Chapter 32: The Deuterostomes in Animal Kingdom
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Adaptive radiation
Formation of many new species from an ancestral species, often occurs rapidly in geological time when a new niche opens up.
Arboreal
Living in the trees.
Cloaca
Common exit point shared by reproductive, excretory and digestive systems (literal translation is sewer).
Desiccate
Dry out from lack of water (dehydration).
Ectothermic
Animal whose body heat goes up and down with changes in the external environmental temperature, 'cold blooded'.
Endothermic
Animal whose body heat is maintained independent of the external temperature.
Eutheria
Animals that nourish the embryo via a placenta.
Metamorphosis
Undergo a change in body form from one developmental stage to another.
Metatheria
Animals that raise their young in a pouch (e.g. kangaroos).
Oviparous
Animals that lay eggs and embryo is nourished by the yolk.
Ovoviviparous
Animals that incubate an egg internally, embryo gets nourishment from the yolk, and have live births.
Protheria
Egg laying mammals (e.g. duckbilled platypus).
Viviparous
Animals where the young develop inside the uterus and nutrients are transferred from mother to embryo.
Deuterostomic development
Developmental pattern characterized by the formation of the anus from the blastopore.
ancestral features for deuterstomes
multicellularity - Organisms composed of multiple cells.
tisses - three layers
triploblastic
bilateral symmetry
true coelom
Segmentation
The division of the body into repetitive segments.
Endostyle
Ciliated groove in urochordates and cephalochordates involved in transporting food to the esophagus; in vertebrates, it is the thyroid gland.
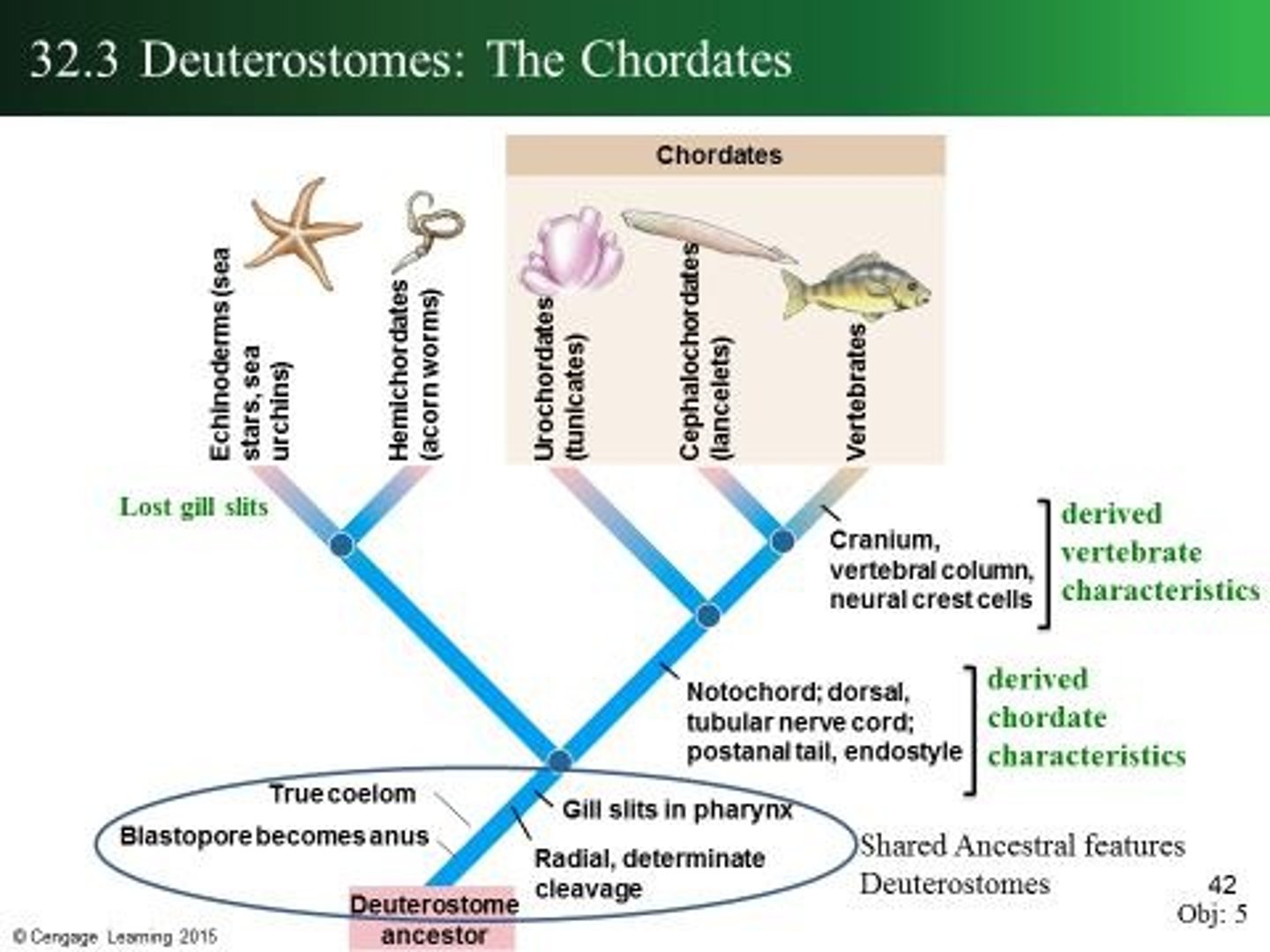
Phylum Echinodermata
A group of marine animals including starfish.
phylum echinodermata: habitat
Marine environments.
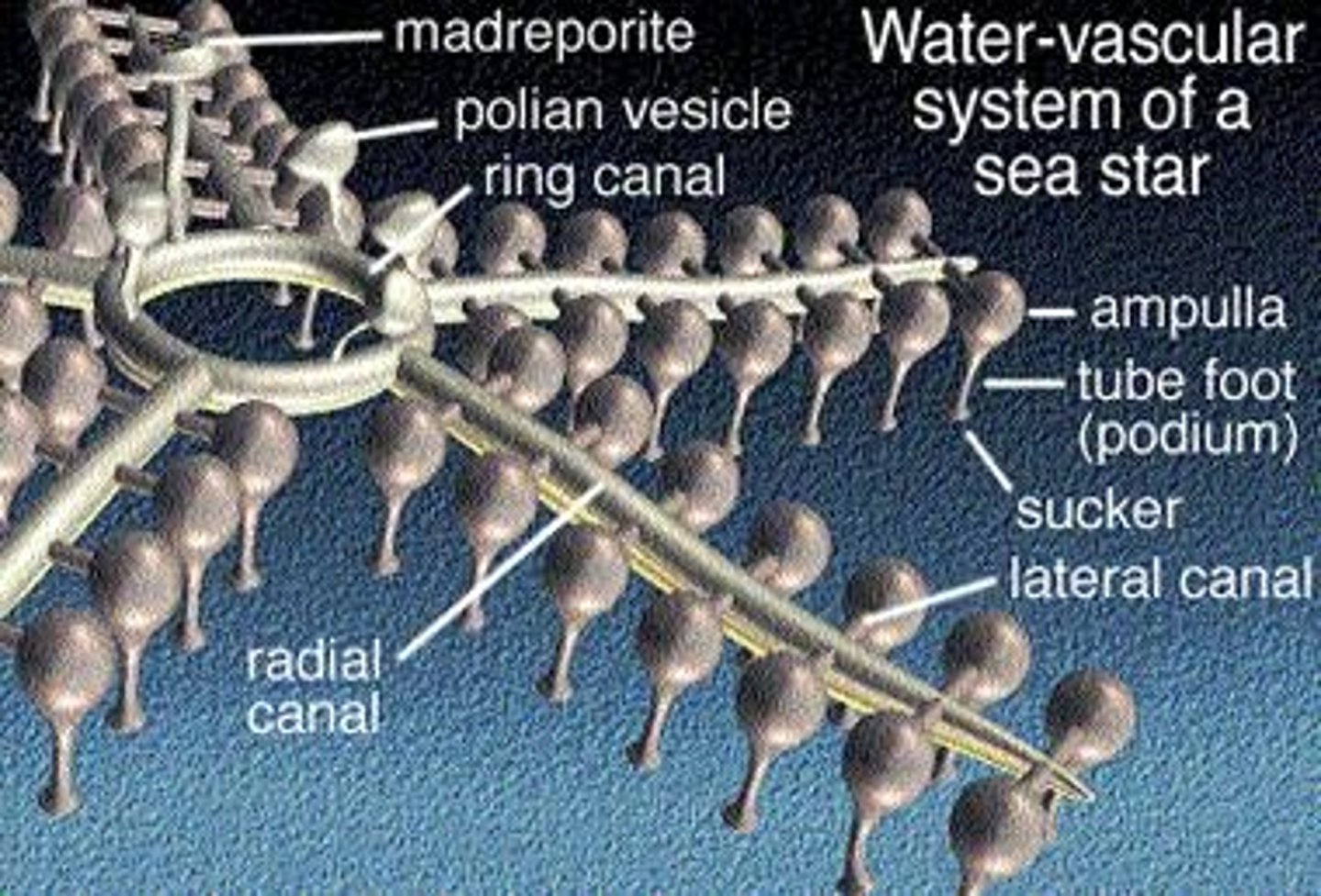
phylum echinodermata: Water-vascular system
Derived defining characteristic used for feeding, gas exchange, and hydrostatic skeleton.
phylum echinodermata: Symmetry
Bilateral in larvae and pentaradial in adults.
phylum echinodermata: Body surfaces
Oral surface- on the bottom
aboral surface- outside or on top.
phylum echinodermata: Madreporite
Silk-like structure on the outside of echinoderms.
Asteroidea
Class of echinoderms that includes sea stars.
Crinoidea
Class of echinoderms that includes sea lilies and feather stars.
Echinoidea
Class of echinoderms that includes sea urchins and sand dollars, characterized by a round flat body with no arms.
Skeleton of Echinoidea
Interlocking calcium carbonate plates called a test.
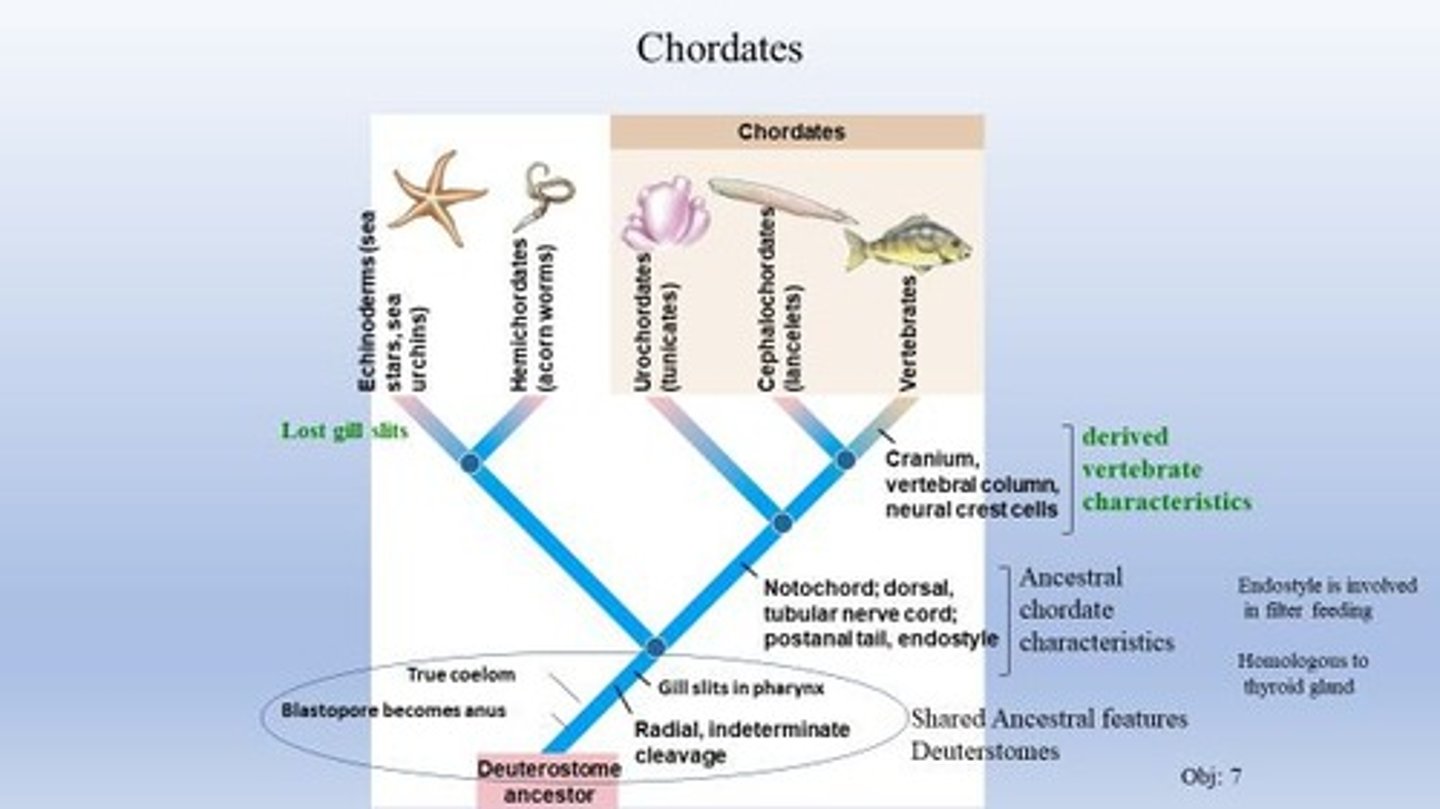
Deuterostomes
A major group of animals that includes echinoderms and chordates.
Phylum Chordata
A phylum that includes all chordates.
Subphylum Urochordata
Invertebrate chordates, including tunicates.
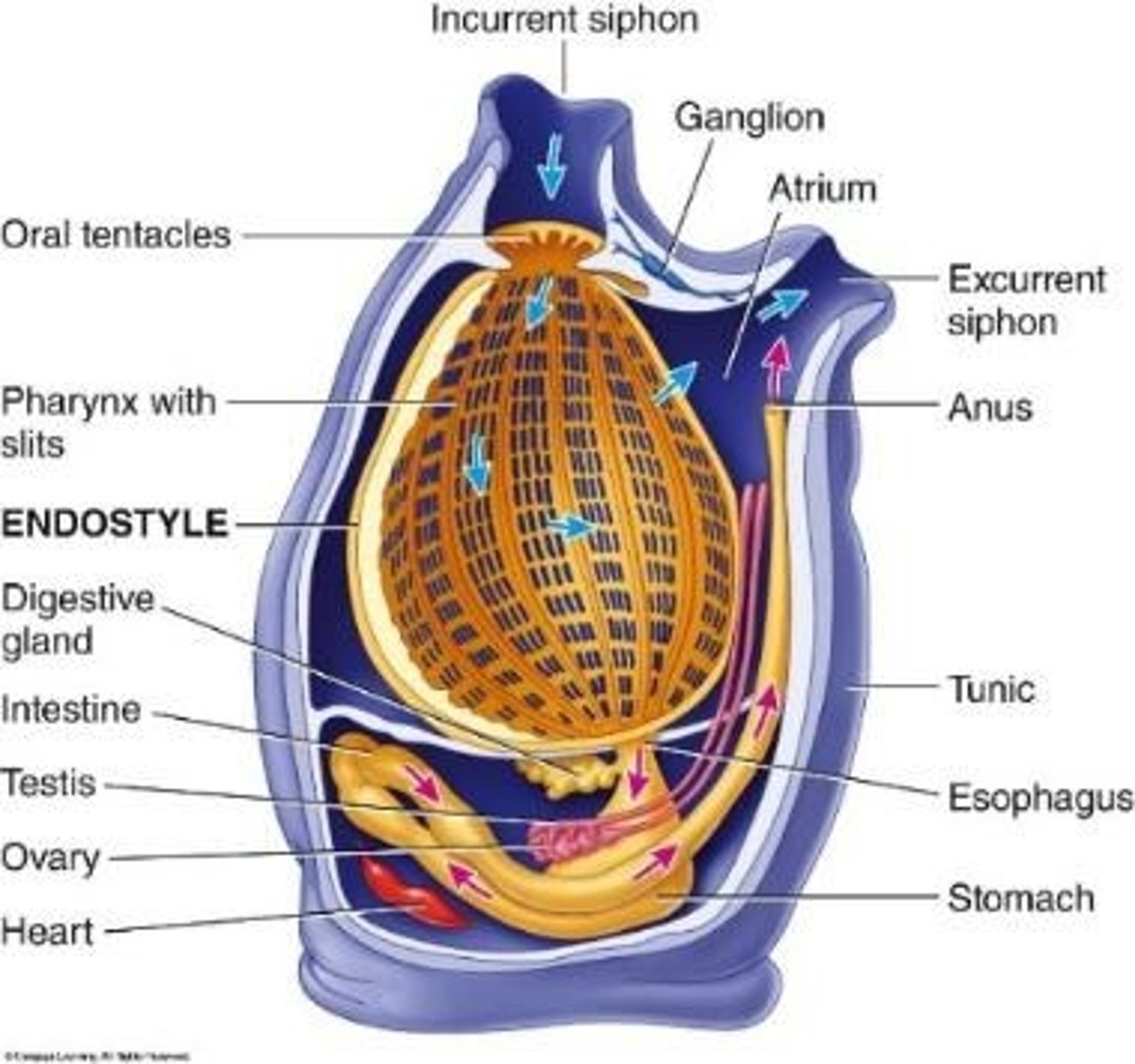
Tunicates
Sea squirts and relatives with a carbohydrate tunic and openings for siphoning.
urochordate features in Larva
All chordate features present and swims.
urochordate features in Adult
Only gill slits present and is sessile.
Feeding in Urochordata
Suspension feeders.
Subphylum Cephalochordata
Invertebrate chordates with all four chordate features in adults.
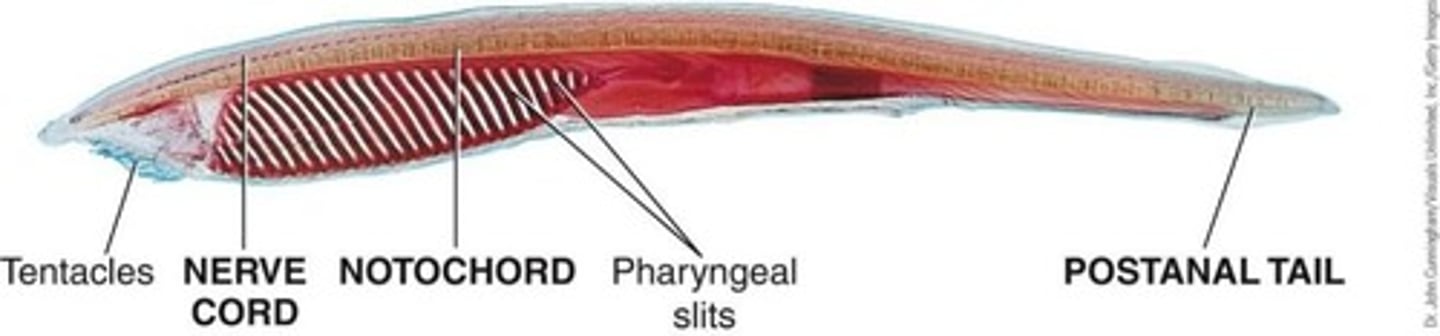
Feeding in Cephalochordata
Filter feeders.
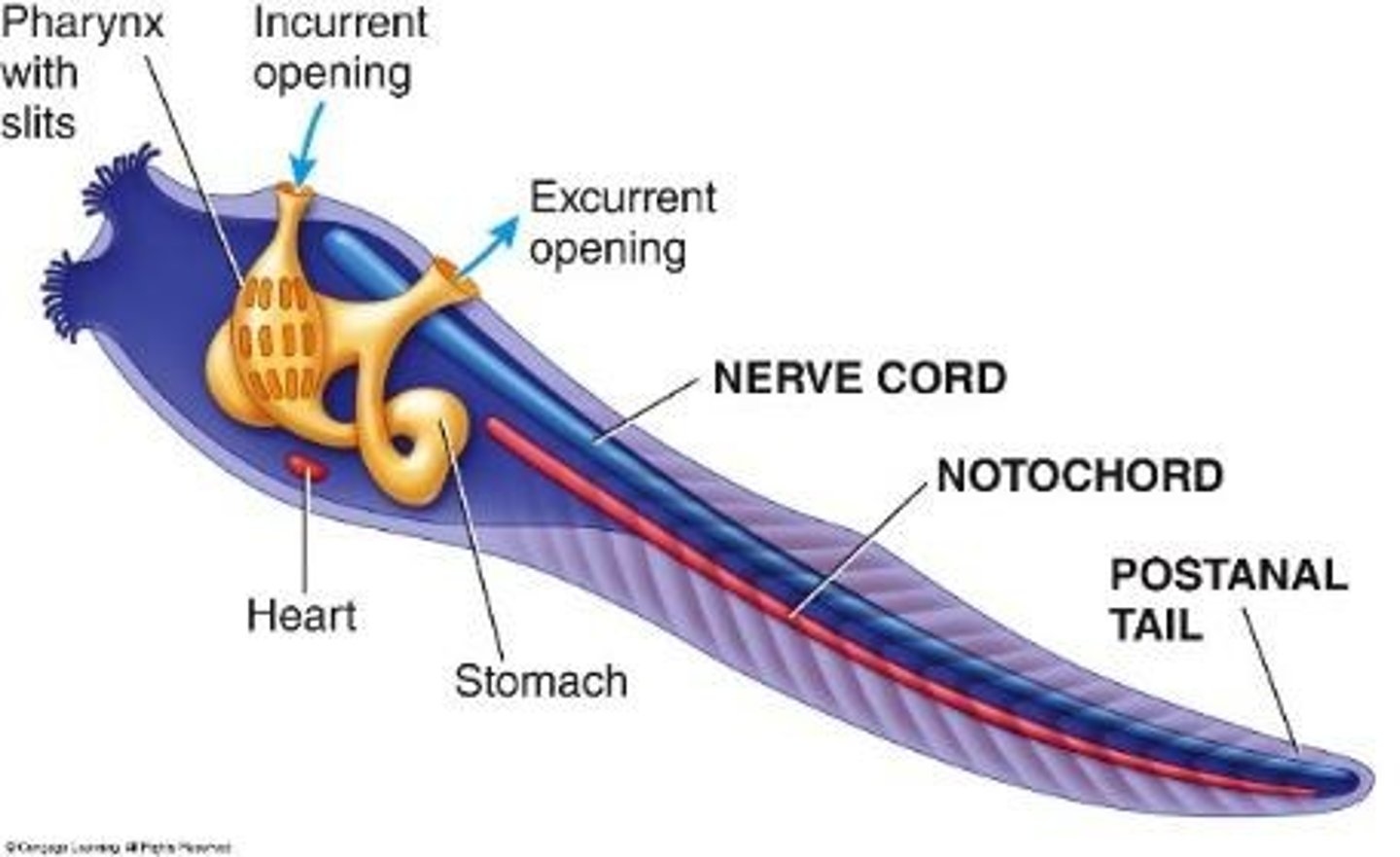
Genus Branchiostoma (subphylum cephalochordata)
gill plus mouth; originally Amphioxous: sharp on both sides.
example of cephalochordata: Fin ray
Blue lining along the outside of the body.
Distinguishing features of vertebrates
Includes vertebral column, pronounced cephalization, brain in cranium, neural crest cells, and Hox gene clusters.
Neural crest cells
Influence the development of many structures including melanocytes, smooth muscle, nerves, and craniofacial cartilage.
Hox gene clusters
Involved in the regulation of development and code for transcription factors.
Systems in vertebrates
circulatory system, digestive system, endocrine system, and endoskeleton.
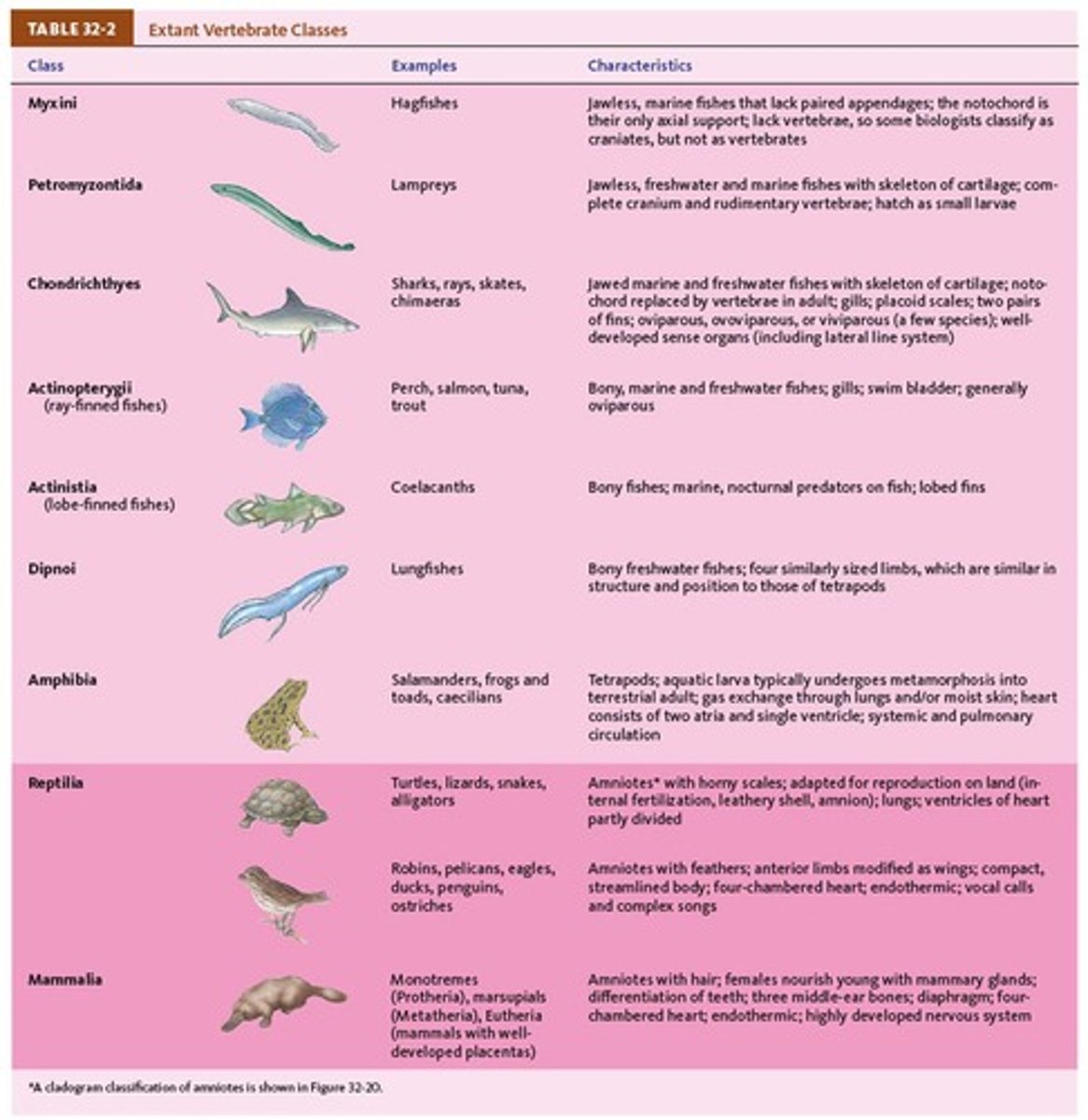
Jawless Fish
Craniate jawless fish
hagfish- class myxini
Habitat of Hagfish
Marine only.
Cranium of hagfish
Brain enclosure.
Teeth of Hagfish
Keratin and on tongue (no jaws) can grasp prey.
Notochord
Flexible cartilage rod.
hagfish- no true vertebrae, partially enclosed nerve cord
Fins of Hagfish
No true fins, long dorsal fold.
Feeding of Hagfish
Either scavenger or predator - mostly scavenger.
Defense of Hagfish
Secretes slim- covers gills of attacking fish or prey.
Body tonicity of Hagfish
Only craniate isosmotic with salt water (ocean/marine environment).
Lampreys (Class Pteromyzontida)
oldest living vertebrate lineage, jawless vertebrae
Habitat of Lampreys
Marine, freshwater, estuaries.
Lifestyle of Lampreys
Parasites.
Cartilaginous Fish
(Class Chondrichthyes) Jawed fishes.
Habitat of Cartilaginous Fish
Mostly marine - some freshwater skates.
Skeleton and cranium of Cartilaginous Fish
Cartilage infused with calcium salts.
Teeth of Cartilaginous Fish
Replaceable modified scales.
Scales of Cartilaginous Fish
Placoid (tooth like), non overlapping.
Gill opening of Sharks
Lateral in sharks.
Cloaca
Common opening to outside for three systems: Reproductive, excretory, digestive (birds and amphibians too).
Sexual dimorphism in Cartilaginous Fish
Clasper (paired) - cartilaginous extensions of male pelvis fin.
examples of Oviparous animals
skates, some sharks, birds, reptiles, fish.
examples of ovoviviparous animals
many sharks, snakes, fish.
examples of Viviparous animals
some sharks, most mammals.
Chordates (Class Osteichthyes)
Bony fish, Jawed fish
Habitat of Class Osteichthyes
Freshwater and marine.
Skeleton and cranium of Class Osteichthyes
Calcified.
Teeth of Class Osteichthyes
Replicable.
Fins of Class Osteichthyes
Paired, supported by cartilage or bone.
Mouth of Class Osteichthyes
Anteriorly directed.
Gills of Class Osteichthyes
Internal, covered by operculum - lid.
Swim bladder in bony fish
Buoyancy - gas exchange in some.
Ray-finned bony fish
Most fish - rays of cartilage or bone run length of fin.
Lobe-finned bony fish
Some use lungs instead of gills - give rise to land dwelling tetrapods.
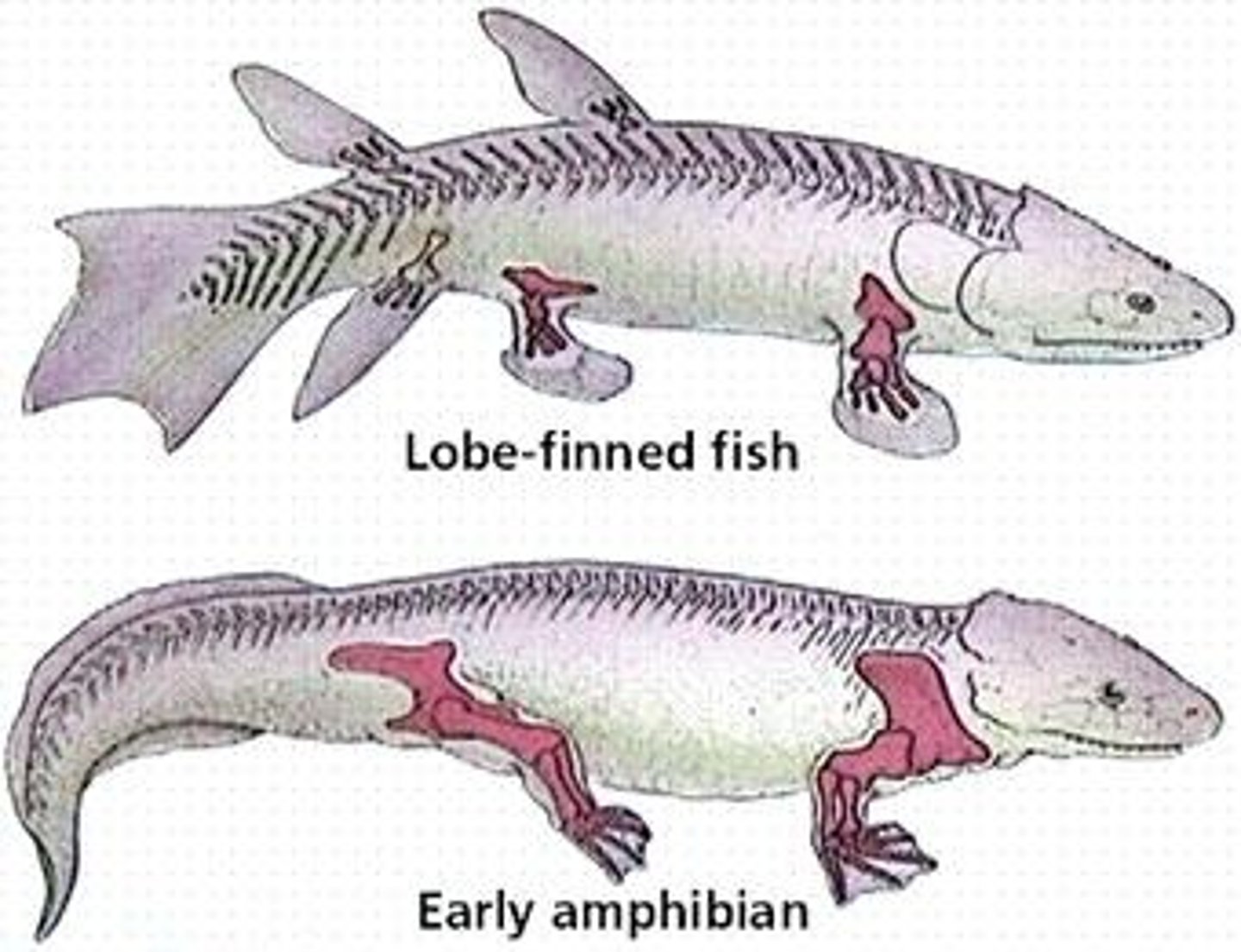
Class Amphibia
Having two lifestyles (one in water and one on land).
Metamorphosis in class amphibia
Many complete - some adults (salamanders) retain many larval characteristics (paedomorphosis).
Respiratory organ of Amphibians
Lungs, gills, skin.
Heart of Amphibians
Three chambers (two atria and one ventricle).
Amphibian orders
Urodela (or Caudata) - visible tail; Anura - no tail; Apoda - no feet.
Aminote egg
An egg that is adapted for life on land, allowing for the development of embryos in a protective environment.
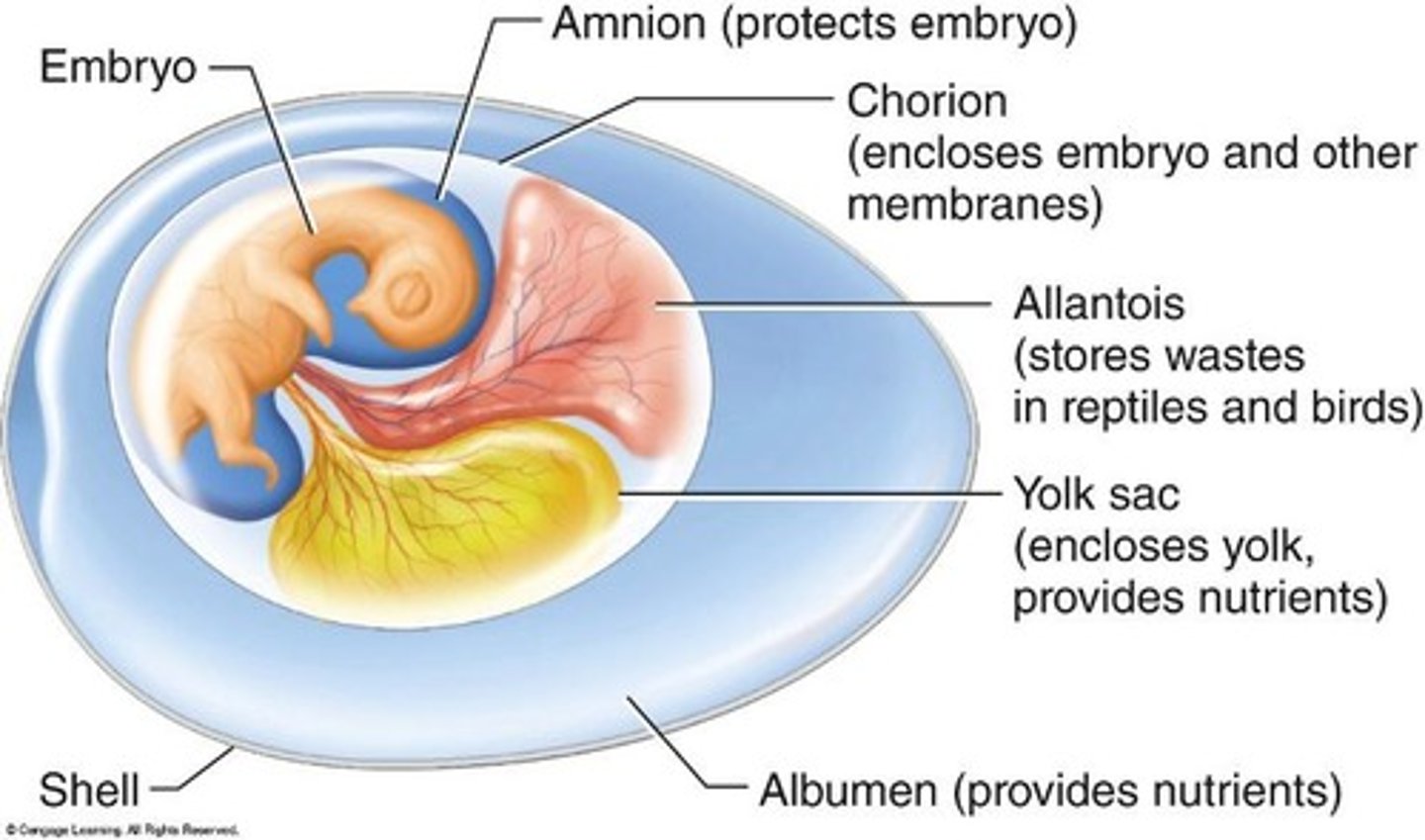
Amnion
A fluid-filled sac that surrounds the embryo, providing cushioning and protection.
Class Reptilia
A class of animals characterized by their shelled eggs, hard scales, and ectothermic physiology.
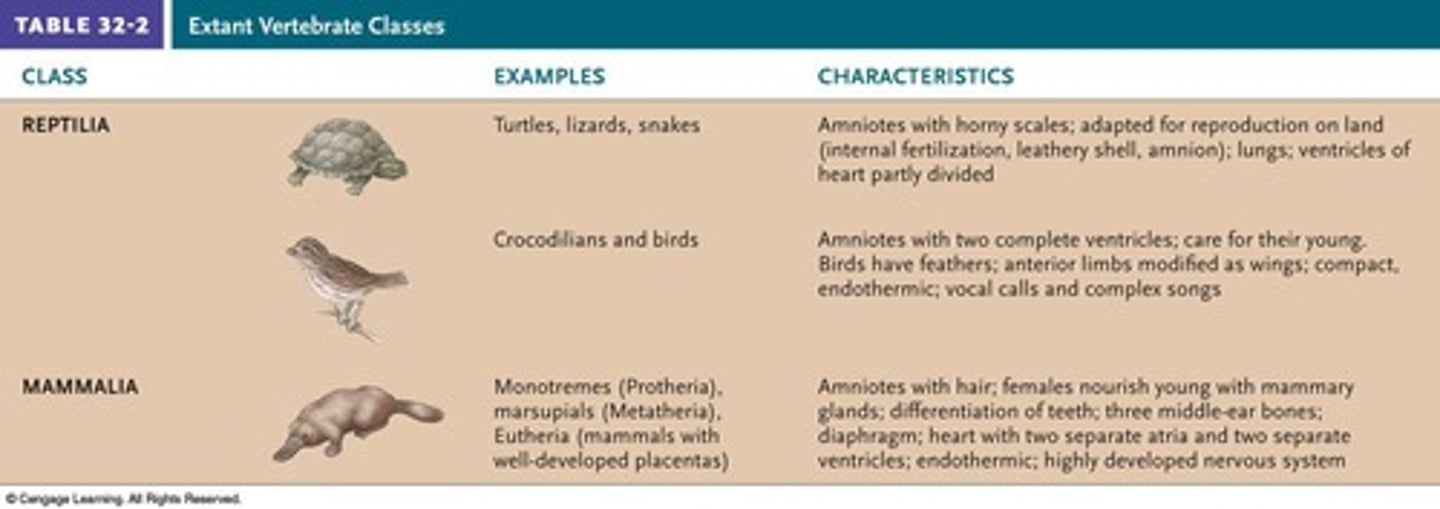
Three-chambered heart in class reptilia
A heart structure in reptiles that separates oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood.
Ectotherms in class reptilia
Organisms whose body temperature changes with the surrounding environment.
Order Testudines
bony shell overlaid by horny scales
vertebrae and ribs are fused to shell, pelvic and pectoral girdles lie inside ribs
mouth covered by beak, no teeth
includes turtles, terrapins, and tortoises.
Carapace
The top, dorsal part of a turtle's shell.
Plastron
The bottom, ventral part of a turtle's shell.
Order Squamata
loosely articulated jaws, hinge construction
elastic skin
tongue used for touch and smell
pit organ used to detect heat from endothermic prey
ecdysis (molt)
includes lizards, snakes, and worm lizards.
Komodo dragon
A large lizard known for its infectious bite and scavenging behavior.
Order Crocodilia
live in swamps, rivers or along seacoasts
feed on various kinds of animals
includes crocodiles, alligators, caimans, and gavials.
Superorder Archosauria
A superorder that includes crocodiles and birds.
Class Aves
The class of animals that includes modern birds, characterized by feathers and beaks.
Palaeognaths
A clade of flightless birds including ostriches, kiwis, and emus.
Neognaths
A clade of birds that are mostly capable of flight.
Class Mammalia
The class of animals characterized by the presence of mammary glands and hair.
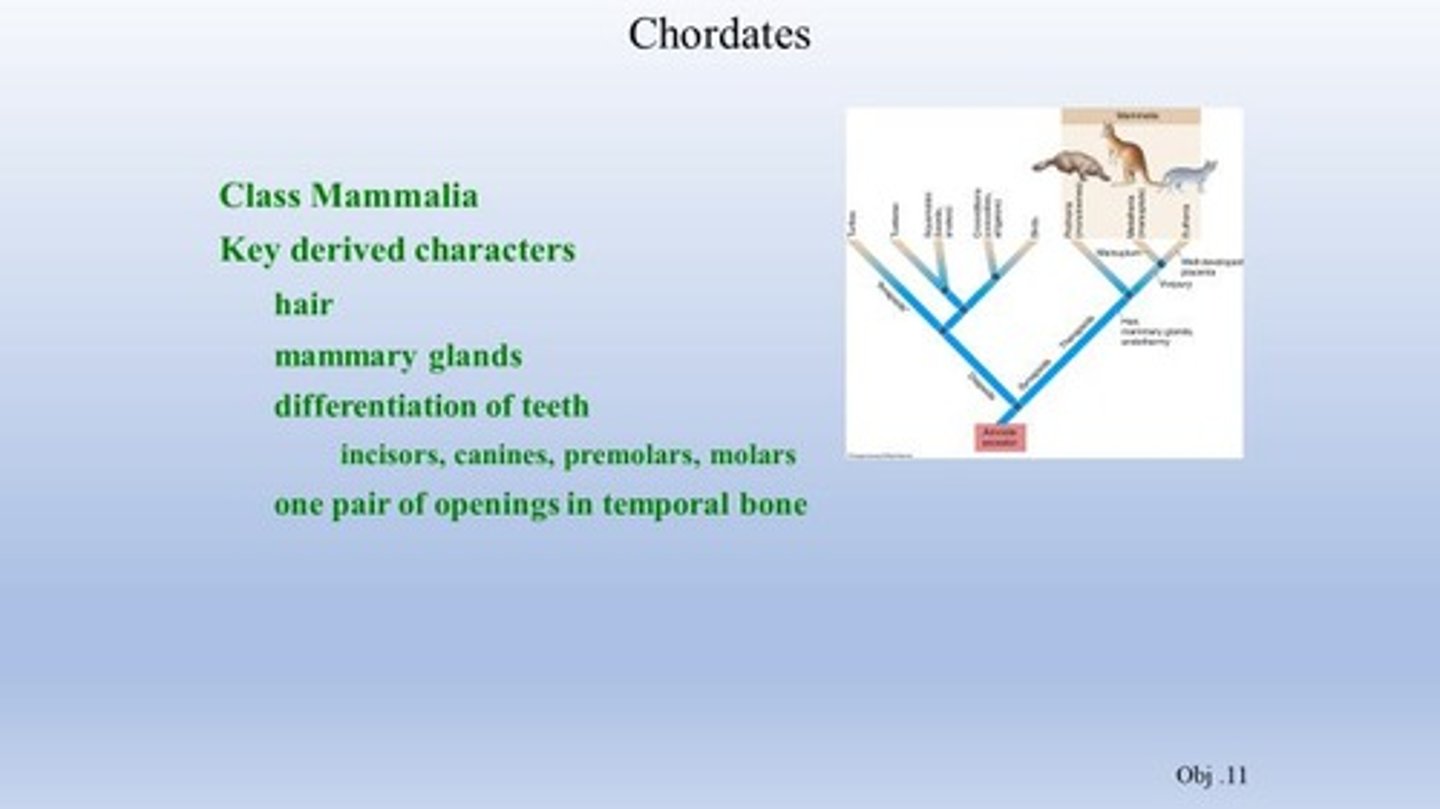
Middle-ear bones
Three bones in mammals (malleus, incus, stapes) that aid in hearing.
Clade Protheria
A clade of mammals that lay eggs, including the duck-billed platypus and echidnas.
Clade Theria
A clade of mammals that bear live young.