APES // Chapter 4: Global Climates & Biomes
1/61
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Terrestrial Biome
Geographic region categorized by their average temperature, precipitation, & plant growth forms.
Aquatic Biome
An aquatic region categorized by the combintion of salinity, depth, & water flow.
Habitat
Tundra
Cold & treeless, but low-growing vegetation
Frozen soil in winter
Short growing season (4 months)
Contains permafrost
Permafrost
Impermeable & permanently frozen layer of soil found in the tundra
Boreal Forest/Coniferous Forest/Taiga
Coniferous evergreen trees
Cold winters & short growing seasons
50-60 Degrees N (Europe Russia N. America)
Nutrient-poor soil from low decomposition
Temperate Rainforest
Oceans currents create moderate temperatures
High precipitation
Found in W. coasts of N. America, S. Chilie, W of New Zealand, Tasmania islands
12 month growing season
Supports very large trees
Temperate Seasonal Forest
Warm summers & cold winters
1m (39inches) of rain per year
Found in E. US, Japan, China, Europe, Chile, E. Australia
Broadleaf deciduous trees (beech, maple, oak, hickory)
More nutritious soil from more decomposition
Woodland/Shrubland
Hot dry summers, mild rainy winters
S. of Cali/Australia/Africa & Mediterranean Sea
12 month growing season, but constrained by low precipitation & low temperatures
Wildfires are common & plants are well adapted
Temperate Grassland/Cold Desert
Cold harsh winters, hot dry summers
Lowest amount of rain in all the temperate biomes
Great Plains in N. America, S. America, centeral Asia, E. Europe
Plant growth restricted by not enough rain in summers & too cold in winter
Grasses & flowers, nonwoody plants with frequent grazing
Tropical Rainforest
A warm & wet, found between 20 N & 20 S of equator
Average temperature >20 C
C. & S. America, Africa, S.E. Asia, N.E. Australia
Very little temperature variation
Most biodiversity per hectare per terrestrial biome (2/3 of land species)
Tropical Seasonal Forest/Savana
Warm temperatures, wet & dry seasons
C. America, Atlantic coast of S. America, S. Asia, N.W. Australia, sub-Saharan Africa
Pretty fertile soil from high decomposition rates
Plants are restricted by low precipitation
Grasses & scattered deciduous trees
Subtropical Desert
30 N & S, hot & very dry condition, very little vegetation
Mojave Desert (S.W. US), Sahara Africa, Arabian (Middle East), Great Victoria (Australia)
Cacti, euphorbs, & succulents are well adapted
Polar Desert/Ice Cap
Littoral Zone
Shallow zone of soil & water where there are emergent plants & algae for lakes/ponds
Limnetic Zone
Open water of lakes & ponds, most phytoplankton are here
Phytoplankton
Floating algae
Profundal Zone
Zone of water in deeper lakes where there’s no sunlight & below the Limnetic zone
Benthic Zone
Muddy bottom of lakes, ponds, and oceans
Streams & Rivers
Flowing fresh water from underground springs/runnoff from rain/snow
Streams are narrow & carry less water than rivers
Lakes & Ponds
Standing water, and lakes are larger than ponds
Some waters are too deep to support emergent vegetation
Contains different zones
Oligotrophic
Lake with low level of productivity, low level of N & P
Mesotropic
Lake with moderate level of productivity, moderate level of N & P
Eutrophic
Lake with high level of productivity, high amounts of N & P
Freshwater Wetland
Submerged/saturated by water for at least part of the year
Shallow enough for emergent vegetation
Very very productive
Salt Marsh
High in salinity
No woody emergent vegetation
Coast of temperate climates
Very very productive
Estuary
Mangrove Swamp
Coast of tropical & subtropical biomes
Salt tolerant trees & submerged roots
Mangrooves help protect from erosion & storm damage
Intertidal Zone
Narrow band between high & low tide
Waves crash onto the shore, challenging for organism to hold on and not get washed aw
Coral Reef
Most diverse marine biome
Warm shallow waters beyong the shoreline
Most diverse corals reefs are found in waters with poor nutrients & food
Coral Bleaching
Algae inside corals die, causing corals to turn white
Open Ocean
Deep ocean water
Far from shoreline
No sunlight at the bottom
Separated into different zones
Photic Zone
Upper layer where photosynthesis is possible from amount of sunlight
Aphotic Zone
Deeper layer of ocean where there’s not enough sunlight for photosynthesis
Chemosynthesis
Some bacteria in the oceans use this to generate energy with methane & hydrogen sulfide
Salinity
Total amount of material dissolved in water (mostly constant)
3.5% salinity in sea water
Increased by evaporation & sea ice formation
Decreased by precipitation, runoff from land, & melting sea ice
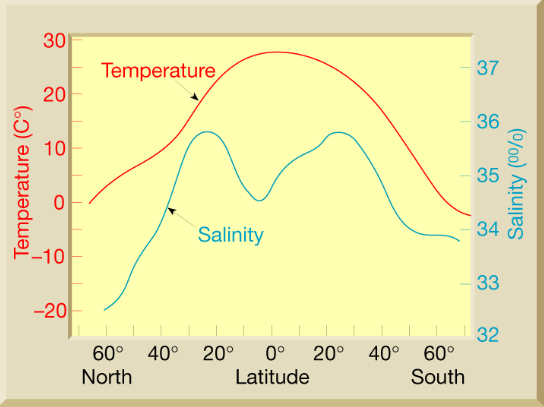
Why does this happen?
High amount of solar radiation at equator (high temperature)
High amounts of precipitation at equator (low salinity)
High amounts of evaporation at 30 N & S (high salinity)
Ocean Density
Higher temperature —> Lower density
Higher salinity —> Higher Density
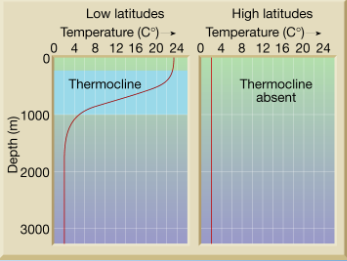
Thermocline
Layer of ocean with rapid change in temperature with depth
Creates a vertical barrier for many marine life,
Strong in low latitudes, nonexistent in high
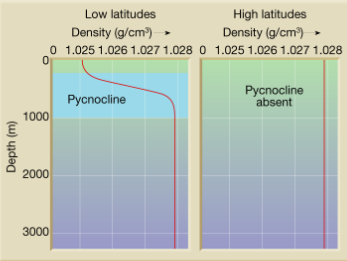
Pycnocline
Layer of ocean with rapid change in density with depth
Strong in low latitudes, nonexistent in high
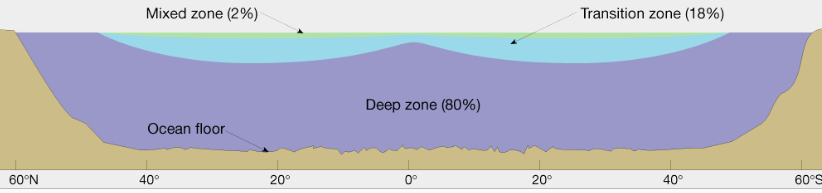
3 layered zones in the ocean according to density
Shallow Surface/Mixed zone —> 2%
Transition Zone —> 18%
Deep Zone —> 80% (only thing found in high latitudes because of constant temperature & density)
Surface Currents
Move warm & cold water around the plant & impact global climate & productivity
Driven by temperature, gravity, wind, Coriolis, continent locations
Surface Waters + Winds + Coriolis = Direction if flows in
(Tropical is 8 cm higher than mid-latitude because of a slight slope that causes water to flow away from the equator)
Gyres
North Pacific (clockwise)
South Pacific (counter-clockwise)
North Atlantic (clockwise)
South Atlantic (counter-clockwise)
Indian (counter-clockwise)
Upwelling
Rising cold water that’s nearing the shore with lots of nutrients from sunken & decomposed organic matter, creates fertile ocean waters with lots of phytoplankton.
Global Conveyor Belt/Thermohaline Circulation
Moves heat & nutrients around the globe
Mixes water across the globe
driven by weird high salinity surface waters at 30 N
Takes hundreds of years to circulate fully
Could be negatively affected by climate change
How could climate change possibly affect thermohaline circulation
Water atmosphere —> increase ice melt —> decrease salinity & density —> less sinking/potential shutdown of the circulation —> no more warm water in western Europe, where climates would be cool
El Nino-Southern Oscillation
Periodic reversal of water/wind currents in the equatorial Pacific
Results from unstable interaction of ocean surface & atmosphere
Creates worldwide effects on weather
Fluctuations of temperatures between ocean & atmosphere in Equatorial Pacific Ocean
El Nino —> Periodic warming
Trade winds weaken/reverse
Upwelling on S. America weakens (bad for commercial fishing)
El Nina —> Periodic cooling
Trade winds strengthen and more warm water eastwards
Upweling in S. America increases
More Hurricanes in the Gulf/Atlantic Ocean
Happened for the last 125k years
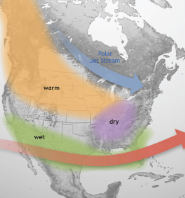
El Nino Conditions in N. America
Warmer in N.W.
Dryer in E.
Wetter in extended Pacific Jet Stream (south)
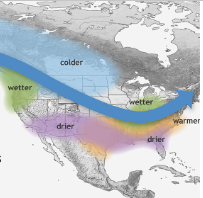
La Nina Conditions in N. America
Cooler above variable Polar Jet stream (N.)
Wetter below variable Polar Jet stream (N.W.)
Warmer below S.E.
Dryer in S.
Saturation Point
Maximum water vapor capacity of the air, warmer air can hold more
Adiabatic Cooling
Warm air rises —> Pressure decreases —> Cooler air —> Cool air falls
Adiabatic Heating
Cool air falls —> Pressure increase —> warmer air —> warm air rises
Latent Heat Release
Heat exchanged in a phase change (cooling from when water vapor turns into liquid water, because latent heat was released)
Atmospheric Convection Current
Hadley Cell
Two cells between 0 & 30 N and 0 & 30 S
Equator has warm air rising, then cool air sinks at 30 N & S
Contains ITCZ
Band of rain clouds that encircles Earth near equator due to Convergence of air from two cells
Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ)
A moving band of rain clouds that encircles Earth near the equator due to Convergence of air from the Hadley Cells
Polar Cell
Between the poles at 60 N & S
Ferrell Cell
Between 60 N & 30 N and 60 S & 30
Coriolis Effect
Earth rotates creating more than 2 convection cells
Wind flows due to differences in horizontal pressure (always from high to low)
Clockwise in the northern hemisphere & counter-clockwise in the southern hemisphere
Rate of rotation is fastest at the equator because of largest circumference
Effect is strongest at the poles & weakens near the equators
Rain Shadow
Rain/Snow in the windward slop of the mountain towards the sea
Wind goes up the mountain, pressure decreases, adiobitc cooling and the moisture condenses & rains
dry slope on the other side because of the rain shadow
Low Pressure System
Decreasing pressure approaching center
counter-clockwise
inwards
air rises
decreasing temperature
Condensation & cloud flormation
cloudy skies (rainy weather)
High Pressure Systems
Pressure increases as you approuce the center
clockwise (opposite in the southern hemisphere)
outwards
sinking
warmer air
clear skies
evaporation & cloud dissipation