carina elasticities
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Elasticities definition
measures the responsiveness of a variable to changes in price of any of the variables determinants
what are the 3 types of elasticities?
price elasticity of demand (PED)
income elasticity of demand (YED)
price elasticity of supply (PES)
Price Elasticity of Demand definition
measures the responsiveness of consumers of a good/service to a change in price of that good/service
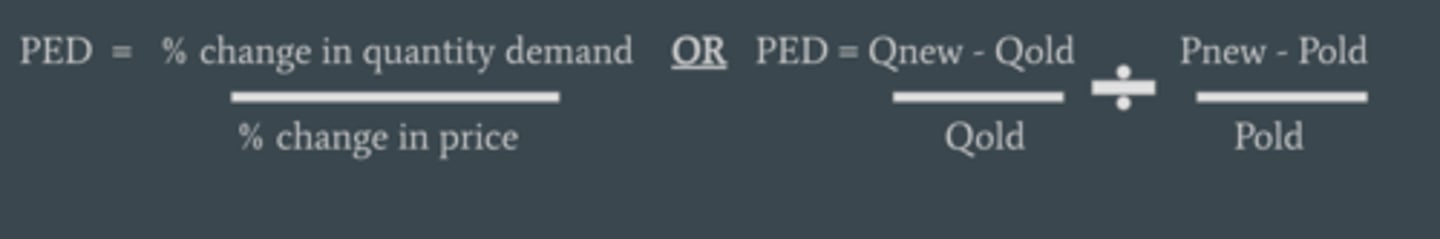
formula for calculating PED
Qnew - Qold/Qold ÷ Pnew - Pold/Pold
why is PED always going to be negative?
because the relationship between price and quantity demand is negative
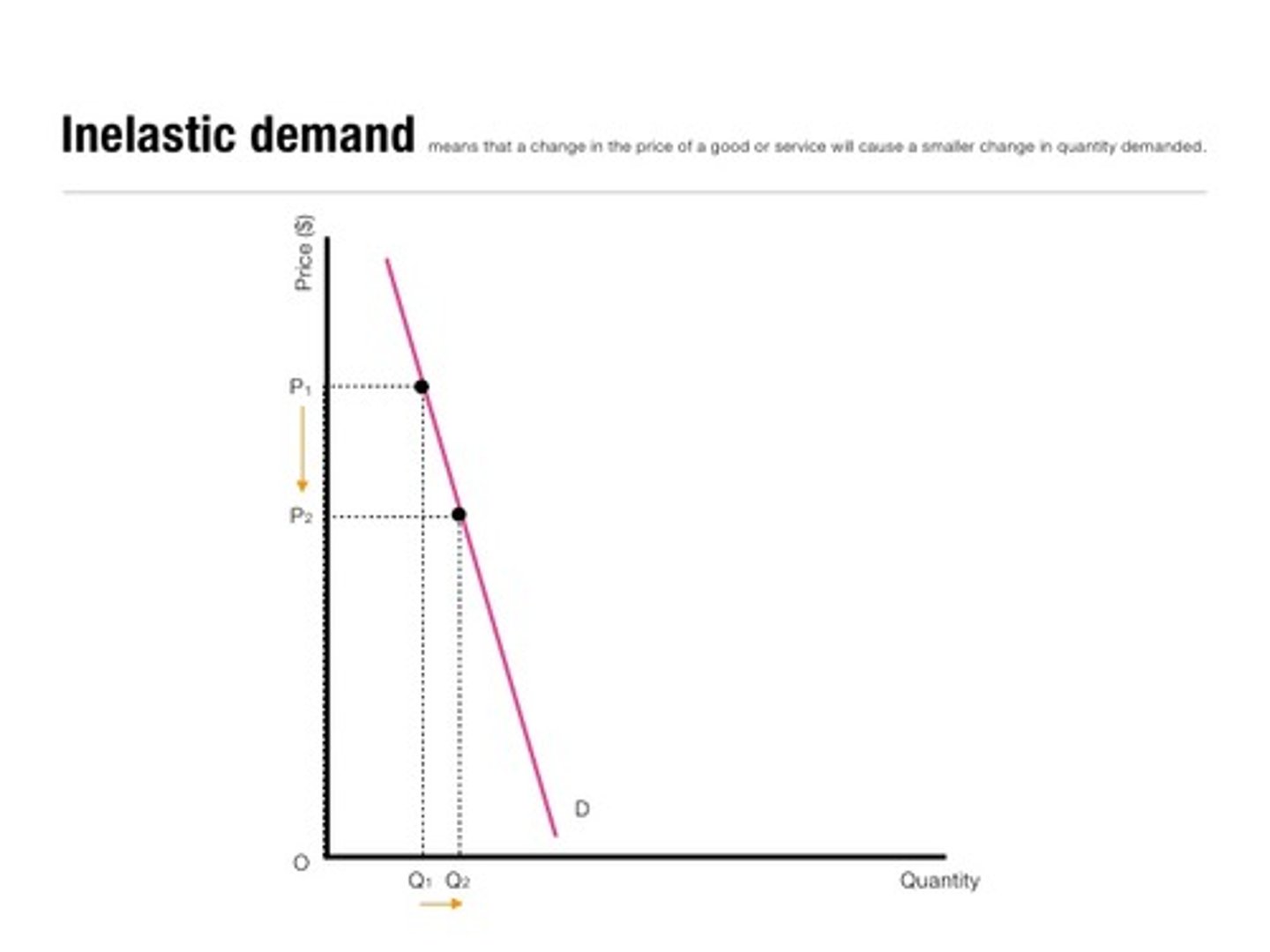
demand when PED = 0 < PED < 1
Inelastic demand, meaning Qd is relatively unresponsive to changes in price
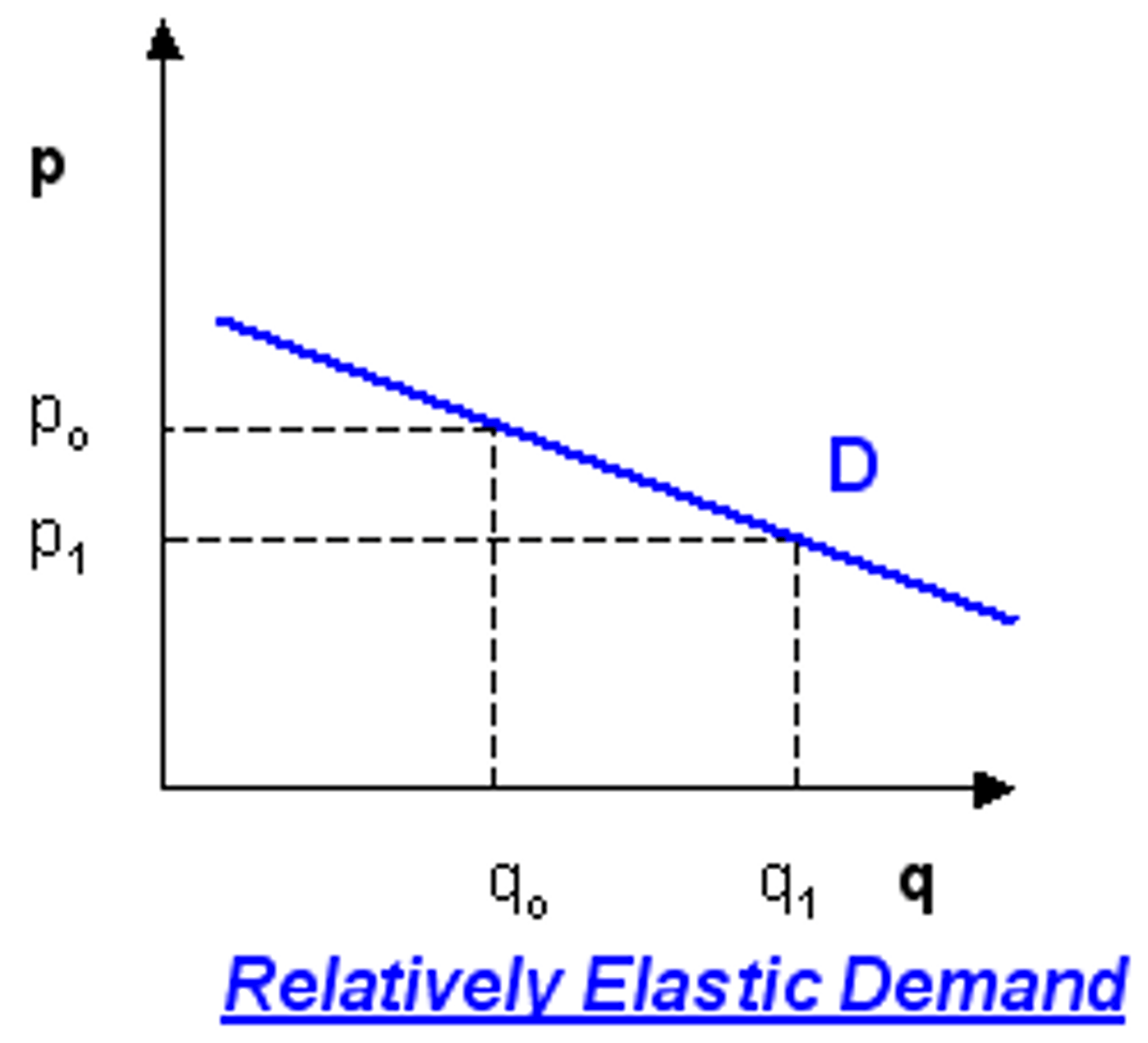
demand when PED = 1 < PED < infinity
elastic demand, meaning Qd is relatively responsive to changes in price
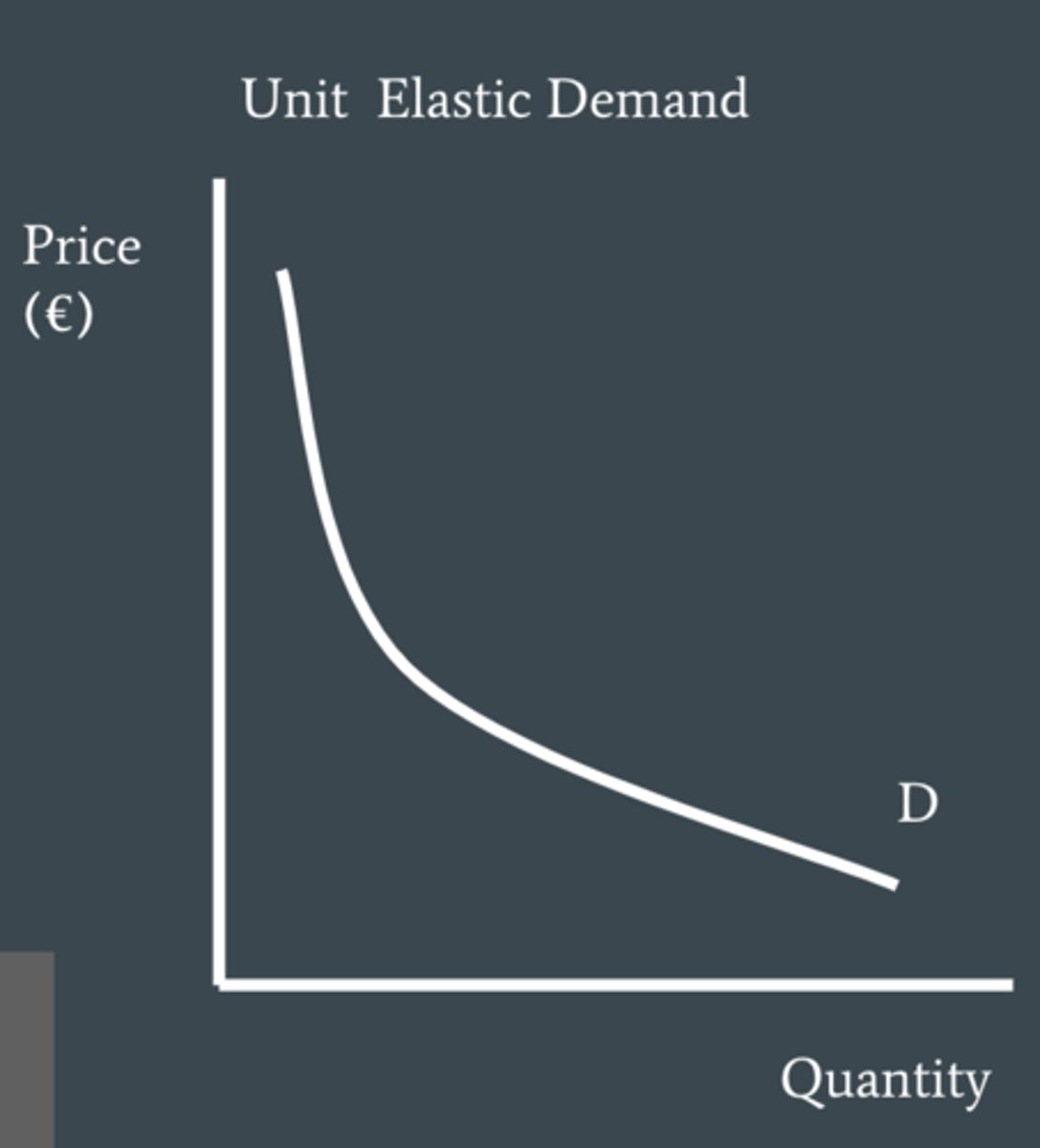
demand when PED = 1
Unit elastic demand, meaning Qd is proportionally responsive to a change in price
what is total revenue when PED=1?
TR is maximized and if there is a change in price after it would only decrease
Demand when PED = 0
Perfectly inelastic demand, meaning Qd is not at all responsive to a change in price
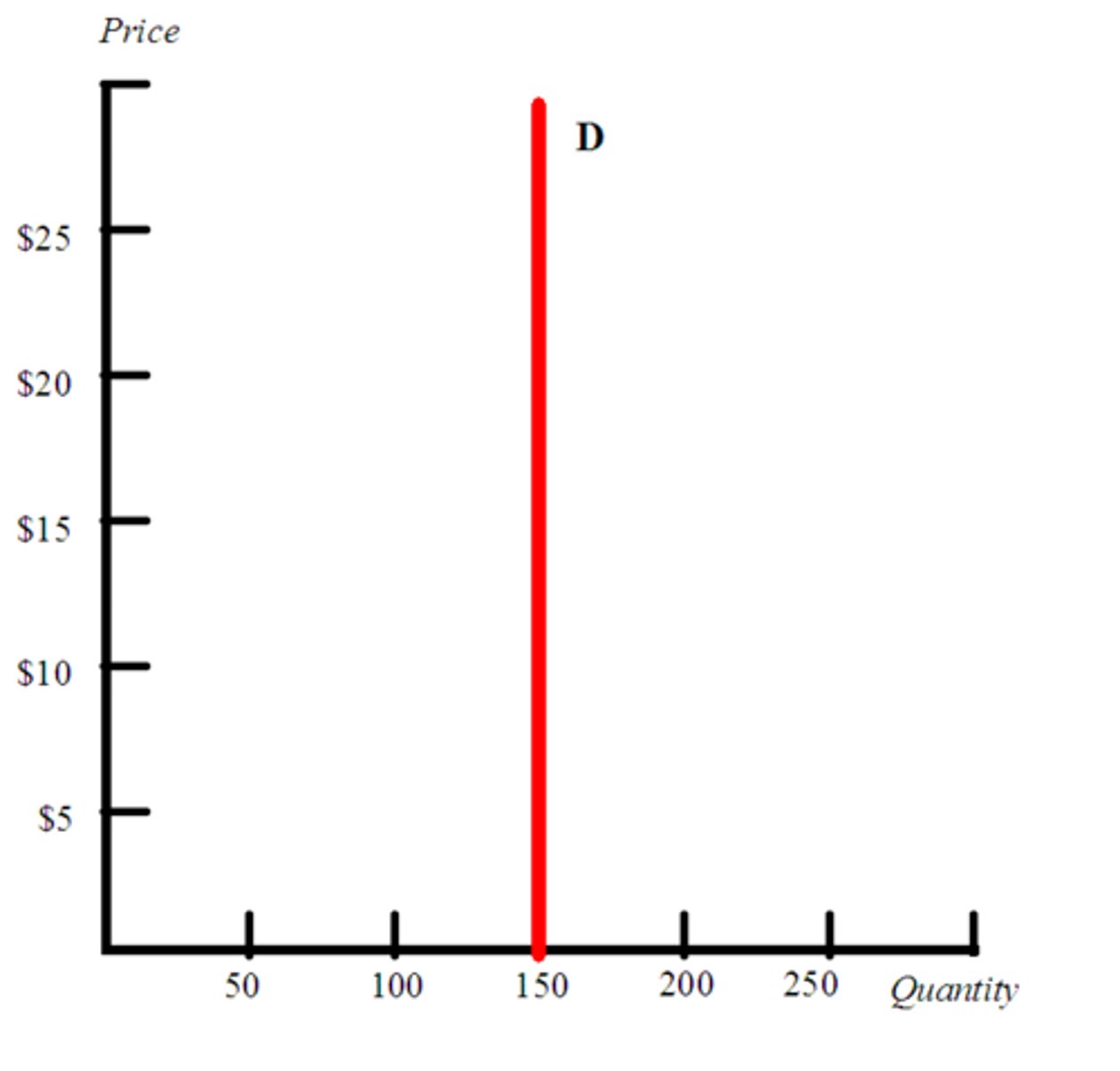
demand when PED = infinity
perfectly elastic demand, meaning Qd is infinitely responsive to a change in price
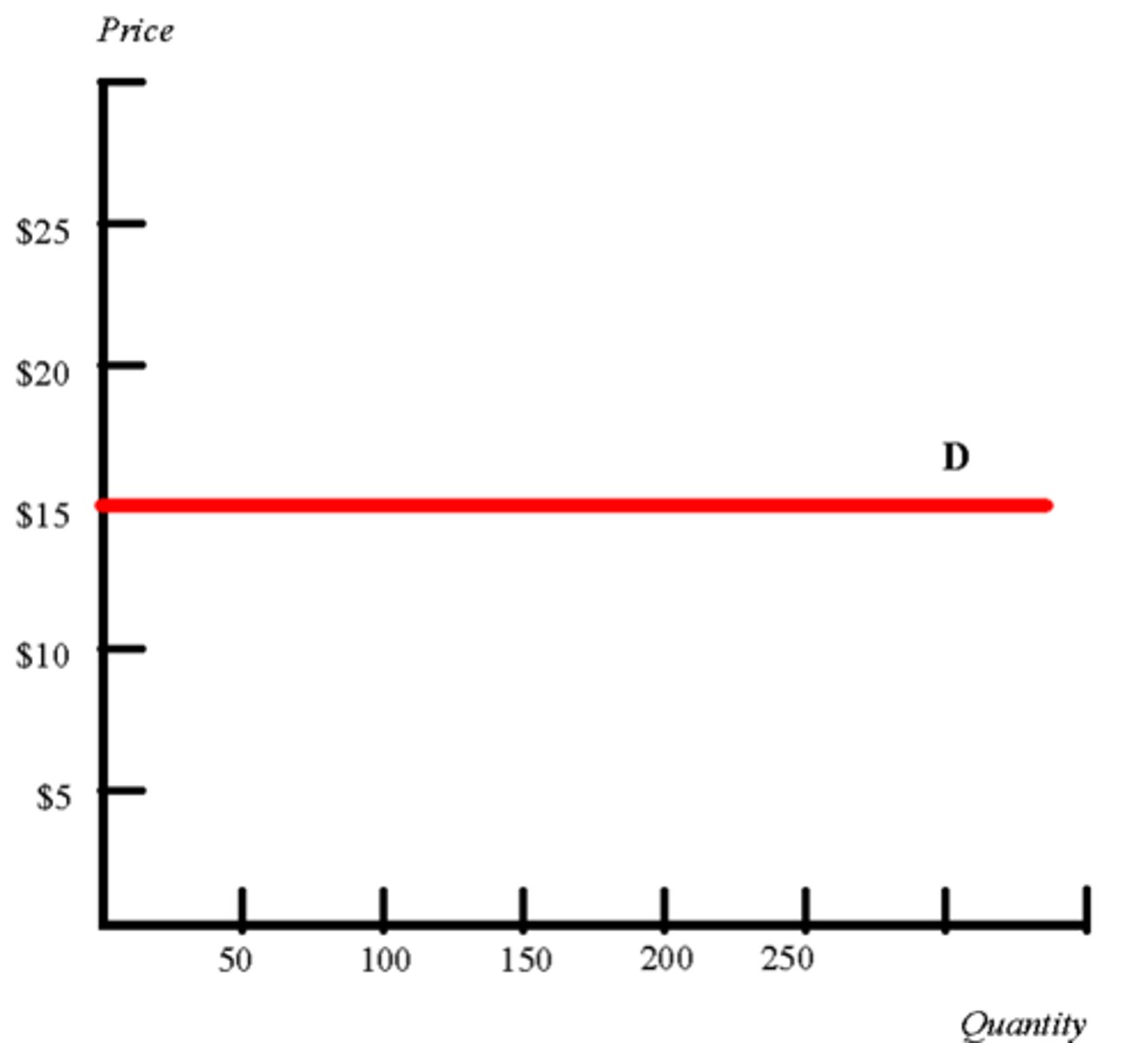
the steeper the gradient the more____
___ inelastic demand is
if prices decreases and demand is inelastic how does it affect TR
decrease in price and an increase in quantity demand = decrease in TR

if prices decrease and demand elastic how does it affect TR
decrease in price and an increase in quantity demand = increase in TR

if prices increases and demand is inelastic how does it affect TR
increase in price, decrease in quantity demand = increase in TR

if prices increases and demand is elastic how does it affect TR
increase in price, decrease in quantity demand = decrease in TR

what is the acronym for the determinants of PED?
SPLAT
what are the determinants of PED? (5)
1 - substitutes
2 - proportion of income
3 - luxury or necessity
4 - addictiveness
5 - Time
if a good has more substitutes it has _____ demand
if a good has less substitutes is has _____ demand
elastic, inelastic
if the good takes up a large proportion of income it has ___ demand
if the good takes up a small proportion of income it has ___ demand
elastic, inelastic
if the good is a luxury good it has ____ demand
if the good is a necessity good it has ____ demand
elastic, inelastic
if you can get addicted to the good it has ___ demand
if not it has ___ demand
inelastic, elastic
the longer the time between a change in price of a good the more ___ demand is. thus the shorter the time the more ____ demand is
elastic, inelastic
how is the knowledge of PED important for firms?
it can help them predict the effects of changes in price on their quantity demand and TR
how is the knowledge of PED important for the government?
it can help them predict the effects of putting indirect taxes on goods/services. E.G - if a good/service has more inelastic demand it will increase revenue rather than if the good had more elastic demand
demerit good definition
good that harms society
excise taxes
taxes placed on a certain good
Primary commodity definition
raw materials that go into the making of other goods
what is the elasticity of primary comodities?
tends to be inelastic as there are few substitues
manufactured goods definition
a good that is produced mainly by the application of labour and capital to raw materials
what is the elasticity of manufactured goods?
tend to be more elastic as there are more alternatives, brands and substitutes
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED) definition
measures the responsiveness of demand to changes in income and involves demand curve shifts.
formula for calculating YED
Qnew - Qold/Qold ÷ Ynew - Yold/Yold

what does a positive YED value indicate?
that it is a normal good, when income increases so does quantity demand
what does a negative YED value indicate?
that it is an inferior good, when incomes increases demand decreases
when YED is absolutely above 1 income is ____
elastic
when YED is absolutely below 1 income is ____
inelastic
if YED is + and above 1
luxury good
if YED is - and below 1
necessity good
Engle Curve
demonstrates the relationship between income and quantity demand of a good
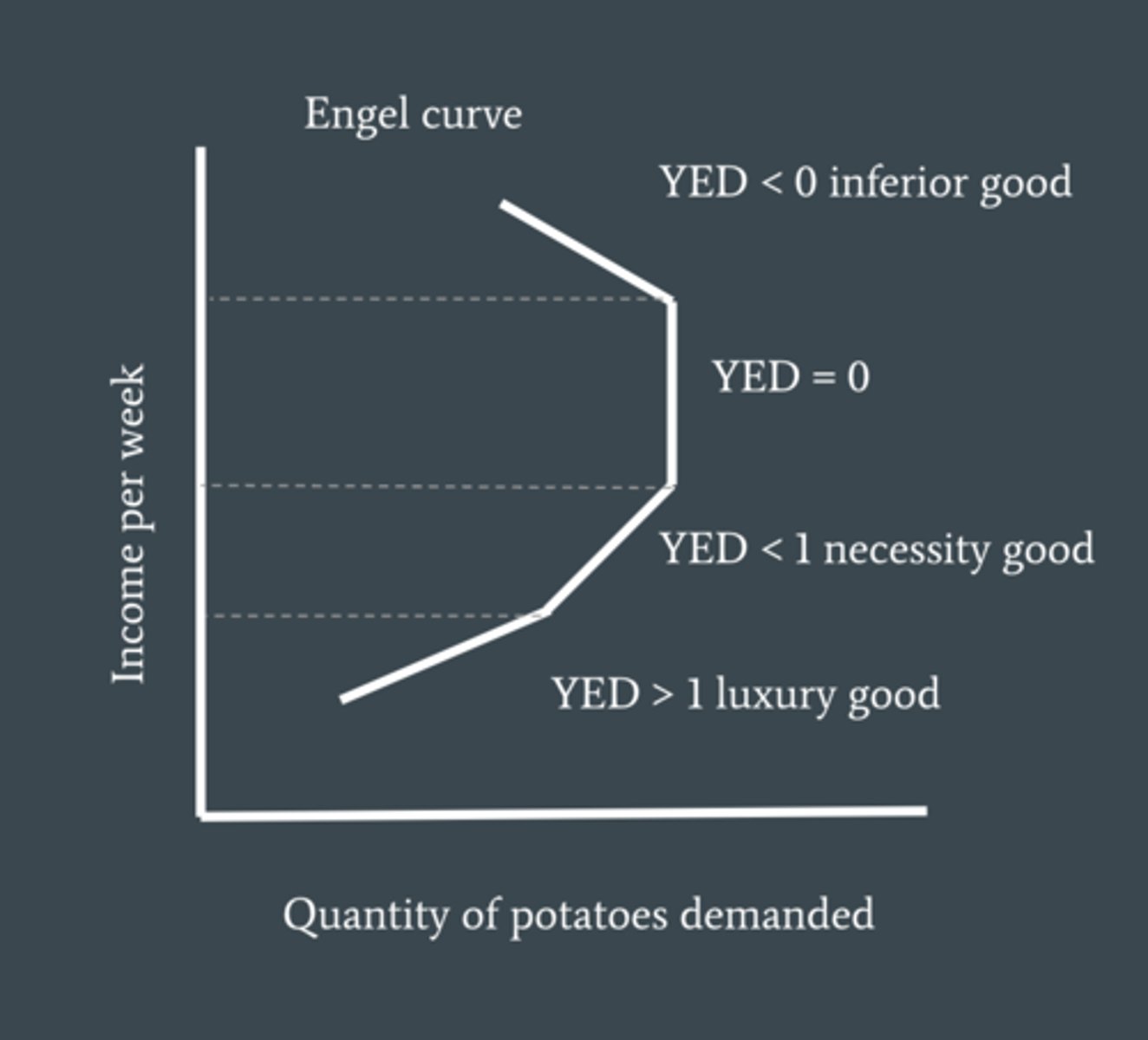
what are the 3 sectors of economy
primary, secondary, tertiary
what does the primary sector include?
agriculture, mining, forestry - raw materials
what does the secondary sector include?
cars, housing, infrastructure, manufacturing
what does the tertiary sector include?
entertainment, travel, banking, health - services
Price Elasticity of Supply (PES) definition
measures the responsiveness of the quantity of a good supplied to changes in its price
formula for calculating PES
Qnew-Qold/Qold ÷ Pnew - Pold/Pold

supply is what when PES - 0 < PES <1
Inelastic supply, meaning Qs is relatively unresponsive to a change in price.
supply is what when 1 < PES < ∞
elastic supply, meaning Qs is relatively responsive to a change in price
supply is what when PES = 1
unit elastic supply, meaning Qs is proportionally responsive to a change in price.
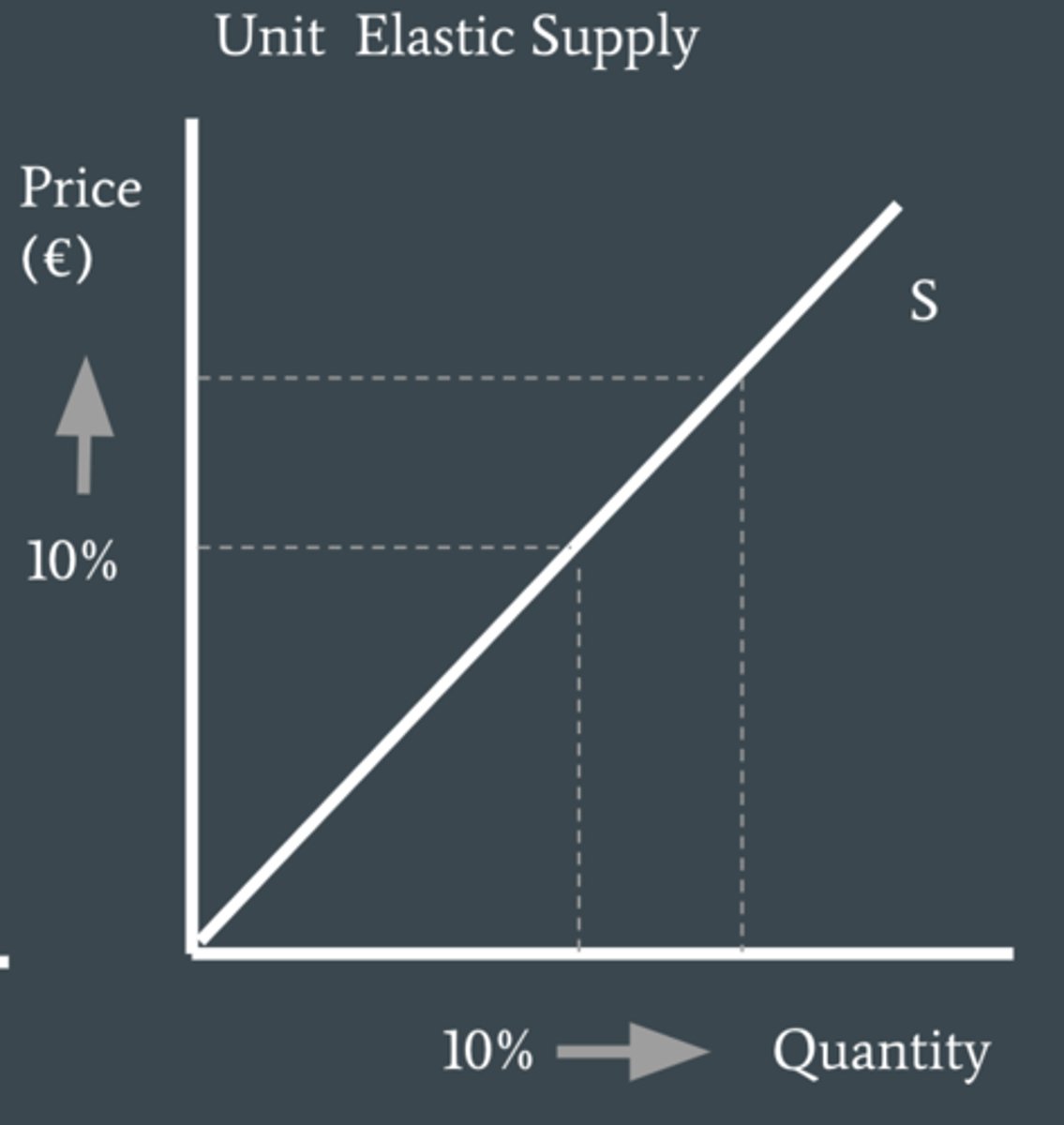
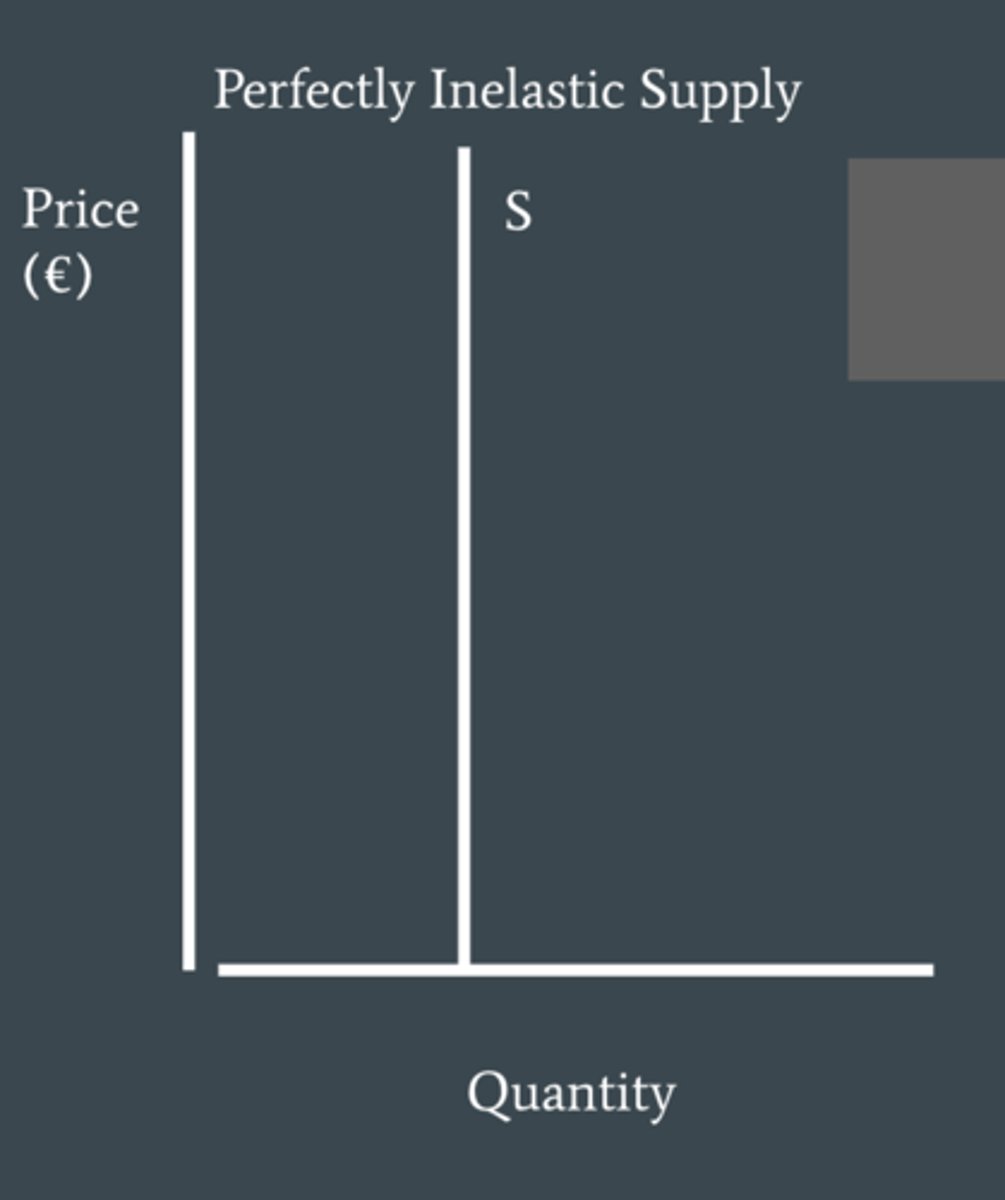
supply is what when PES = 0
perfectly inelastic supply, meaning Qs is not responsive to a change in price.
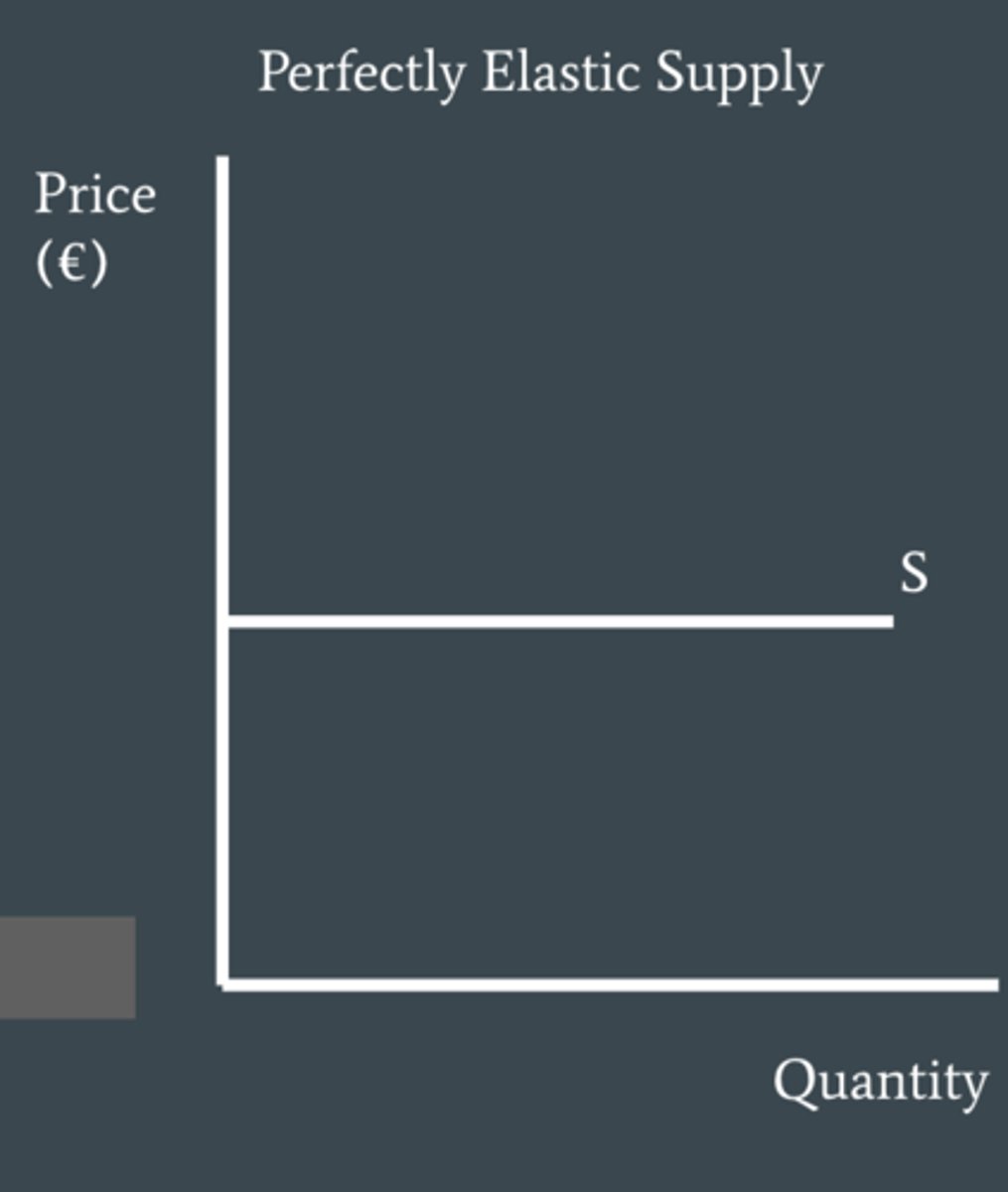
supply is what when PES = ∞
perfectly elastic supply, Qs is infinitely responsive to a change in price.
What are the determinants of PES? (5)
1 - Time
2 - Mobility of resources
3 - ability to stores stocks
4 - unused capacity
5 - Rate of cost of production
Time as a determinant of PES
The more time that firms have to respond to changes in price the greater ability they have to increase or decrease their quantity supply.
Mobility of resources as a determinant of PES
The easier that firms can switch resources from one type of production to another (where price is increasing) the more responsive they can be to changes in price.
Ability to store stocks as a determinant of PES
The longer that firms can store stocks of their goods the easier it is for them to increase their quantities in the short term.
Unused capacity as a determinant of PES
If firms have more unused capacity in their factories then it is easier and cheaper to increase their quantity supply. If there is less spare capacity it will be more expensive and take longer to increase their quantity supply.
Rate of cost of production as a determinant of PES
supply will be inelastic if costs of producing extra output increases rapidly, because firms will struggle expanding their output as they are unlikely to incur large costs. but if costs of production of extra output rises slowly they are more able to expand their output making supply elastic