Dielectrics and Magnetic Materials Overview
1/533
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
534 Terms
What is a dielectric?
A dielectric is an insulator that can be polarized.
What is the opposite of a conductor?
An insulator, which does not allow electric charge transport when an electric field is applied.
What is polarization in the context of dielectrics?
Polarization is the tendency to have charge separation in a material when an electric field is applied, without the charges becoming free.
What are two main functions of dielectrics?
1. Serve as insulators to prevent shorting or arcing in electrical applications. 2. Enhance the capacitance of capacitors.
What is a capacitor?
A capacitor is a device that stores charge on its plates.
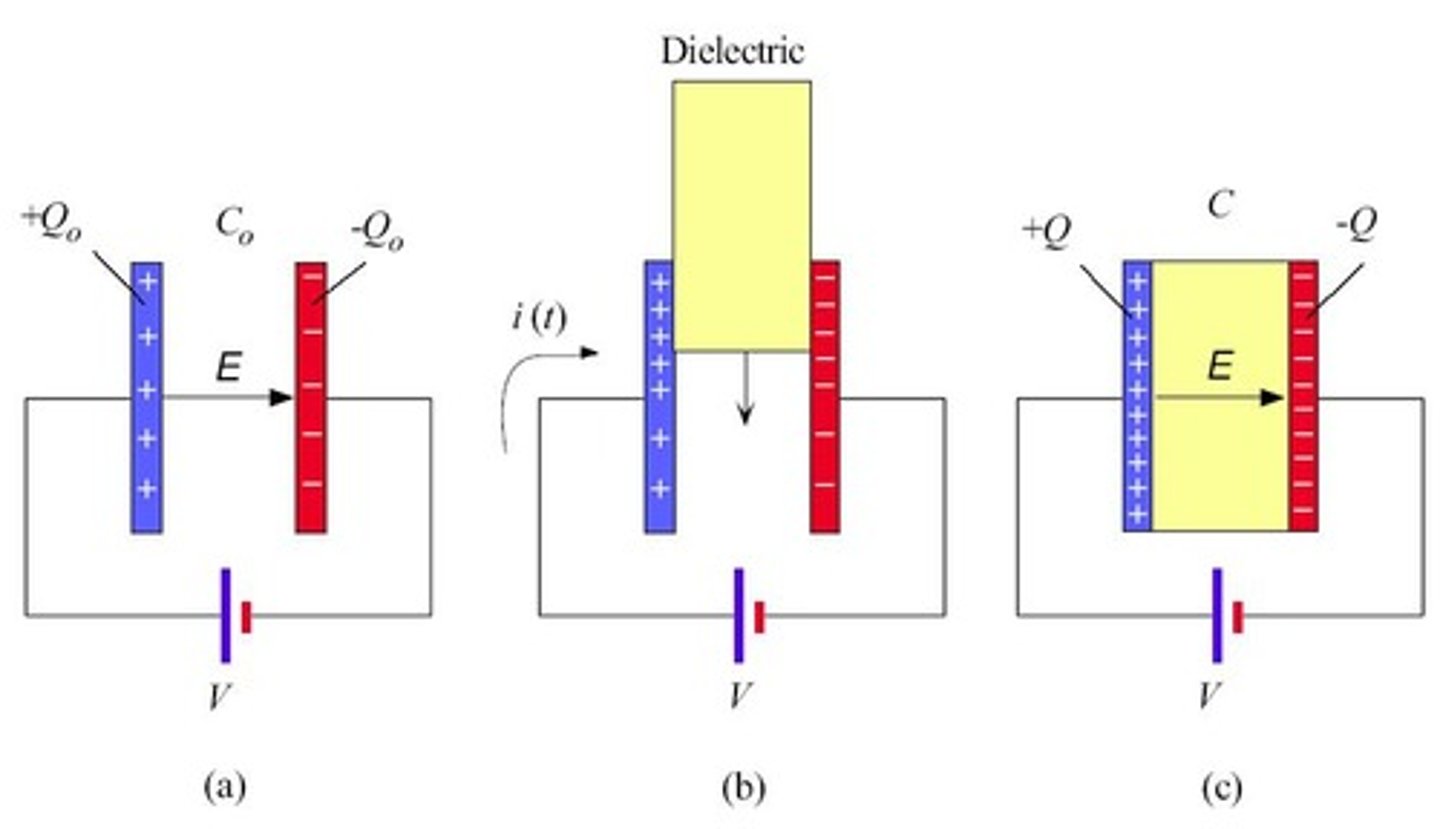
How does inserting a dielectric affect the capacitance of a capacitor?
Inserting a dielectric increases the capacitance, allowing more charge to be stored for a given voltage.
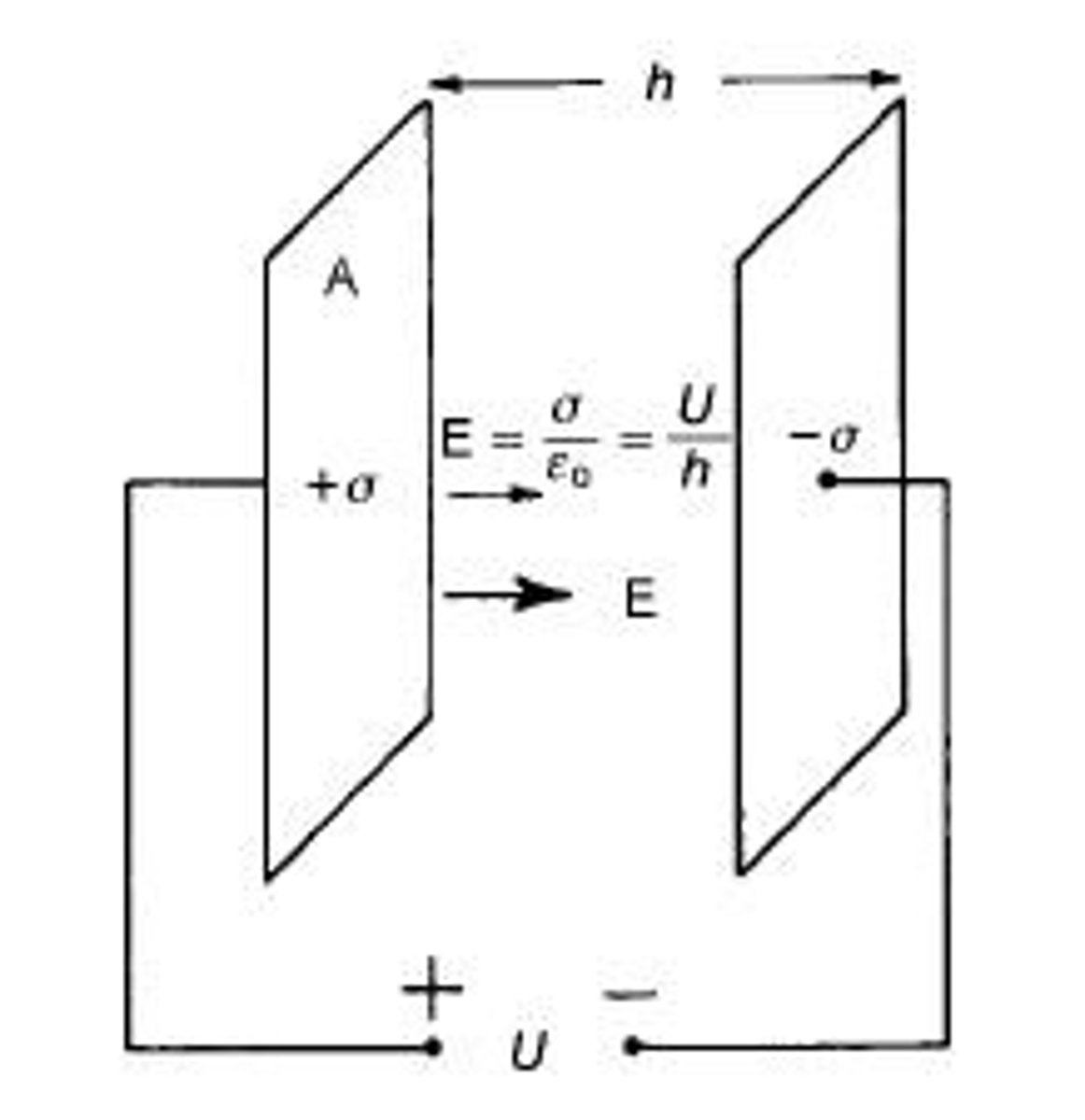
What is the formula for capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor in free space?
C = Q / U, where C is capacitance, Q is charge, and U is voltage.
What does the symbol ε0 represent?
The permittivity of free space, which is a constant value of 8.85 x 10^-12 F/m.
What is relative permittivity (εr)?
Relative permittivity is the measure of a substance's permittivity relative to that of a vacuum, ranging from 1 to several hundred.
What is the significance of the breakdown field in dielectrics?
The breakdown field indicates how much electric field (V/m) a dielectric can withstand before electric breakdown occurs.
What happens to the charge on the plates of a capacitor when a dielectric is inserted?
The charge on the plates increases due to the enhanced capacitance.
What is the relationship between plate area, plate separation, and capacitance?
Capacitance is proportional to the plate area and inversely proportional to the plate separation.
What is the role of dielectrics in capacitors?
Dielectrics enhance the charge storage capacity of capacitors by increasing their capacitance.
What is dielectric loss?
Dielectric loss refers to the energy lost as heat in a dielectric material when it is subjected to an alternating electric field.
What are some applications of dielectrics?
Dielectrics are used in power lines, various machine and device applications, and computers.
What is the effect of dielectric materials on electric fields?
Dielectric materials permit more electric field within them compared to a vacuum, which is described by their relative permittivity.
What is the significance of the Clausius-Mossotti relation?
The Clausius-Mossotti relation connects the macroscopic dielectric constant of a material to its microscopic polarizability.
What is the typical metric used to evaluate the quality of insulators?
The breakdown field (V/m) is the typical metric for evaluating insulators.
What is the difference between a vacuum and a dielectric?
A vacuum is an insulator but not a dielectric because it lacks substance to be polarized.
What is the effect of dielectric materials on the electric field in capacitors?
Dielectric materials increase the capacitance, allowing for more charge storage at a given voltage.
What are the main topics covered in Part III of the course?
Dielectric, Magnetic, and Optical Materials.
What are the dates for the exams in Part III of the course?
Exam for Part II: March 27; Exam III (Chapters 7-9): April 28.
What is polarization in a material with an applied electric field?
The tendency to have charge separation without the charges being free.
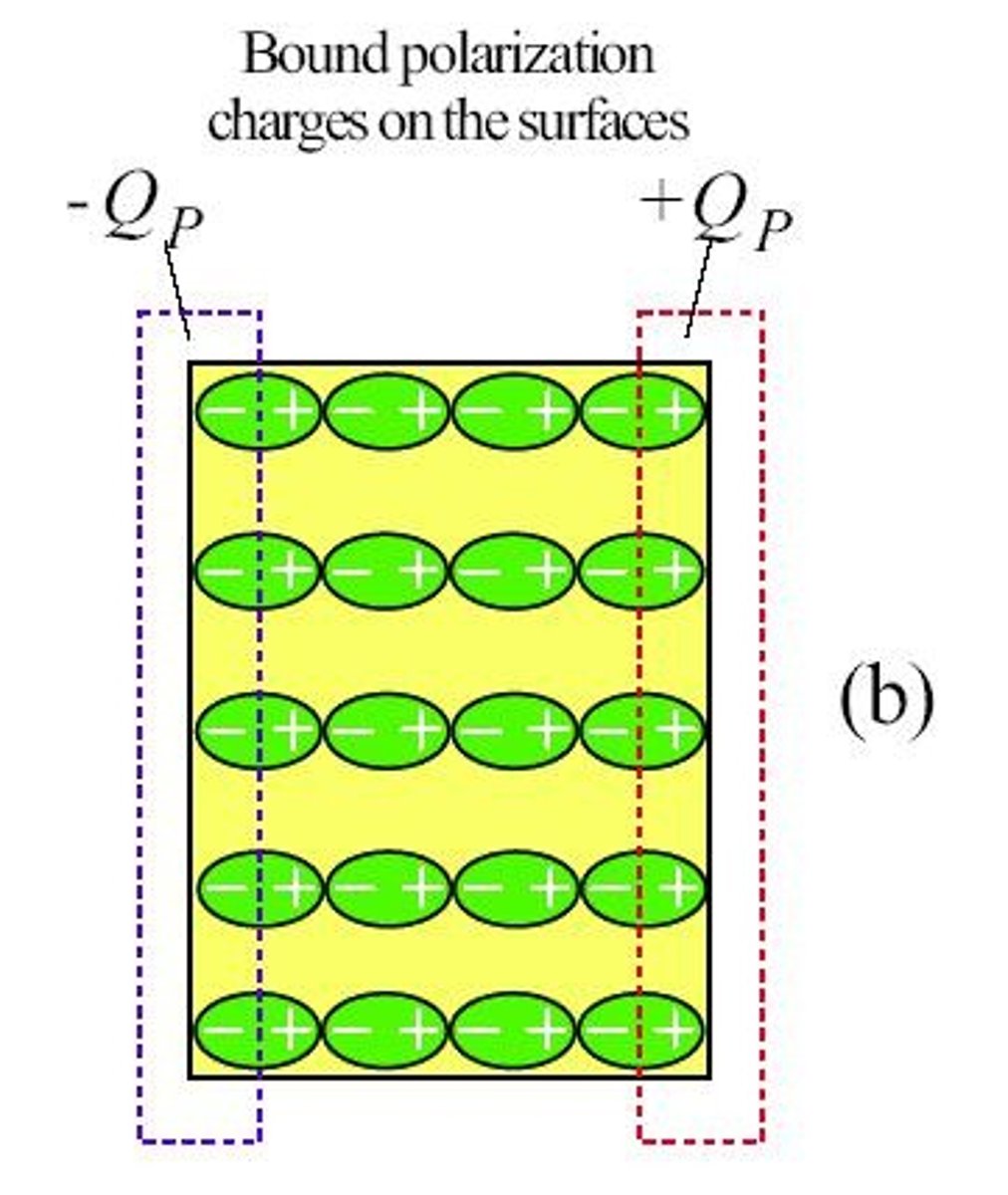
How does polarization affect capacitance and permittivity?
Polarization induces a surface charge on the dielectric, allowing a given voltage to push more charge to the plates, which increases capacitance (C) and permittivity.
How is polarization defined mathematically?
Polarization (P) is defined as the sum of all electric dipole moments divided by the total volume.
What is the formula for calculating polarization?
P = (p1 + p2 + ... + pN) / Volume, where p1, p2, ..., pN are the dipole moments.
What is an electric dipole moment?
The size of a balanced charge couple multiplied by the distance separating them.
What is the relationship between polarization and surface charge density?
Polarization (P) can be represented in terms of surface charge density (σp).
What happens to bound charges when a dielectric is placed in an electric field?
Bound polarization charges appear on the opposite surfaces of the dielectric.
What is the formula relating total charge on the plates to polarization?
σT = ε0 + σp, where σp = P.
What is the displacement field (D) in relation to electric charges?
D is the electric flux density that accounts for both free and bound charges.
What is electric susceptibility (χ)?
A measure of how much a material will become polarized in response to an electric field.
What is the definition of polarizability (α)?
Polarizability is the proportionality constant relating the induced dipole moment (pinduced) to the electric field (E).
What is the relationship between induced dipole moment and electric field?
pinduced = αE.
What is the formula for electronic polarization?
ZeE = βx, where Ze is available charge, β is a constant, and x is the displacement.
What does the term 'unbalanced charges' refer to in the context of dielectrics?
It refers to the charges that appear on the surfaces of a dielectric when placed in an electric field.
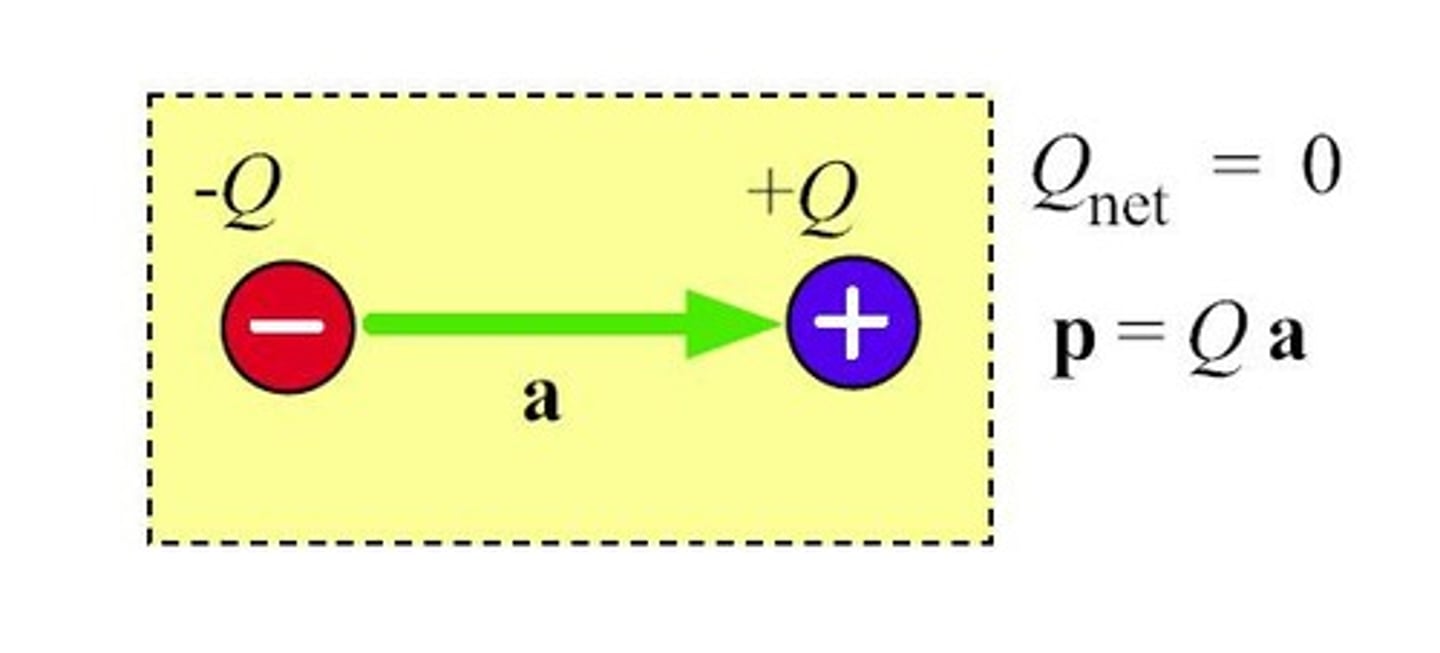
What is the significance of the average dipole moment (pav) in polarization?
pav is the average dipole moment per molecule used to calculate total polarization.
What is the relationship between electric field (E) and polarization (P) in linear dielectrics?
In linear dielectrics, P is proportional to E.
What is the formula for the total polarization charge density on the surface?
P = σp, where σp is the polarization charge density.
What are the four types of forces described in the context of displacement and polarization?
Forced, unforced (free), damped, and undamped.
What is the role of the restoring force in electronic polarization?
The restoring force counteracts the displacement caused by the electric field, maintaining equilibrium.
How is the displacement field (D) related to free and bound charges?
D accounts for both free charge density (σ) and bound charge density (P).
What does the term 'damped' refer to in the context of forces acting on a system?
A system is damped if the damping coefficient (c) is greater than zero.
What is the significance of the constant β in the context of electronic polarization?
β relates to the restoring force and is used to calculate the induced dipole moment.
What is the equation of motion for electronic polarization?
−𝛽𝑥 = 𝑍𝑚𝑑²𝑥/d𝑡².
What is the solution to the equation of motion for electronic polarization?
𝑥𝑡 = 𝑥0cos(𝜔0𝑡), where 𝜔0 = √(𝛽/𝑍𝑚).
What does 𝜔0 represent in the context of electronic polarization?
The electronic polarization resonance frequency.
How is the average space charge density (𝜌𝑒) calculated for electrons uniformly distributed within an atomic radius (r0)?
𝜌𝑒 ≈ −(𝑍𝑒)/(4/3π𝑟0³).
What electric field (𝐸𝑟) is generated when charge is displaced from the centroid?
𝐸𝑟 = 𝜌𝑒𝑥/(3𝜖₀) ≈ (𝑍𝑒𝑥)/(4π𝜖₀𝑟0).
What is the expression for the restoring force (𝐹𝑟) in electronic polarization?
𝐹𝑟 = −(𝑍𝑒)𝐸𝑟 = (𝑍𝑒)²𝑥/(3) = −𝛽𝑥/(4π𝜖₀𝑟0).
What is the classical electronic polarizability (αe) in relation to β?
αe ≈ (4πε₀r₀/3)β.
What are the atomic radii (r0) and polarizability (αe) values for Sodium (Na) in Period 3?
Z = 11, r0 = 190 pm, αe = 26.8 × 10⁻⁴⁰ F m².
What is the relationship between relative permittivity (εr) and polarizability (α)?
εr = 1 + χ, where χ = Nαe/ε₀.
What is the Clausius-Mossotti equation?
It relates the macroscopic properties of materials to atomic level properties, specifically the local field and polarization.
What factors must be considered to calculate the true local field in a polarized dielectric?
1. The depolarizing field. 2. The field due to other dipoles in the medium. 3. Direct contributions from nearby dipoles.
How is the electric field inside a dielectric expressed?
E = E₀ + Edep, where E₀ is the field due to free charges and Edep is the depolarization field.
What is the depolarization field (Edep) in a dielectric?
Edep = P/ε₀, where P is the polarization.
What is the significance of the depolarization factor (N) in a dielectric?
N ranges from 0 to 1, affecting the depolarization field based on the shape of the dielectric.
What is the relationship between the polarization charge density and the polarization vector?
The polarization charge density on the surface is related to the normal component of the polarization vector.
What does the term 'local field' refer to in the context of dielectrics?
The actual electric field acting on molecules within a polarized dielectric.
What is the approximate nature of the equation relating χe and αe?
The equation is approximate because it assumes the field for αe is the field experienced by the dipole, not the applied field.
What is the trend observed in electronic polarizability (αe) versus atomic radius (r0) for elements in Period 3?
The basic trend shows a functional dependence, but the actual slope and values may differ from classical theory.
What is the significance of the dashed line in the graph of electronic polarizability versus r0³?
It represents the best fit passing through the origin, indicating the relationship between polarizability and atomic radius.
What is the approximate relationship between the induced polarization (P) and the electric field (E)?
P = Npinduced = NαE.
How does the electric field inside a dielectric differ from the applied field?
The electric field inside is influenced by both free charges and the polarization of the dielectric.
What is the role of the average space charge density in determining electric fields in atoms?
It provides a basis for calculating the electric field generated by displaced charges within the atomic structure.
What is the significance of the polarization surface charges in a dielectric?
They contribute to the local electric field and affect the overall polarization of the material.
What is the local electric field (Eloc) in a dielectric material?
Eloc = Emedium + ES + Edipoles, where Emedium is the external field, ES is the field due to surface charges, and Edipoles is the field due to dipoles.
What is the Clausius-Mosotti relation?
The Clausius-Mosotti relation connects the polarization P, the electric field E, and the polarizability α, valid for cubic systems and glasses.
What are the mechanisms of polarization in materials?
1. Electronic Polarization of isolated atoms or noble gases 2. Electronic Polarization of Covalent Solids 3. Ionic Polarization 4. Orientational Dipolar Polarization 5. Interfacial Polarization.
How does electronic polarization occur in noble gases?
It occurs due to the shift of the valence electron cloud of the ions within the materials with respect to the positive nucleus, typically at frequencies around 10^15 Hz.
What happens to covalent solids under an applied electric field?
The valence electrons in covalent bonds shift with respect to the positive ionic cores, resulting in polarization of the solid.
What is ionic polarization?
Ionic polarization occurs when ions in a crystal lattice are displaced under an electric field, leading to a net dipole moment per ion.
Describe the process of orientational dipolar polarization.
In the absence of an electric field, thermal agitation results in zero net dipole moment. When an electric field is applied, dipoles align with the field, creating a net dipole moment.
What is the formula for average dipole moment in orientational polarization?
P = p0 * (kT / E), where pav is the average dipole moment, po is the permanent dipole moment, E is the electric field, k is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the temperature.
What is the significance of the Lorentz relation in dielectric materials?
It explains that polarizable objects inside a dielectric feel enhanced fields due to the background of surface charges.
What is the relationship between local electric field and polarization?
The local electric field Eloc is influenced by the polarization P, as it includes contributions from the external field and the induced dipoles.
What is the effect of temperature on dipolar orientational polarizability?
Dipolar orientational polarizability is strongly temperature-dependent, affecting the alignment of dipoles in an electric field.
How does interfacial polarization occur in dielectrics?
Interfacial polarization occurs when mobile ions migrate toward fixed charges in the presence of an electric field, causing a separation of charge.
What is the formula for the Clausius-Mosotti relation in terms of polarizability?
𝜒 = Nα / (1 + (𝜒/3)), where χ is the electric susceptibility, N is the number of polarizable entities per unit volume, and α is the polarizability.
What does the term 'Edipoles' refer to in the context of local electric fields?
Edipoles refers to the electric field contribution from the dipoles present in the material.
What is the role of the Boltzmann constant (k) in the context of dipolar polarization?
The Boltzmann constant relates temperature to the energy distribution of dipoles, influencing their alignment in an electric field.
What is the relationship between the electric field and the induced polarization in a dielectric?
The induced polarization P is proportional to the local electric field Eloc, which is affected by the applied field and the material's properties.
How does the index of refraction relate to electronic polarizability?
The index of refraction of a material depends on its electronic polarizability, which affects how light interacts with the material.
What happens to the dipole moment of HCl molecules in an electric field?
In an electric field, HCl dipoles experience a torque that aligns them with the field, resulting in a net dipole moment.
What is the significance of the term 'Pinduced' in the context of polarization?
Pinduced represents the polarization induced in a material due to the applied electric field.
What is the formula relating polarization and electric field in the context of Clausius-Mosotti?
P = NαEloc, where P is the polarization, N is the number of dipoles per unit volume, and Eloc is the local electric field.
What does the term 'Demag corrected' refer to in the context of electric fields?
Demag corrected refers to the adjustment made to account for the demagnetizing effects in the calculation of the electric field in a material.
What is the effect of surface charges on the local electric field in a dielectric?
Surface charges create additional electric fields that enhance the local electric field experienced by polarizable objects within the dielectric.
What phenomenon occurs at grain boundaries and interfaces between different materials?
Interfacial polarization.
How do positive and negative ions behave within a grain boundary under an electric field?
They can jump to neighboring vacant sites, forming dipoles.
What are the typical polarization mechanisms listed in the notes?
Electronic, ionic, and orientational polarization.
What is the static dielectric constant (εr) of Argon gas?
1.0005.
What is the static dielectric constant (εr) of water?
80
What is the Clausius-Mossotti equation used for?
It relates the dielectric constant to the polarizability of atoms or ions in a material.
What does εr represent in the Clausius-Mossotti equation?
The dielectric constant.
What are the two types of dielectric response characterized in the notes?
Resonant and relaxation responses.
What is the difference between resonant and relaxation responses in dielectric materials?
Resonance involves a Hooke's law response of bound particles, while relaxation involves non-interacting dipoles rotating in a medium with friction.
What does the relaxation time (τ) represent in the context of dipolar relaxation?
The time it takes for the induced dipole moment to respond to a change in the electric field.
What is the equation for the rate of change of the induced dipole moment?
dp/dt = -αd(E - E0)/τ.