audition
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
audition
sense of hearing
goals of auditory system
detect sound; localize sound; identify and differentiate sound
loudness
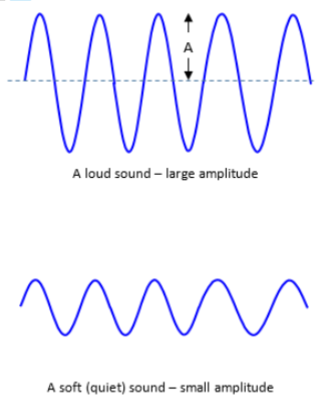
determined how different that compressions and expansions (rarefactions) are from one another; the unit is decibel; visualized as the amplitude of waveform
frequency
determined by how many cycles of compression and expansion (rarefaction) occur each second; unit is hertz; perceive sounds between 30-20000 hz, not all perceived equally
timbre
quality of sound; if sounds have the same frequency and loudness, we can still perceive them as different effects of the sound; effects are made up of the complexities of the sound, which generally includes different sub-frequencies that co-occur with the dominant frequency
outer ear middle ear inner ear
three major parts of ear
outer ear
sound is funneled through the pinna; sound travels through the ear canal; sound reaches and vibrated the tympanic membrane
middle ear
three bones in the middle ear (collectively called ossicles) ear help to start transducing sound -malleus (hammer) - incus (anvil) - stapes (stirrup); these bones transmit vibrations received by the tympanic membrane to the cochlea
inner ear
sound pressure from the air is converted via the tympanic membrane and ossicles (middle ear bones) into fluid pressure in the cochlea; cochlea divided into three sections: scala vestibuli, scala media, scala tympani; the receptive part of the ear is known as the organ of cortici; it has three major parts: basilar membrane, hair cells that are anchored to the basilar membrane; tectorial membrane thar makes contact with the cilia of he hair cells; sound is transduced into a signal when sound waves cause basilar membrane to move relative to the tectorial membrane, bending the cilia of the hair cells and producing receptor potentials