Week 2: Arterial & Venous Insufficiency Wounds
1/338
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
339 Terms
Arterial wound
Wounds that result from a lack of blood flow which deprives the area of oxygen
5% to 10% of all lower extremity ulcerations are because of
AI
AI affects
23% of all Americans age 55+
AI treatment costs
4.37 billion
AI cost reason
surgical debridement
Arterial ulcers are likely to progress without
holistic and meticulous interventions
Arterial flow
artery-->ateriole-->capillary
average arter size
37 Micrometers
Capillary size
1 mm in length and 8-10 micrometers in width
Tunica adventitia
The outer layer of tissue of a blood vessel wall, composed of elastic and fibrous connective tissue.
tunica media
middle layer of artery; made up of smooth muscle fibers and thick layer of elastic connective tissue
tunica media innervation
sympathetic
tunica intima
the innermost layer of a blood vessel
tunica intima contacts
blood cells
Larger arteries closer to heart have
HIGH Pressures
etiology of arterial insufficiency
-Trauma
-Acute Embolism
-Diabetes
-RA
Thromboangitis
-ARTERIOSCLEROSIS
Truma and arterial etiology
damage to an artery
Acute embolism
stops blood flow
Diabetes and AI
Microvascular diseases
Thromboangiitis
inflamed and occluded Blood vessel
Thromboangiitis aka
Buerger's disease
#1 reason for arterial insufficiency
Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis
hardening of the arteries
Atherosclerosis
condition in which fatty deposits called plaque build up on the inner walls of the arteries
narrowing of arteries
atherosclerosis
atherosclerotic plaque is caused by
High LDL
Presentation of Arterial Insufficiency
-Intermittent claudication
-Ischemic rest pain
-Gangrene
Intermittent Claudication
Activity-specific discomfort due to local ischemia
Pain with Intermittent claudication
ceases after 1-5 mins of rest
Rate of plaque progression exceeds
angiogensis rate
% Of stenosis to feel claudication
50%
Pain from Intermittent claudication occurs
distal to site of occlusion
Iliofemoral artery obstruction pain
buttock, thigh, or calf
Infrapopliteal artery obstruction pain
foot
Ischemic Rest Pain
A more severe symptom of diminished blood flow to the most distal portion of the extremity
Ischemic Rest Pain is more signifacnt than
Intermittent claudication
Ischemic Rest Pain is increased with
elevation
Ischemic Rest Pain is decreased with
rest
increasing tissue O2 demand can fatally upset the balance between O2 supply and tissue demand, causing
ulceration
Repeated bouts of ischemia/reperfusion can lead to
AI ulcer
AI wounds are typically from
trauma
Gangrene occurs in
distal extremities
When oxygen supply does NOT equal demand
cell death occurs
Gangrene
death of tissue associated with loss of blood supply
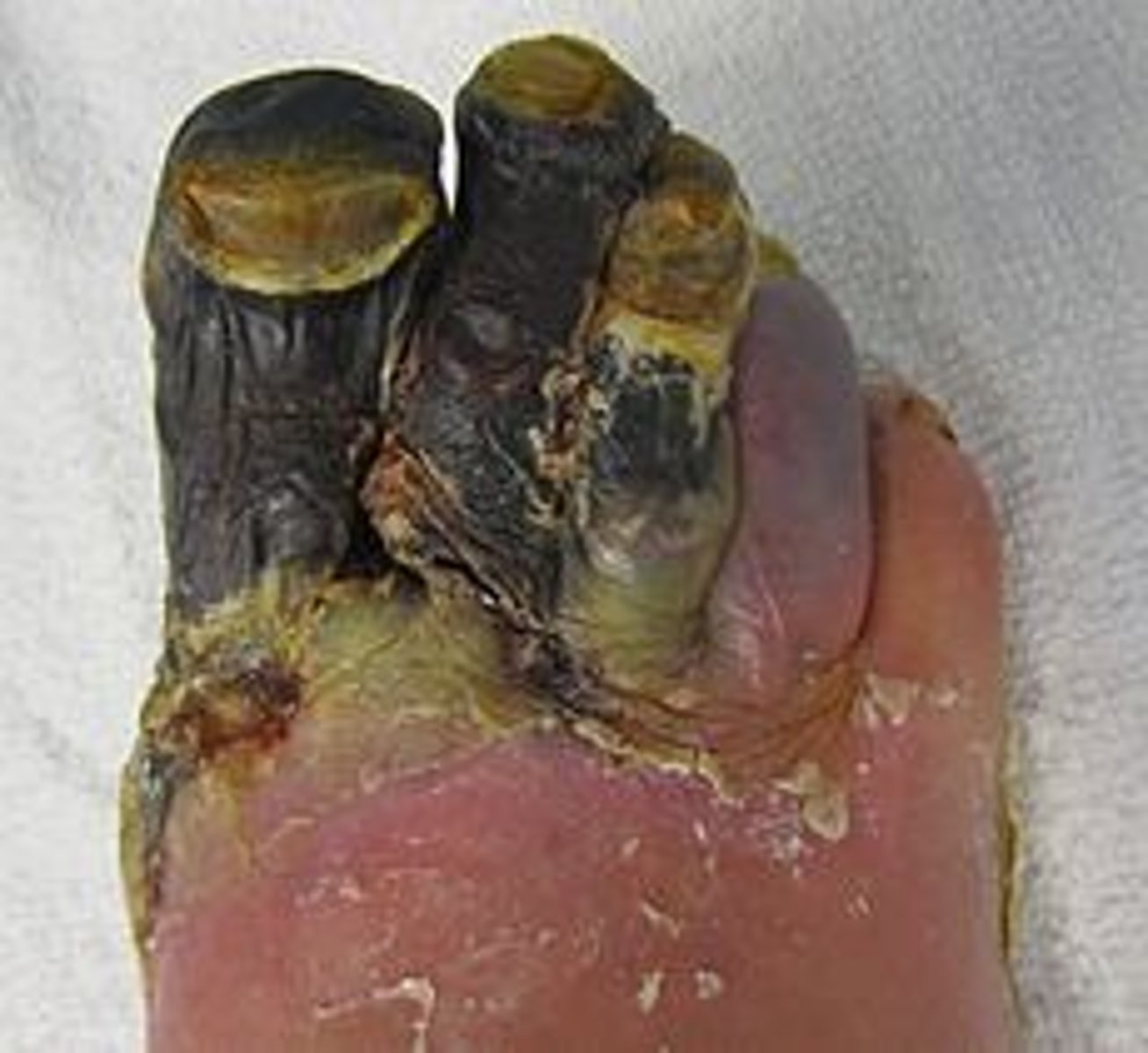
Gangrene
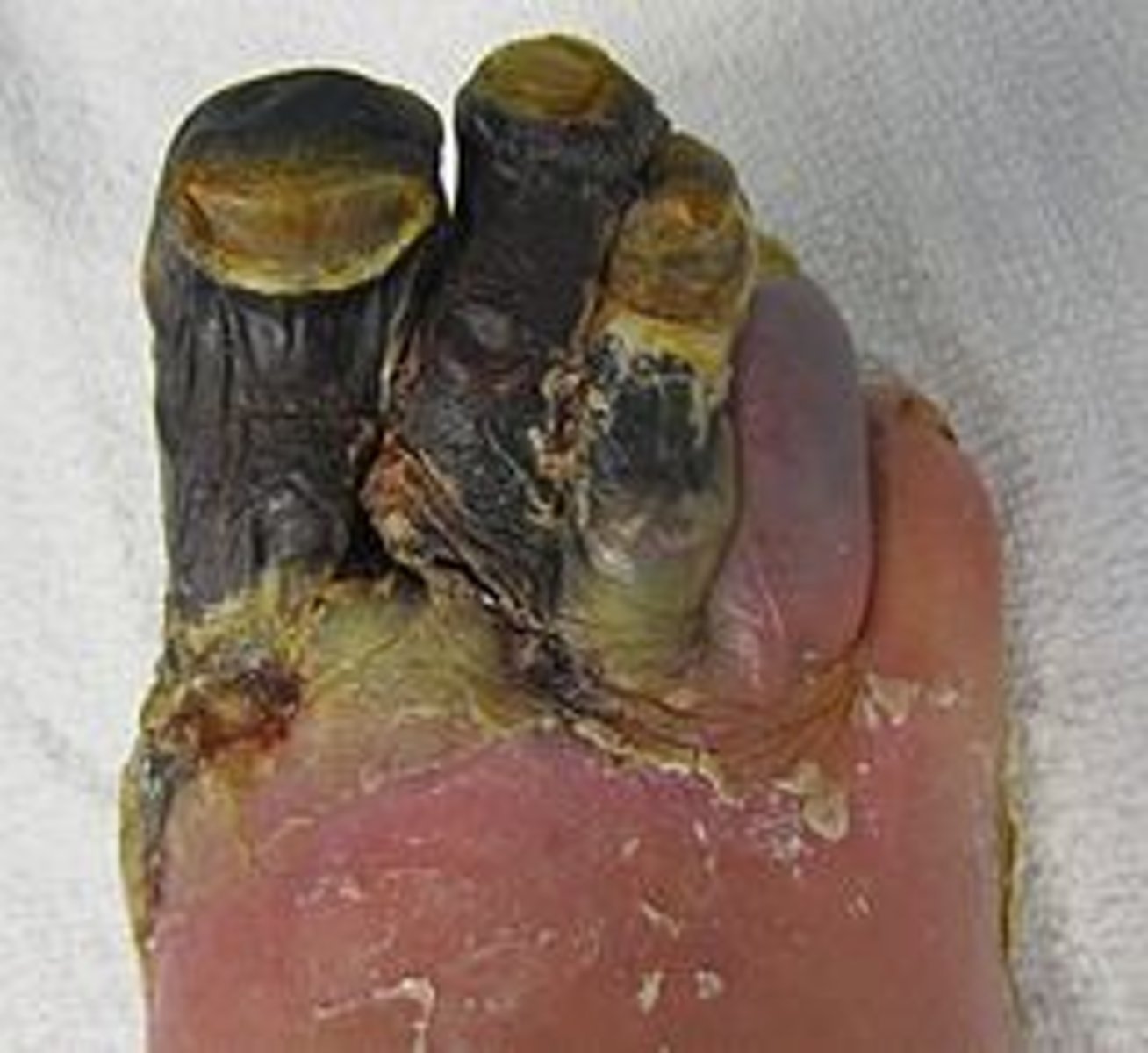
intermittent claudication
Gangrene presents as
Dead tissue typically dry, dark, cold, and contracted
Dry gangrene
stable and has circulation proximal to it
Wet gangrene
an area of gangrene that becomes secondarily infected by pus-producing bacteria
Dry vs wet gangrene
Dry - ischemia of tissue, looks mummified
its the better of the two
Wet - superimposed infection of dry gangrene (liquefactive necrosis)
Contributing Factors to Arterial Disease
-Hyperlipidemia/ elevated LDL
-Hypertension
-Smoking
-Advanced Age
-trauma
-diabetes
Chronic hypertension causes
thickening and loss of elasticity of the arterial wall
what hypertension is worse
systolic
1 multiple choice option
1 cigarette can do what
decreases wound and O2 saturation by 30% for an hour
Nicotine causes
vasoconstriction
Advanced airway
more susceptible to wounds
mechanical trauma
An injury that results when applied physical force exceeds the tensile strength of the tissue to which the force is applied.
thermal trauma
exposure to excessive heat or cold
chemical trauma
An injury caused by a chemical, such as an acid or an alkali
Diabetes causes
calcification of the arteries
calcification
hardens and narrows vessels
Hyperglycemia impairs
all 3 phases of wound healing
Hyperglycemia decreases
infection fighting ability
A1C
glucose over last 3 months
Normal a1c
less than 5.7%
Diabetic a1c
want it less than 7
ulcers are caused by
underlying pathologies
wounds are caused by
trauma
Pain arterial wounds
Severe unless masked by Neropathy
What increases pain in AI ulcers
elevation
Position of arterial ulcers
distal toes, dorsal foot, areas of trauma
Presentation of arterial ulcers
-Round, regular
-May conform to precipitating trauma
-Pale granulation tissue if present
-Possible necrotic tissue/black eschar
-Minimal or no bleeding/drainage
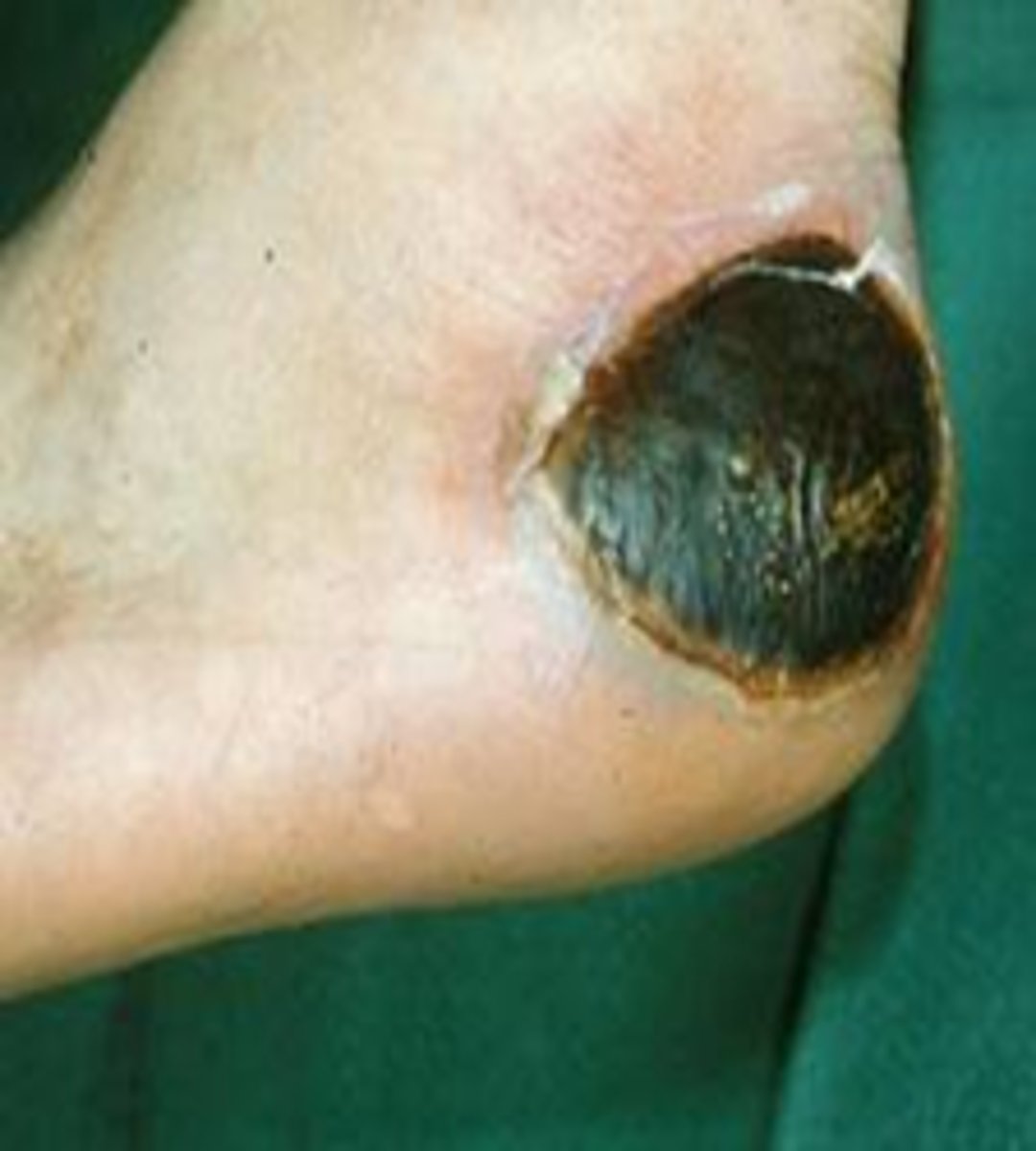
black eschar
Dead tissue forming a black scab.
gangrene
death of tissue associated with loss of blood supply
periwound and extrinsic tissue of arterial ulcer
-o Thin, shiny, anhydrous skin
-Lack of hair growth
-Thcikened yellow nails
o Pale, dusky, or cyanotic skin
o Dependent Rubor
o Edema unusual, may indicate VI or CHF
periwound
skin around the wound
anhydrous
lack of moisture
why no hair with AI
Lack of blood flow means no nutrients to grow hair
Pulses in Arterial Ulcers
decreased or absent
Temperature and arterial ulcers
cool or decreased
Characteristics of Arterial insufficient wounds
o Begin small and shallow
o Round and regular or conform to trauma
o Any granulation tissue will be pale or grey
o Necrotic tissue desiccated with black eschar
granulation tissue in arterial ulcers
pale or grey
Physical Therapist Tests for Arterial Insufficiency
o Pulses
o Doppler Ultrasound
o Ankle-Brachial Index
o Rubor of Dependency
o Capillary Refill
o Venous Filling Time
Grade 0 pulse
absent, unable to palpate
Grade 1 pulse
diminished
Grade 2 pulse
normal
3 pulse
bounding
Most common pulse occlusion site
The bifurcation of the common femoral artery
blood flow to dorsum of foot
dorsalis pedis
main foot blood supply
posterior tibial artery
Absence of palpable pules should be followed by
more sensitive testing
Just because a pulse is present does not mean
there is no underlying pathology
diabetic pulses
· bounding pulses from arteriosclerosis
femoral pulse site
femoral triangle just inferior to inguinal ligament halfway between pubic tubercle and ASIS
Popliteal artery is continuation
femoral artery
Posterior tibial pulse is between
FDL and FHL
Doppler ultrasound indication
decreased or absent pulses
Doppler ultrasound transducer angle
o parallel to blood flow but angled against the flow
doppler ultrasound assess
o arterial patency
ABI
ankle brachial index