Brain and Cranial Nerves
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
14a
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Brain volume
1200 ml (750-2100 ml range)
Brain Weight
around 3 pounds (1.4 kg)
How many neurons and connections in brain?
100 Billion neurons, 500 trillion connections
Female and male differences
Males have greater volume, females have more connections
Gyri
rounded elevations
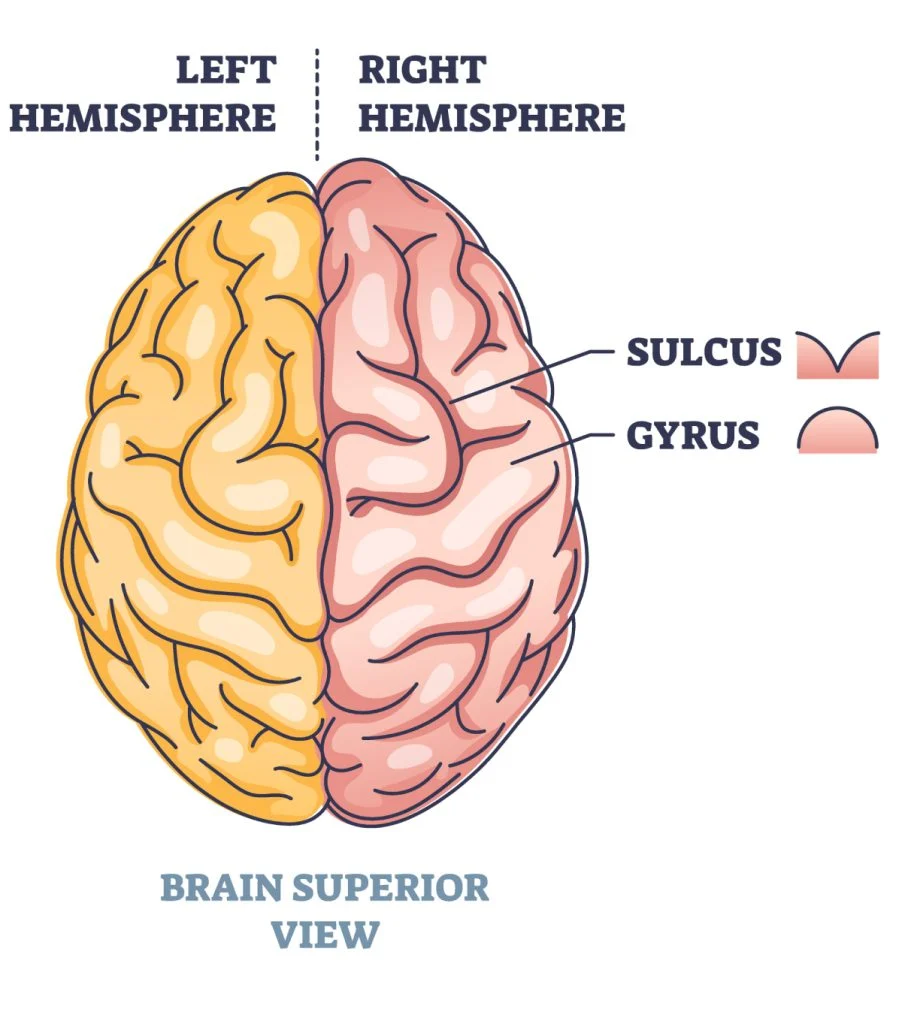
Sulci
Shallow grooves
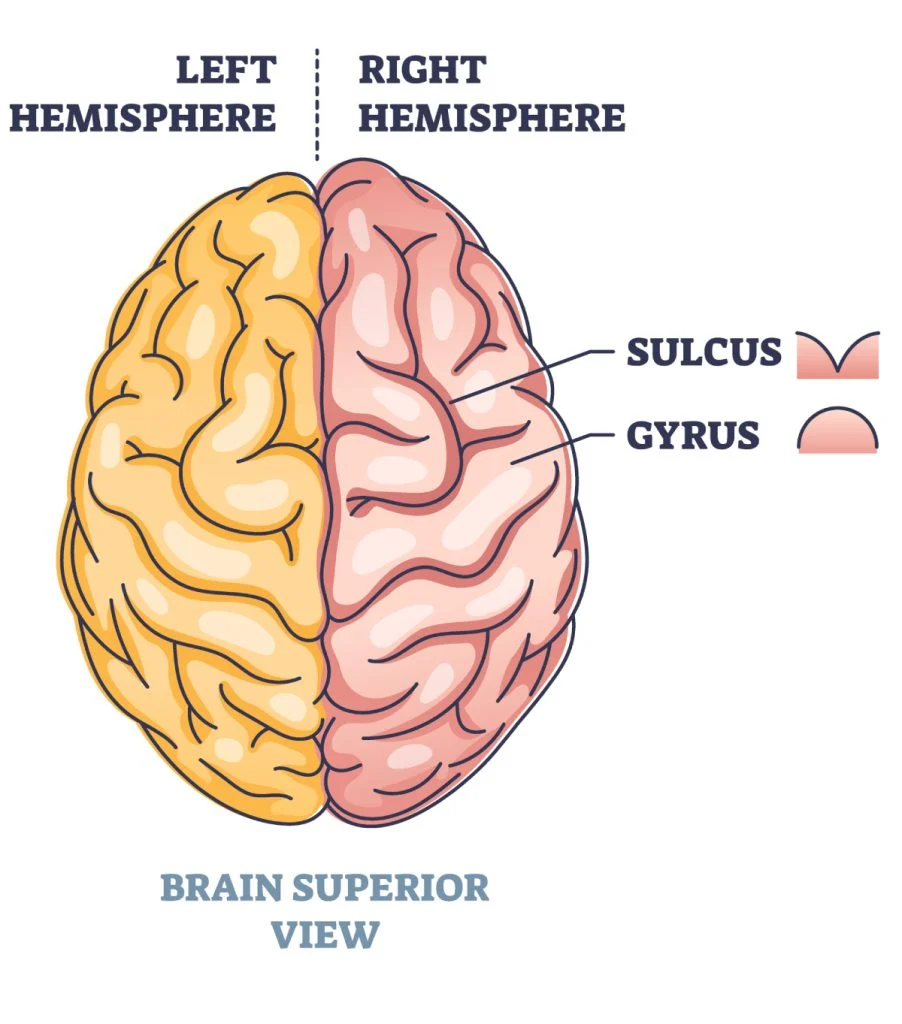
Fissues
deeper grooves
Four “regions” of brain
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Diencephalon
Thalamus
hypothalamus
Brainstem
Midbrain
pons
medulla oblongata
During embryonic development, the CNS develops from
neural tube
Ventricular system of brain
Lateral ventricles (2)
Third ventricle
fourth ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
intraventricular foramen
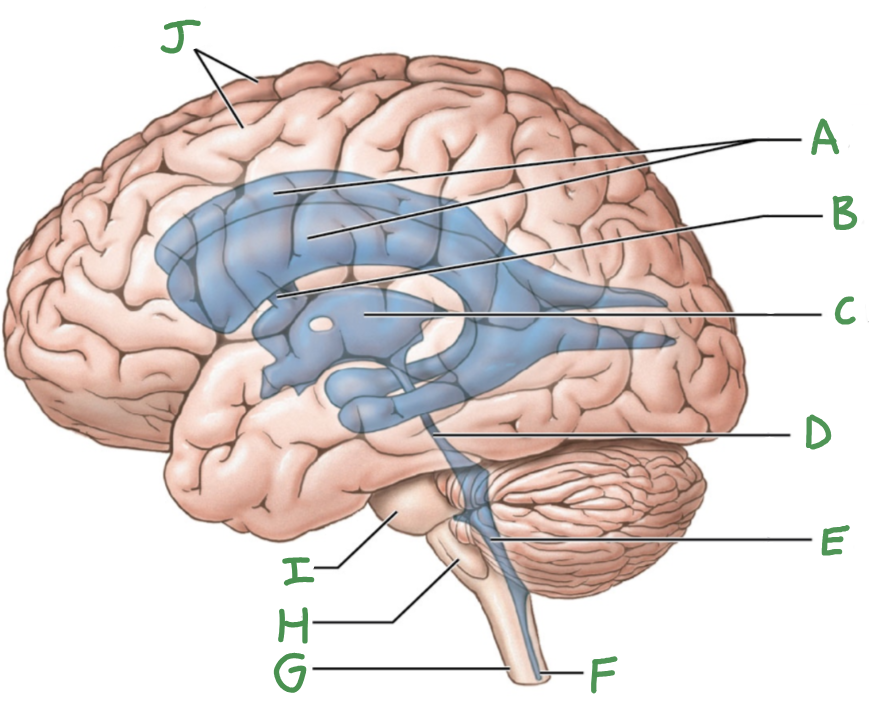
A
lateral ventricles
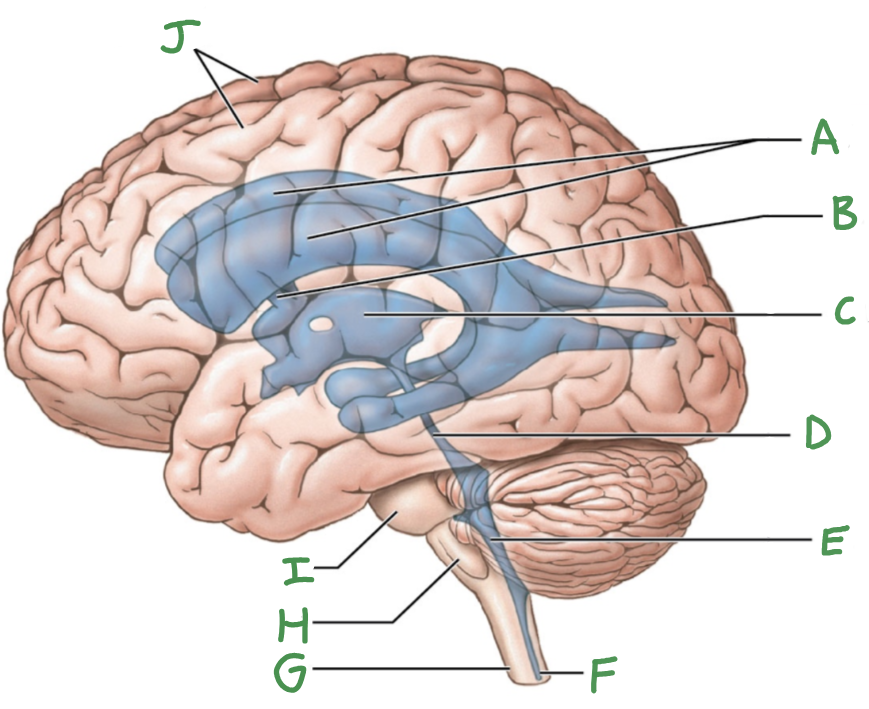
B
interventricular foramen
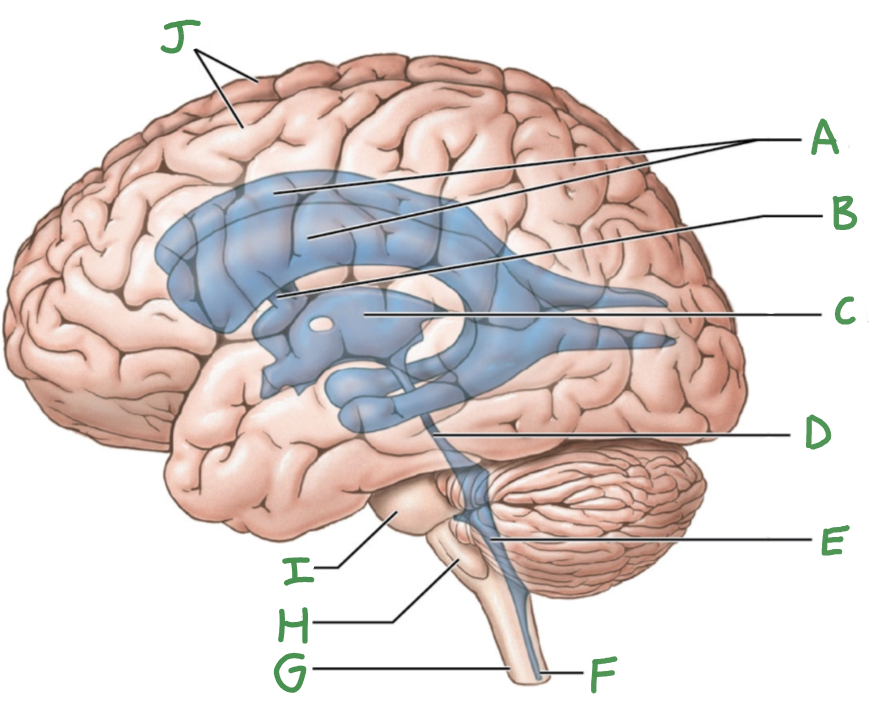
C
third ventricle
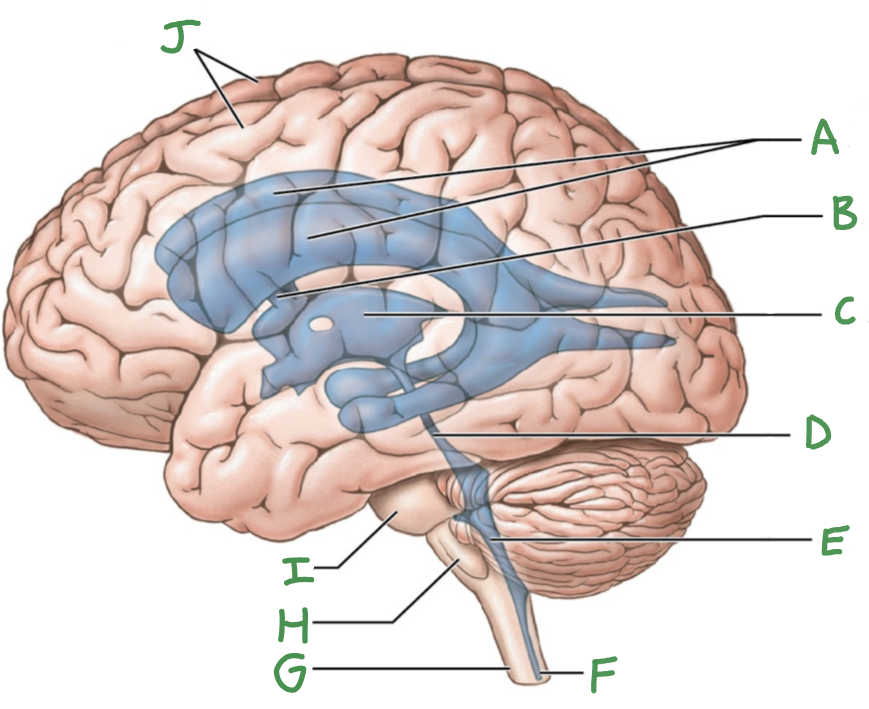
D
cerebral aqueduct
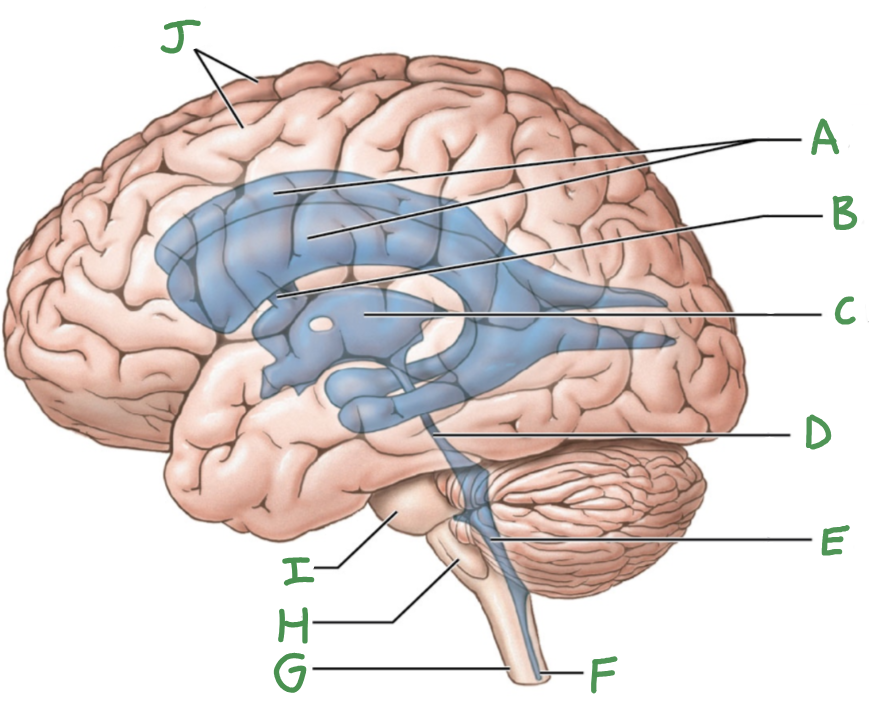
E
Fourth ventricle
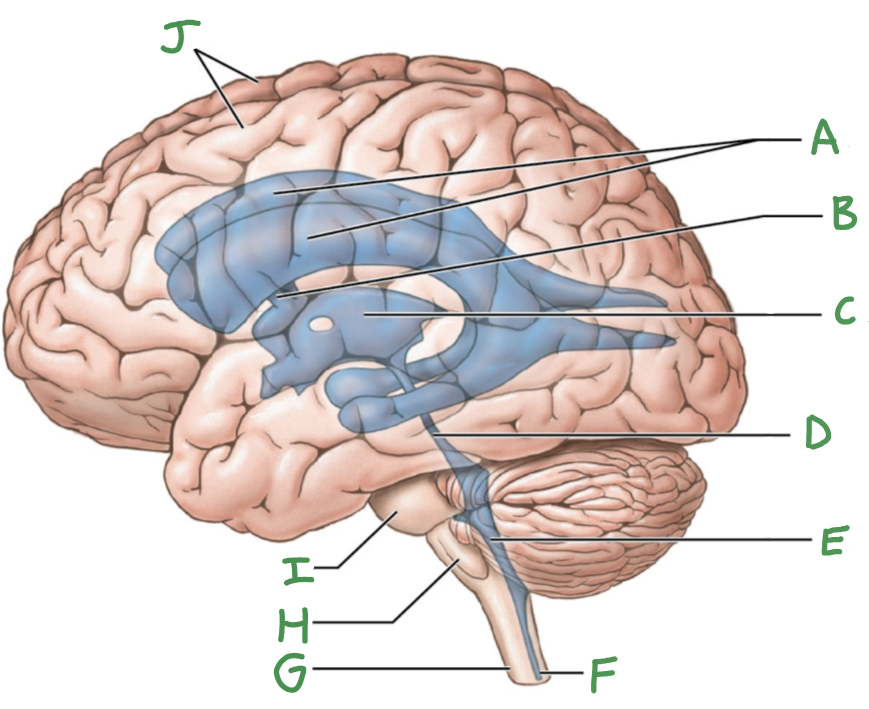
F
central canal
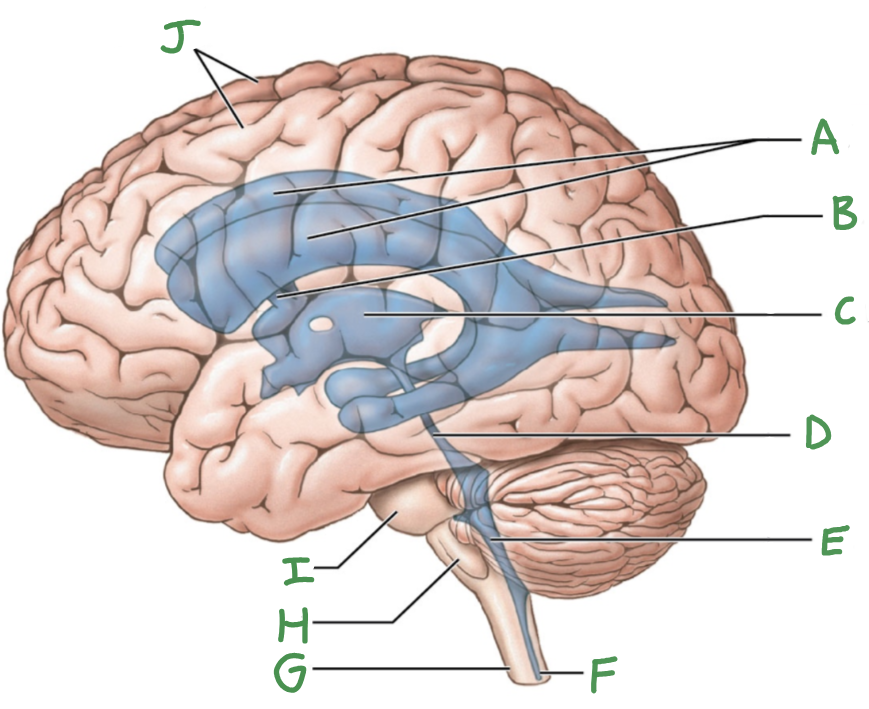
G
Spinal cord
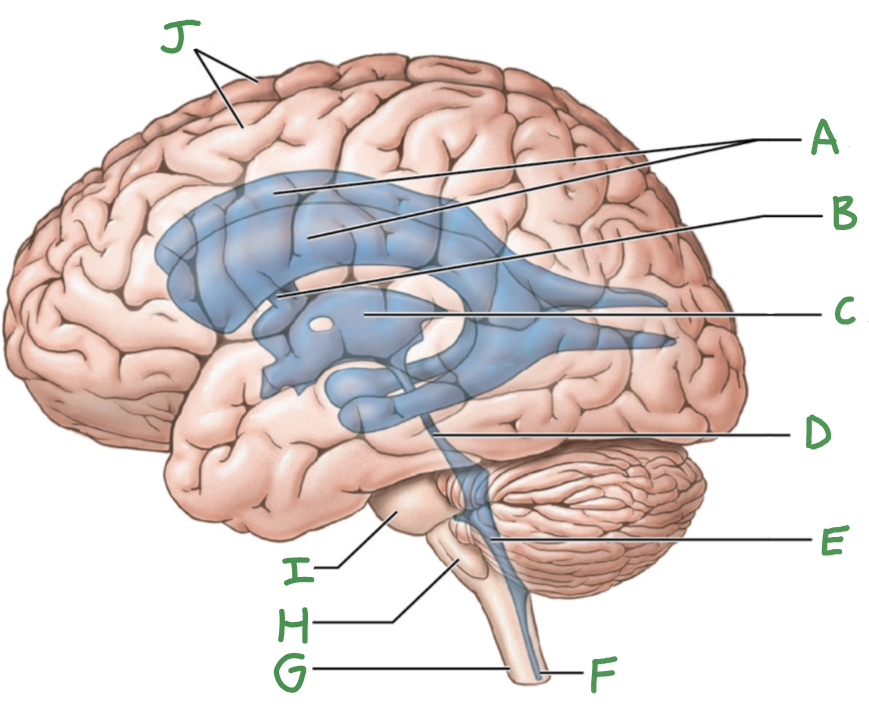
H
Medulla oblongata
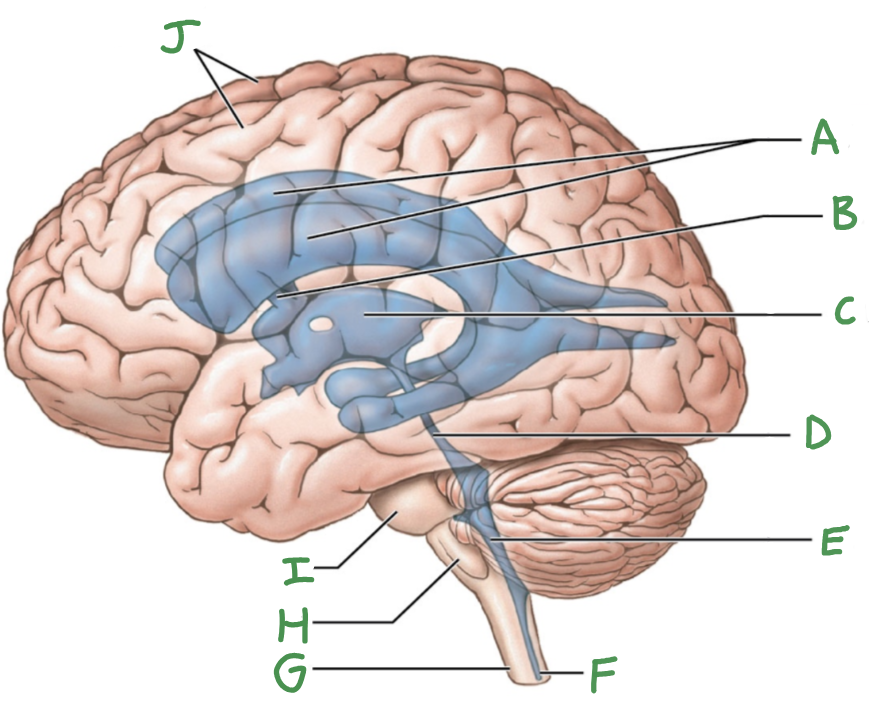
I
Pons
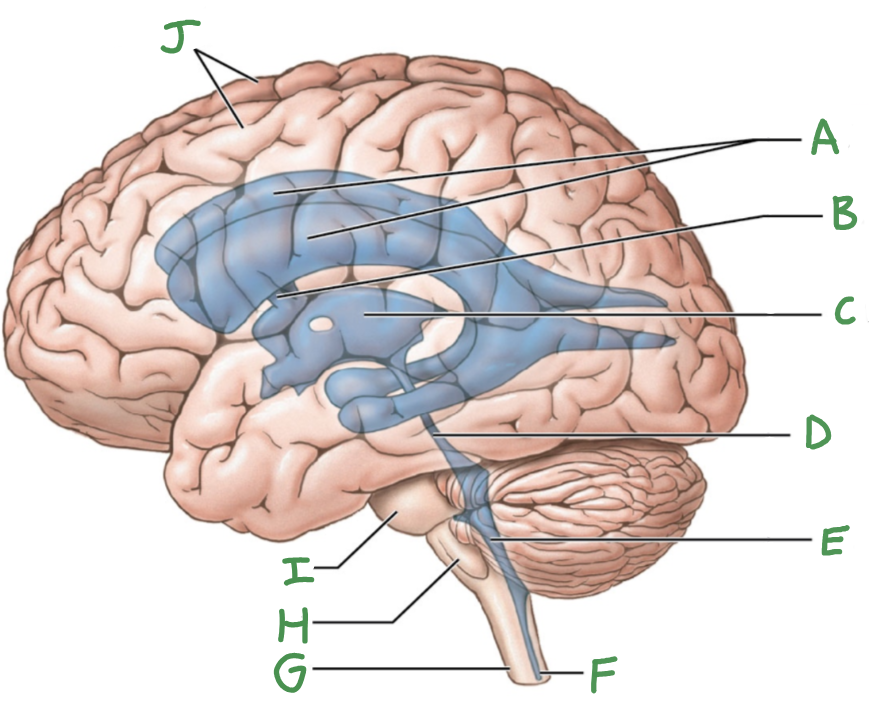
J
Cerebral hemispheres
Ventricles of the brain
fluid filled spaces/ openings
continuous with spinal cord
contain CSF fluid, ependymal cells
Cerebrospinal Fluid Function
support (our brain floats)
cushioning (absorbing impact)
transport (nutrients, hormones, waste)*
still remember that brain is vascularized
What three structures (aside from scalp and skull) protect the brain?
Cranial meninges (DAP)
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
CSF
CSF produced each day
500 ml/2 cups, but sometimes 150ml every moment
*Replaced every 8 hours
**Extra CSF absorbed into venous circulation (veins)
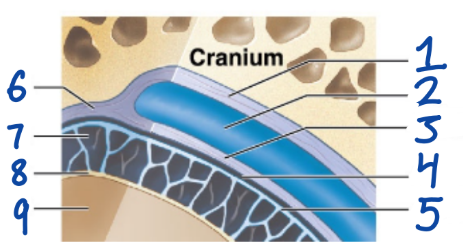
1
Periosteal cranial dura
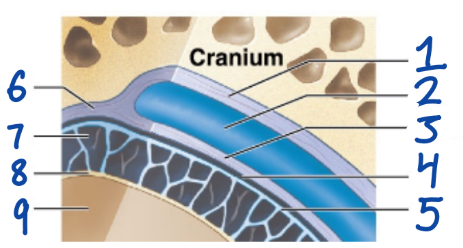
2
Dural sinus
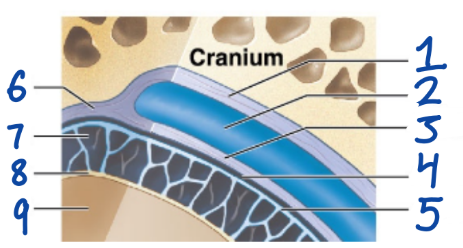
3
Meningeal cranial dura
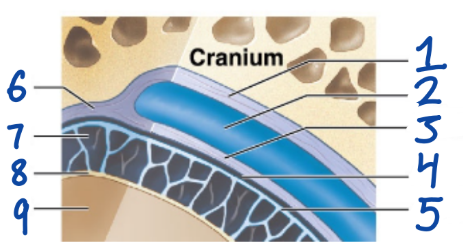
4
Subdural space
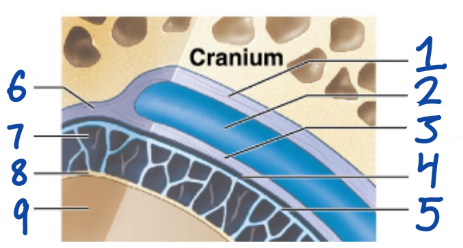
5
Arachnoid mater
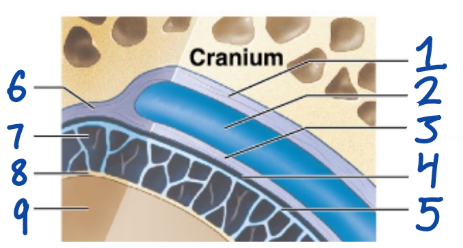
6
Dura Mater
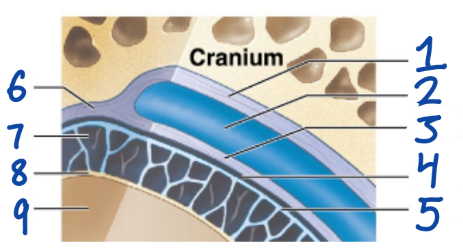
7
Subarachnoid space
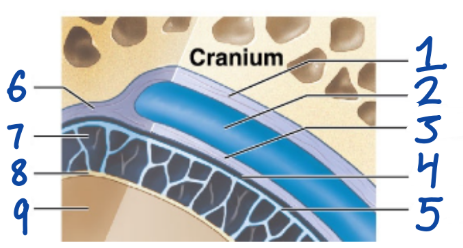
8
Pia Mater
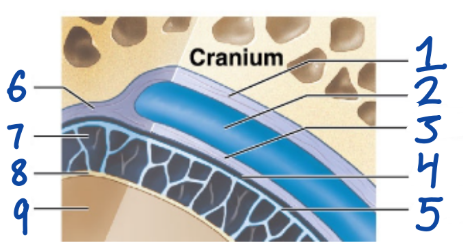
9
Cerebral Cortex
Dura Mater
outermost, fused to periosteum of cranial bones
Subdural space (below it)
Arachnoid Mater
“spiderlike”, has subarachnoid space
Pia Mater
anchored by processes of astrocytes, sticks to surface of brain
Blood Brain Barrier (BBB)
formed by capillary endothelial cells connected by tight junctions
prevent materials from diffusing between endothelial cells
Small capillaries that are 1 cell thick
NOT fenestrated (no holes/apertures)
What glial cell maintains BBB?
Astrocytes
ends “endfeet” of astrocytes surround blood vessel (capillary) that produces substance, which supports thigh junctions
regulates interstitial environment (between tissue)
determining ions, neurotransmitters needed for homeostasis, etc….
ex. not eating until 12, but brain uses glucose storage while thinking
What provides nutrients for astrocytes?
Pericytes
Transport across BBB
lipid soluble (Oxygen, alcohol, CO2)
lipid based sterol hormones (insulin, leptin, viruses)
**NOT glucose, needs active transport
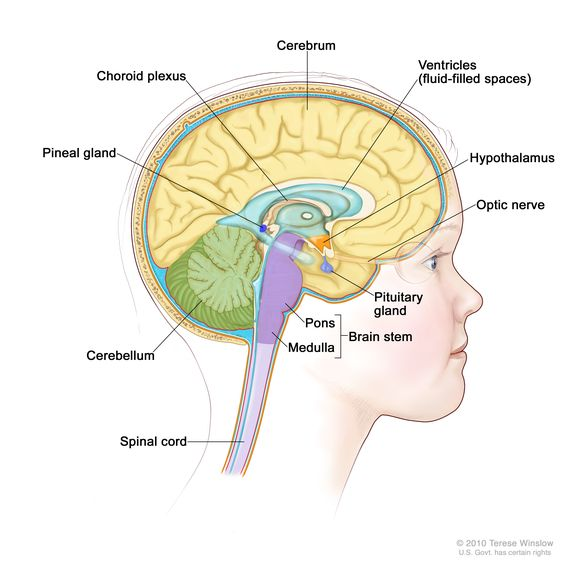
Circumventricular Organs
have fenestrated capillaries
Hypothalamus (which secretes neurohormones ADH and Oxytocin)
Posterior Pituitary Gland (where ADH and Oxytocin move around)
Pineal Gland (melatonin)
Choroid Plexus (in each of the ventricles)
Choroid Plexus
network of blood vessels, exchange between blood and CSF takes place here
lines all ventricles of brains
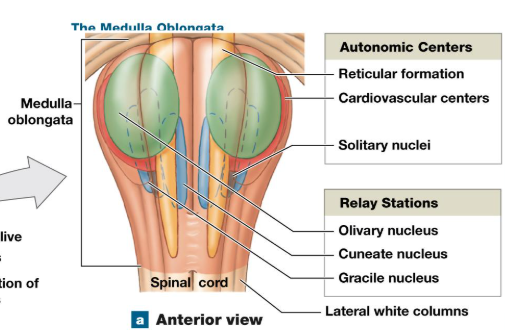
Medulla Oblongata
Cranial nerves 8-12
Three groups of nuclei
Reflex center for autonomic activity
sensory and motor nuclei of cranial nerves
relay stations for sensory, motor pathways
Brainstem
processes and relays info from spinal cord to higher brain (cerebellum, cerebrum)
two way street (sensory info goes up, motor info goes down)
thalamus, pons, medulla*
Medulla Oblongata Reflex Center (1st nuclei group’s automatic activity)
cardiovascular
adjust HR, cardiac contractility, peripheral resistance in <3, blood vessels
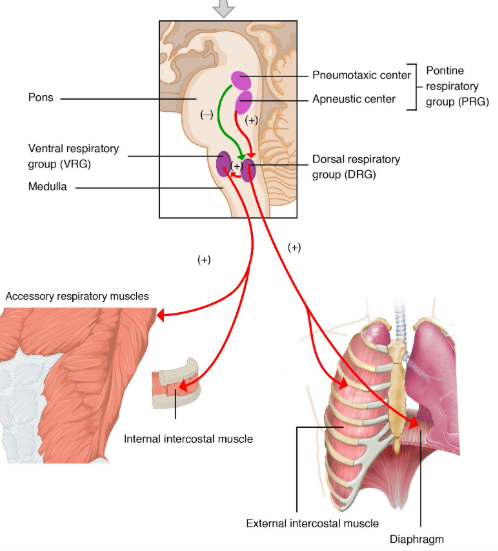
Respiratory Rhythmic
Set basic pace for respiration**
**pons also regulate breathing
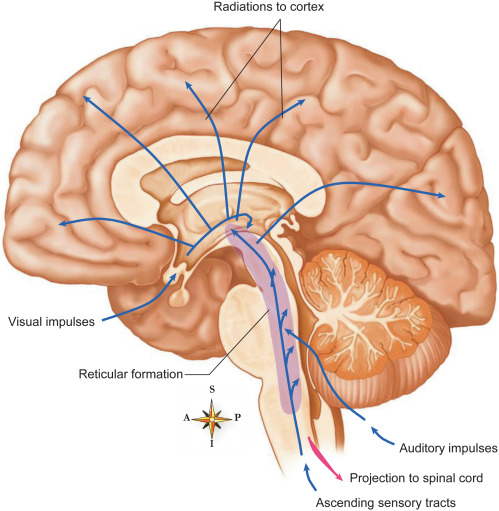
Reticular Formation (a part of medulla)
gray and white matter, relay station
Pons
Largest part of brainstem, medial to midbrain and medulla oblongata
5-8 cranial nerve, no. 8 is shared
also regulates breathing
Apneustic and pneumotaxic centers in gray matter region of pons
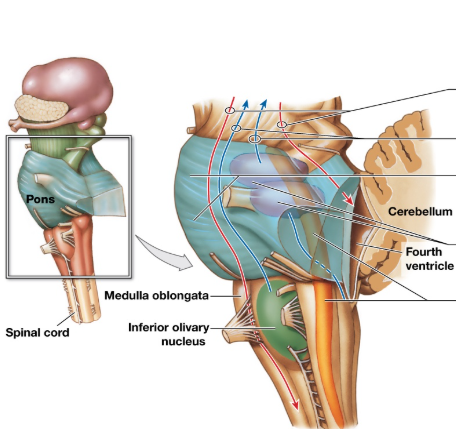
Apneustic and pneumotaxic centers
respiratory rhythmicity centers, control respiration (shared task between pons and medulla)
Midbrain
Most superior
cranial nerves 3-4
hand eye coordination, connect to cerebellum
auditory and visual processing
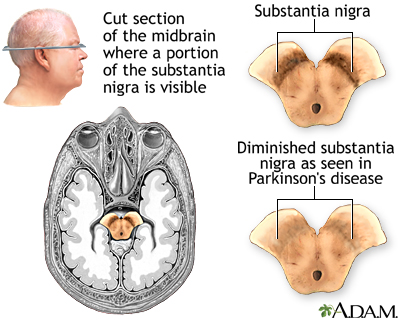
Substantia nigra is here
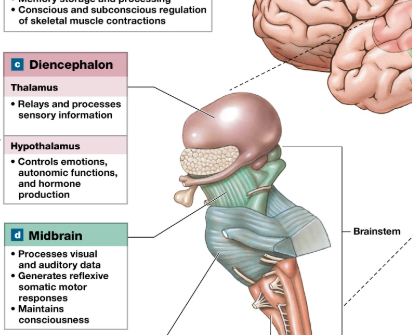
Substantia nigra
Regulates basal nuclei activity in midbrain
dopamine producing nuclei here
production of neuromelanin
maintain consciousness
controls body movements
controls learning, mood, judgement decision-making
Diminished SN —> Parkinson’s disease
Cerebellum
10% of brain volume, 50% of total brain neurons found here
posterior to brainstem, inferior to cerebrum
Rich in Purkinje Cells (branched, dense, highly connected)
found in cerebellar cortex
axons are myelinated
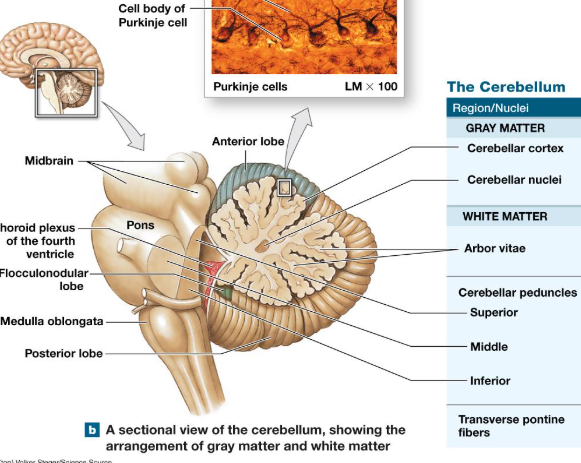
Gray matter of Cerebellum
Cerebellar cortex
cerebellar nuclei
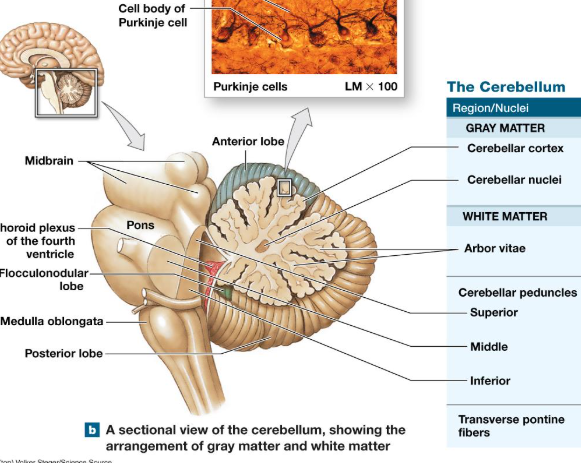
White Matter of Cerebellum
Arbor Vitae (tree of life striations)
cerebellar peduncles
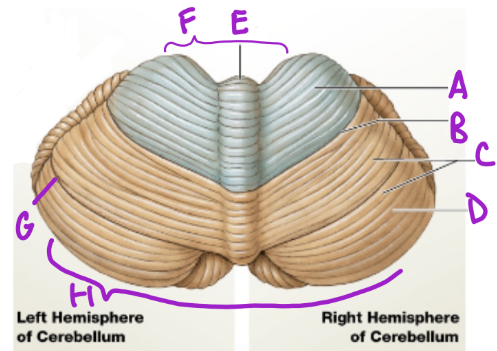
A
Anterior
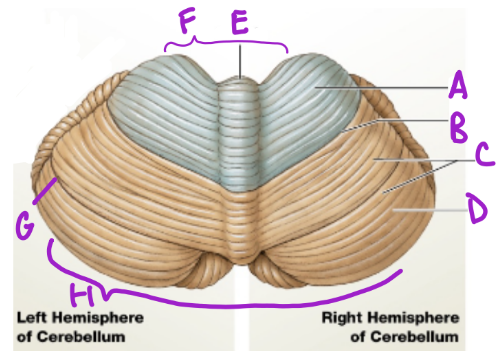
D
Posterior
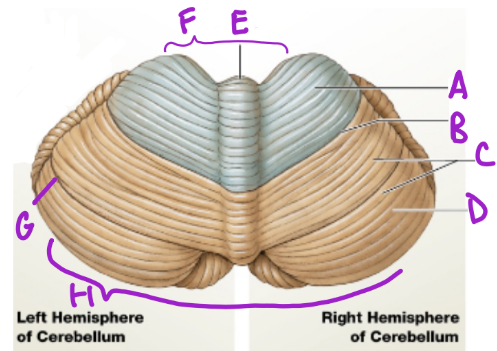
B
Primary fissure
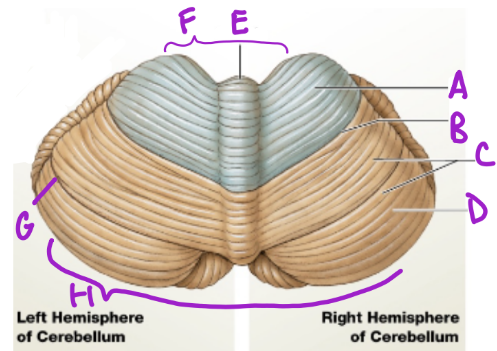
C
Folia
more folia, more neurons
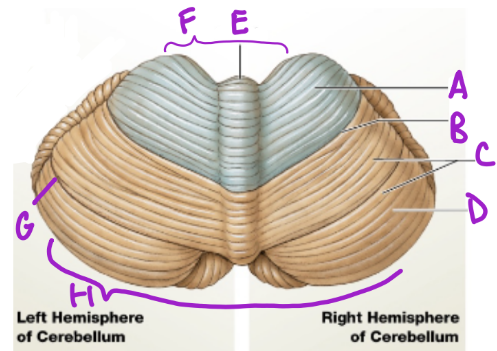
E
Vermis
separates cerebellum into 2 lat. hemispheres
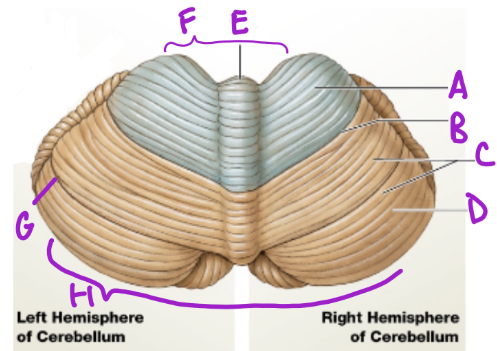
F
Intermediary zone
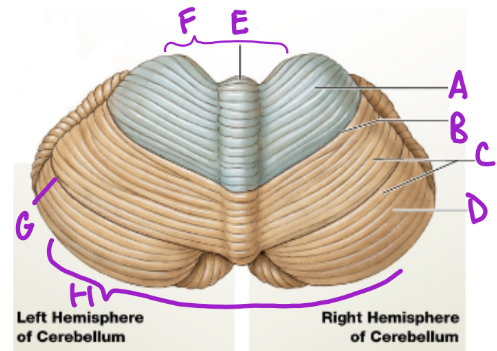
G
Horizontal fissure
creates superior and inferior areas
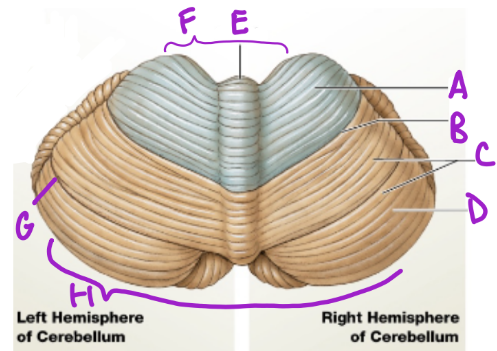
H
Flocconobular lobe
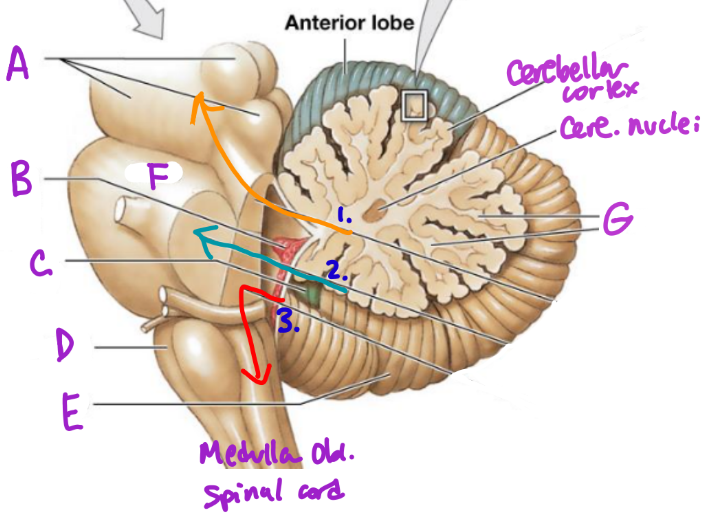
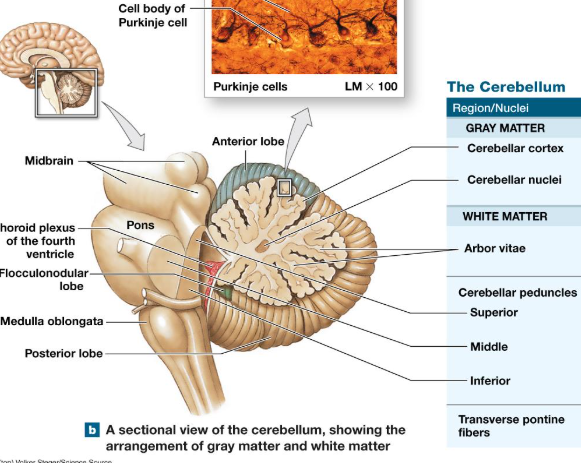
A
Midbrain
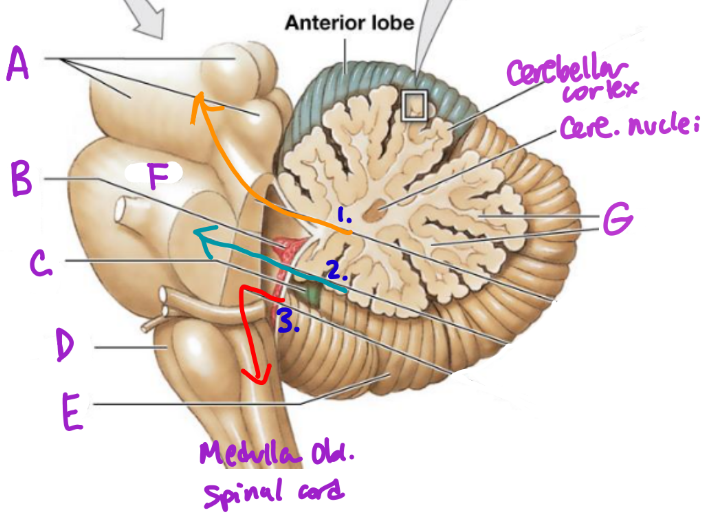
B
Choroid plexus
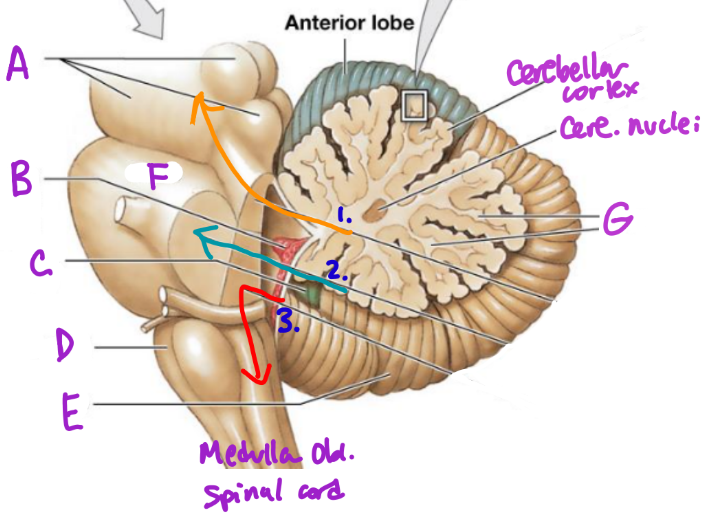
C
Flocculonodular lobe
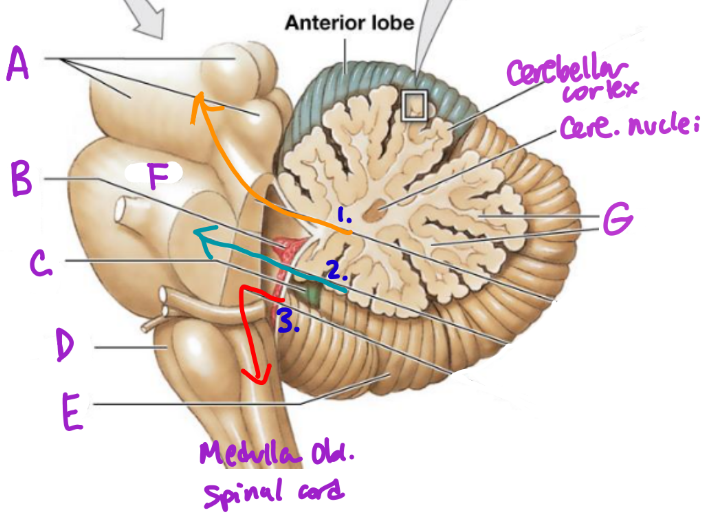
D
Medulla Oblongata
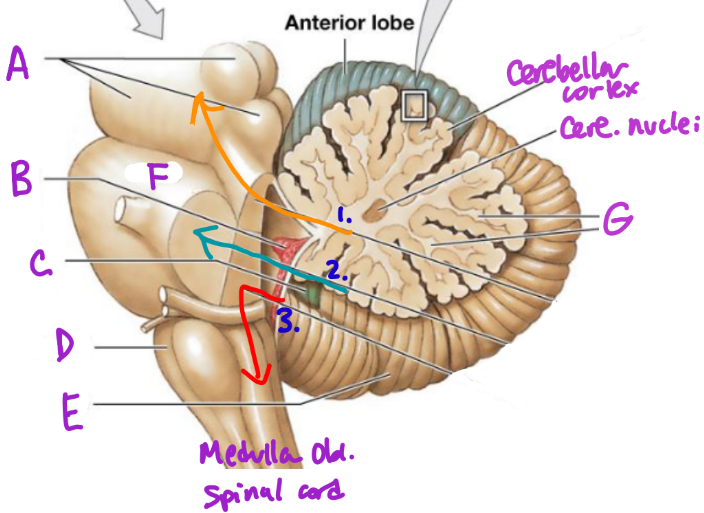
E
Posterior Lobe
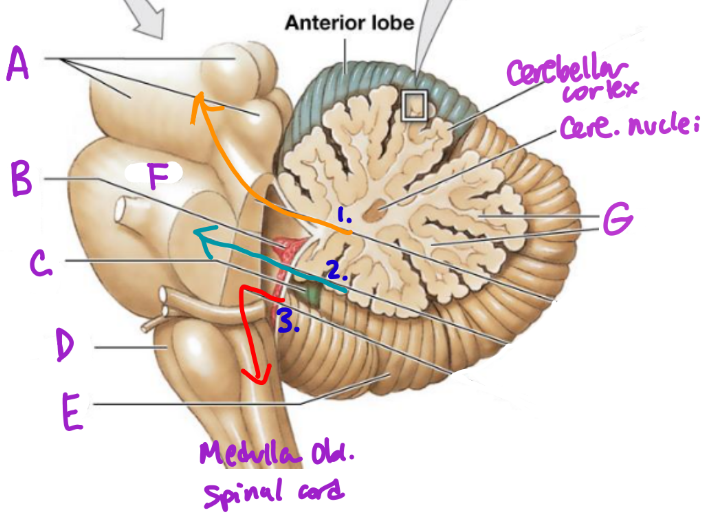
F
Pons
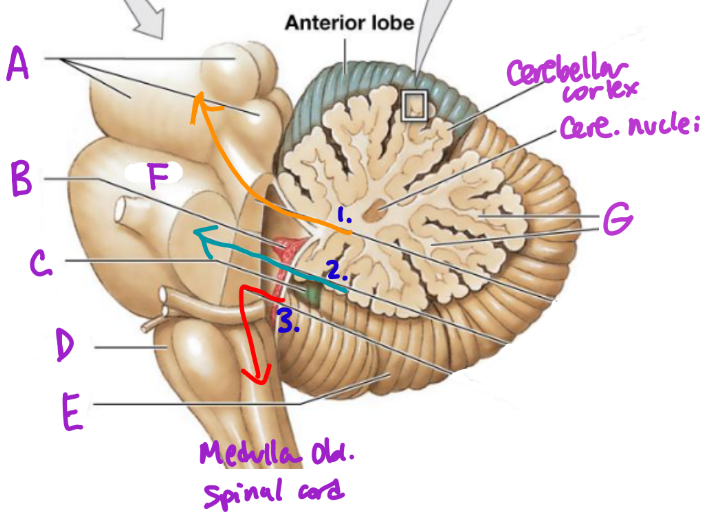
G
White matter/arbor vitae
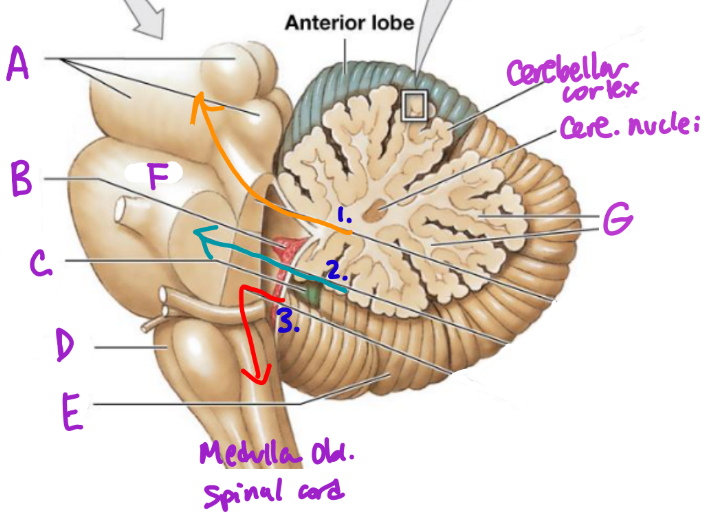
1
Superior Peduncle
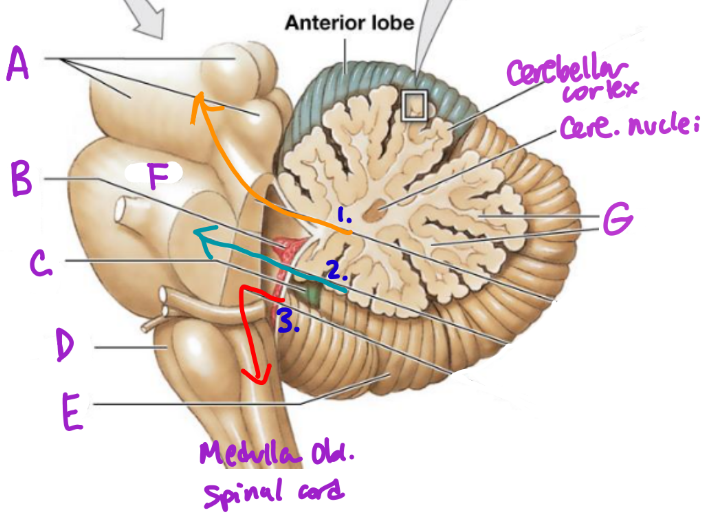
2
Middle peduncle
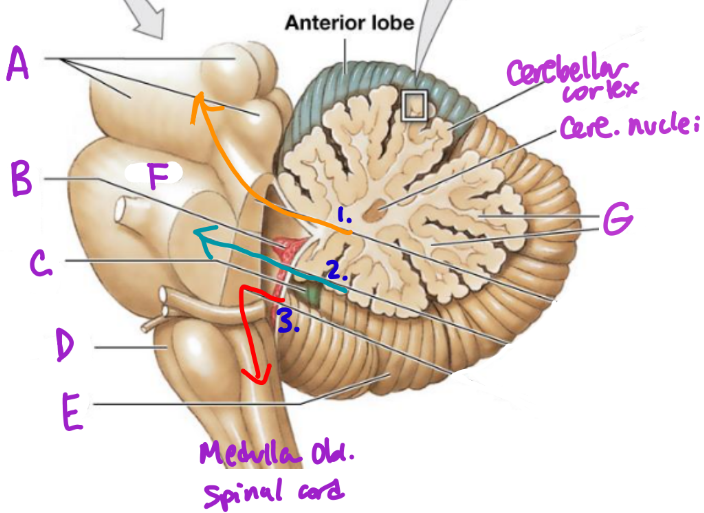
3
Inferior peduncle
Cerebellum Functions
hand eye coordination (guitar)
rehearsing learned movements/ learning
balance (muscle “tone”)
Coordination, tone, balance
relate back to somatic nervous system controlling skeletal muscle
Spinocerebellar pathways (tracks)
cerebellum doesn’t work in isolation
afferent/efferent (arrive/sensory and exit/motor)
enter and exit through peduncles
Ataxia
disturbance in muscle coordination
temporary cause: alcohol
slurred speech, awkward gait, trouble with fine motor movements
Dysmetria: type of ataxia
inability to control distance, speed, range of motion
Diencephalon (3 areas)
epithalamus
thalamus
hypothalamus
Epithalamus
roof of dienceph, superior to 3rd ventricle
anterior side has choroid plexus of 2 lat. ventricles
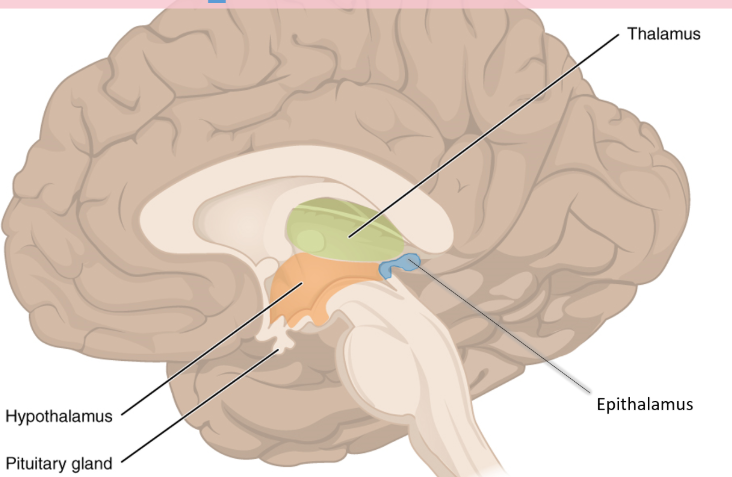
Pineal Gland
near posterior portion of epithalamus
melatonin production
Circadian rhythm and melatonin cycle
body adjusts
can be impacted/rewired with drugs
blue light inhibits melatonin prod
Thalamus
major part of diencephalon
central relay****
made of many nuclei
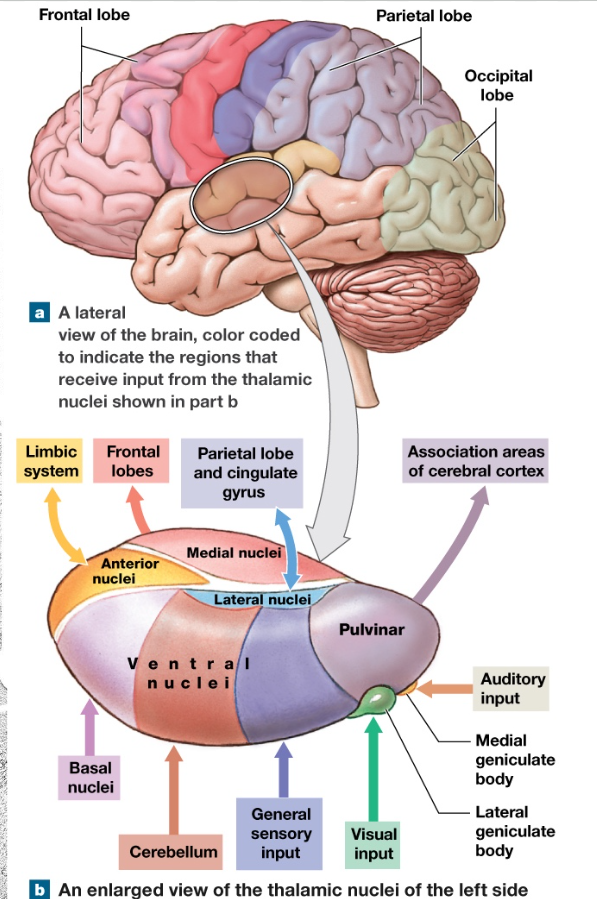
Nuclei is
cluster of nerve cell bodies in CNS
analogous to PNS’s ganglia/ganglion
Hypothalamus
floor of diencephalon
has mamillary bodies (memory?)
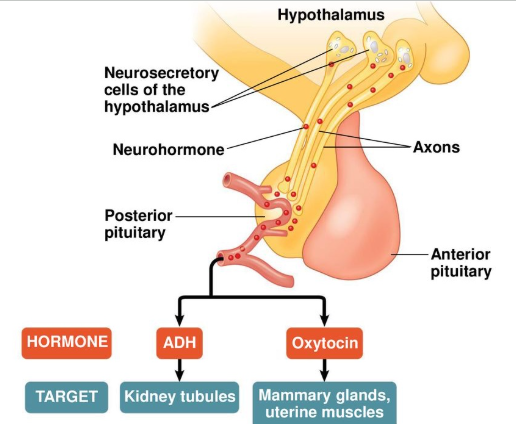
Funct of Hypothalamus
produce and secretes ADH (antidiuretic), oxytocin
sends to posterior pituitary gland
Thermoregulation
“Internal Thermostat”
Homeostasis
neg. feedback
circadian rhythm
auto centers: regulating blood pressure and heart rate
Subconscious control of skeletal muscle
direct motor patterns associated with emotions
Emotional, Behavioral drive
Feeding, thirst, satiety center
Limbic (“border”) Center
Emotion Center, basic emotional states
works with hypothalamus
link conscious funct of cerebrum to automatic functs of brainstem
memory, storage, retrieval
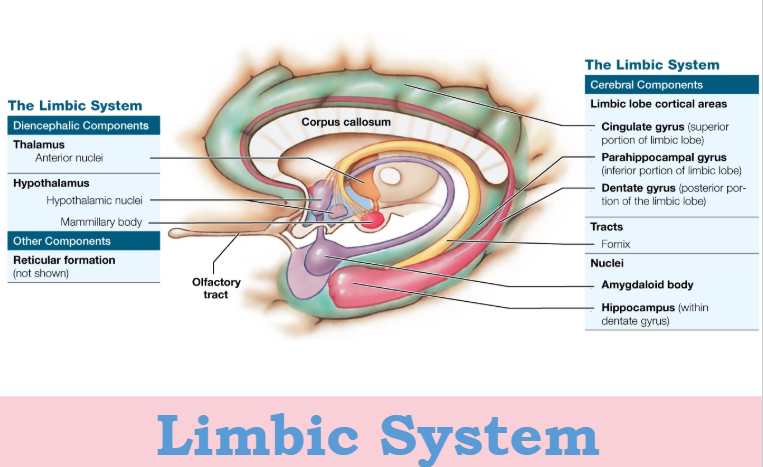
Hippocampus
memory
Amygdala
“Fight or flight response, freeze”
interface between limbic system & cerebrum & sensory organs
sympathetic NS stimulated (typically)
Cerebrum
Surface a: 2200
largest part of brain
highest level of thinking
somatosensory info
cerebral cortex: outermost portion
What splits the cerebrum into 2 hemispheres?
Longitudinal Fissure
Basal Nuclei
masses of gray matter, UNmyelinated neurons
function via feedback loop with cerebral cortex
constantly adjusting muscle tone
Commissural Fibers
White Matter connecting lobes of brain
Fibers connecting 2 hemispheres
best example of c.fibers is Corpus Callosum
C.C. is cut to prevent seizures (epilepsy)
Frontal Lobe
its anterior contains prefrontal cortex (developed by 25, last part to fully develop)
motivation, planning, exec. funct, attention and focusing
short term mem
What’s in the frontal lobe?
Prefrontal Cortex
Precentral gyrus
Broca’s area
Parietal lobe
posterior and dorsal to frontal lobe
proprioceptive (where body is in space)
mechanoreceptive (touch)
language processing
contains post-central gyrus
Post central gyrus
contains somatosensory cortex (AFFERENT info, goes up to brain to be processed)
Temporal Lobe
Inferior, posterior to frontal lobe
Auditory complex (hearing), and some visual input
Wernicke’s area
Wernicke’s area
temporal lobe
for comprehension of language (written and spoken)
unilateral, dominant hemisphere
If Rightie, left side of brain
Occipital Lobe
Vision