L6 - Digestive Tract Secretions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the two main functional sections of the canine digestive system?
Alimentary Canal and Accessory Structures.
What is the role of the alimentary canal in the digestive system?
It is a tube-like structure running continuously from mouth to anus, including the pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
What structures are included in the accessory system of the canine digestive system?
Teeth, tongue, salivary glands, gallbladder, liver, and pancreas.
What are the four layers of the alimentary canal?
Mucosa, Submucosa, Muscularis, and Serosa.
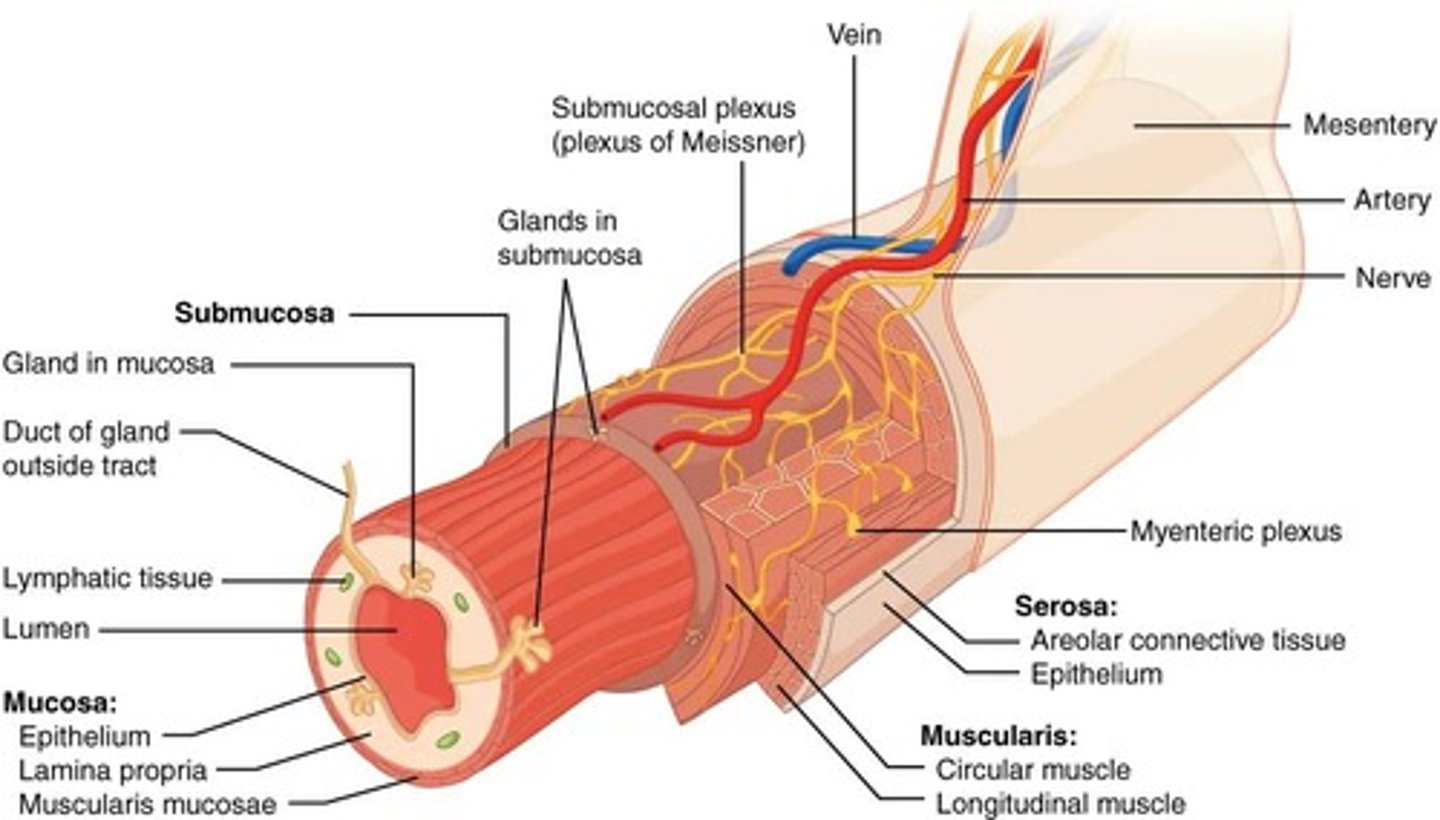
What is the function of the myenteric plexus?
It is located in the muscularis layer and is responsible for motility.
What does the submucosal plexus regulate?
It regulates digestive secretions.
What is the arterial blood supply to the anterior alimentary tract?
Arterial branches of the aortic and thoracic arches.
What is the venous blood supply system for the digestive tract?
The hepatic portal system.
What is mechanical digestion?
A purely physical process that makes food smaller to increase surface area and mobility, including mastication and tongue movements.
What is chemical digestion?
The process where digestive secretions break down complex food molecules into their chemical building blocks, starting in the mouth and completed in the small intestine.
What are the three pairs of major salivary glands in mammals?
Parotid glands, mandibular glands, and lingual glands.
What is the composition of saliva?
Saliva contains water, various enzymes, acids, salts, and antimicrobial products.
What are the two types of secretions produced by salivary glands?
Serous (liquid) and mucous (viscous).
What is the role of mucous in saliva?
It binds to bacteria and foreign agents, assists with secretion, and flags the immune system to target.
How is saliva produced?
Through a two-step secretion process: Acinar (efflux of NaCl and H2O) and Ductal (reabsorption of NaCl and efflux of K+ and HCO3-).
What is the role of the autonomic parasympathetic nervous system in saliva production?
It controls the production and secretion of saliva, stimulated by anticipation of eating.
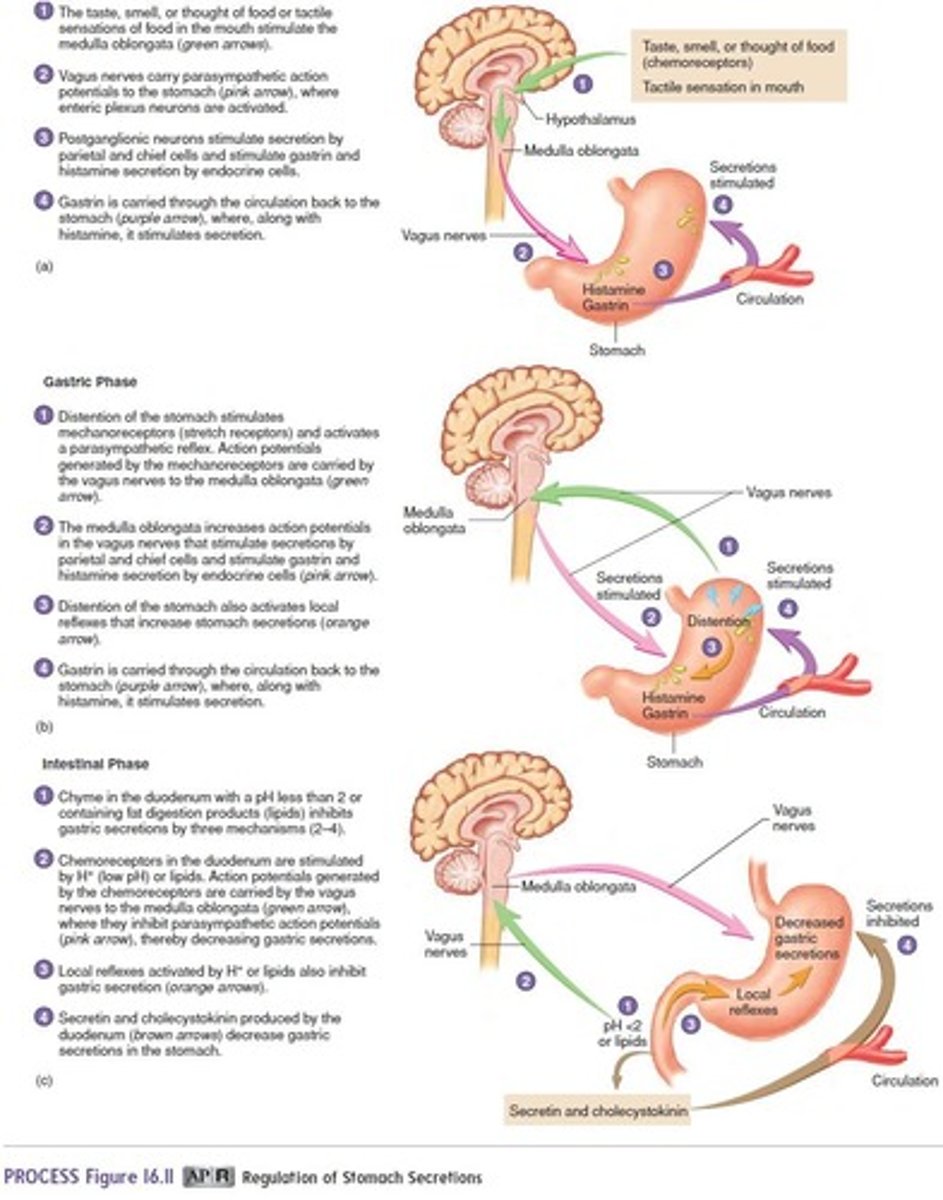
What are the phases of gastric secretions?
Cephalic phase, gastric phase, and intestinal phase.
What initiates the cephalic phase of gastric secretion?
The sight, smell, and taste of food.
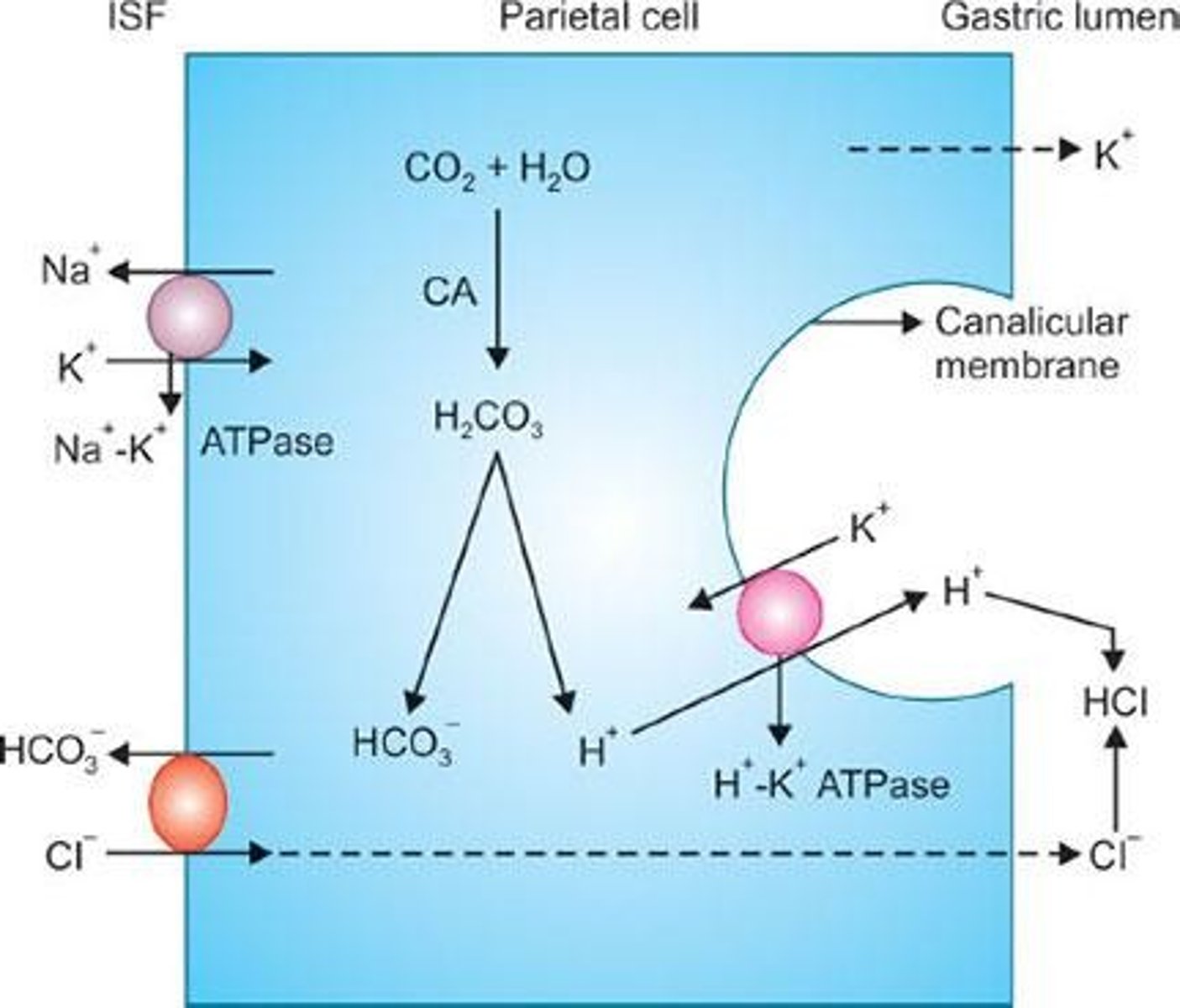
What is the role of parietal cells in gastric secretions?
They secrete H+ ions into the gastric lumen, contributing to the formation of hydrochloric acid (HCl).
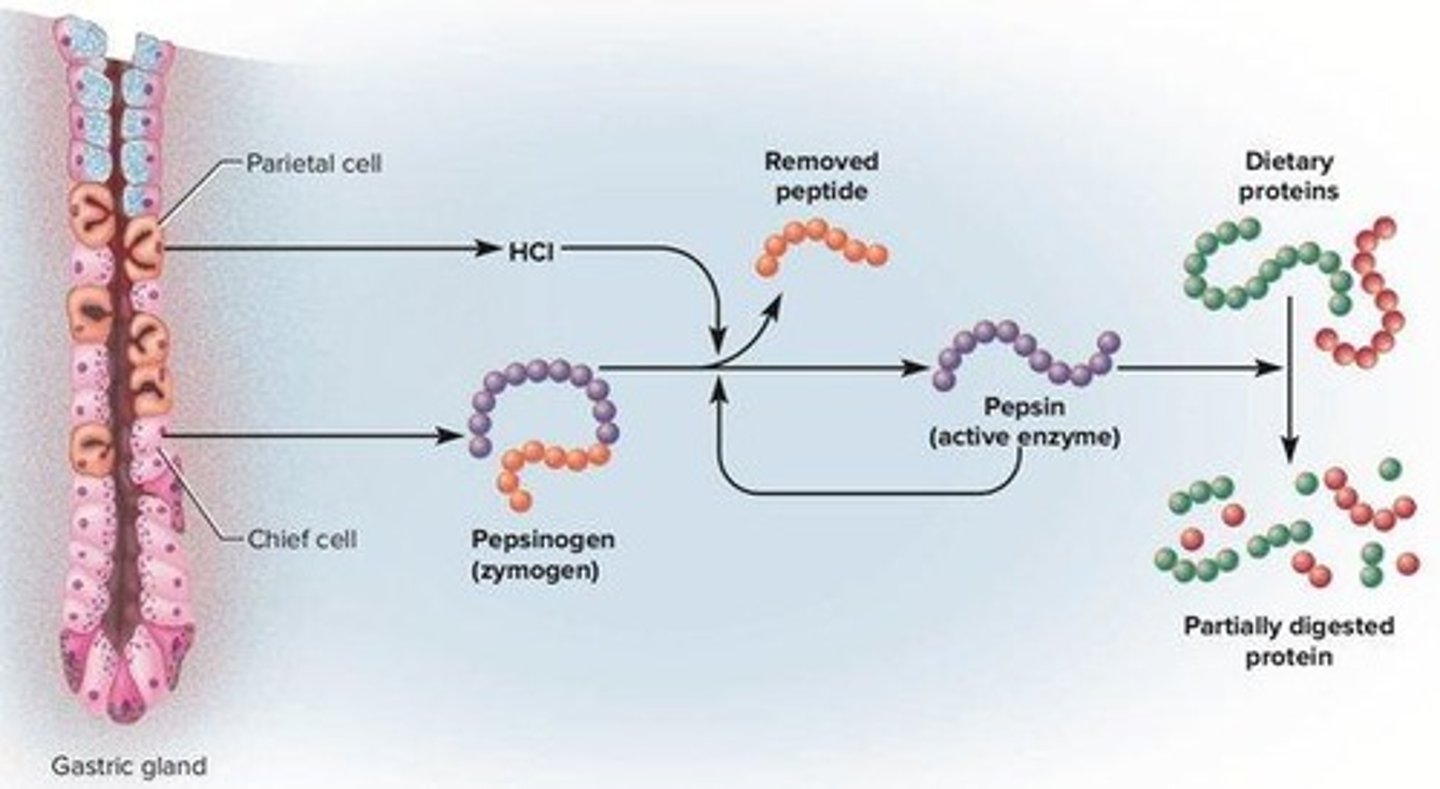
What activates pepsinogen in the gastric lumen?
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) activates pepsinogen to form pepsin, an active digestive enzyme.
What does the pancreas secrete?
Pancreatic juice containing bicarbonate and digestive enzymes into the duodenum.
What stimulates the release of CCK from the pancreas?
The presence of digestive products in the duodenum.
What is the function of bile?
Bile aids in the digestion of fats in the duodenum.
What is the composition of bile?
Water, bile salts, bilirubin, and fats (cholesterol, fatty acids, and lecithin).
What is enterohepatic circulation?
The process where biliary secretions are synthesized in the liver, released into the duodenum, and 90% reabsorbed in the ileum.
What controls biliary secretions?
The vagus nerve (CNX), CCK, H+, and secretin.