Unit 8
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Defensive Design, Testing and IDEs (J277)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
What are High-level languages?
Programming languages that have statements resembling English or math, making them easier to learn and understand. (Like Python, C++, Java)
What are Low-level languages?
Programming languages that are closely related to machine code, requiring detailed knowledge of the hardware.
What is a Compiler?
A program that translates a high-level language into machine code, producing object code.
What is an Interpreter?
A program that translates and executes high-level language code line by line, with no object code produced, it translates each line of the source code then executes it. The interpreter needs to be installed on your device to run the code.
What is Machine code?
The fundamental language of computers, consisting of binary instructions that are directly executed by the CPU.
What is Assembly language?
A low-level programming language that uses symbolic instructions corresponding directly to machine code.
What is an Assembler?
Program that converts assembly language into machine code.
What is Source code?
The code written by a programmer in a high-level language before translation to machine code.
What is Object code?
The machine code generated by a compiler from a high-level programming language.
What is Input Sanitization?
Removing any unwanted characters before passing data through the program
What is Input Validation?
Checking if the data meets certain criteria before passing it into the program. (E.g. Checking if an email address contains an @ symbol)
How to perform a Range Check?
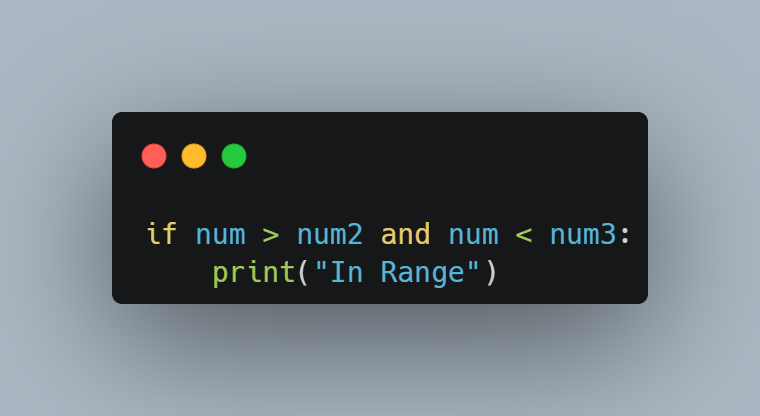
How to perform a Length Check?

What does isalnum() do?
Checks if all characters are alphanumerical (letters or numbers)
What does isdigit() do?
Checks if all characters are digits (0-9)
What does islower() do?
Checks if all characters are lowercase
What does isupper() do?
Checks if all characters are uppercase
What does startswith() do?
Checks if the string starts with a specific substring
What does endswith() do?
Checks if the string ends with a specific substring
What is Authentication?
Authentication is when you confirm the identity of a user before they’re allowed to access certain pieces of data or features of a program.
How can you maintain/improve your code?
Use:
Comments
Indentation
Variable (names)
What is the purpose of comments?
Useful for explaining what are the key features of a program.
What is the purpose of indentation?
Used to separate different statements in a program, allowing other users to clearly understand the logic of the code.
Why should you use useful naming conventions?
Allows users and other programmers to keep track and recognize what the variables are.
What is a syntax error?
The program doesn’t run because the code doesn’t follow the rules or grammar of the programming language,
What is a Logic Error?
When the program can run, but produces an unexpected output.
What is Iterative Testing?
The program goes through the development cycle multiple times, and the program is tested while it is written and before it is published.
What is Final Testing?
The program only goes through the development cycle once, and all the features are added at the same time.
What is Normal Data?
Data that is accepted by the program.
What is Boundary Data?
Data that is at the limit of the program (should be accepted)
What is Erroneous Data?
Data that is of the invalid data type, and should not be accepted.
What is Invalid Data?
Data that is outside of the program’s acceptable range.
What is a NOT gate?
The gate will invert the input. (1 —> 0) (0 —> 1)

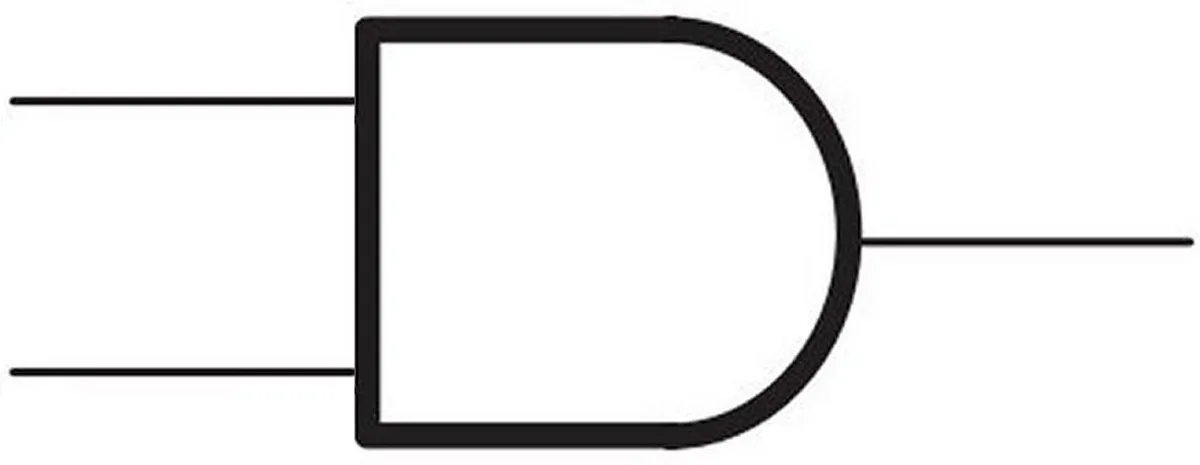
What is an AND gate?
Both inputs must be true for the program to proceed.
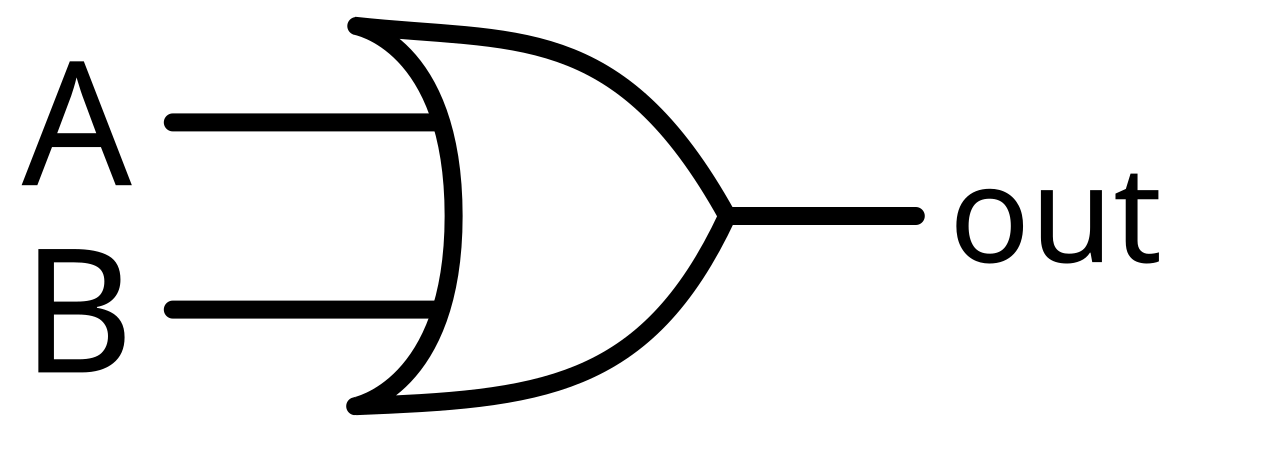
What is an OR gate?
One of the inputs must be true for the program to proceed.
What is an IDE (Integrated Development Environment)?
Piece of software that provides features to help a programmer to develop their program.
What are some features of IDEs?
Line numbers
Autocorrect
Auto complete
Auto indent
Auto color coding
Error diagnostics and debug tools
Breakpoints
Syntax highlighting