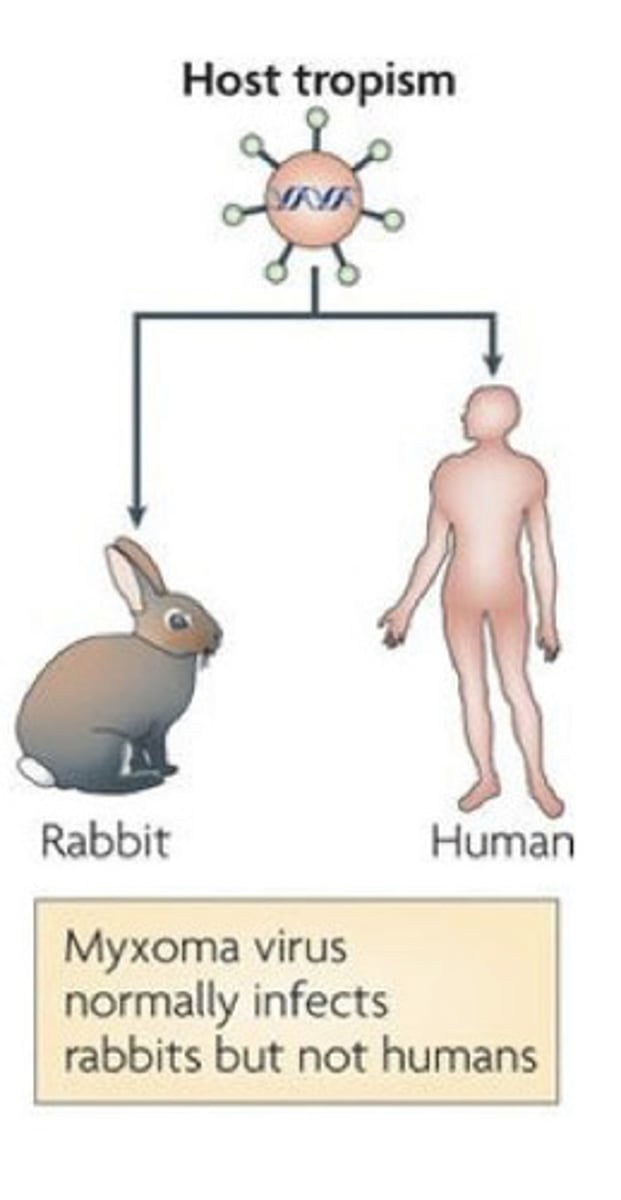
host range (aka host tropism)
the limited number of species whose cells can be infected by a particular virus
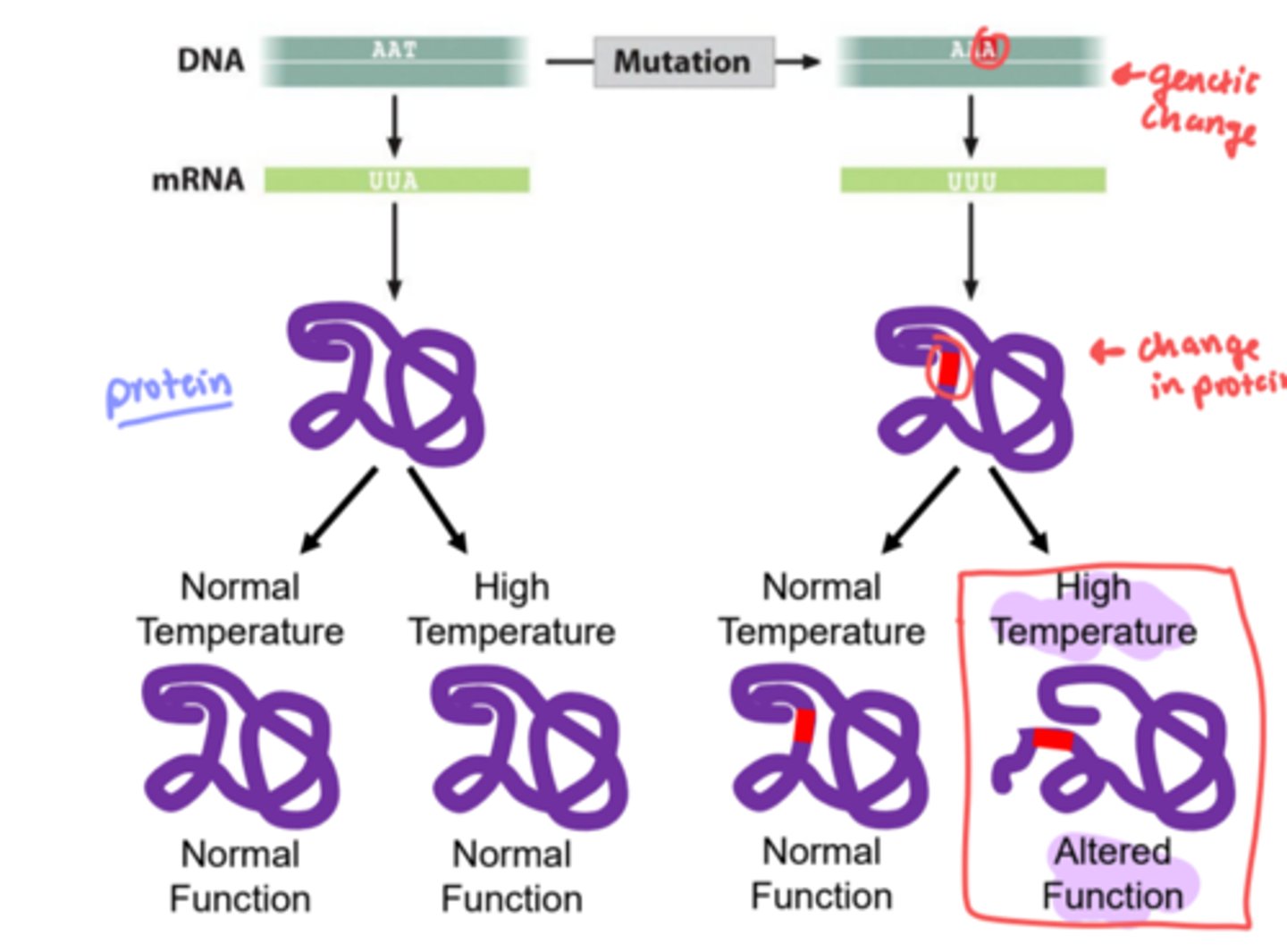
conditional mutants
a mutant whose phenotype depends on the environmental conditions, such as a temperature-sensitive mutant