BIOL 109 LAB Practical 1 Study Guide - Vocabulary Flashcards
1/236
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of anatomy vocabulary covering directional terms, planes, regional terms, body cavities, organ systems, integumentary structures, tissues, and the axial/appendicular skeleton with major bones and landmarks.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
237 Terms
Superior
Toward the head; upper part of a structure (cranial/cephalic).
Inferior
Toward the feet; lower part of a structure (caudal).
Medial
Toward the midline of the body.
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body.
Anterior
Toward the front of the body (ventral).
Posterior
Toward the back of the body (dorsal).
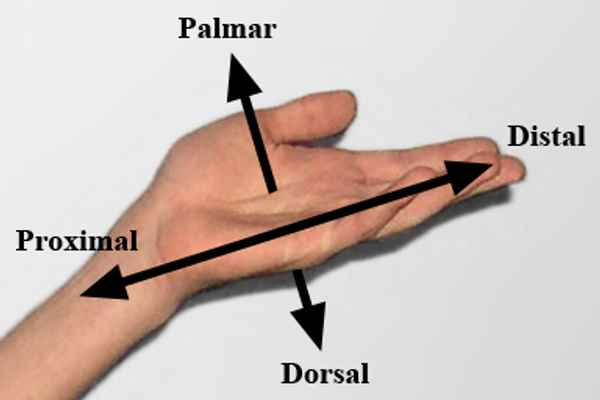
Proximal
Near the point of attachment or origin.
Distal
Farther from the point of attachment or origin.
Superficial
Toward or at the body surface.
Deep
Away from the surface; internal.
Sagittal plane
Vertical plane that divides the body into left and right parts.
Frontal (coronal) plane
Vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior portions.
Midsagittal plane
Sagittal plane that divides the body into equal left and right halves.
Transverse (horizontal) plane
Horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts.
Parasagittal plane
Vertical plane that divides the body into unequal left and right parts.
Anterior View
Front-facing view or description of the body.
Abdominal
Region of the body pertaining to the abdomen.
Crural
Shin/knee region; leg area.
Palmar
Palm of the hand.
Antebrachial
Forearm region.
Digital
Fingers or toes.
Patellar
Knee region.
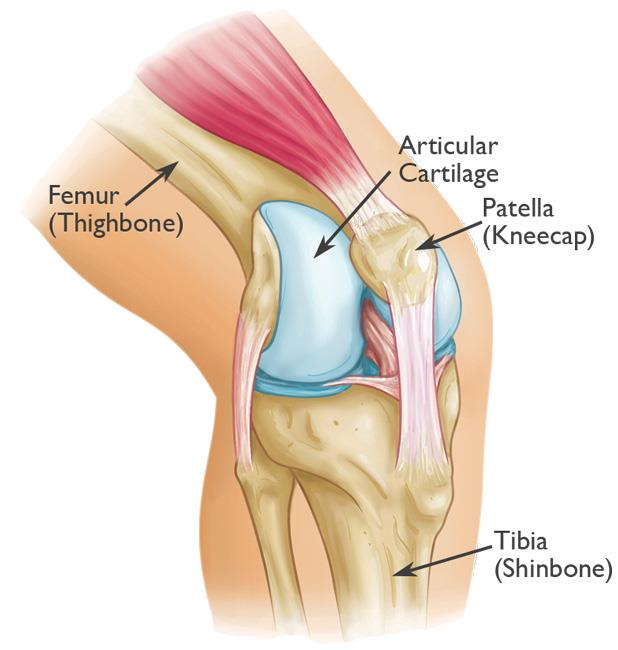
Antecubital
Front of the elbow region.
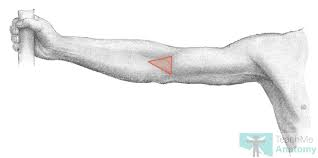
Femoral
Thigh region.
Pedal
Foot region.
Axillary
Armpit region.
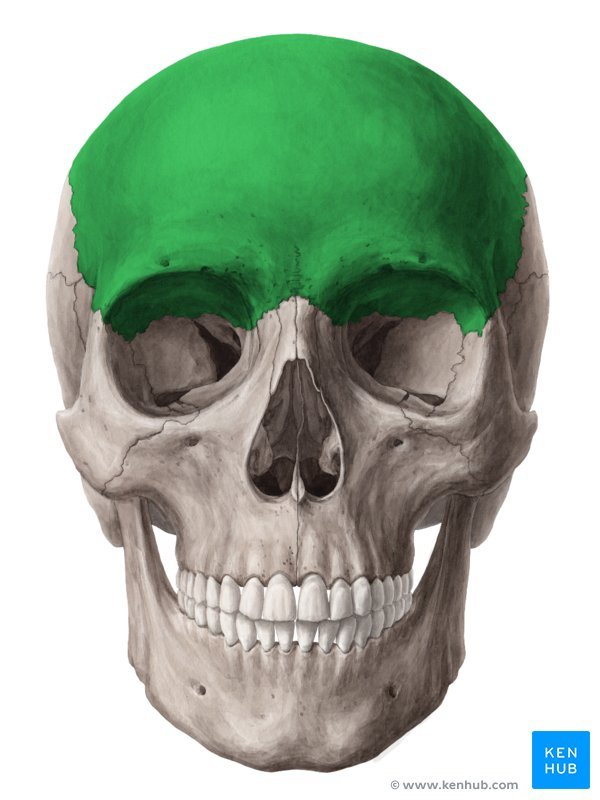
Frontal
Forehead region or the frontal bone area.
Pelvic
Pelvis region.
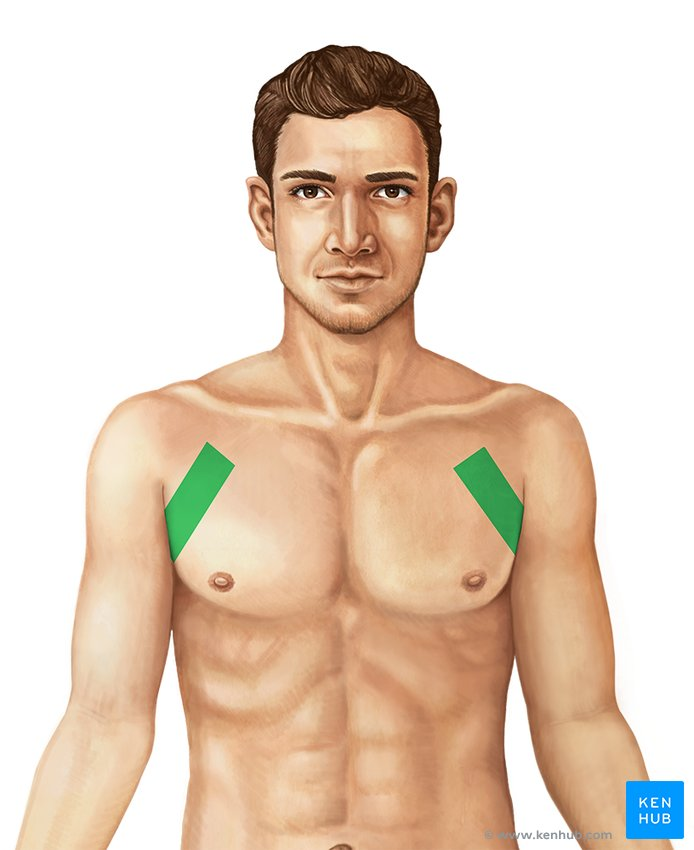
Brachial
Arm region.
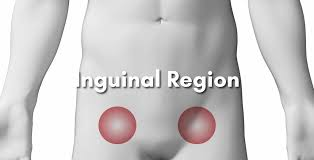
Inguinal
Groin region.
Pubic
Genital/pubic region.
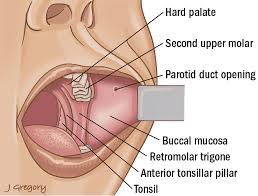
Buccal
Cheek region or mouth-related region.
Nasal
Nose region.
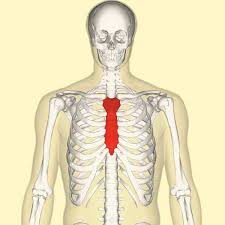
Sternal
Breastbone region.
Carpal
Wrist bones.
Oral
Mouth region.
Tarsal
Ankle region.
Cervical
Neck region or cervical vertebrae.
Orbital
Eye socket region.
Cephalic
Head region.
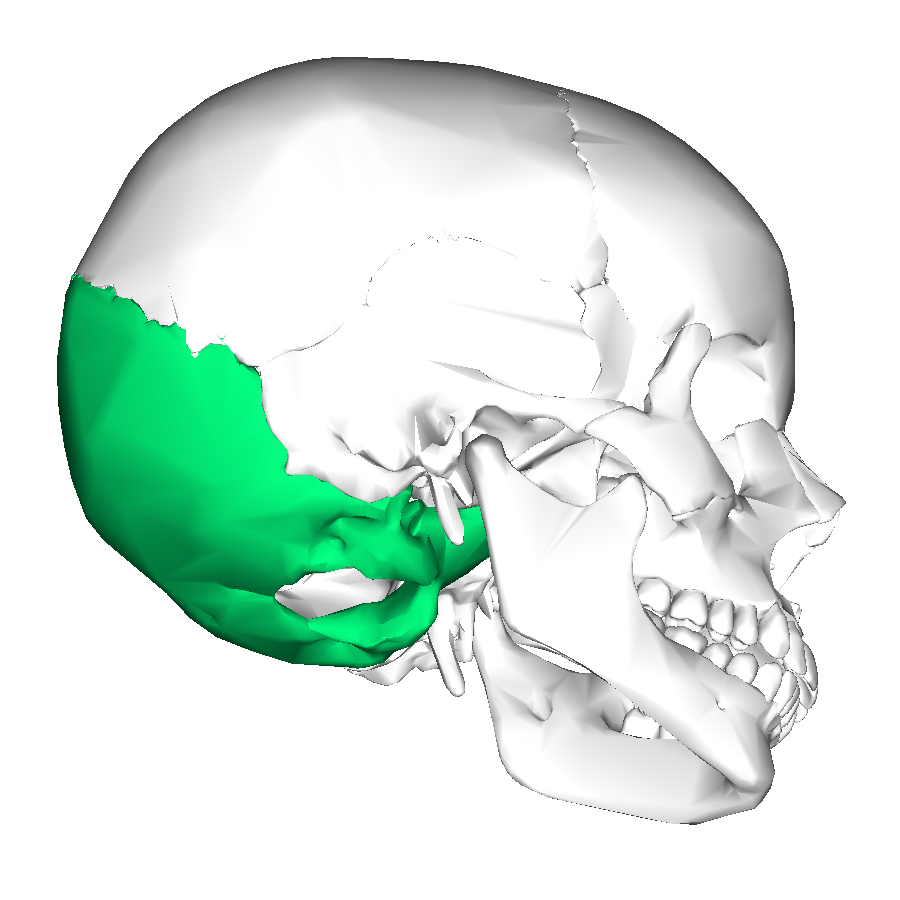
Occipital
Posterior skull region; occipital bone.
Gluteal
Buttocks region.
Plantar
Sole of the foot.
Lumbar
Lower back region.
Vertebral
Spinal column region.
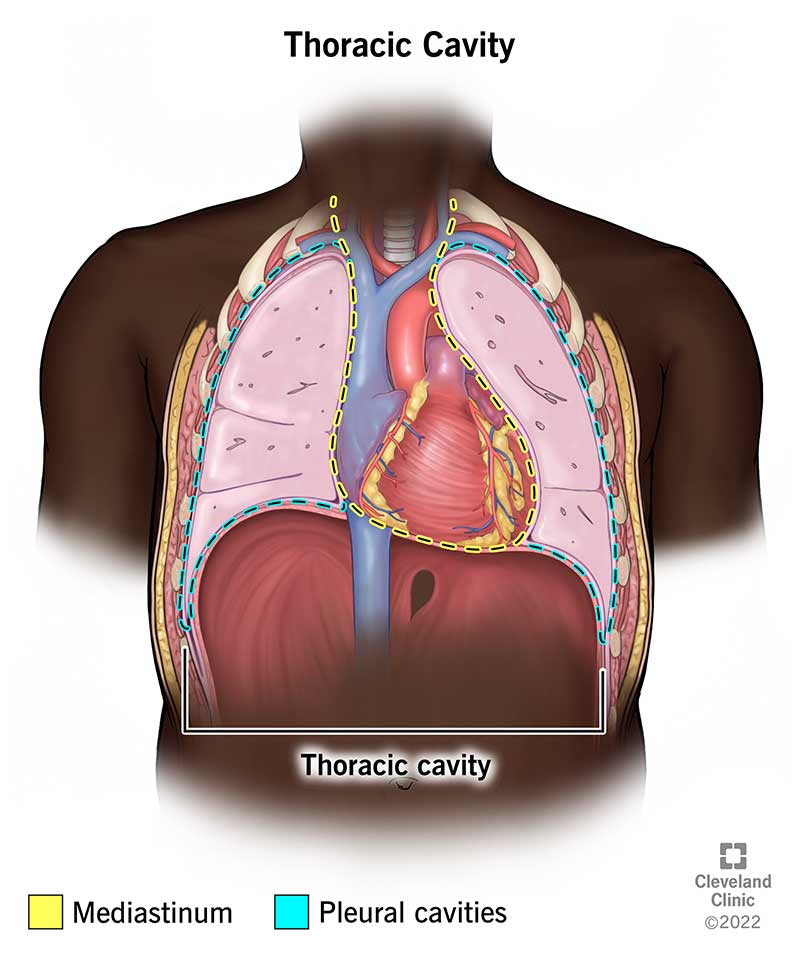
Thoracic cavity
Cavity housing the heart and lungs within the rib cage.
Cranial cavity
Dorsal body cavity that houses the brain.
Vertebral (spinal) cavity
Dorsal cavity within the vertebral column that houses the spinal cord.
Dorsal body cavity
Back side body cavity containing brain and spinal cord.
Ventral body cavity
Front body cavity containing thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
Pleural cavities
Two cavities surrounding the lungs within the thoracic cavity.
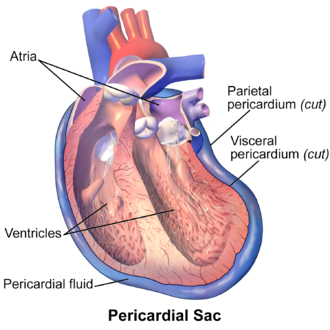
Pericardial cavity
Cavity containing the heart within the mediastinum.
Mediastinum
Central compartment of the thoracic cavity between the lungs.
Abdominopelvic cavity
Cavity that combines the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
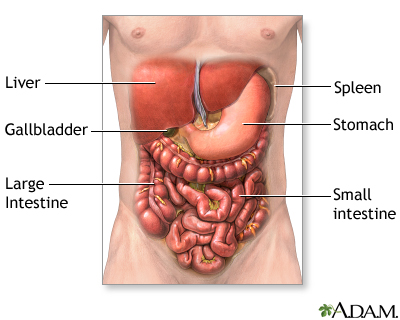
Abdominal cavity
Cavity housing organs of digestion.
Pelvic cavity
Cavity housing reproductive and some urinary organs.
Right upper quadrant (RUQ)
Upper-right quadrant of the abdomen (e.g., liver, gallbladder).
Left upper quadrant (LUQ)
Upper-left quadrant of the abdomen (e.g., stomach, spleen).
Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
Lower-right quadrant of the abdomen (e.g., appendix).
Left lower quadrant (LLQ)
Lower-left quadrant of the abdomen (e.g., sigmoid colon).
Integumentary system
Protective body system; includes skin and accessories; functions in protection, temperature regulation, and sensation.
Endocrine system
Glands producing hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
Digestive system
Organ system that breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and eliminates waste.
Skeletal system
Supports the body, protects organs, assists movement, stores minerals, and forms blood cells.
Cardiovascular system
Heart and vessels supplying blood throughout the body.
Urinary system
Organs that remove waste and regulate water and electrolyte balance.
Muscular system
Muscles that produce movement and maintain posture.
Lymphatic system
Returns fluid to blood and defends against infection; includes lymph nodes.
Reproductive system
Organs involved in producing offspring.
Nervous system
Fast-acting control system; responds to internal and external changes.
Respiratory system
Gas exchange system; supplies oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Epidermis
Outer skin layer; provides protection; avascular.
Dermis
Middle skin layer; contains vessels, nerves, and glands.
Hypodermis
Not part of skin; subcutaneous layer beneath the dermis.
Stratum corneum
Outermost epidermal layer of dead cells.
Stratum lucidum
Thin, clear layer in thick skin (palms/soles) between granulosum and corneum.
Stratum granulosum
Granular layer of epidermis; keratinization begins here.
Stratum spinosum
Spiny layer of epidermis; strengthens skin.
Stratum basale
Deepest epidermal layer; contains stem cells and melanocytes.
Papillary layer
Superficial dermal layer; contains dermal papillae and capillaries.
Reticular layer
Deeper dermal layer; contains dense connective tissue.
Dermal papillae
Fingerlike projections that strengthen the dermal-epidermal junction.
Sebaceous gland
Oil-secreting gland associated with hair follicles.
Merocrine (eccrine) sweat gland
Sweat gland widespread on body; produces watery perspiration.
Apocrine sweat gland
Sweat gland in specific areas; associated with hair follicles and odor.
Nail
Hard accessory structure protecting the dorsal fingertips.
Hair shaft
Part of hair that projects above the skin surface.
Hair root
Hair portion beneath the skin within a hair follicle.
Nail plate
Hard, visible nail at the tip of the finger or toe.
Nail folds
Folds of skin surrounding the nail plate.
Eponychium
Also called cuticle; skin at the nail border.
Lunula
Pale crescent area at the base of the nail.
Arrector pili muscle
Muscle that raises hair (goosebumps) when activated.
Meissner’s corpuscle
Touch receptor in the dermal papillae; detects light touch.
Pacinian corpuscle
Pressure and vibration receptor in the dermis.
Nail matrix
Tissue that produces new nail cells.
Simple squamous epithelium
Flat, single-layer epithelium; rapid diffusion (e.g., alveoli).
Simple columnar epithelium
Tall, single-layer cells; often with microvilli/goblet cells; absorption/secretion.
Stratified squamous epithelium
Multiple cell layer; protects against abrasion (e.g., skin, esophagus).
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Cube-shaped, single-layer; secretion and absorption (kidney tubules).