STAT 164 - 3RD LE - CHAPTER 5.3
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
RANDOMIZED EXPERIMENT
a longitudinal study characterized by the presence of experimental units and treatments that are manipulated, randomized or controlled by chance to detect cause-and-effect relationship
RANDOMIZED EXPERIMENT
goal is to see the effect of the treatment or exposure to the response while controlling for other factors
RANDOMIZED EXPERIMENT
In terms of causation, _________________ presents the strongest support to causation.

ADVANTAGES OF EXPERIMENTS
Allow set-up of direct comparison between treatments of interest (_________)
randomization
ADVANTAGES OF EXPERIMENTS
Minimize any bias in the comparison (_____________)
replication
ADVANTAGES OF EXPERIMENTS
Minimize error in the comparison (error control and ____________)

ADVANTAGES OF EXPERIMENTS
____________ are in control of the experiment (experimental vs observational)
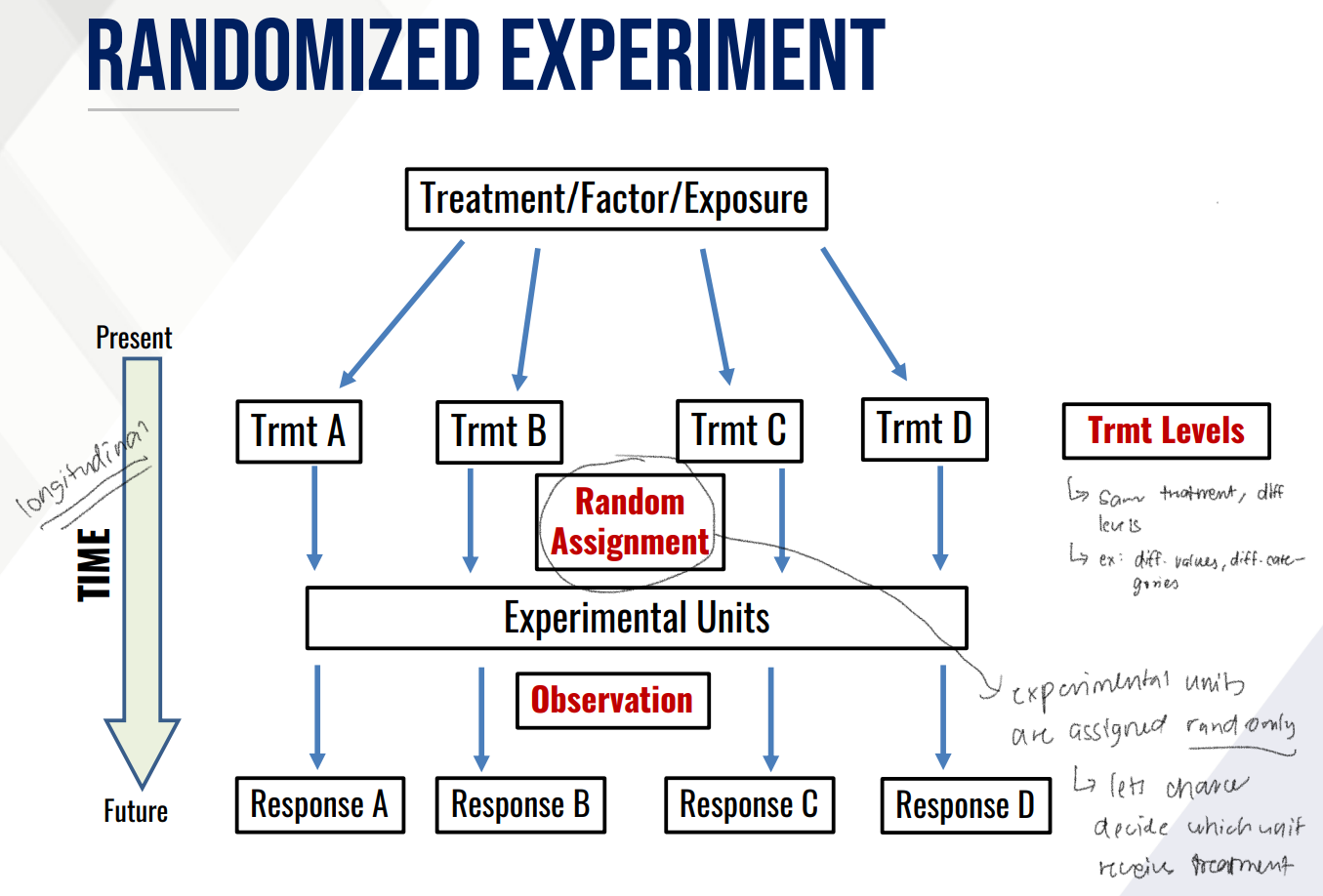


set of experimental procedures or conditions whose effects are to be measured and compared
Treatment Levels
pre-set quantities of a quantitative factor or categories of a qualitative factor
Response Variable
characteristic used to measure the effect of a treatment
Response Variable
the dependent variable or outcome that we observe after applying a treatment to an experimental unit
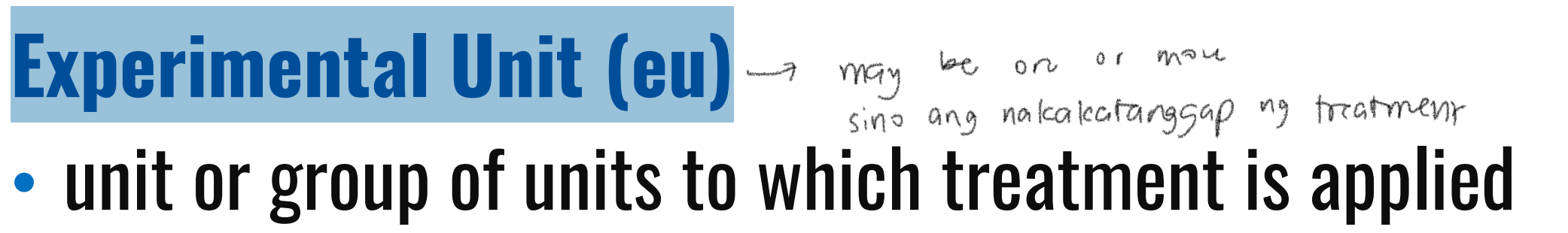
unit or group of units to which treatment is applied

unit on which the response variable is observed or measured

variation in the observed values of the response variable from experimental units treated alike

variation among sampling units within an experimental unit, and so were also treated alike


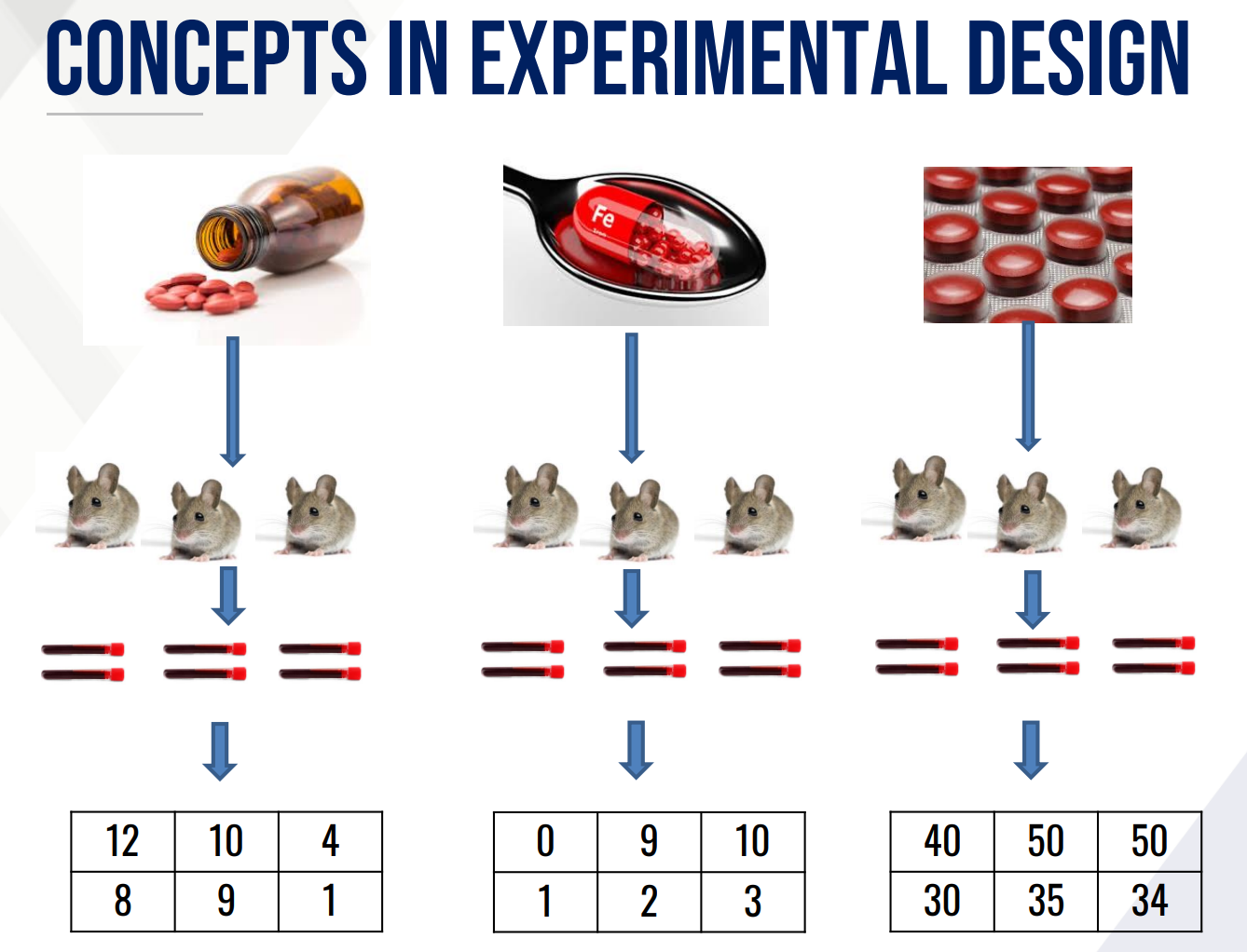
Provide the following:
Treatment/Factor:
Treatment Levels:
Response Variable:
Experimental Unit:
Sampling Unit:



Provide the following:
Treatment/Factor:
Treatment Levels:
Response Variable:
Experimental Unit:
Sampling Unit:

involves the assignment of treatments to the experimental units

practice of deliberately changing or manipulating treatments in a specified manner in order to evaluate the effect of these changes on the response variable

concerned with planning experiments in order to obtain maximum amount of information from the available resources
design structure
Component of the experimental design:
the way we randomly assign our treatment units.
treatment structure
Component of the experimental design:
set of factors or treatment units we want to measure

allows a trmt to be applied and observed more than once and provides an estimate of the experimental error
experimental error
It is the variation among responses of the EU, which cannot be obtained from only one replicate.

ensures trmts will have equal chance of being assigned to an eu that makes the estimate of the experimental error valid
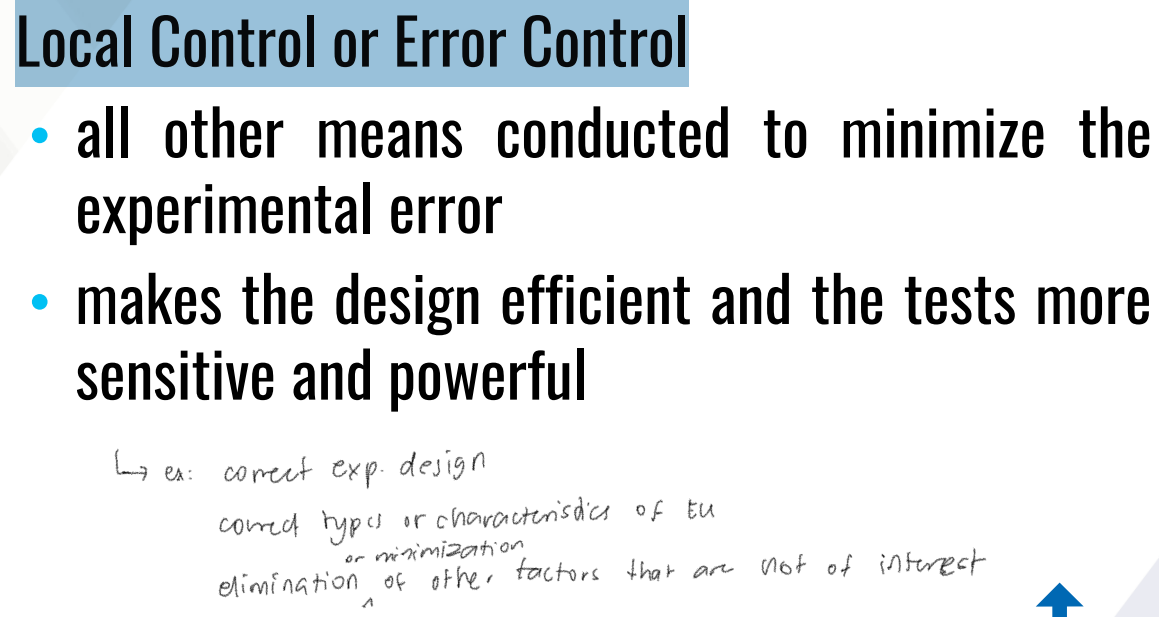
all other means conducted to minimize the experimental error

makes the design efficient and the tests more sensitive and powerful
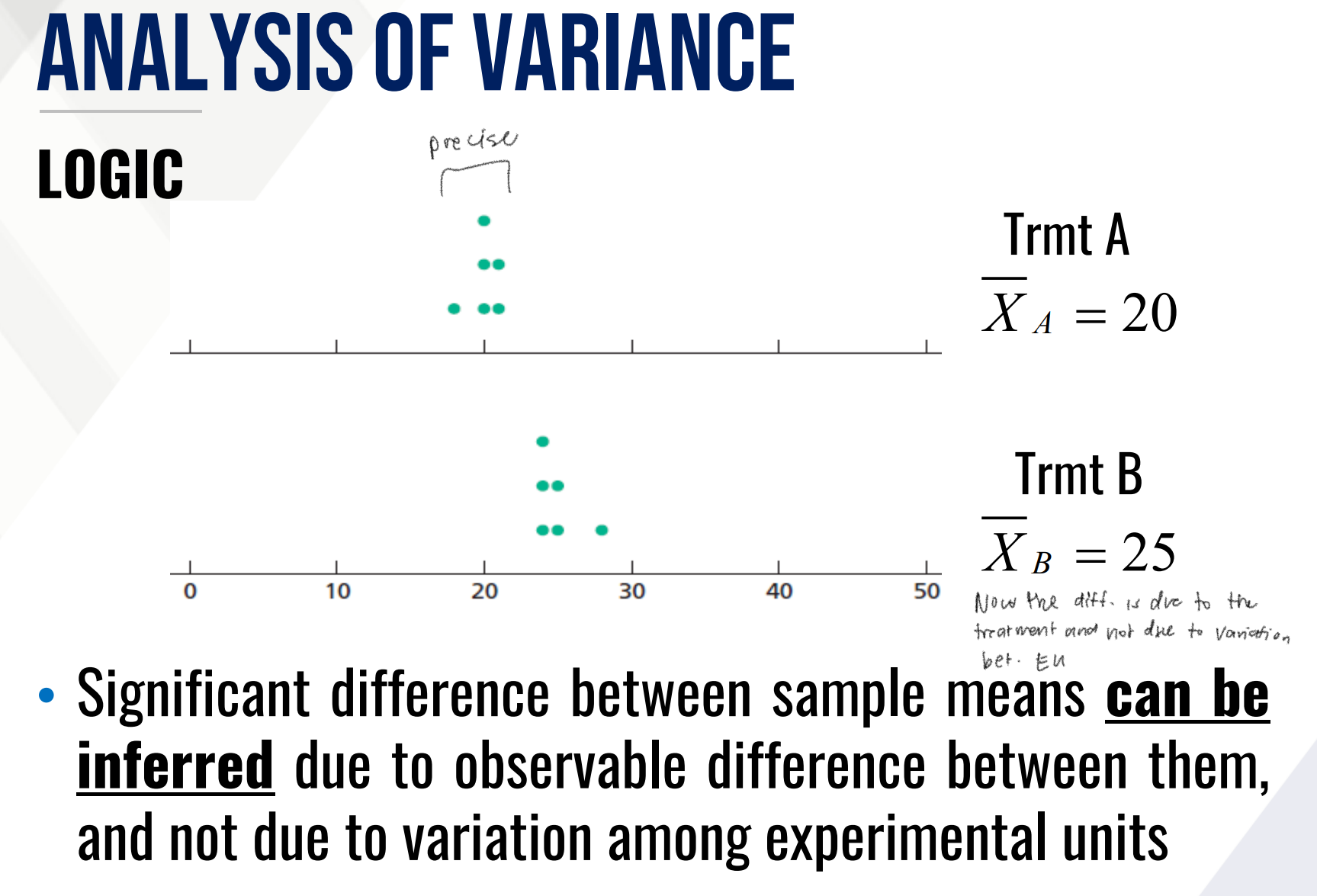
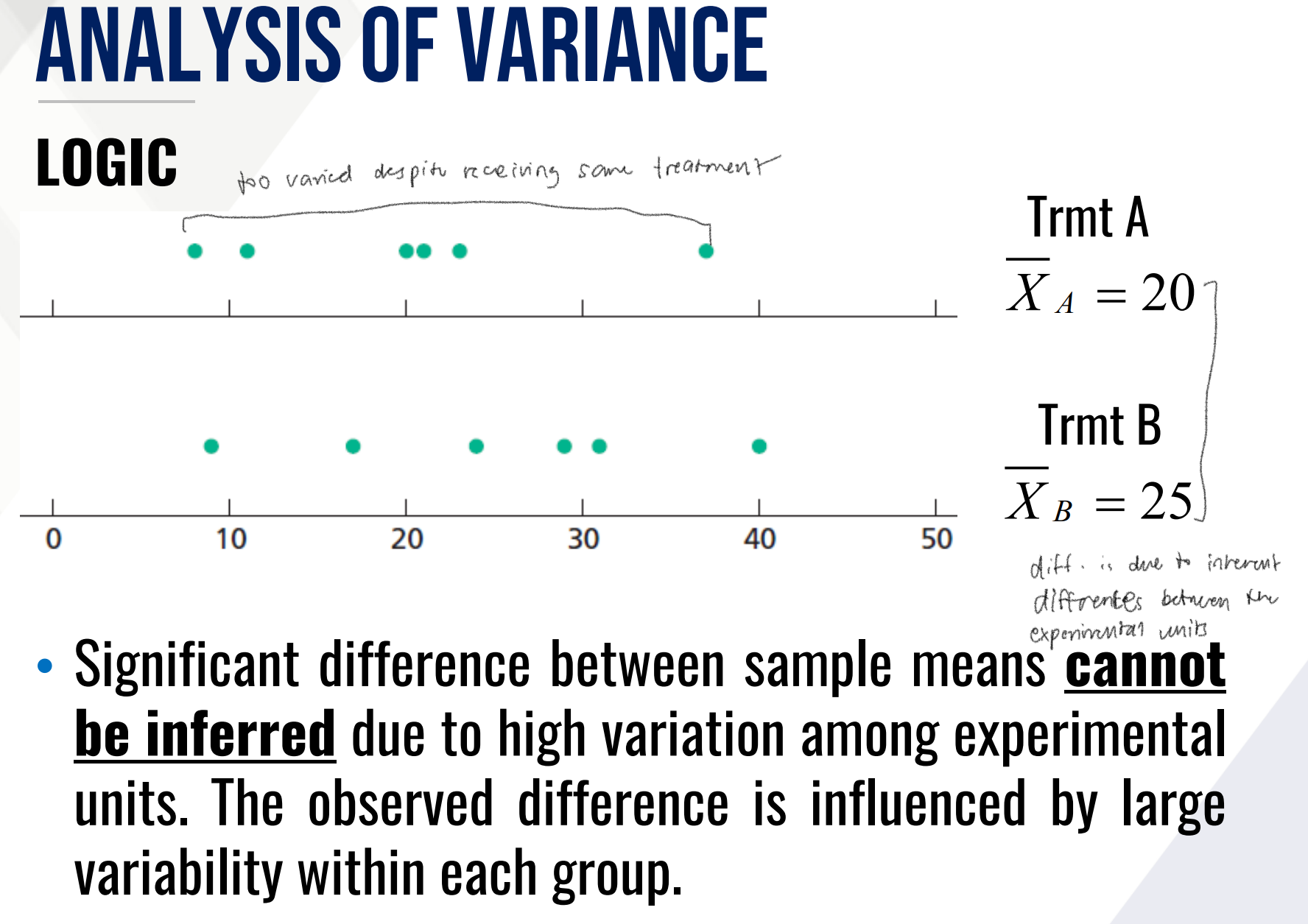
ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
a technique that compares the means of a response variable among groups dictated by the treatment levels
ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
main analytical tool used as a method to compare several means from a randomized experiment
ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
uses two measures of variances to detect differences among means
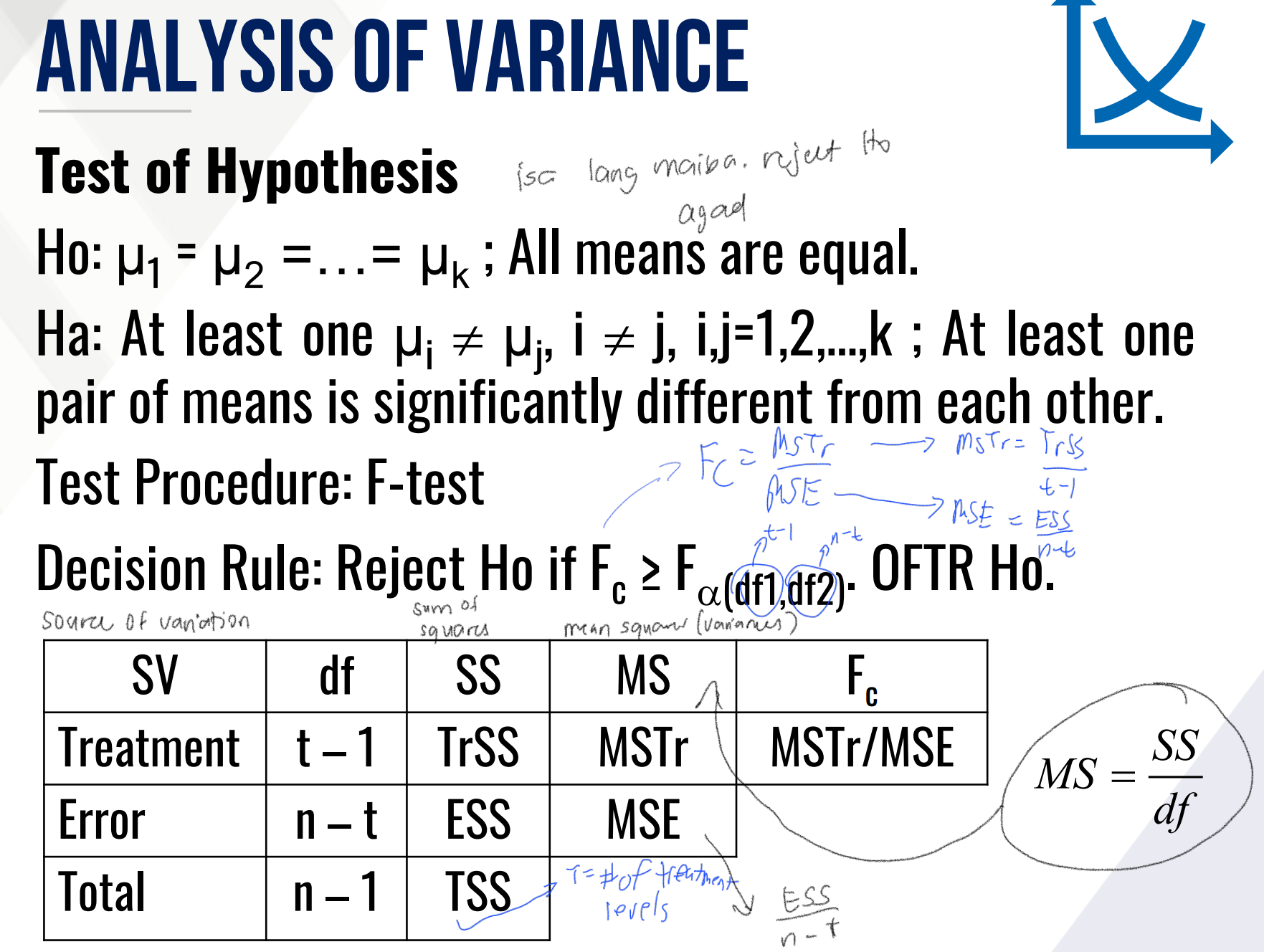
Provide the Test of Hypothesis informaiton for ANOVA:
Ho (in words)
Ha (in words)
Test Procedure
Decision Rule
And fill in the table:
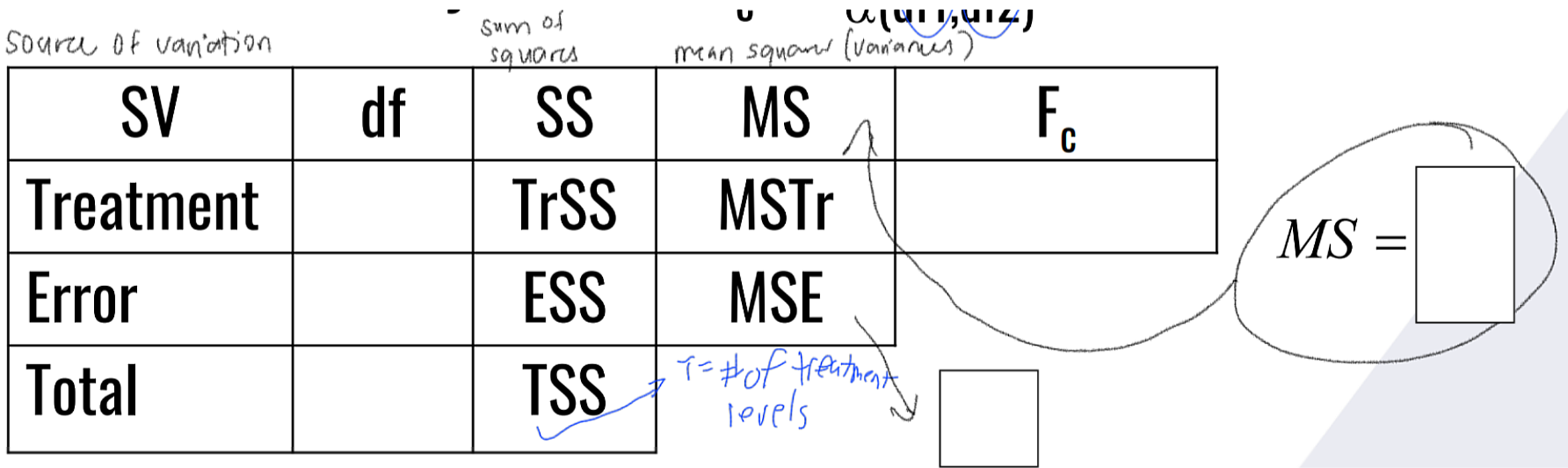
Error
__________ is the difference between the observed response and the model predicted response.
quantitative
Normality
Homoscedasticity
Independence
ASSUMPTIONS OF ANOVA
Response variable must be ____________
__________ of Errors
Errors or residuals must be normally distributed with mean equal to zero.
________________of Errors
Errors must have constant variance
____________of Errors
An error must not depend on another error.
Automatically satisfied when randomization is properly performed.
Normality
normally
not normally
Homoscedasticity
have constant; homoscedastic
do not have constant; heteroscedastic
ASSUMPTIONS OF ANOVA
Test of Hypothesis
__________ of Errors
Ho: The errors are _________ distributed.
Ha: The errors are _________ distributed.
_______________ of Errors
Ho: Errors ______________ variance (_______________).
Ha: Errors ______________ variance (_______________).
Decision Rule: Reject Ho if p-value ≤ α, oftr Ho.
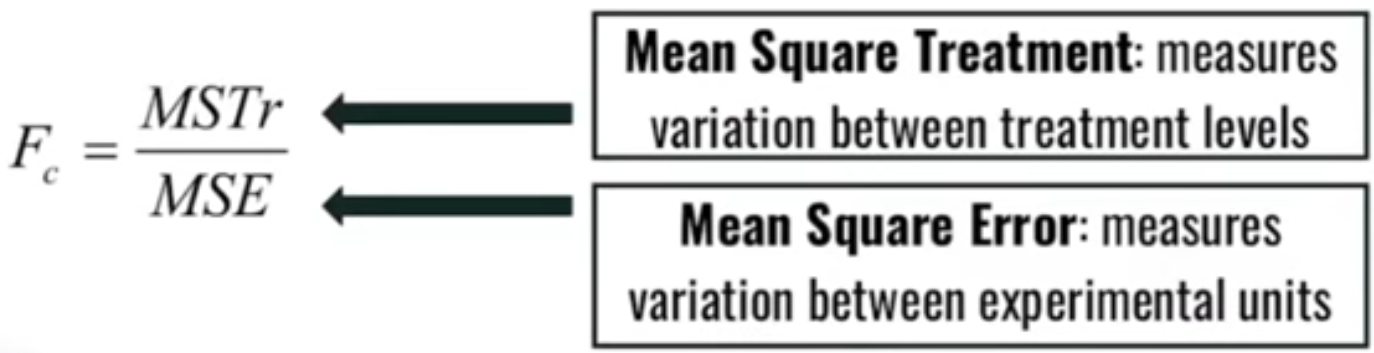
What is the formula for the computed F-statistic in ANOVA?

ANOVA - measures of variances
__________________: measures variation between treatment levels
__________________: measures variation between experimental units
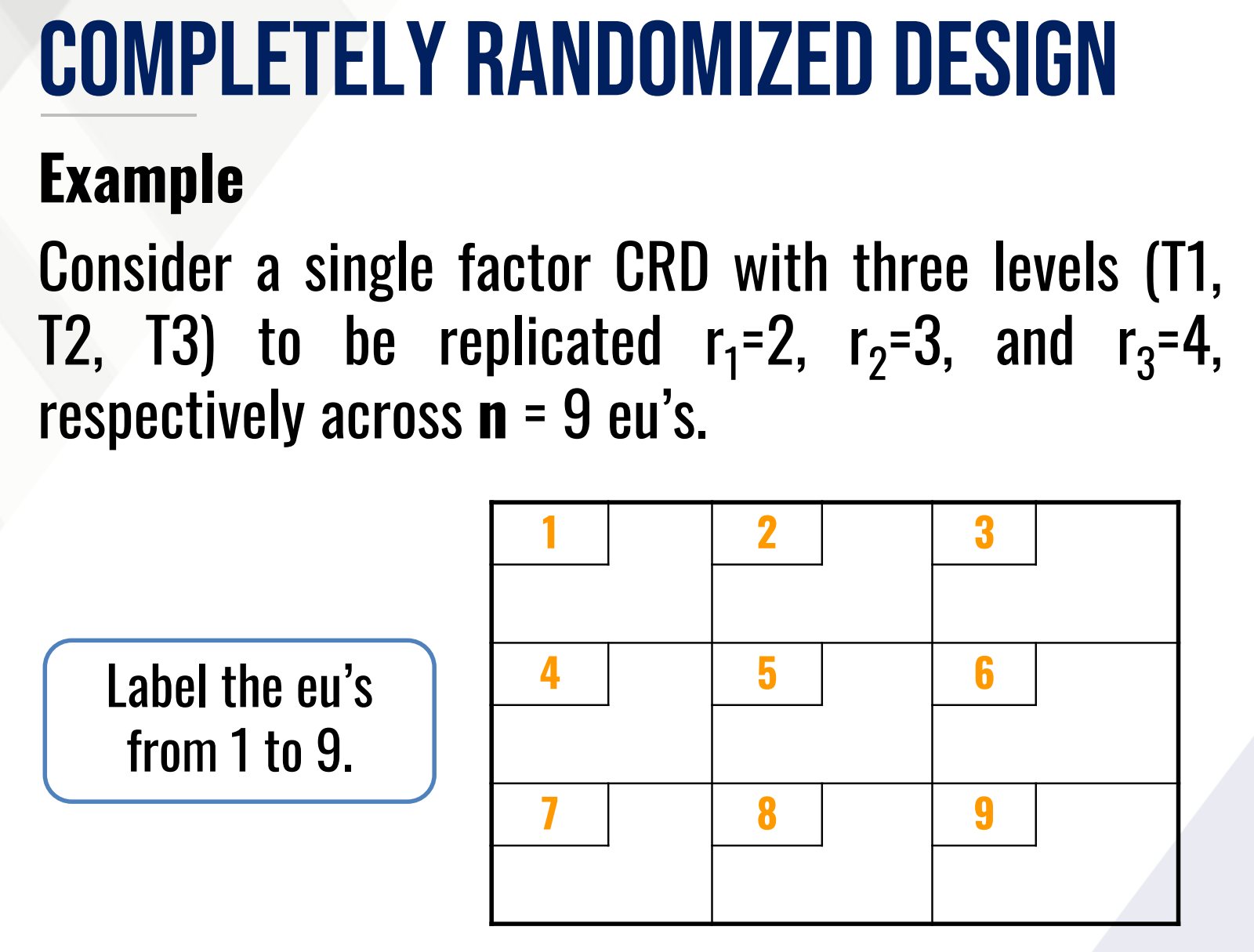
COMPLETELY RANDOMIZED DESIGN
most basic experimental design
COMPLETELY RANDOMIZED DESIGN
allocation of treatments is done by randomizing the treatments completely over the entire set of eu’s without any restriction imposed on the units
COMPLETELY RANDOMIZED DESIGN

the only criteria for data classification is the factor/s under test so eu’s must be as homogenous as possible
COMPLETELY RANDOMIZED DESIGN

applicable for both balanced and unbalanced replication


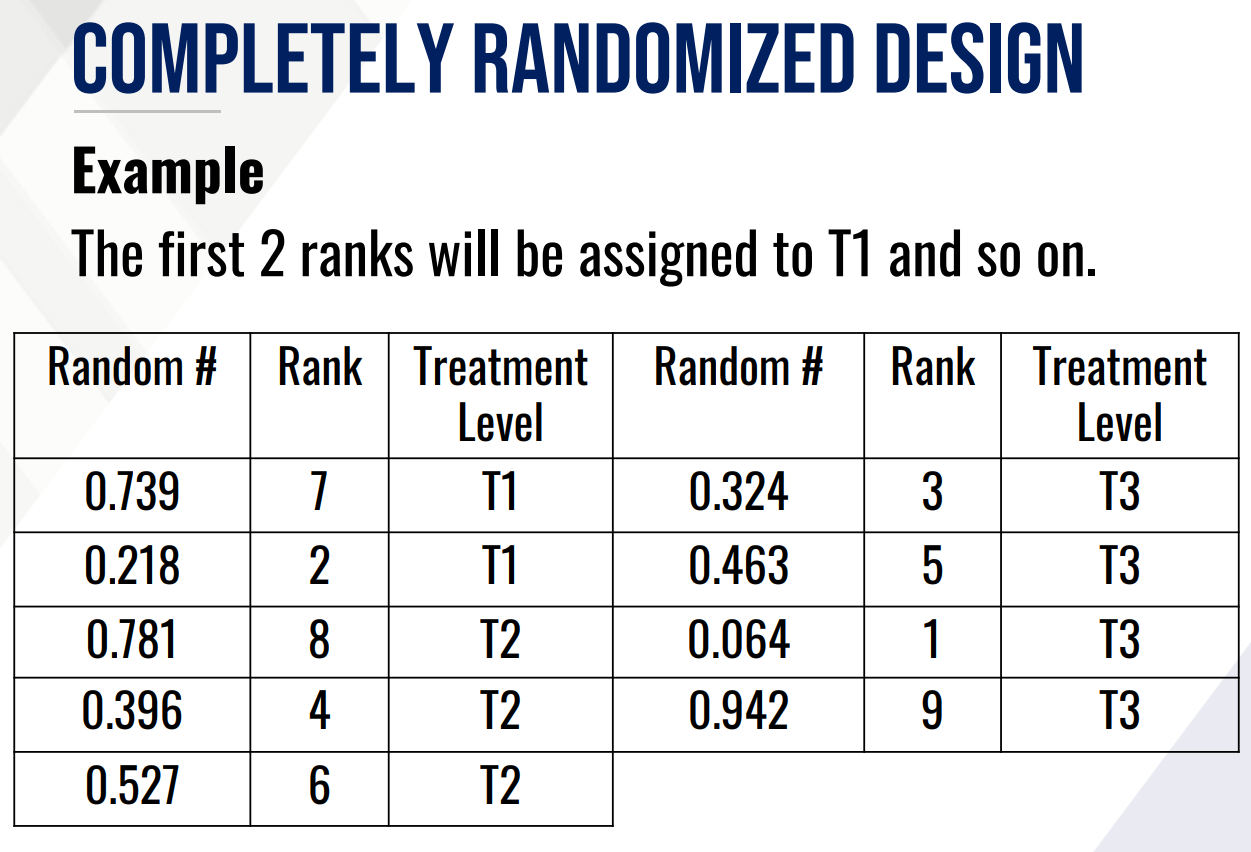
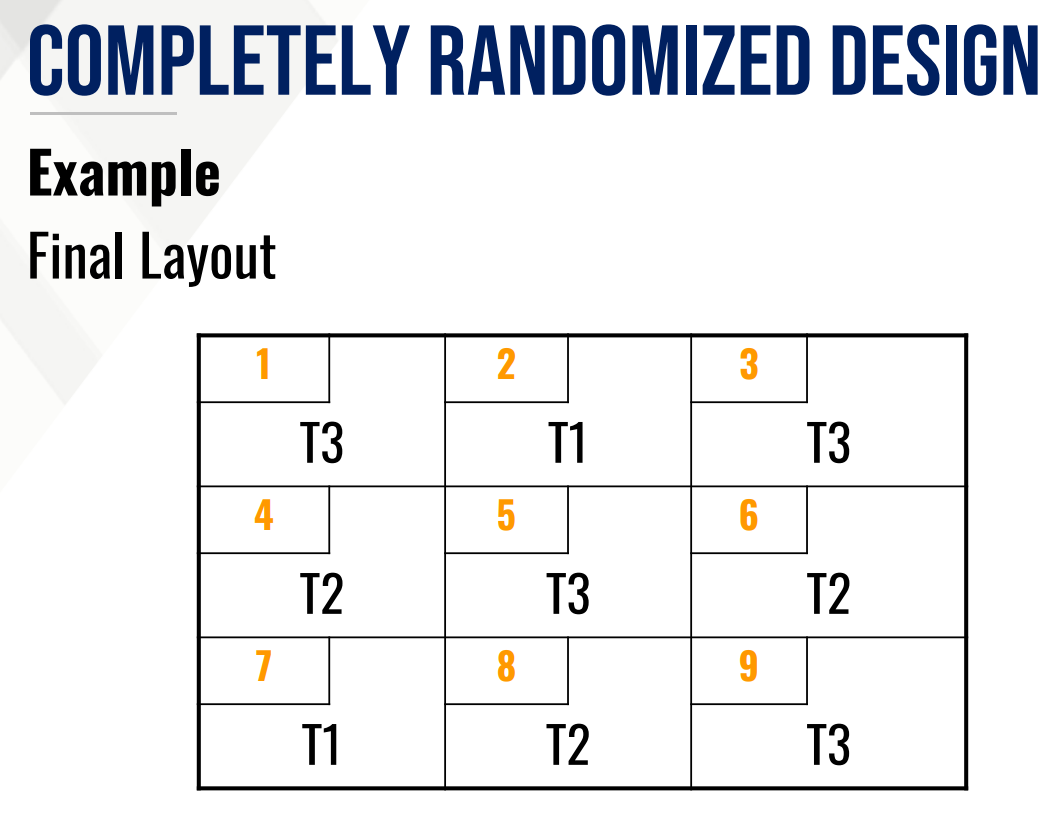
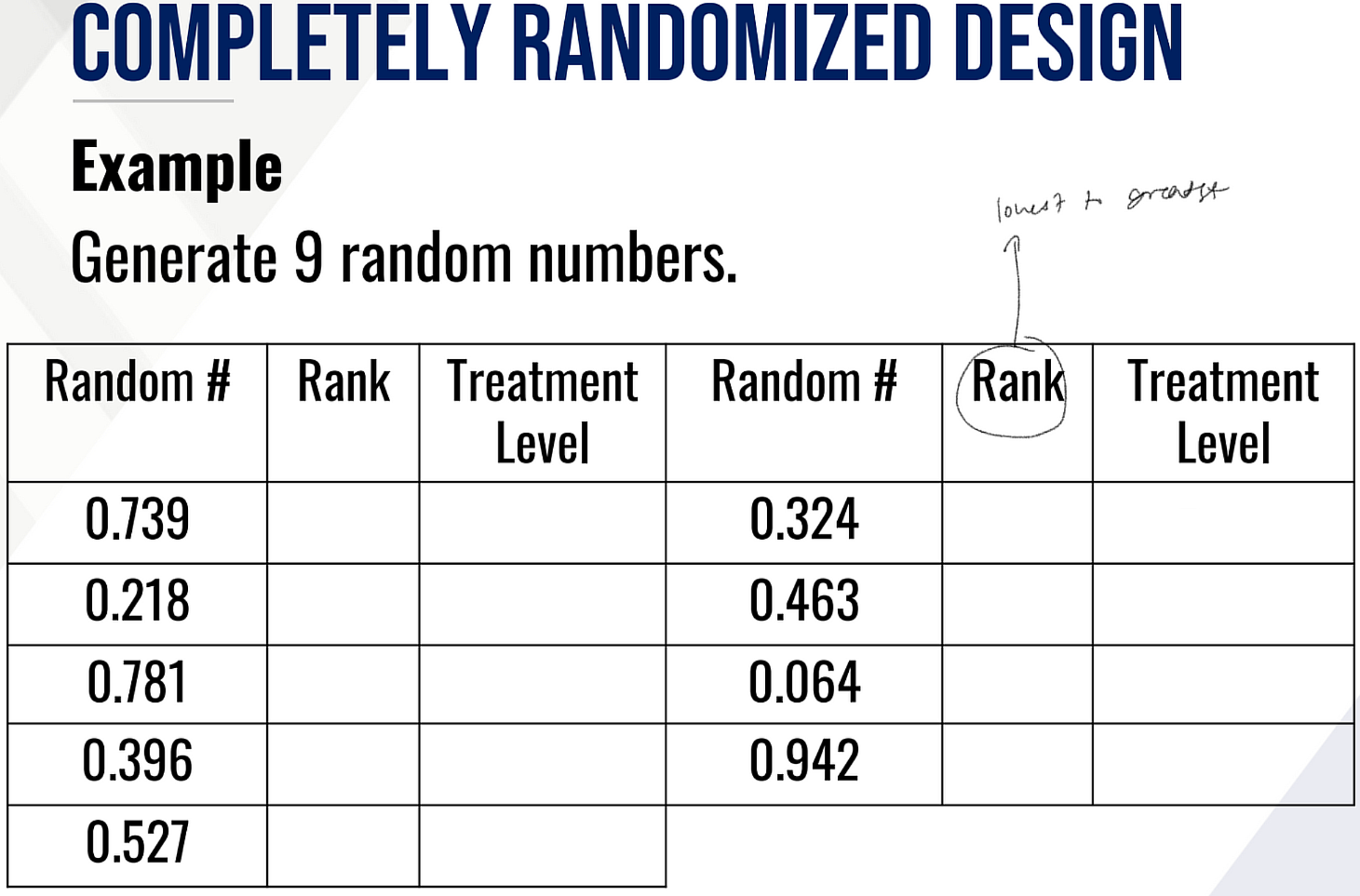
Provide/perform the following:
Rank the random #s
Treatment level of each random #
The final layout
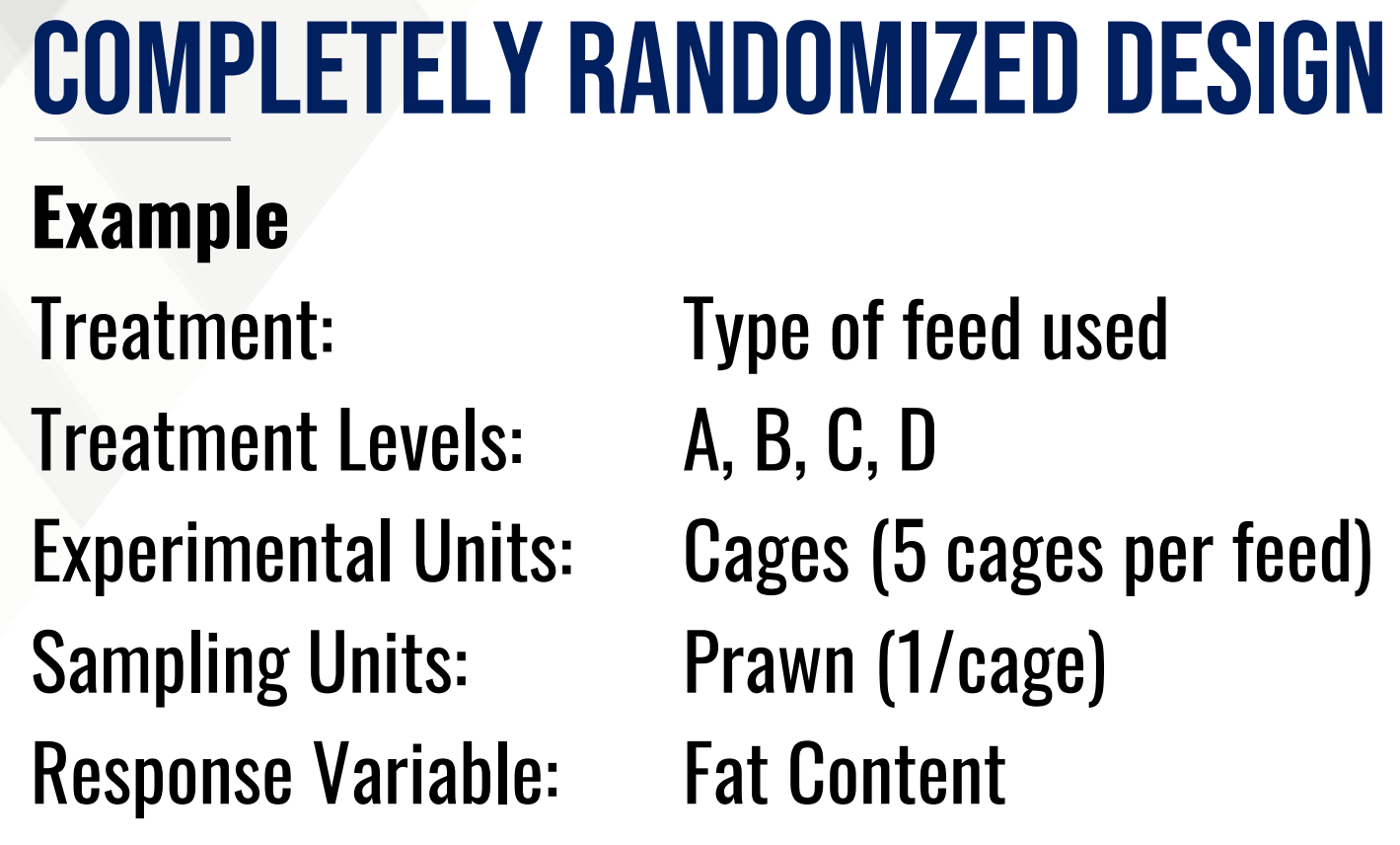

Provide the following:
Treatment/Factor:
Treatment Levels:
Response Variable:
Experimental Unit:
Sampling Unit:

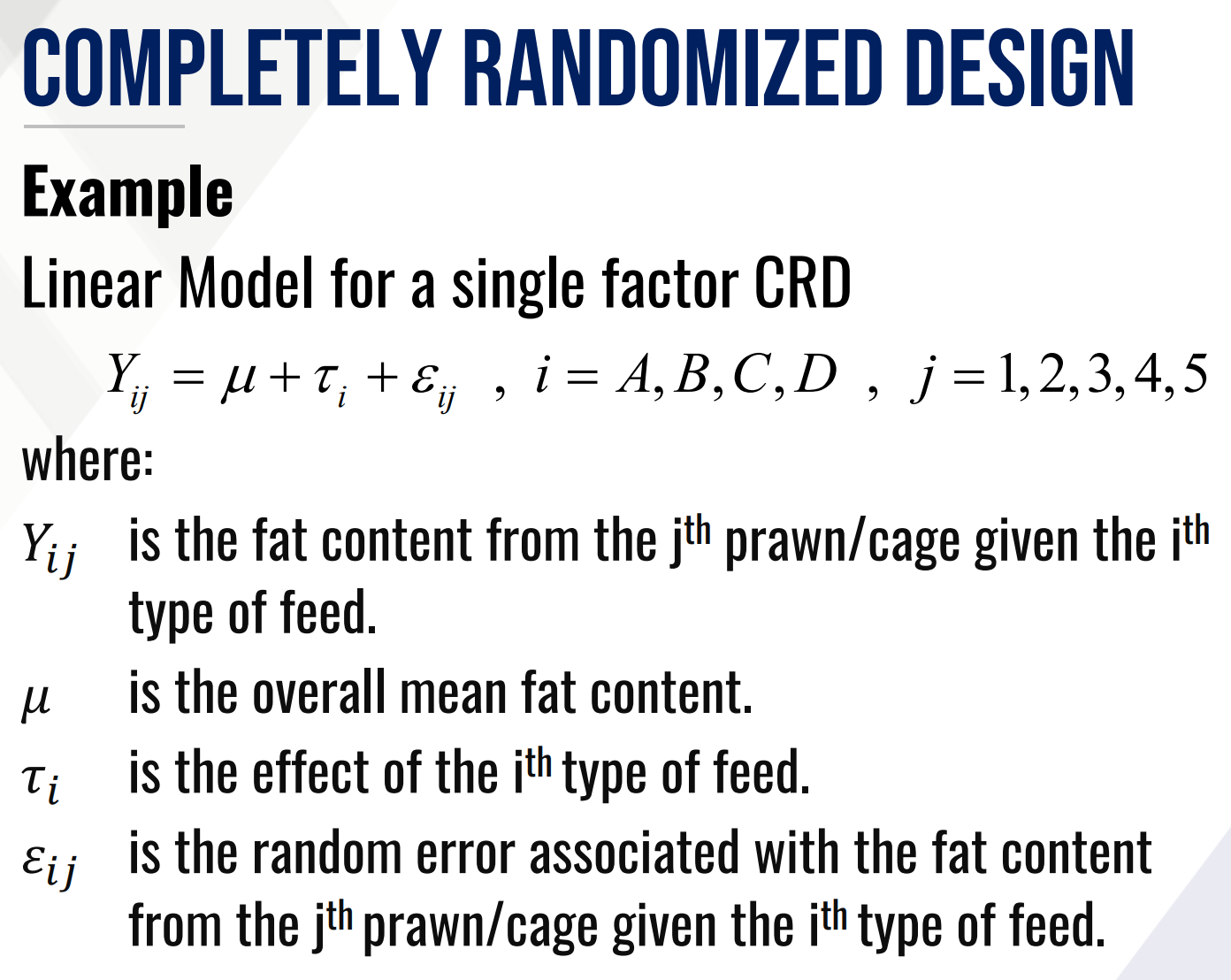
What is the formula for a Linear Model for a single factor CRD?

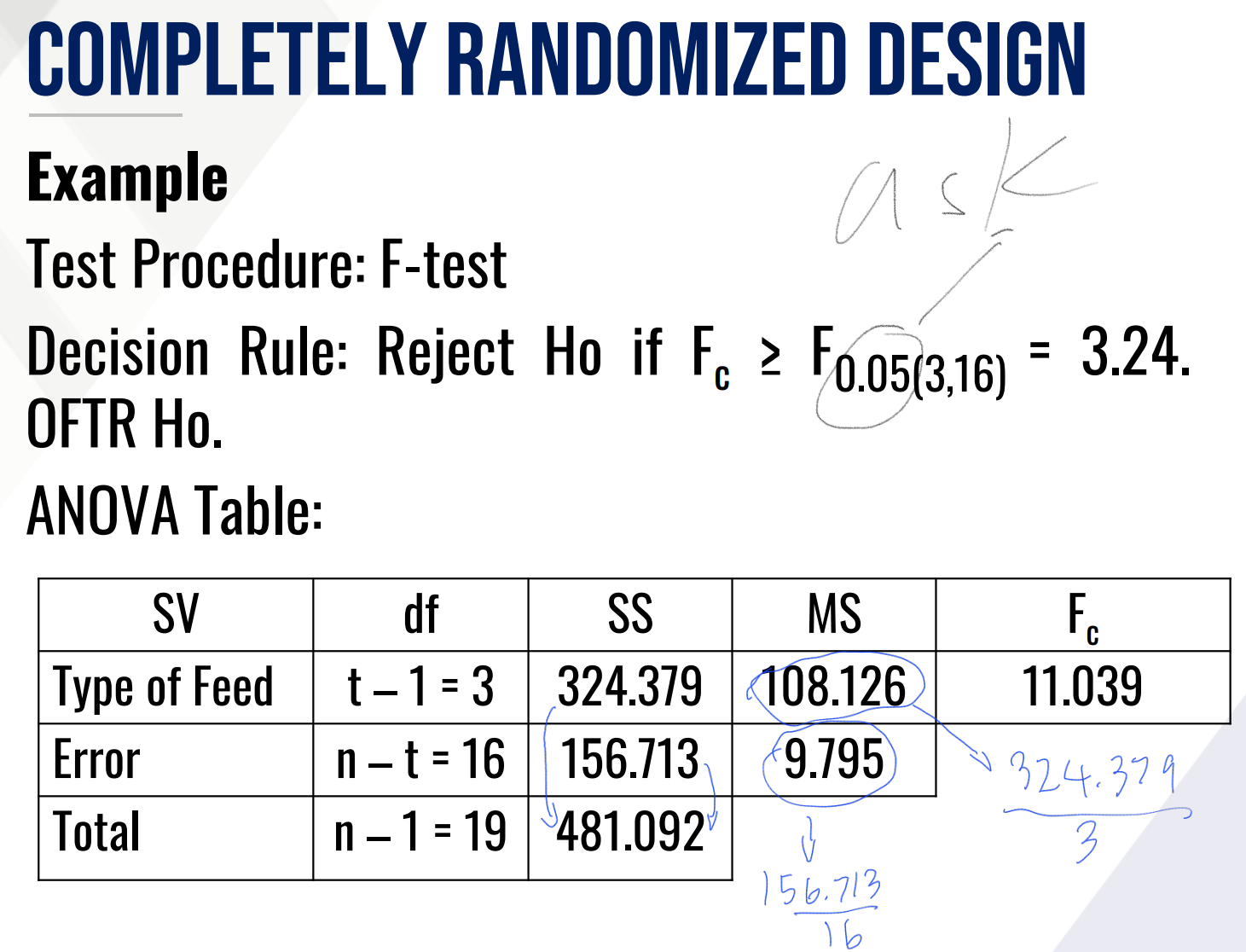
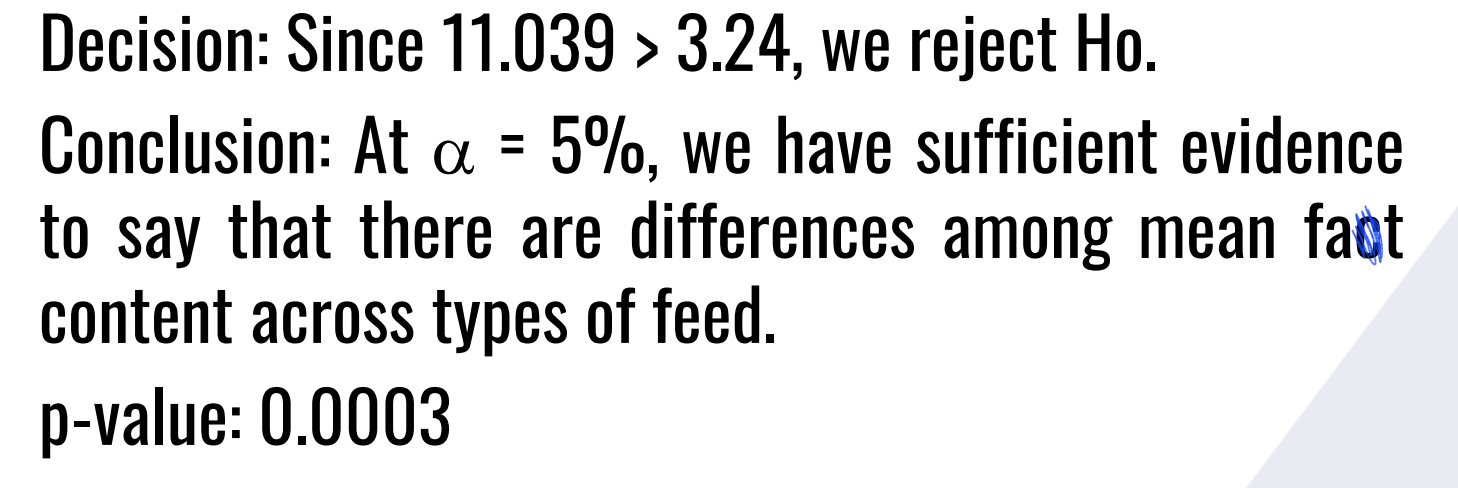

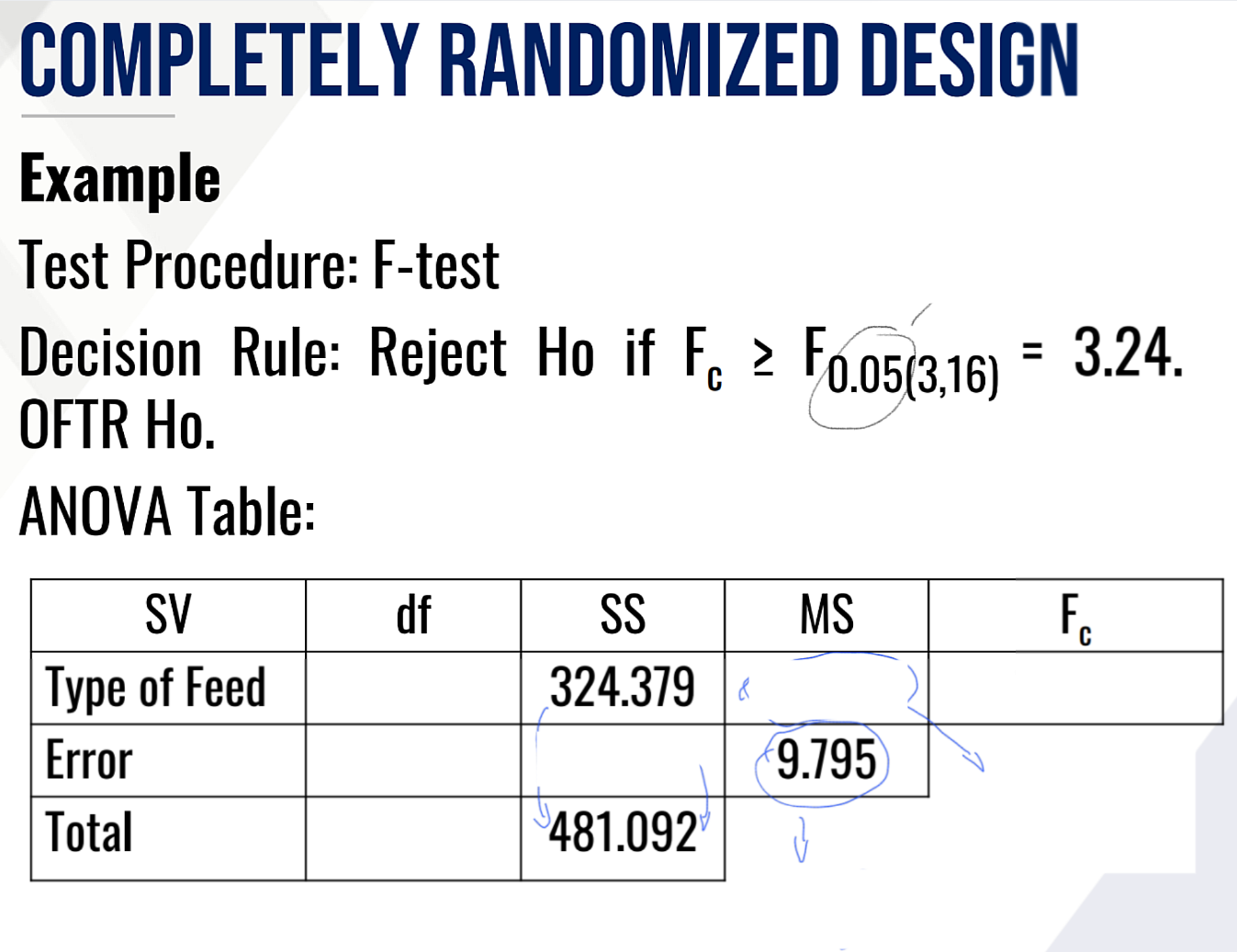
Also Provide the following:
Decision:
Conclusion:
PAIRWISE MEAN COMPARISON

_______________ - compares ALL possible pairs of treatment means and tests if they are significantly different.
For example, in the aquaculture example you would have: AvsB, BvsC, CvsD, AvsC, AvsD, BvsD
Provide also the Ho and Ha of this in words.
RANDOMIZED COMPLETE BLOCK DESIGN
Blocks
____________________________
assumes that another single factor aside from the treatment is classifying the experimental units
eu’s are grouped into r blocks
The variability among the blocks is taken out of the experimental error thereby improving the precision of the experiment.
__________
groups of eu’s that are more or less homogeneous
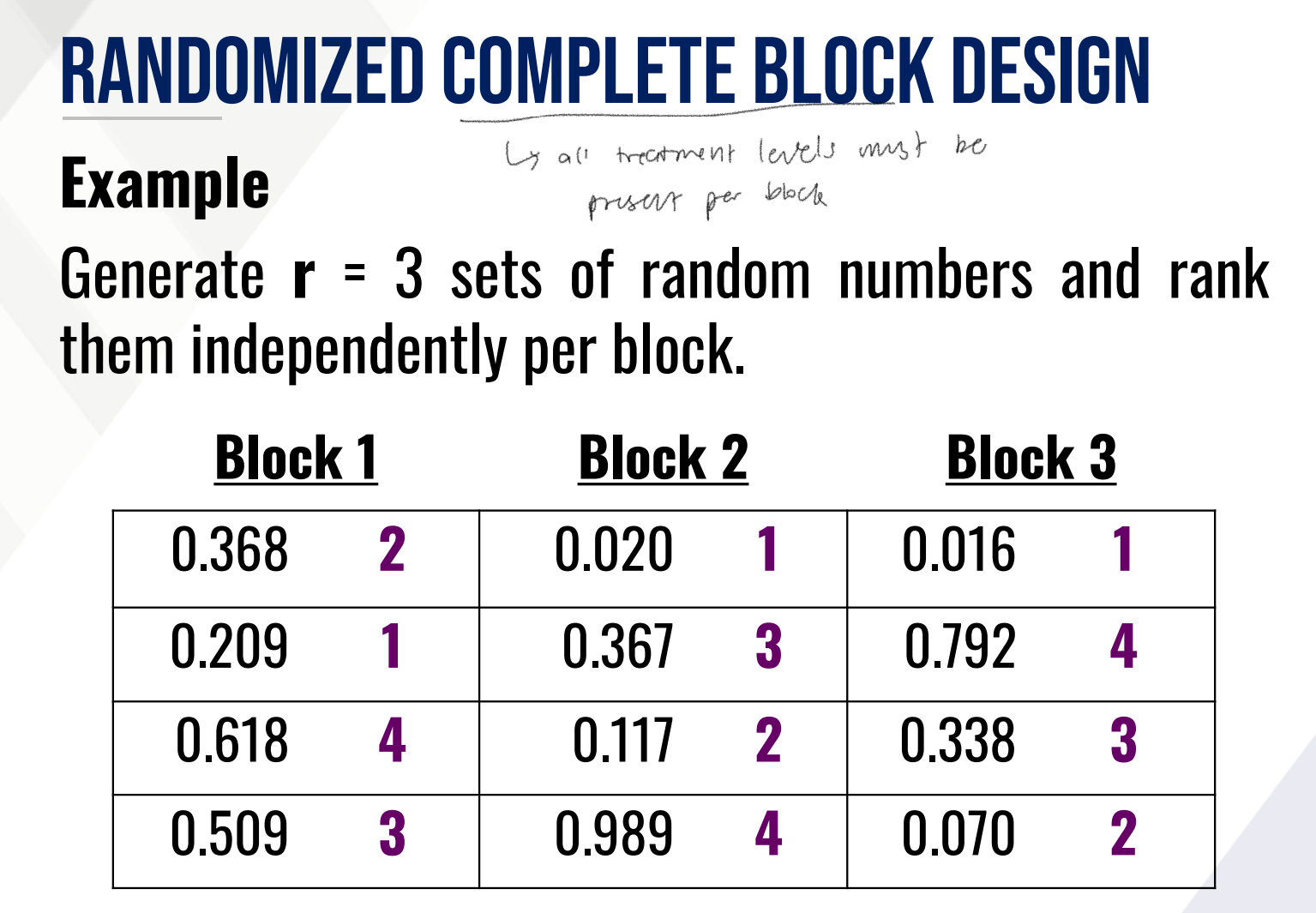
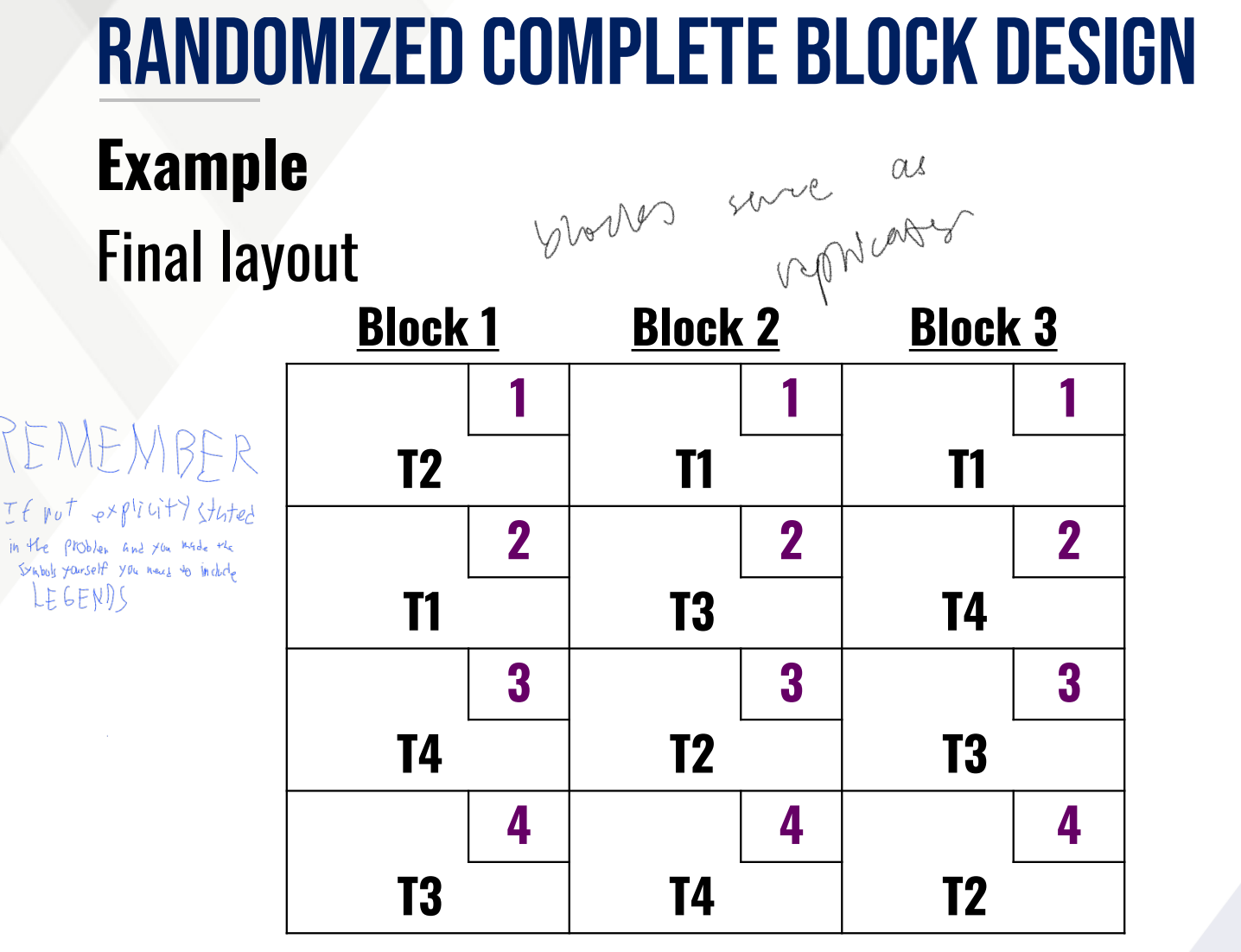


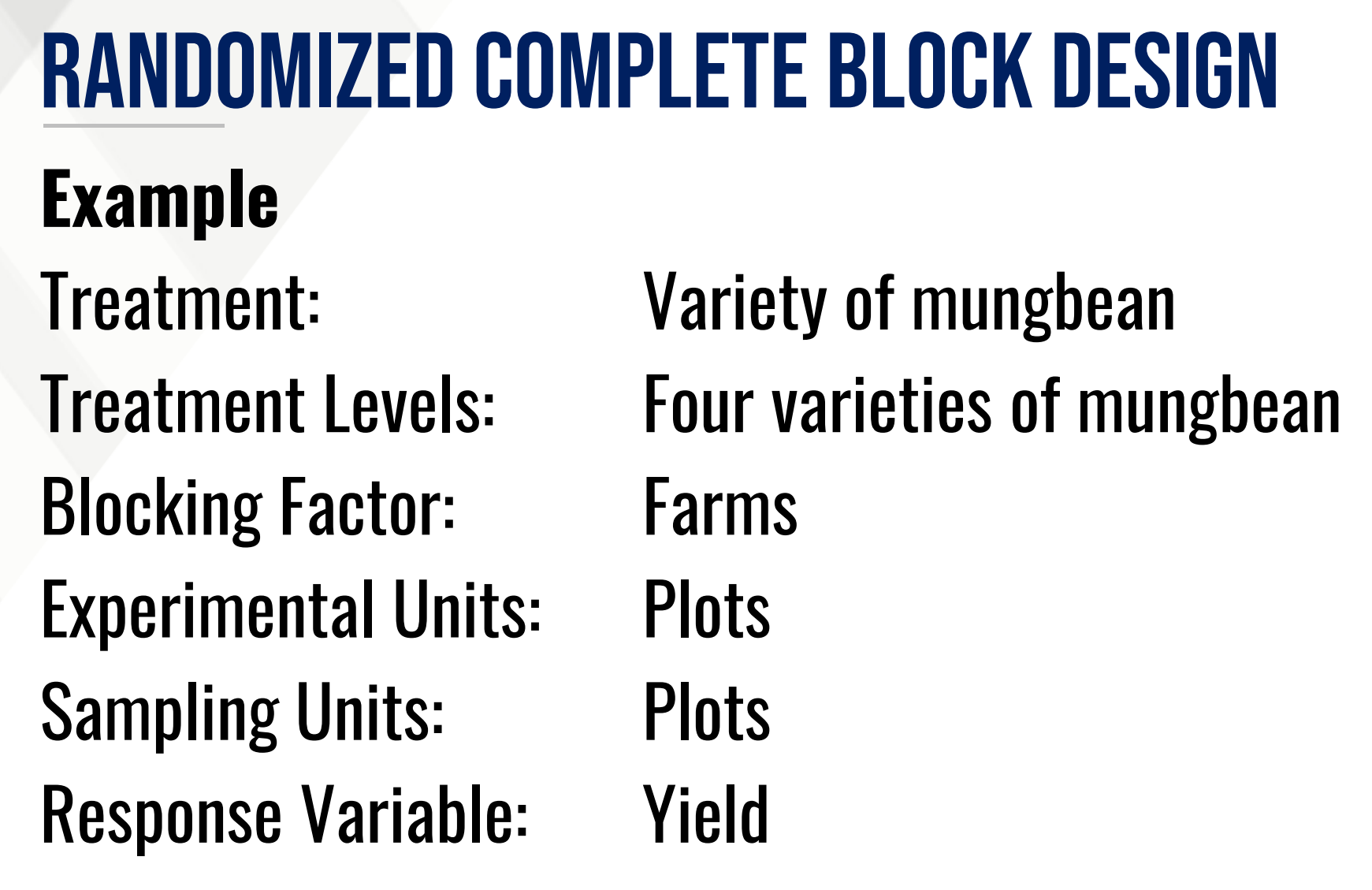
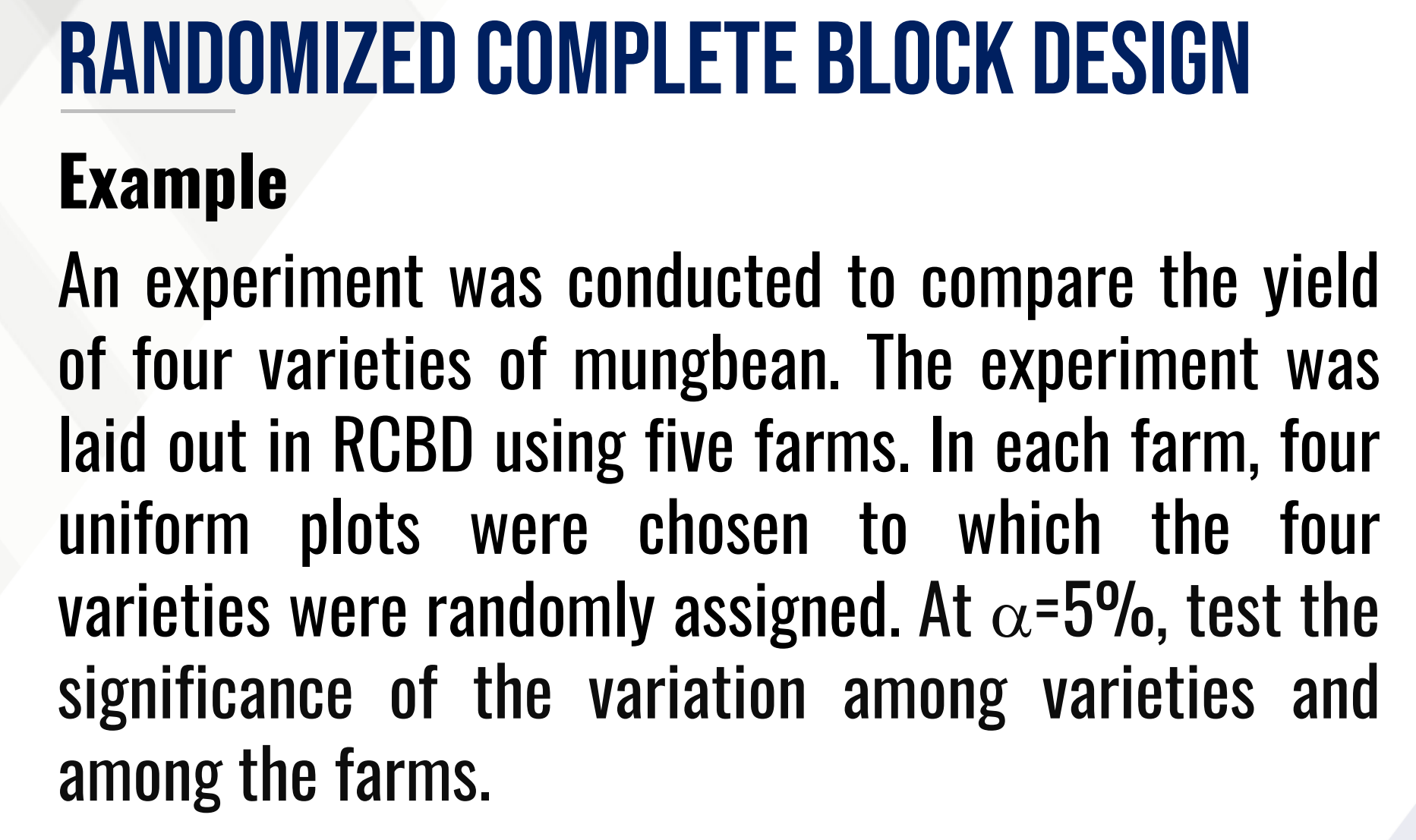
Provide the following:
Treatment/Factor:
Treatment Levels:
Blocking Factor:
Experimental Unit:
Sampling Unit:
Response Variable:
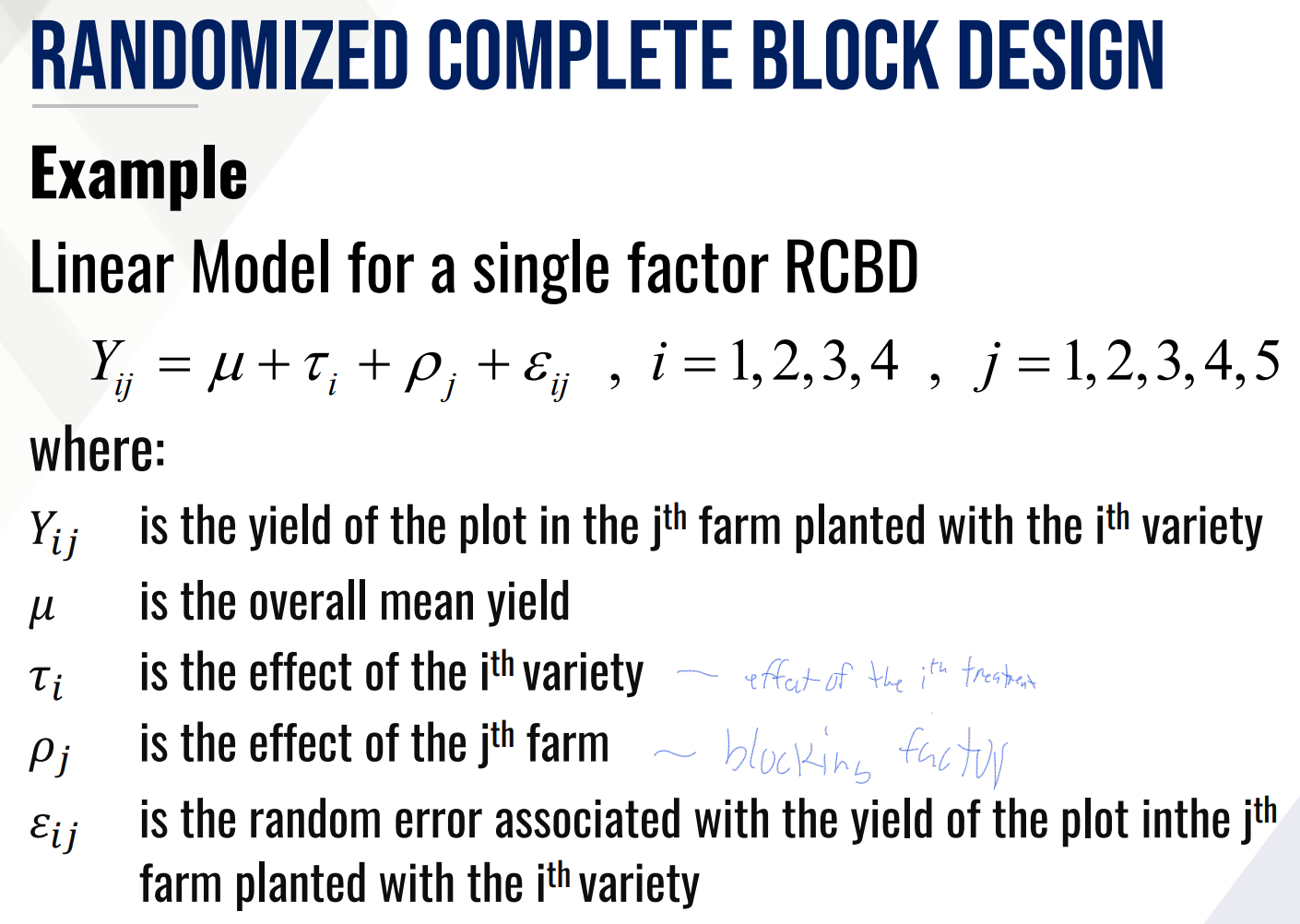

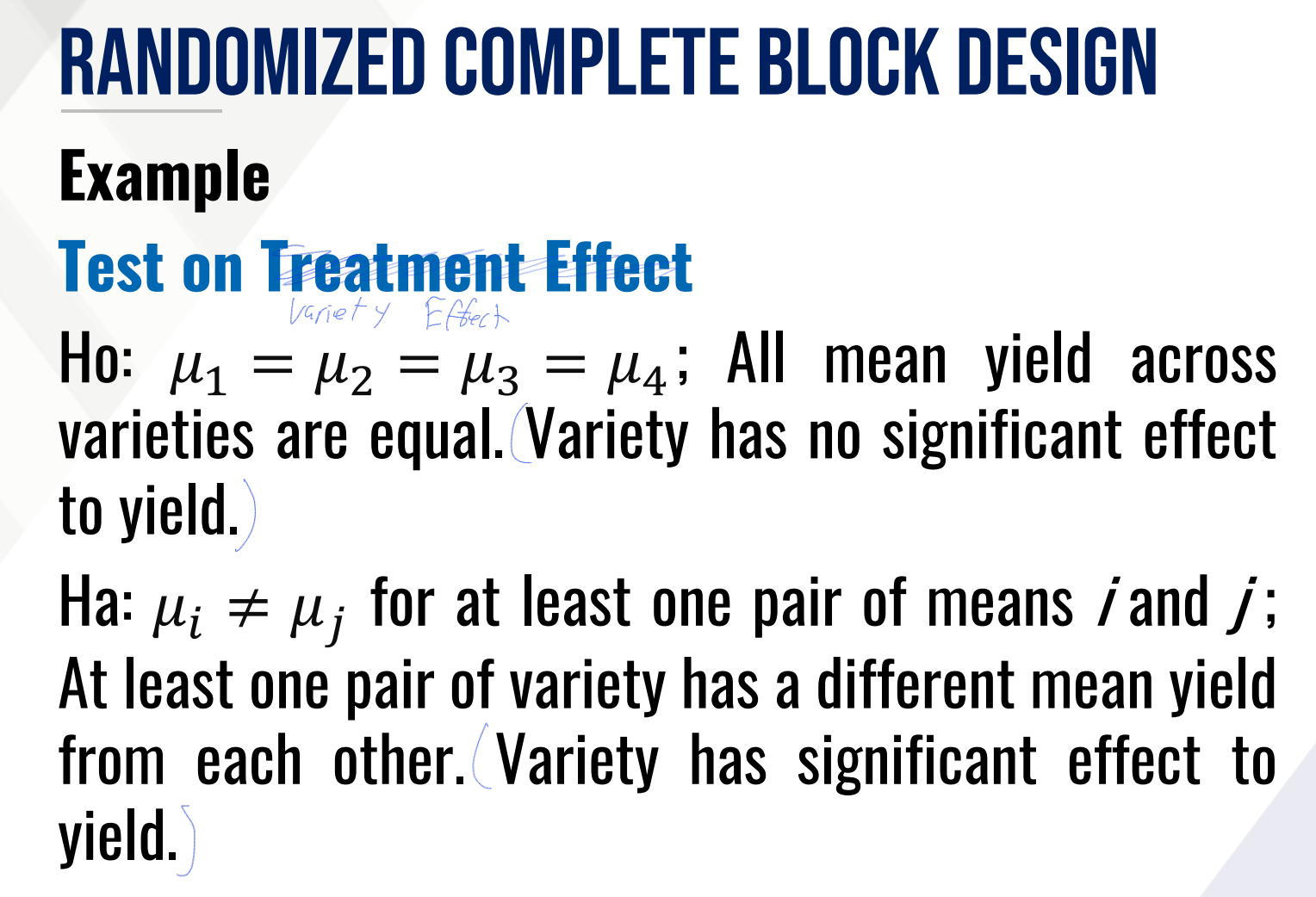
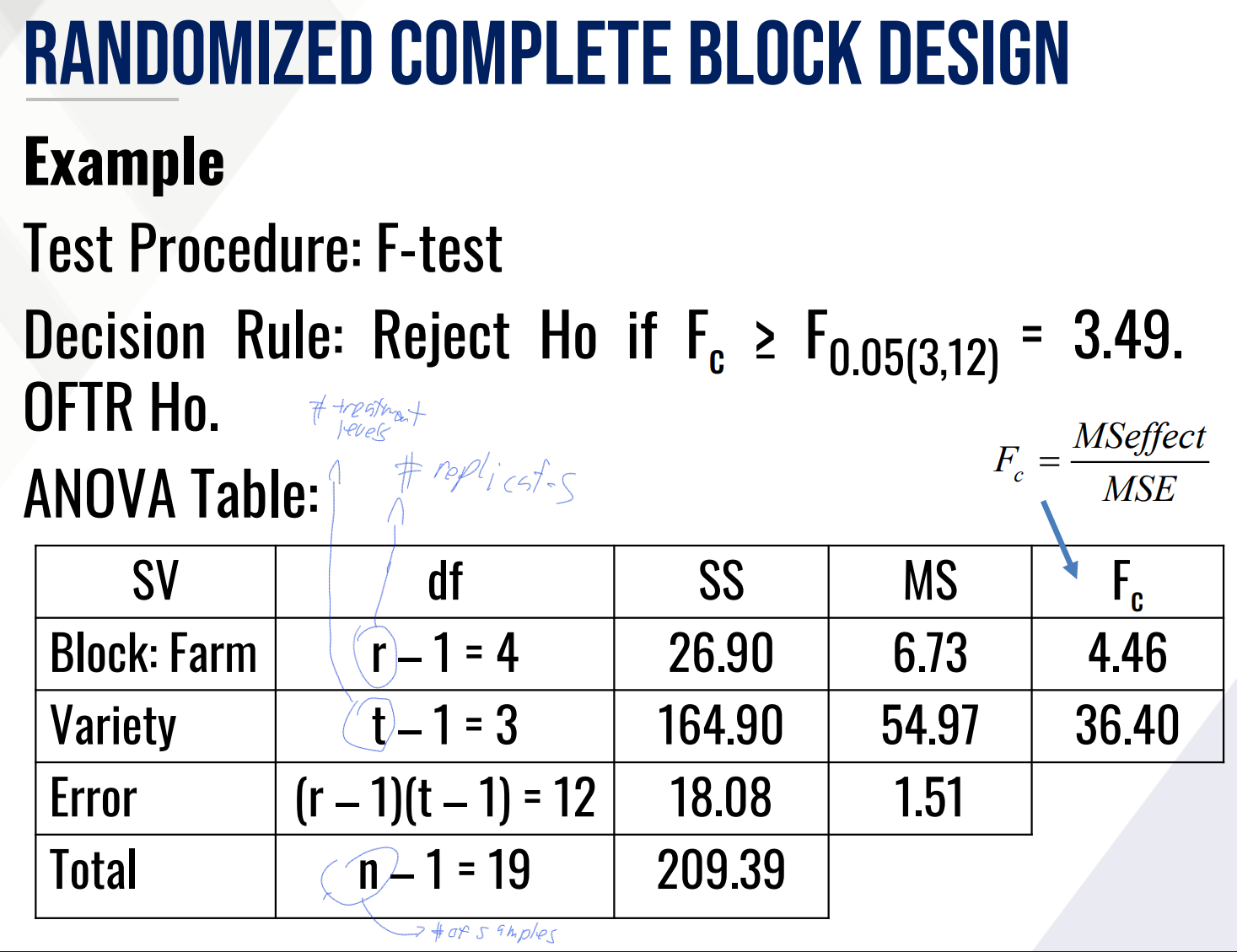
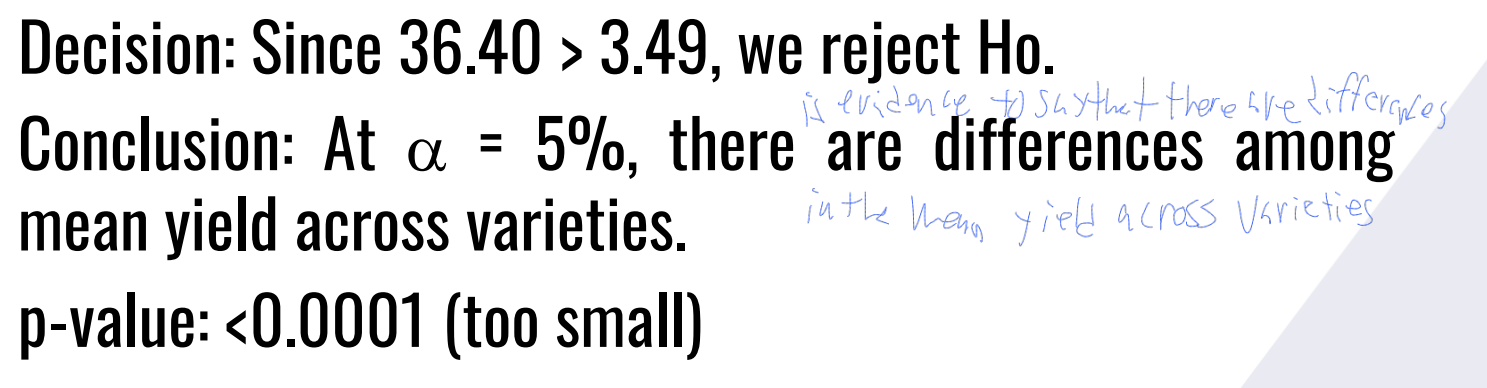

Provide Ho and Ha in words for the TEST ON VARIETY EFFECT and fill in the blanks:
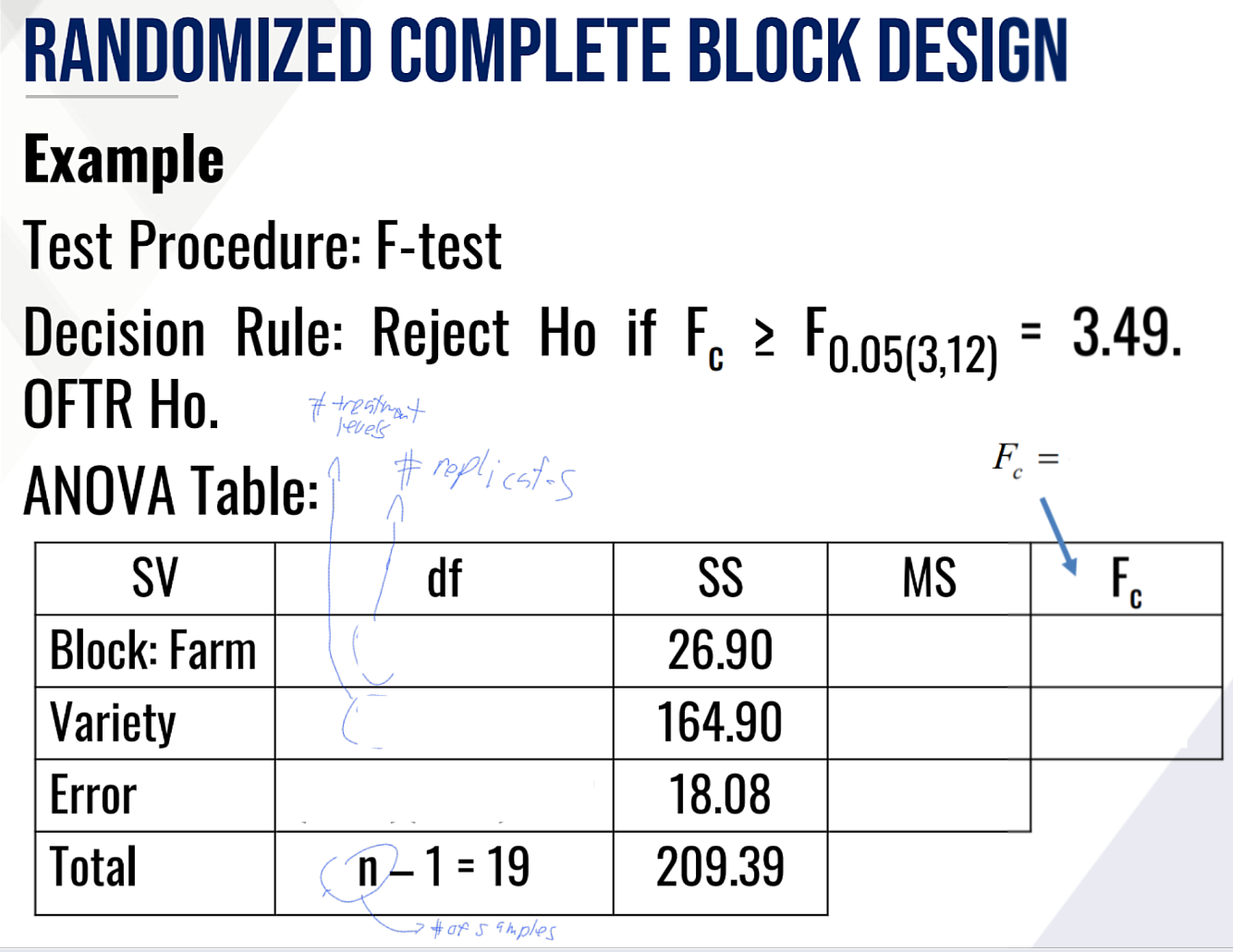
Then provide the decision and conclusion.
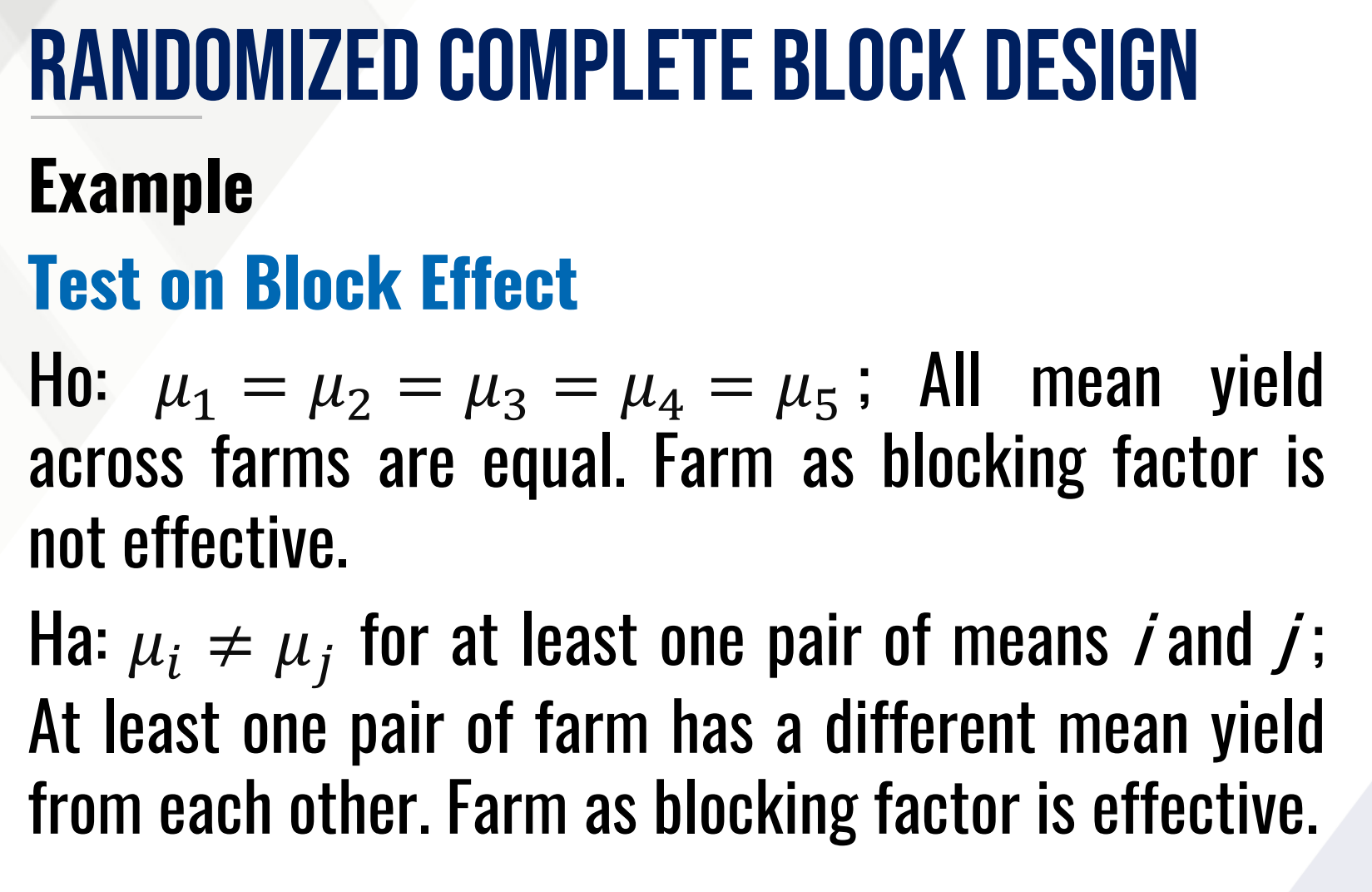


Provide Ho and Ha in words for the TEST ON BLOCK EFFECT and fill in the blanks:

Then provide the decision and conclusion.
FACTORIAL DESIGN
Most efficient for experiments involving two or more factors whose levels are often said to be crossed to allow interaction
FACTORIAL DESIGN
In each complete trial of the experiment, all possible combinations of the levels of the factors are investigated.
FACTORIAL DESIGN
Ex. If there are 3 levels for Factor A, 4 levels for Factor B, and 2 levels for Factor C, then each experiment contains all 3 x 4 x 2 = 24 trmt combinations.

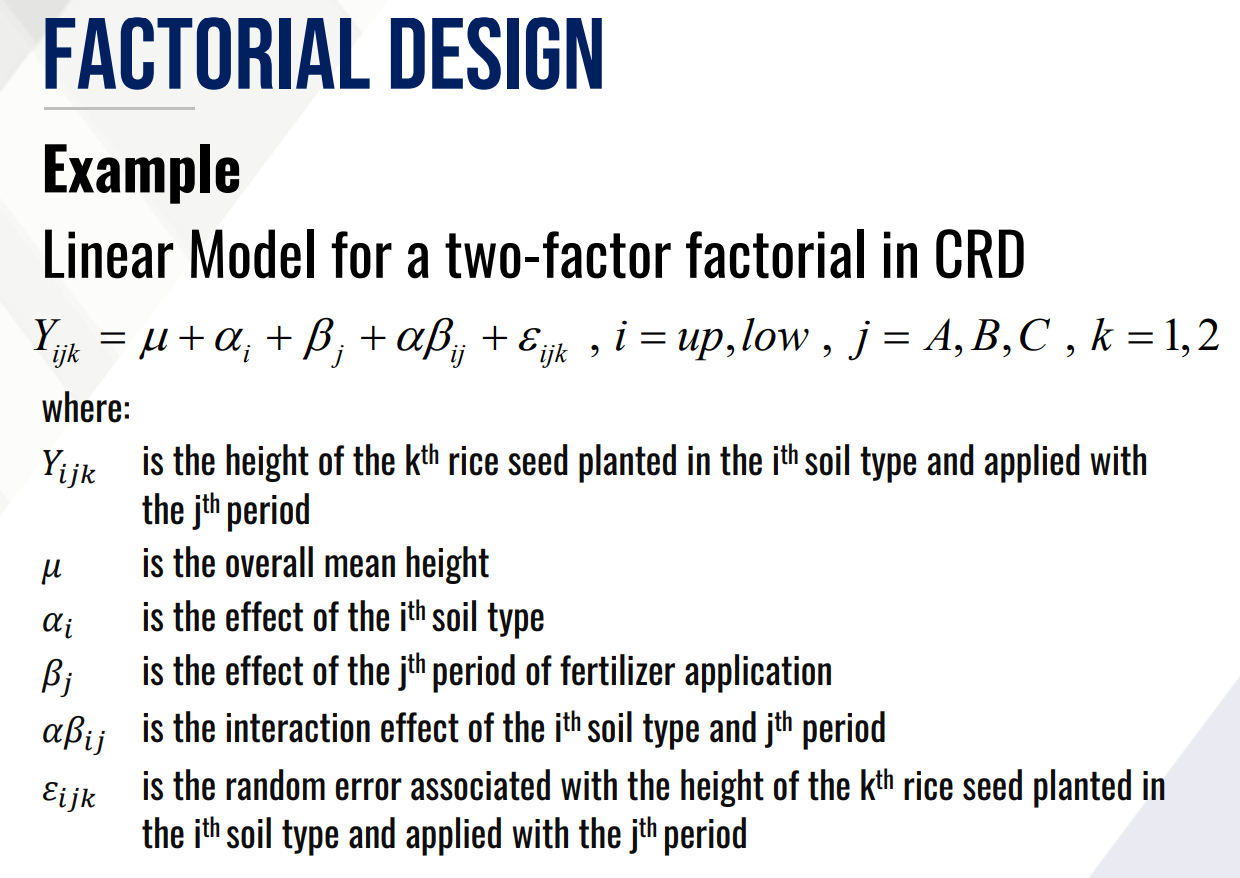

Provide the following:
Experimental Design
Treatment/Factor:
Treatment Combination:
Experimental Unit:
Response Variable:
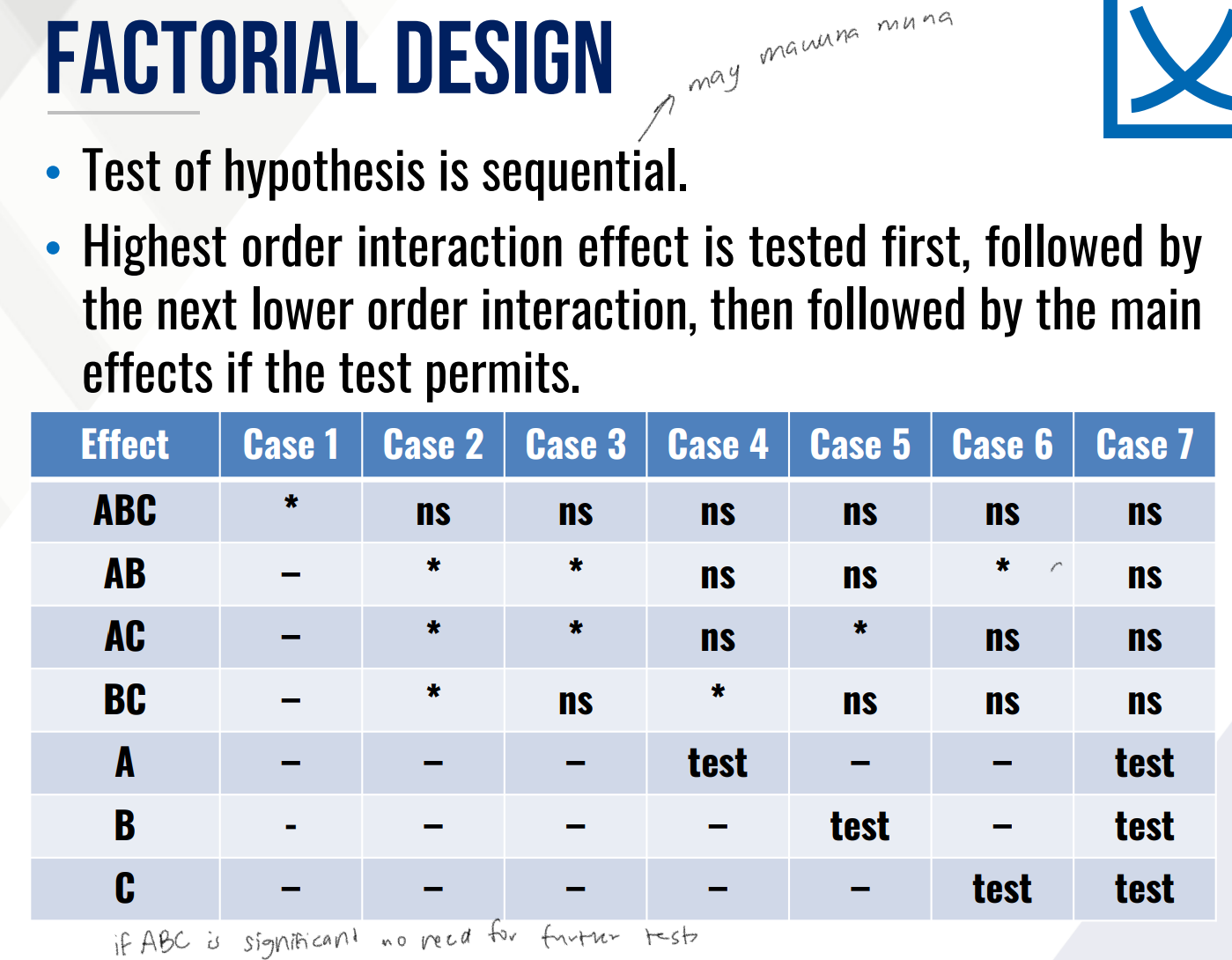
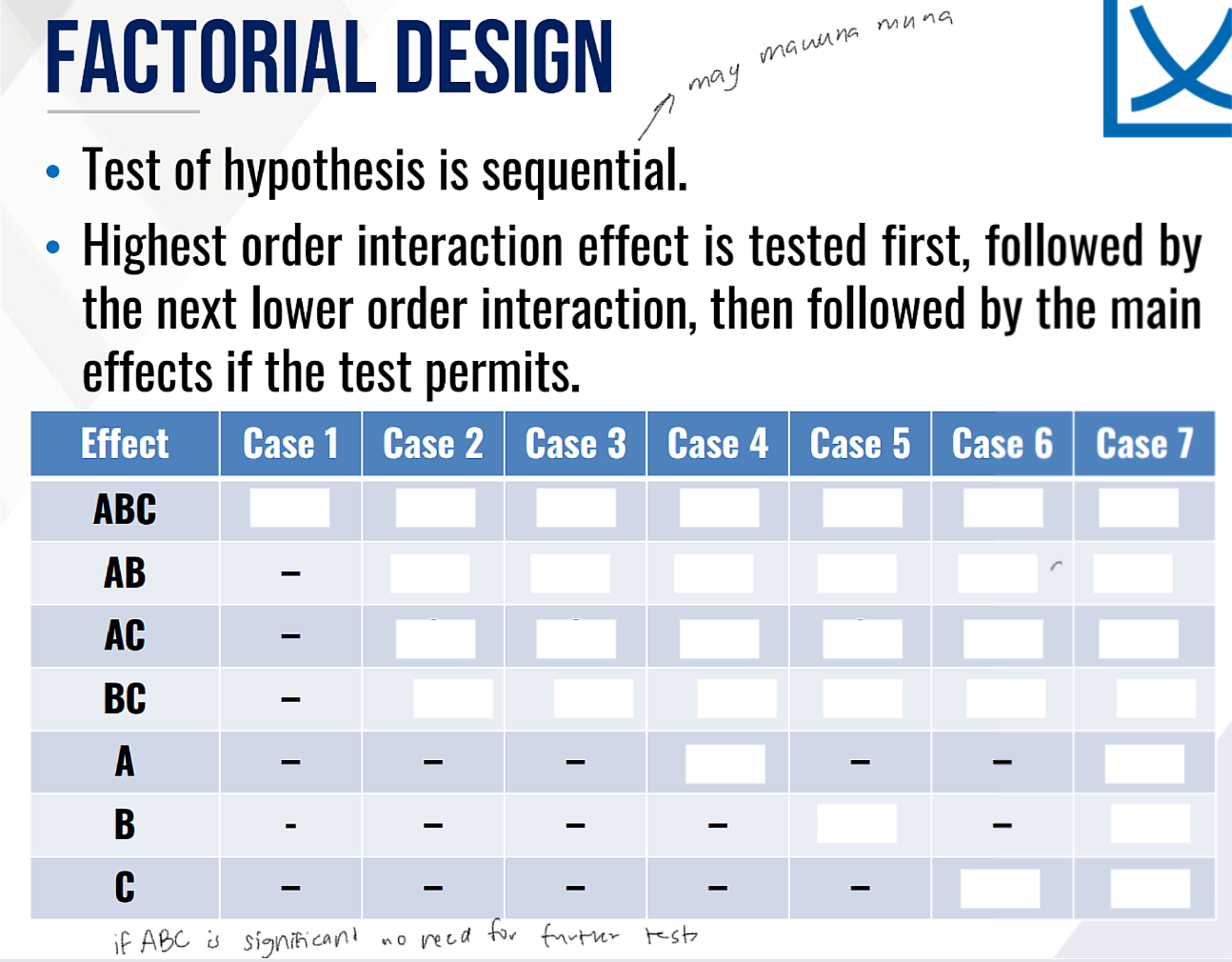
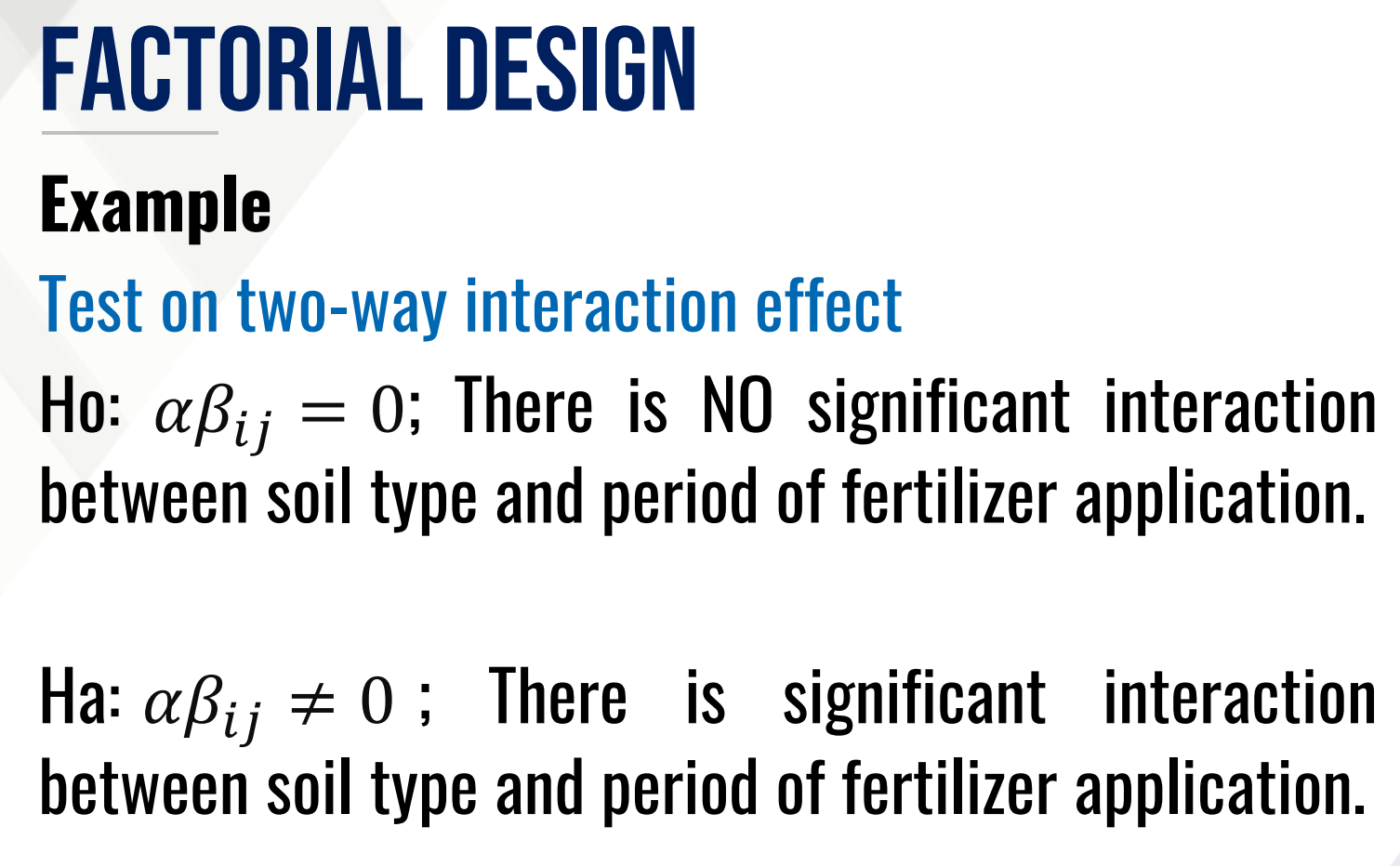
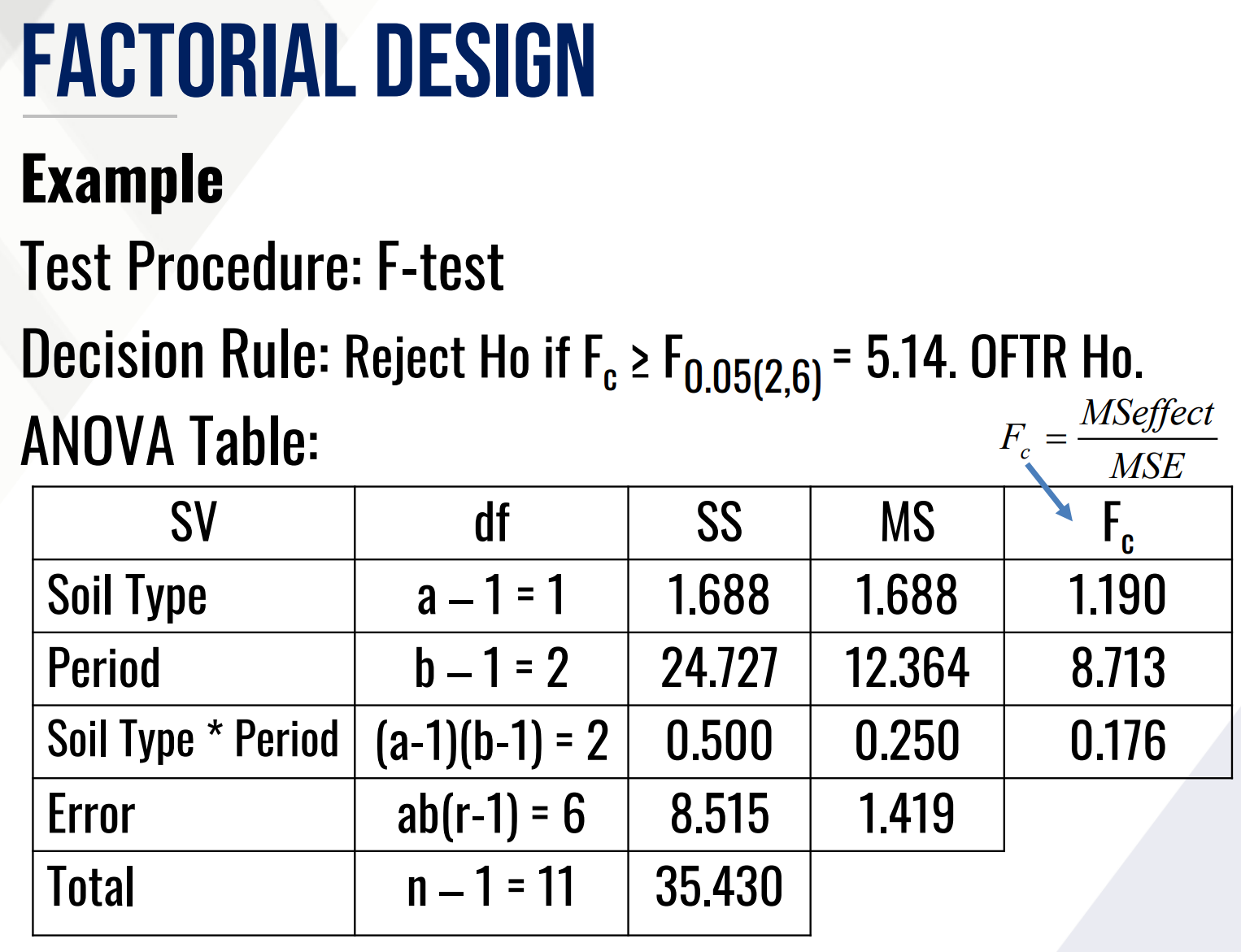


Provide Ho and Ha in words for the Test on two-way interaction effect and fill in the blanks:
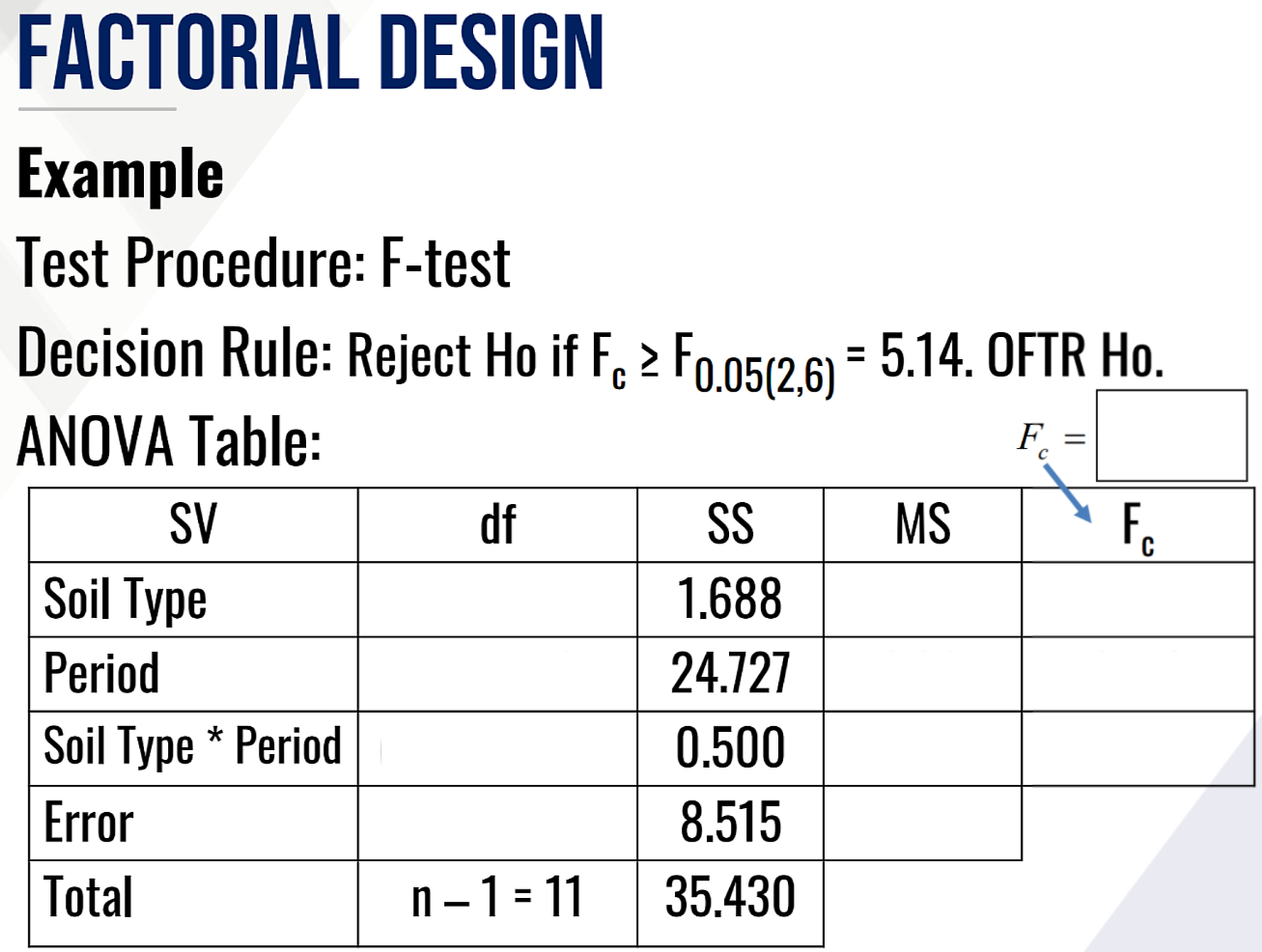
Then provide the decision and conclusion.


Provide Ho and Ha in words for the Test on main effect of Soil Type.

Then provide the decision and conclusion.



Provide Ho and Ha in words for the Test on main effect of Period.

Then provide the decision and conclusion.