Nervous System Prac Test
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
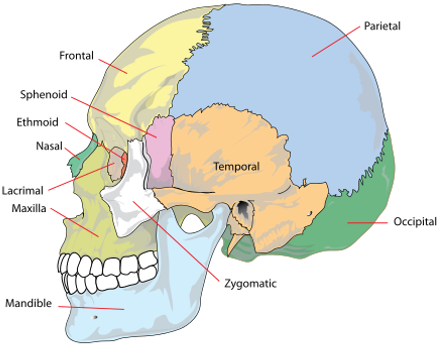
Identify the 8 cranial bones of the skull.
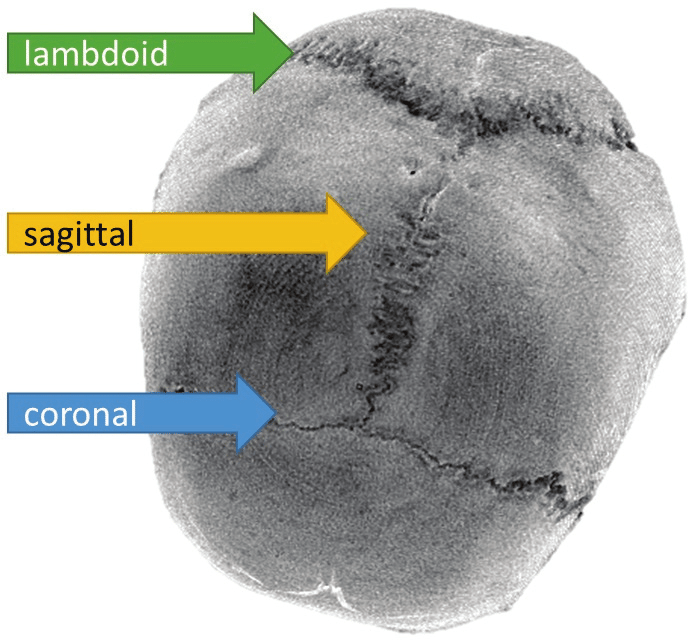
Cranial Stutures & Junctions
The frontal and parietal bones? Coronal
The parietal and occipital bones? Lambdoid
Between parietal bones? Sagittal
Nasion (joins the nasal part of the frontal bone and the nasal bone)
Pterion (joins frontal, parietal, temporal and sphenoid bones)
Bregma (joins frontal and parietal bones)
Lambda (joins occipital and parietal bones)
Cranial fossa
Anterior, middle, and posterior.
Identify cranial foramina associated with cranial nerves and blood supply
Corpus collosum
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
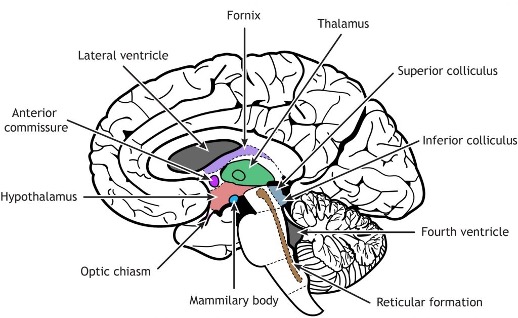
Corona radiata

Cerebral peduncles

Brain stem
Olive
Pyramids
Mid brain
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Superior (visual) and inferior (auditory) colliculi
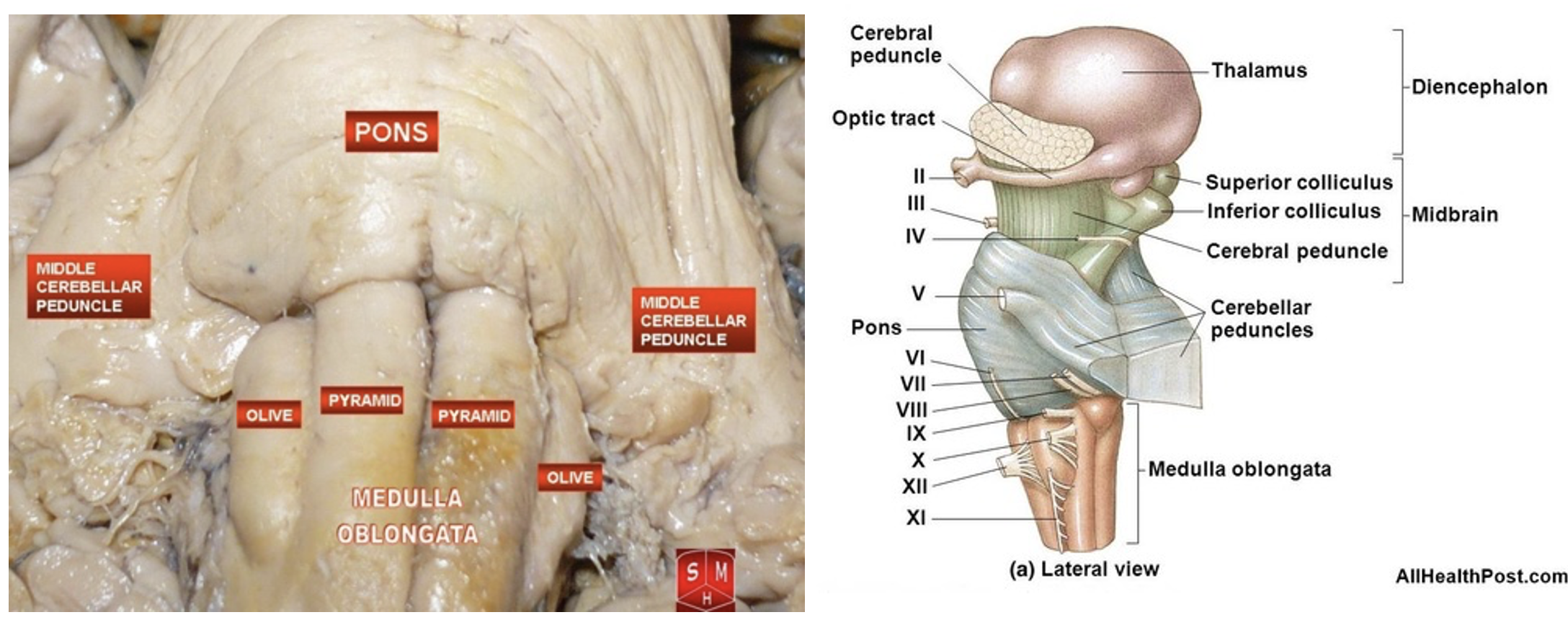
What is ‘closed’ vs ‘open’ medulla referring to?
The "open" medulla is where the fourth ventricle opens, forming the dorsal surface, while the "closed" medulla is where the fourth ventricle is surrounded by the medulla, and the central canal is still enclosed.
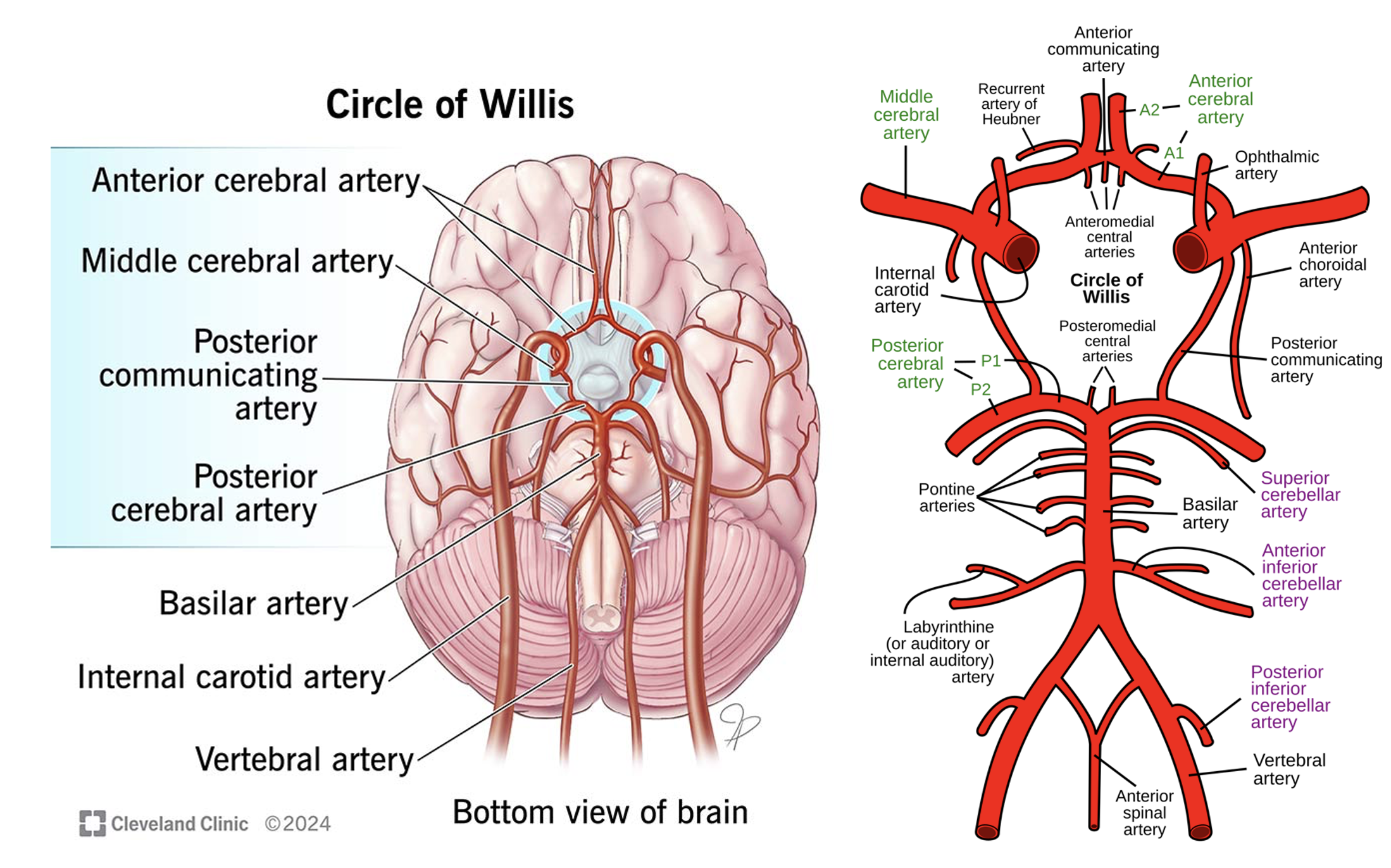
Circle of Willis
3x cerebral arteries – which regions of the cortex do they supply?
3x cerebellar arteries.
3x communicating arteries.
3x ‘other’ arteries (basilar, vertebral, ICA)
Sinuses
Superior sagittal sinus
Inferior sagittal sinus
Straight sinus
Transverse sinus
Sigmoid sinus

Sinuses & CSF
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates within the subarachnoid space, the area between the arachnoid and pia mater layers of the meninges
It is reabsorbed into the venous system via dural venous sinuses through the arachnoid granulations.
Spinal cross section (1)
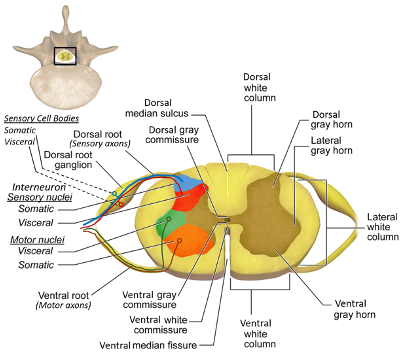
Spinal cross section (2)

What information is transmitted via each peduncle?
Middle Cerebellar Peduncle:
Transmits cortico-ponto-cerebellar afferent fibers from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum via the pons.
Superior Cerebellar Peduncle:
Transmits efferent fibers from the cerebellum to the red nucleus and thalamus, particularly the ventrolateral nucleus, which then influences the rubrospinal and corticospinal systems.
Inferior Cerebellar Peduncle:
Carries both afferent and efferent fibers. Afferents include spinocerebellar, medullocerebellar, and vestibular fibers, while efferents connect the cerebellum to the vestibular and reticular nuclei.
Would a lesion of the left cerebellar hemisphere have ipsilateral or contralateral effects in the spinocerebellar pathway?
Ipsilateral effects in the spinocerebellar pathway, meaning that the symptoms (such as limb ataxia) would be on the left side of the body. The cerebellum processes information about the body's movement on the same side of the body,
Anterior thalamic nuclei

How does the limbic system work together to form the Papez circuit?

Identify the amygdala in coronal slices.
Which structure is posterior to the amygdala?
How might this relationship impact the creation of memories?
The hippocampus is posterior and caudal to the amygdala.
The amygdala adds emotional significance to memories, making them more vivid and enduring. It's essential for recognizing and remembering emotionally salient events.

globus pallidus
component of the basal ganglia that connects to the thalamus which relays information to the motor areas and the prefrontal cortex

Putamen
regulate movements and influence various types of learning

internal capsule brain

subthalamic nucleus
a small nucleus, located ventral to the thalamus, that is part of the basal ganglia (anterior to red nucleus)

corpus callosum

caudate nucleus - part of basal ganglia
lateral ventricles
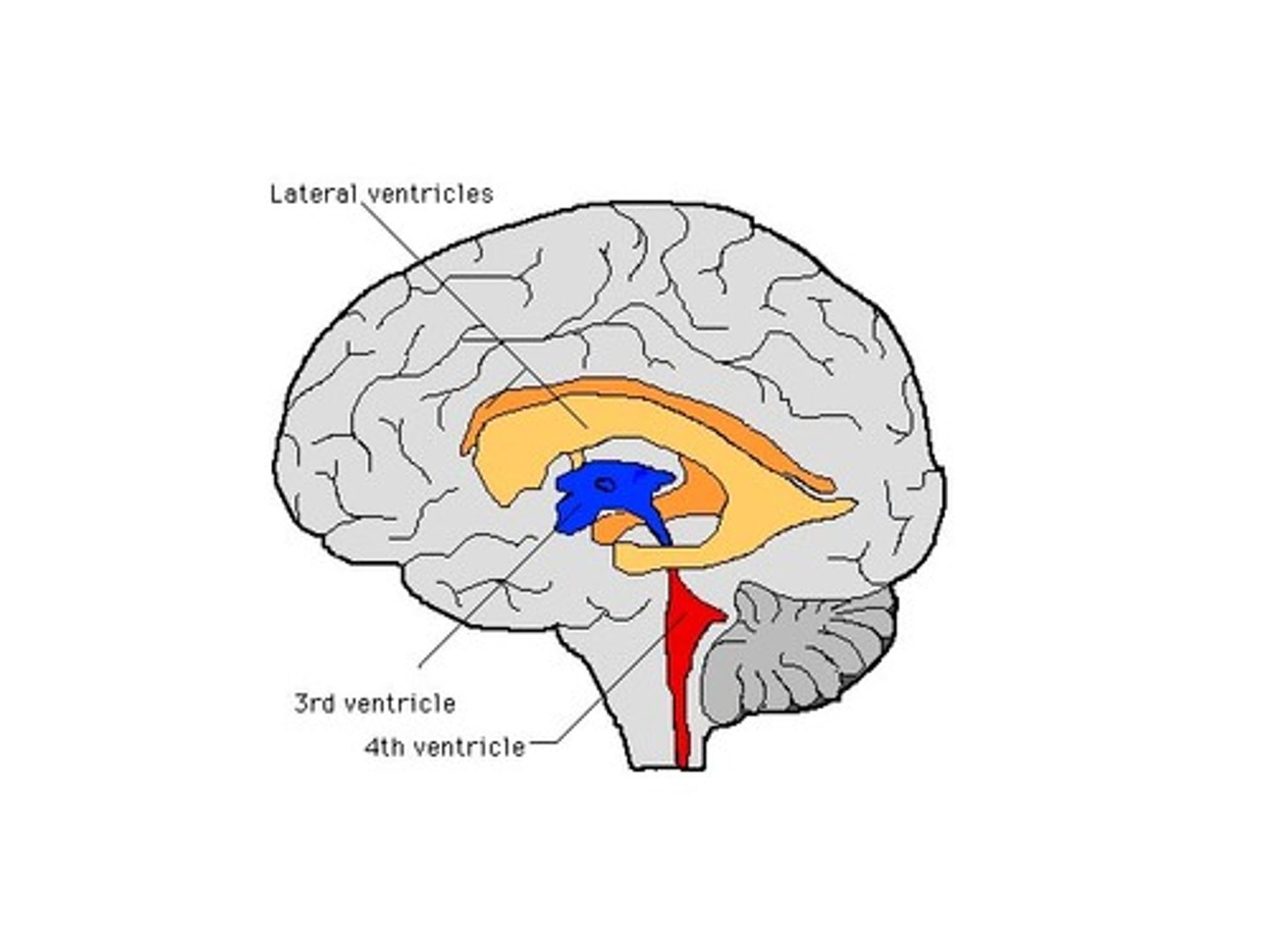

3rd ventricle

tentorium cerebelli
separates cerebrum from cerebellum

anterior lobe of cerebellum upper half

Lobe of cerebellum that is separated from anterior via primary fissure (bottom half)
posterior lobe of cerebellum
vermis of cerebellum
The tissue between the two cerebellar hemispheres: concerned with regulation of muscle tone for posture and locomotion.

Nodule of cerebellum
has important connections to the vestibular nuclei and uses information about head movement to influence eye movement
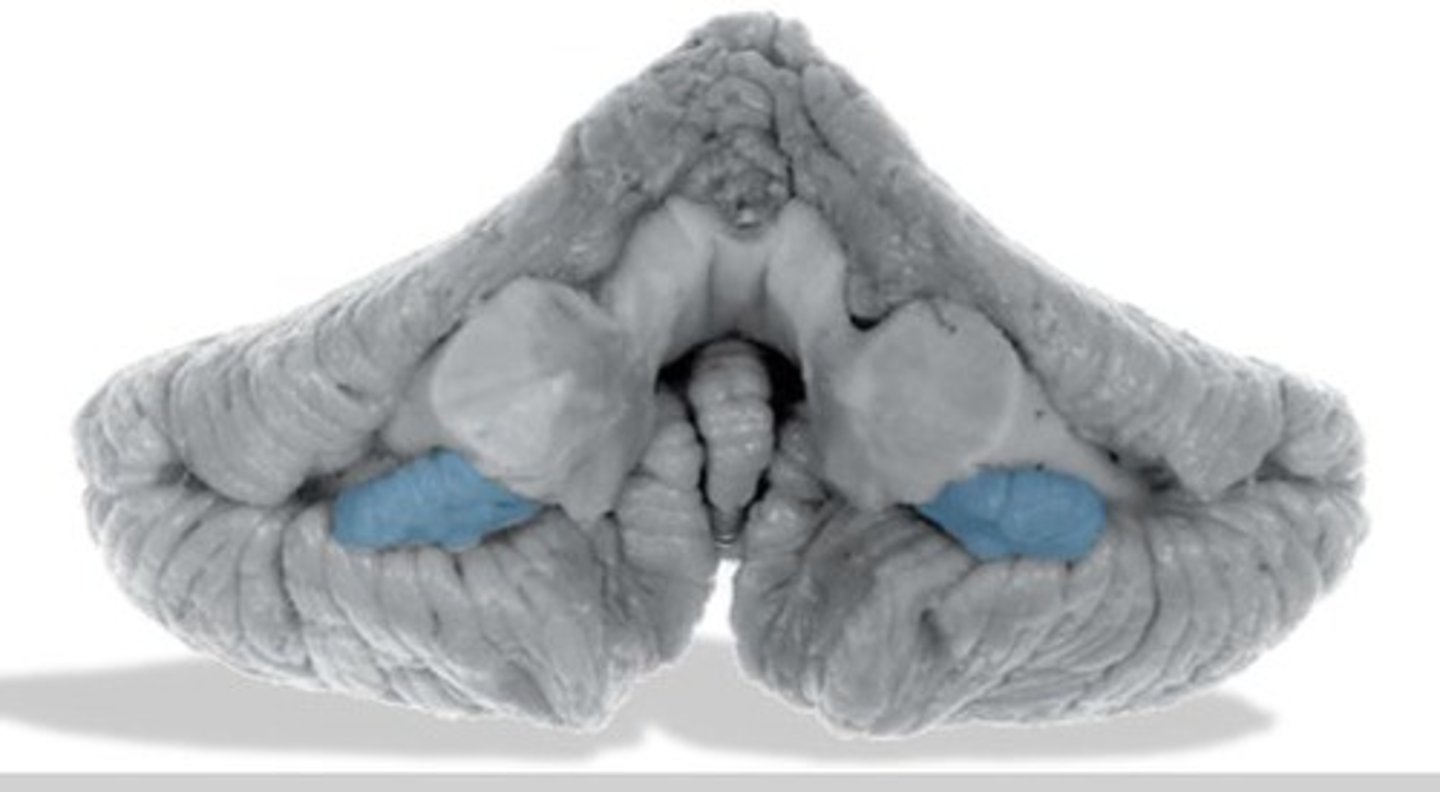
flocculonodular lobe of cerebellum
part of the vestibulo-ocular reflex system and is used to help stabilize gaze during head rotation about any axis of space.

tonsil of cerebellum - planning of motor activity
cerebellar peduncles


4th ventricle
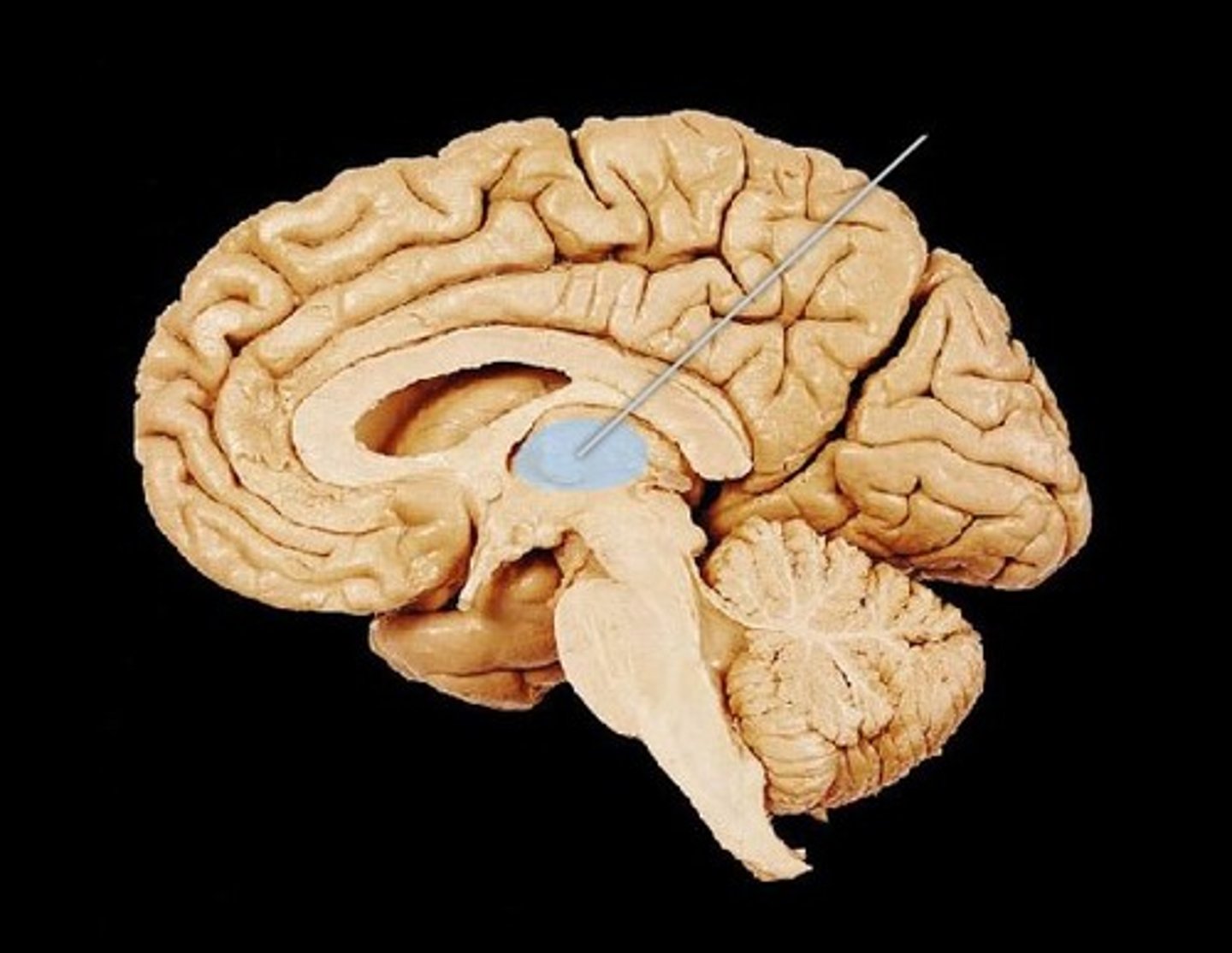
Thalamus

Hypothalamus
hypothalamic sulcus
separates thalamus from hypothalamus


mammillary body

16
thalamic adhesion

pineal gland - regulates melatonin
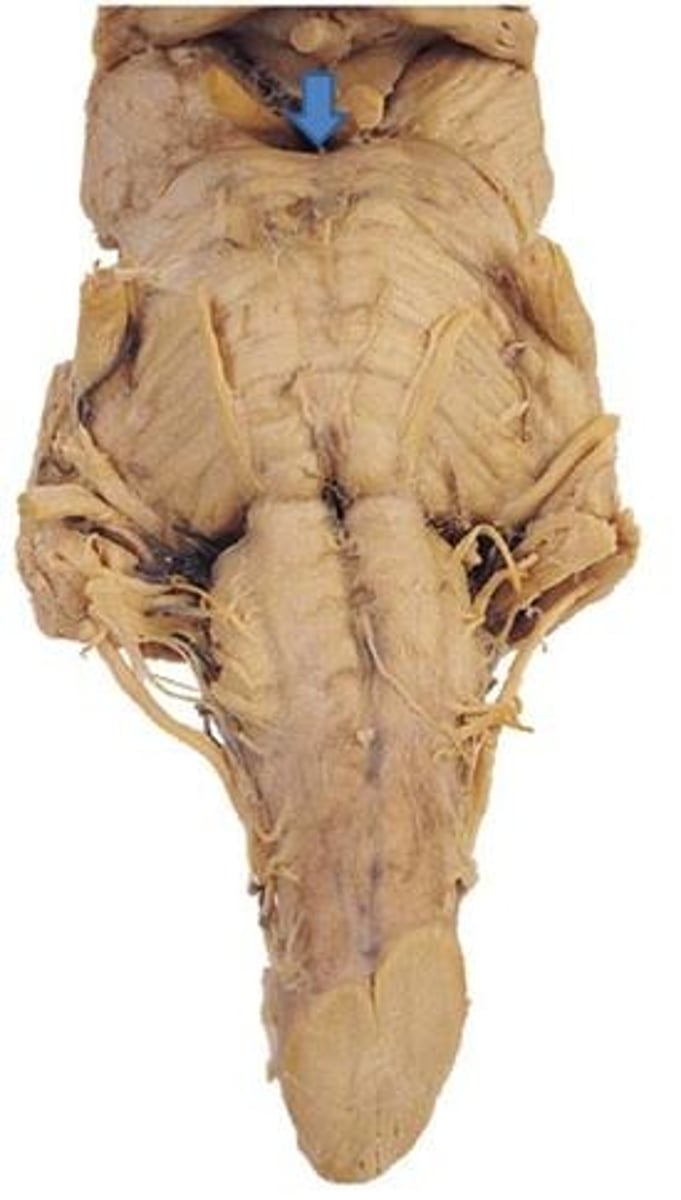
interpeduncular fossa - space between cerebral peduncles.
red nucleus
(red circle) - motor coordination
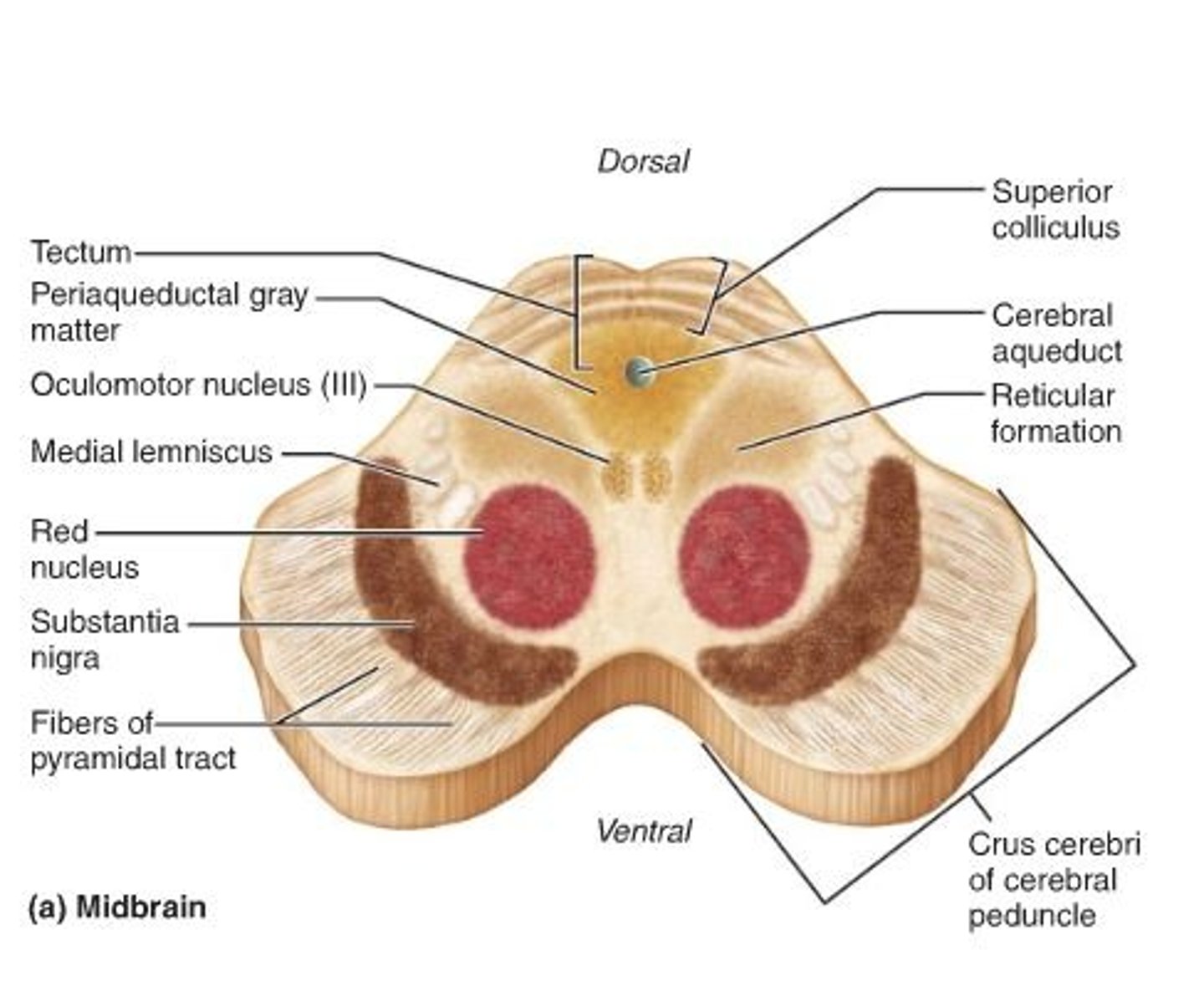

substantia nigra

uncus - on medial surface of temporal lobe (olfactory area)

optic chiasm

optic tract

Hippocampus

fornix- a fiber tract that extends from the hippocampus to the mammillary body
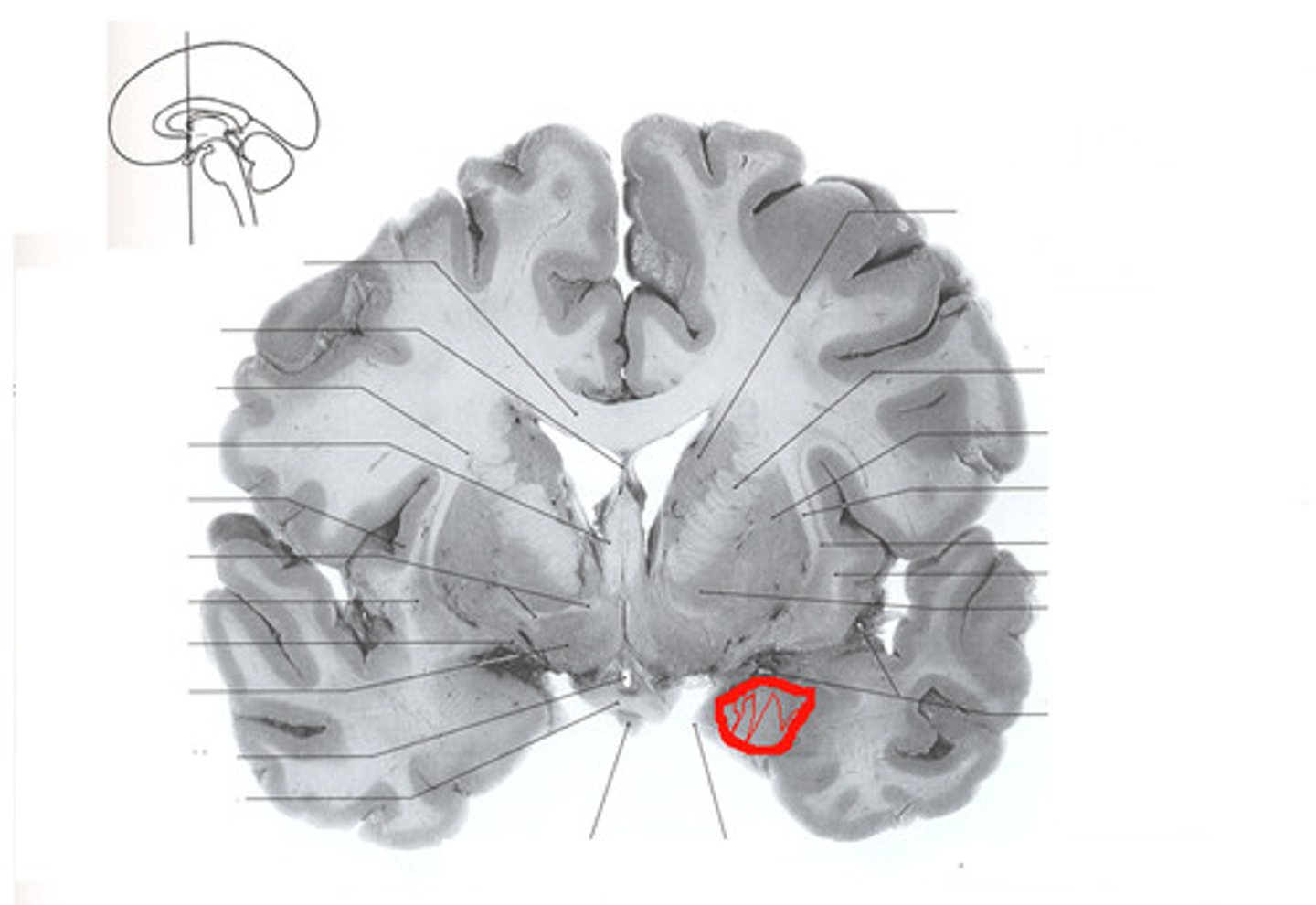
Amygdala- fear and aggression
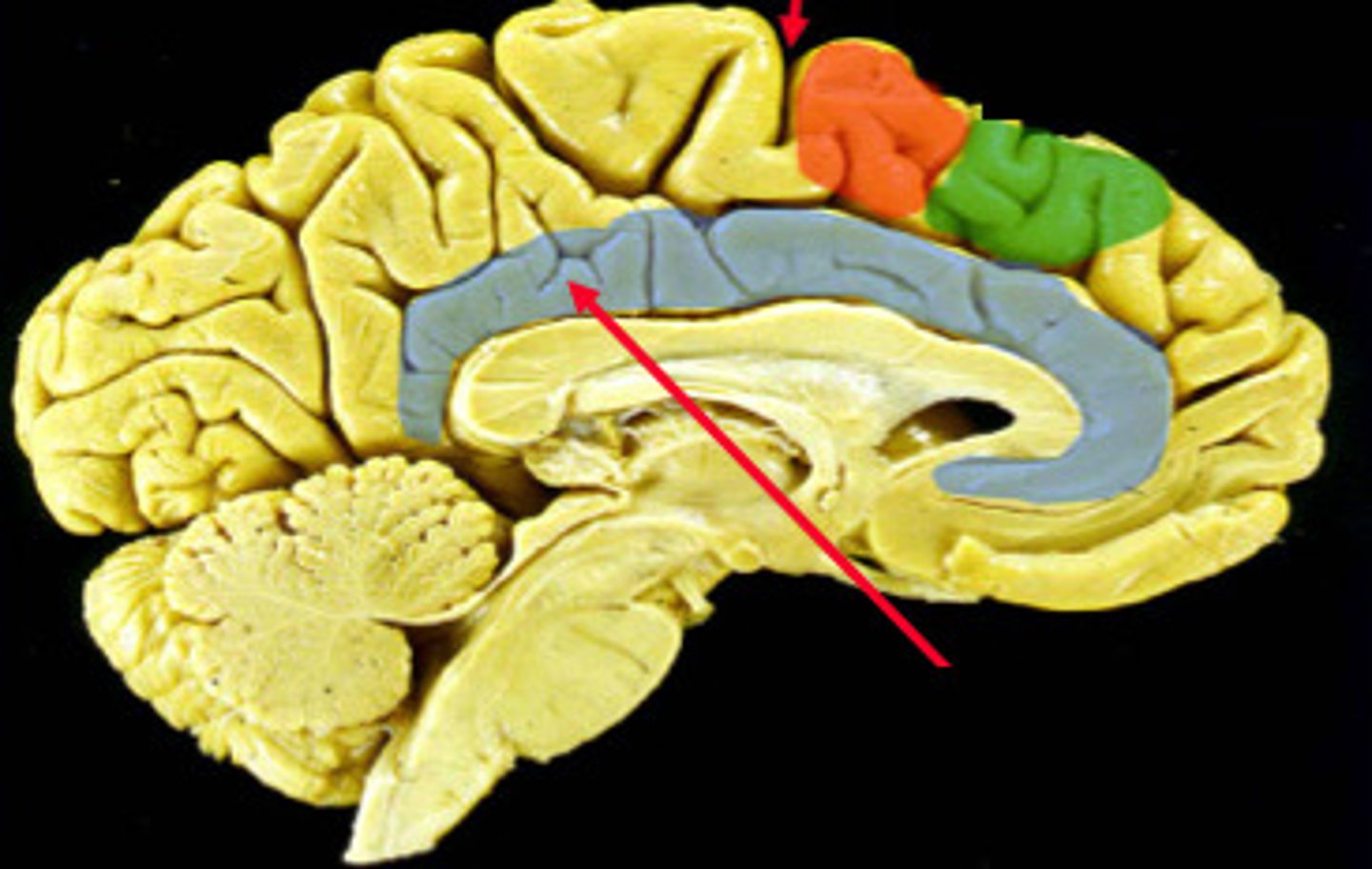
cingulate cortex - emotional and motor processing (cognition)

longitudinal fissure

lateral fissure (sylvian fissure)

central sulcus

Pre-occipital notch

parieto-occipital sulcus
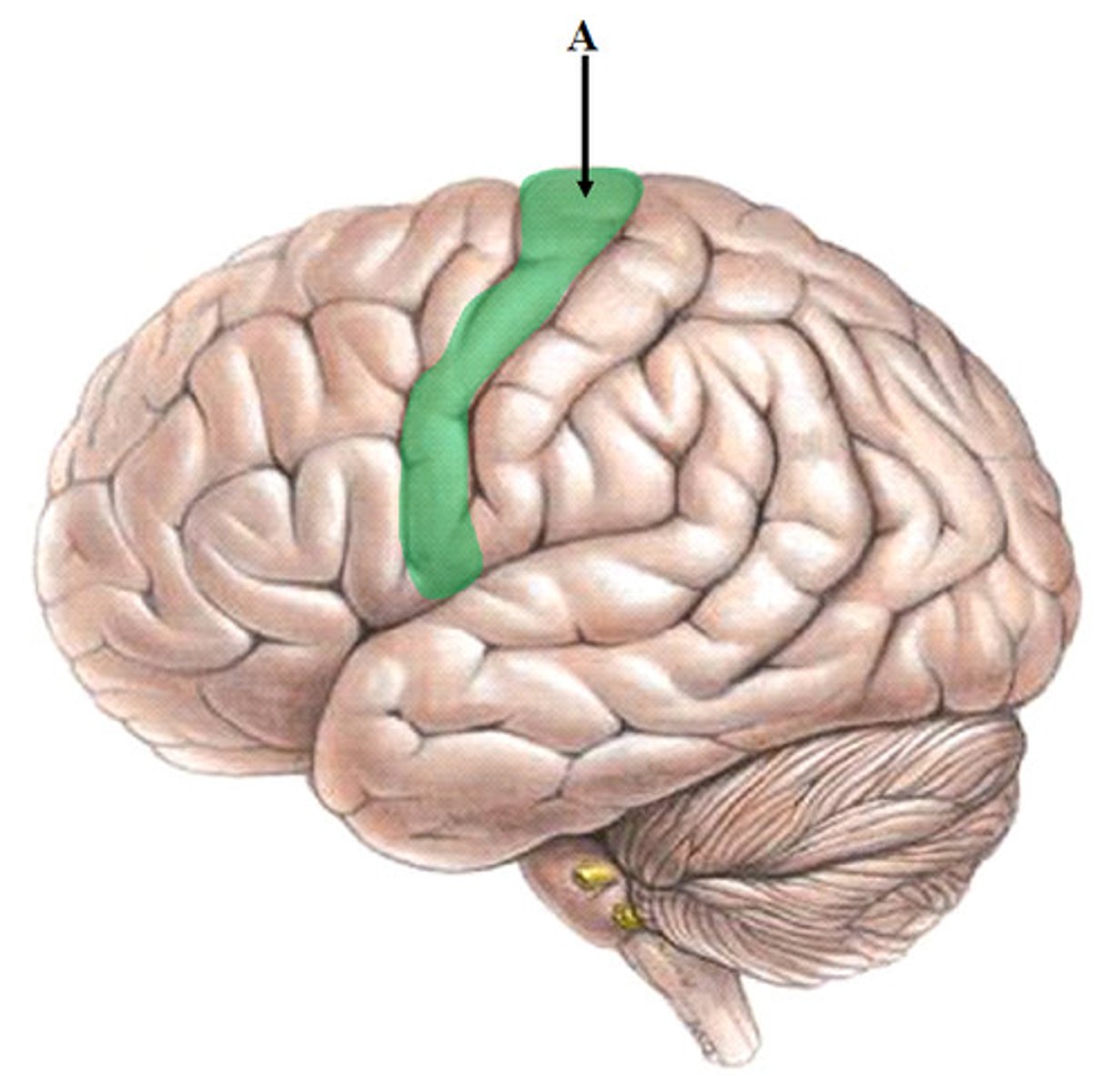
M1
primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus)

S1
primary somatosensory cortex

olfactory bulb

brocas area - controls language expression - an area, usually in the left frontal lobe, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.

Wernicke's area - language comprehension

olfactory nerve

optic nerve

Oculomotor Nerve (III) - narrows pupil and focuses lens

Trochlear Nerve (IV) - eye movement

Trigemminal Nerve
Abducens Nerve (VI) - lateral eye movement

Facial Nerve (VII) - Movement of facial expression muscles, taste (from anterior 2/3 of tongue)

Vestibulocochlear (VIII) - Equilibrium and Hearing (Special Somatic Sensory)

glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)

vagus nerve

Hypoglossal Nerve (XII) - Controls muscles of tongue

Accessory nerve (XI) - controls trapezius & sternocleidomastoid
controls swallowing movements

dorsal horn of spinal cord
cell bodies synapsed by afferent neurons (sensory)

ventral horn of spinal cord
The upper motor neurons that control the skeletal muscles are found in

lateral horn of spinal cord
Contains the cell bodies of the preganglionic ANS neurons

dorsal column
a white matter tract on the dorsal side of the spinal cord, carrying fine touch and proprioceptive axons to the brain stem
spinothalamic tract
pain and temperature

corticospinal tract
What tract is responsible for voluntary refined movements of distal extremities?


dorsal rootlets

ventral rootlets

spinal nerves
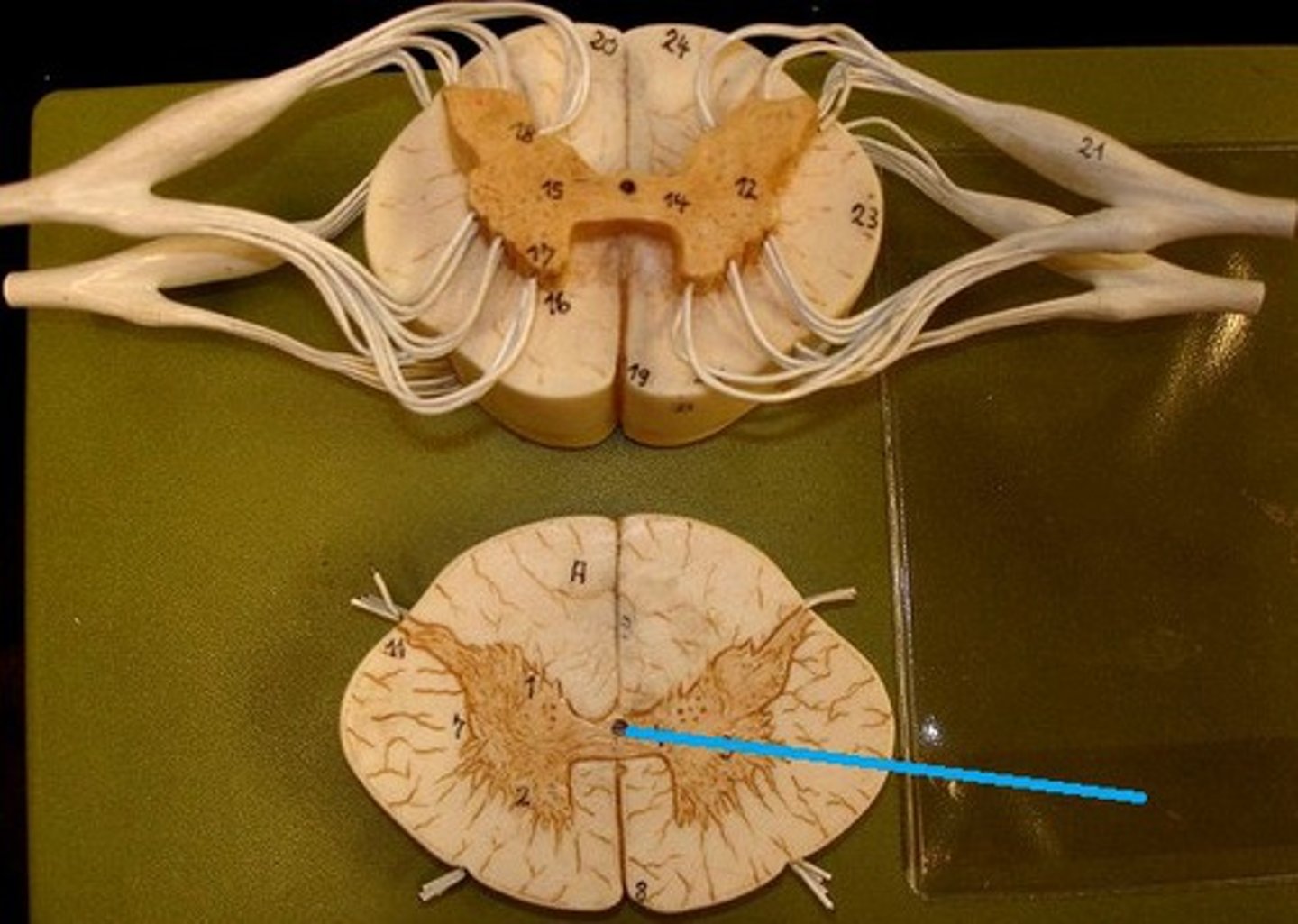
central canal of spinal cord

ventral white comissure

Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG)
associated with the dorsal horns; cell bodies of sensory neurons are located here

filum terminale. - extension of piamater
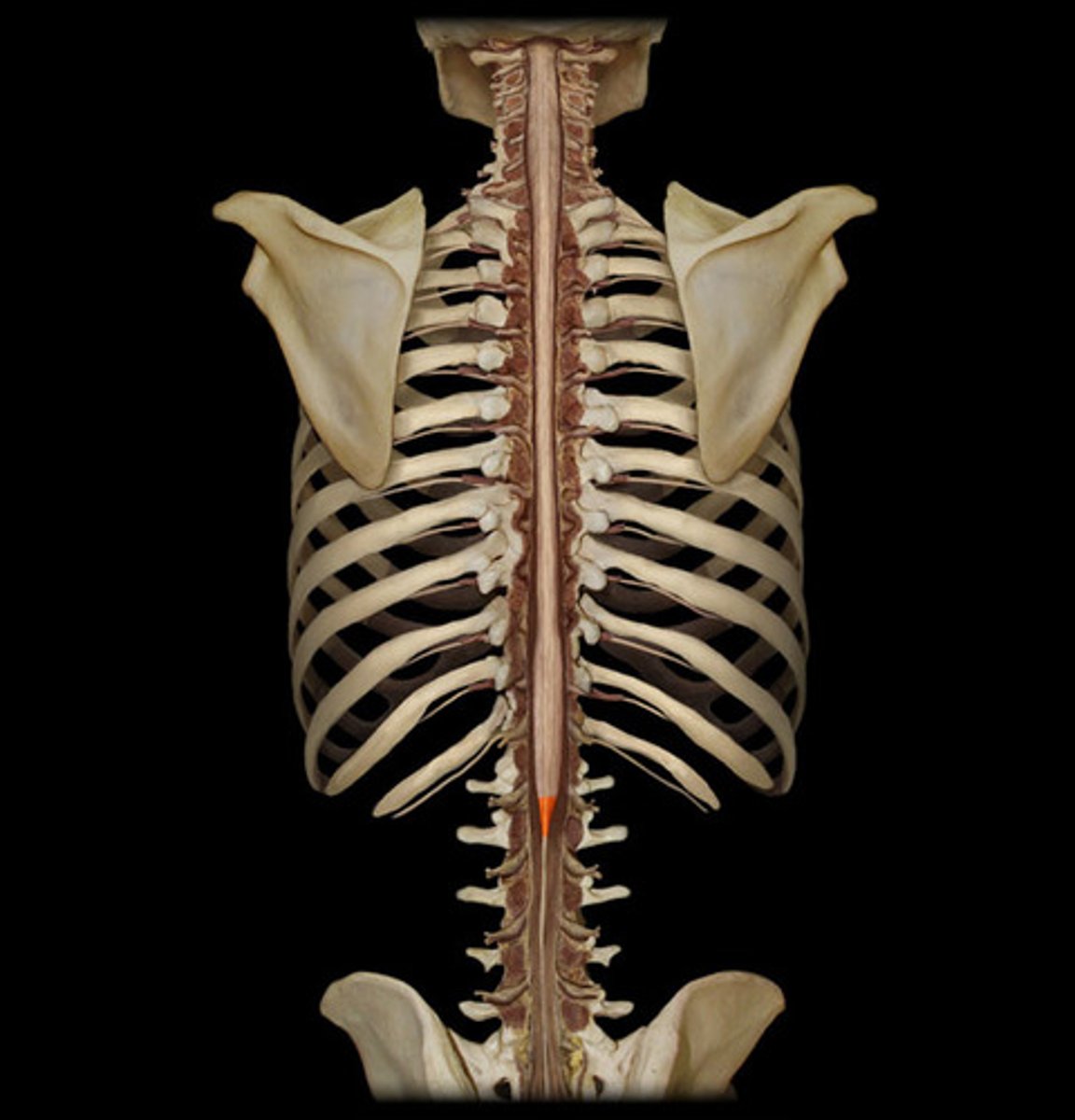
conus medullaris

denticulate ligaments
extensions of pia mater that secure cord to dura mater

cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord (L2 onwards)
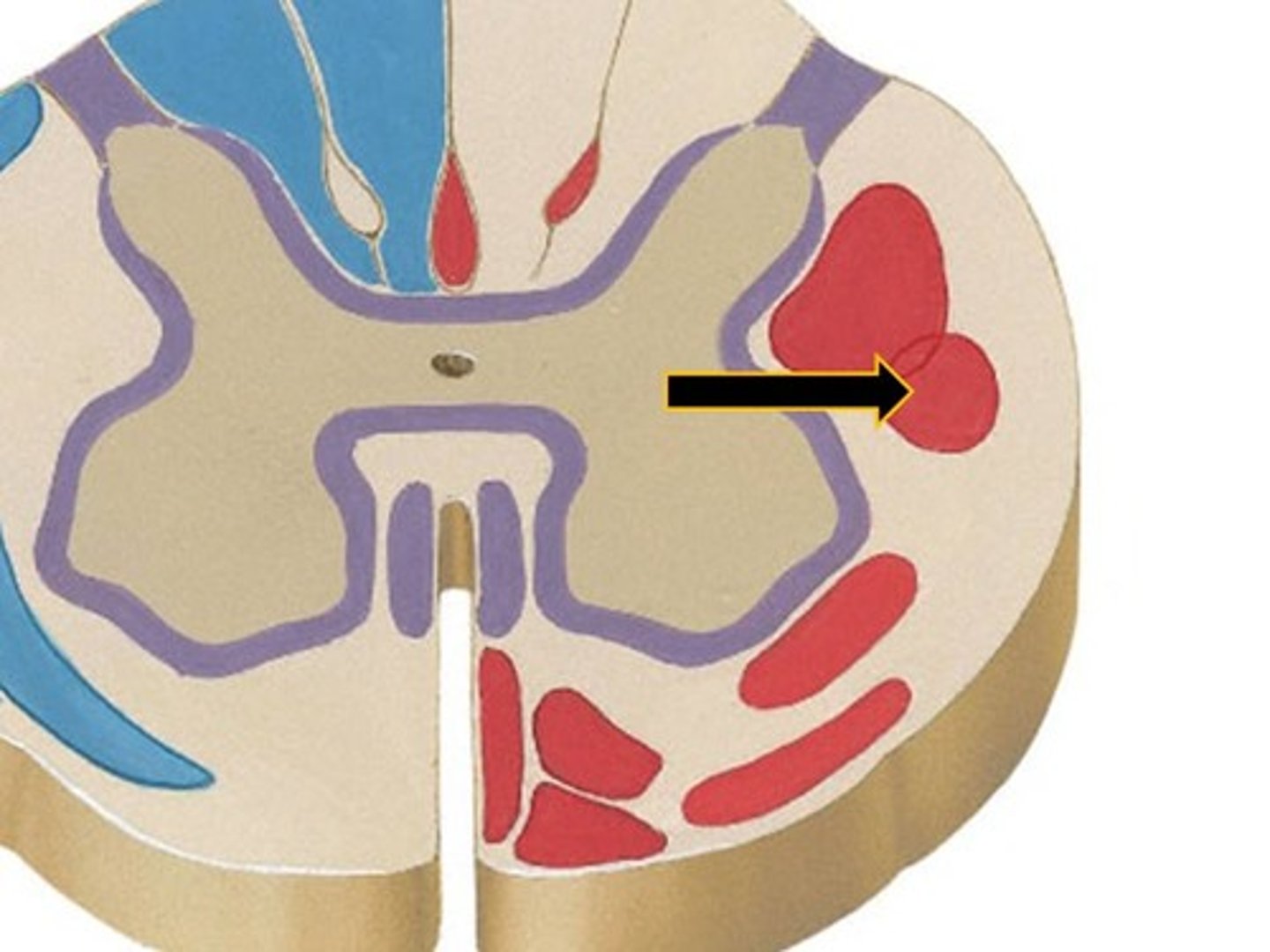
rubrospinal tract
locomotion and postural control.

lower motor neurons
ventral horn motor neurons, innervate skeletal muscles
decussation of corticospinal tract
medulla - in the pyramids

Decussation of dorsal column
also medulla - but medial lemniscus.

decussation of spinothalamic tract
spinal cord - white commissure

Diencephalon
thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus, subthalamus


basal ganglia - intentional movements

Midbrain

Pons

Medulla Oblongata