Adrenal hormones
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
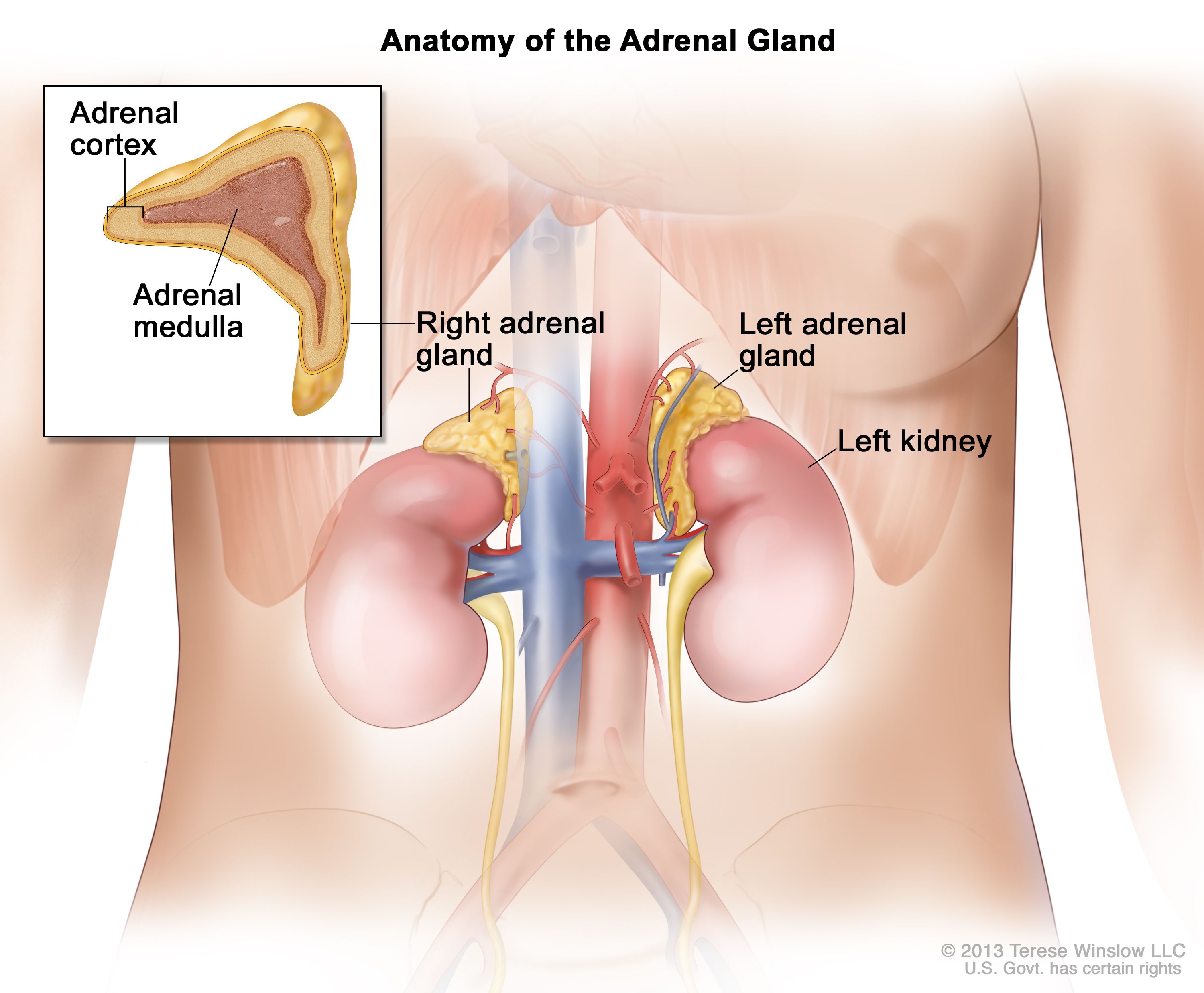
Corticosteroids
Hormones made by and secreted by the adrenal cortex from cholesterol; include
mineralocorticoids,
glucocorticoids, and
androgens.
mineralocorticoids
Hormones like aldosterone that regulate sodium and potassium balance; produced by the zona glomerulosa.
Glucocorticoids
Hormones like cortisol that regulate glucose metabolism; produced by the zona fasciculata.
Androgens
Weak sex hormones like DHEA that support gonadal hormones; produced by the zona reticularis.
What is the primary function of aldosterone in the kidney?
Aldosterone promotes sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion in the nephron, helping maintain fluid balance and potassium levels in the blood.
meaning moving sodium from the nephron back into the blood.
Why must potassium levels in the blood be tightly regulated?
Because doubling the normal extracellular potassium concentration (4.5 mMol/L) can be lethal.
How are potassium ions processed in the nephron?
They pass freely through the glomerulus and are almost completely reabsorbed; the amount lost in urine depends on how much is secreted.
aldosterone regulates the level of potassium in the blood
What triggers aldosterone release during low blood volume or pressure?
A drop in body sodium or blood plasma volume, which lowers blood pressure, activates body systems to release aldosterone from adrenal cortex. It then increases sodium reabsorption, which increases water reabsorption (water follows sodium) as a resukt blood plasma volume increases helpign to raise blood pressure.
Why doesn’t sodium reabsorption usually affect blood sodium concentration?
Because water is reabsorbed along with sodium, keeping plasma sodium levels stable.
How does aldosterone regulate sodium and potassium in the kidneys?
Aldosterone enters kidney cells, binds to intracellular receptors, and the complex moves to the nucleus to trigger mRNA production. This leads to protein synthesis, including Na⁺-K⁺ ATPase and channel proteins, which help reabsorb sodium into the blood and excrete potassium into the urine.
Role of Na⁺-K⁺ ATPase in aldosterone action
An enzyme produced in response to aldosterone that actively pumps sodium into the blood and potassium into kidney tubules, maintaining ion balance and blood pressure.
Sodium movement (under aldosterone influence)
Sodium flows from the tubule → kidney cell → blood plasma.
Potassium movement (under aldosterone influence)
Potassium flows from the blood → kidney cell → tubule (urine).
Why do aldosterone’s effects on sodium and potassium take time to appear?
Because aldosterone triggers the production of new RNA and proteins in kidney cells, its effects begin about 45 minutes after release and take several hours to reach full strength.
Rundown of Aldosterone Action
Aldosterone is released from the adrenal glands, travels to kidney cells, enters the cells, and stimulates RNA and protein synthesis. This causes sodium reabsorption, potassium secretion, and a small amount of hydrogen ion secretion, but the effects are delayed due to the time needed for gene expression.
Aldosterone is released into the blood by the adrenal glands (not the kidney).
It travels through the blood to the kidney cells.
Once aldosterone enters the kidney cells, it triggers new RNA and protein production.
This process takes time—about 45 minutes before changes in sodium transport begin, and several hours to reach full effect
What are the main triggers for aldosterone release, ranked by importance?
High potassium in extracellular fluid
(aldosterone will help kidneys to secrete potassium into the urine, lowering levels) even a small rise can increase aldosterone release alot
Renin-angiotensin system (via angiotensin II)
Aldosterone makes the kidneys reabsorb more sodium and water, which increases blood volume and blood pressure, restoring balance.
Low sodium in extracellular fluid
Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption from kidneys to blood raising sodium levels.
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
has a small effect but if its missing aldosterone secretion cna drop alot
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
A system activated by low blood flow to the kidneys, leading to the release of angiotensin II, which stimulates aldosterone secretion. Aldosterone then promotes sodium and water reabsorption and potassium excretion, helping to restore blood volume and pressure.
Adrenal Medulla
The inner part of the adrenal gland that secretes adrenaline and noradrenaline.
Adrenaline and Noradrenaline (Catecholamines)
Hormones released by the adrenal medulla that mimic the sympathetic nervous system’s fight or flight response but last longer.
they can increase heart rate and strength of contraction, and widen blood vessels around the heart
they sharpen mental focus
they increase metabolism and speed up glucose breakdown
so they are released during stress or fight or flight responses
Adrenaline and noradrenaline also raise blood sugar levels by
helping the liver release more glucose and
by increasing how quickly the body breaks down glucose for energy.
How is the adrenal medulla controlled?
By nerve signals from the sympathetic nervous system, releasing hormones during stress or fight-or-flight situations.