Working memory model
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Who proposed the working memory model?
Baddeley and hitch 1974
What does the working memory model suggest about short term memory?
That short term memory is made up of 4 components
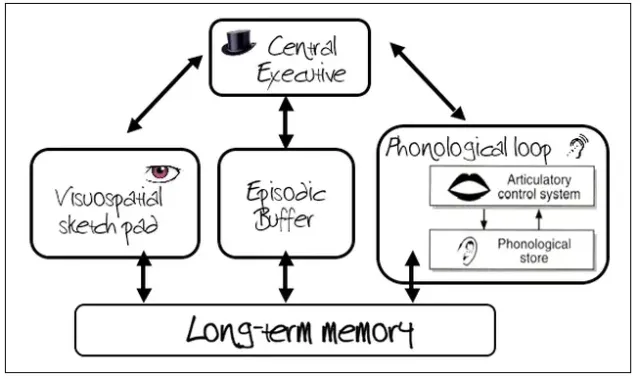
Central executive, phonological loop, visuospatial sketch pad, episodic buffer
What is the role of the central executive?
Control system that coordinates the activities of other components, limited capacity and is responsible for directing attention and decision making.
Allocates resources to the slave system.
What is the role of the phonological loop?
Process auditory and verbal information. Has 2 substores;
phonological store/inner ear - stores sound for a brief period of time
Articulatory rehearsal system/inner voice - allows for the repetition or rehearsal of verbal information
What is the Visuo-spatial sketch pad ?
Process visual images and spatial information
What is the episodic buffer?
Integrates information and helps create a coherent memory
Working memory model - diagram
Supporting research for the working memory model
Shallice and Warrington (1970) patient KF
Suffered severe brain damage after a motorcycle incident.
He had affected STM for verbal (auditory) information suggesting his phonological loop was damaged, but he had a normal STM for visual information suggesting his phonological loop was intact, proving that the 2 are distinct systems.
Dual task studies - proving that visual and verbal information are processed seperately
Baddeley 1975 - participants could perform visual and verbal tasks simultaneously without much difficulty. When asked to do 2 visual tasks or 2 verbal tasks simultaneously performance dropped. Proves that visual and verbal tasks are processed separately as they do not interfere with each other.
Evaluate the working memory model - strength
Case study support
Supported by KF case study
Shallice and Warrington found that KF had an impaired phonological loop as his STM for verbal information was affected but an intact Visuospatial sketch pad as his STM for visual information was normal
Suggests that STM is made up of distinct sub stores, in separate parts of the brain rather than one system.
Provides support for the distinct STM stores
Evaluate the working memory model - strength
Dual task studies
Other studies carried out by Baddeley support the idea that the central executive has a limited capacity
Dual task studies - higher performance rates when asked to perform visual and verbal tasks simultaneously compared to 2 visual tasks or 2 verbal tasks simultaneously.
Easier to perform 2 different tasks because info doesn’t interfere with each other
Supports the distinction between the phonological loop and visuospatial sketch pad
Evaluate the working memory model - strength
Neuroscience
Neuroscience shows that different parts of the brain are activated for different memory tasks
Braver et al. Used fmri scans found that tasks involving the central executive activated the prefrontal cortex and task using the phonological loop actives areas associated with language processing.
Components of WMM have distinct biological bases.
Brain scanning - credible - objective empirical evidence.