Darwin and Evolution – Key Vocabulary
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of vocabulary flashcards covering foundational terms and concepts from the lecture on Darwin and Evolutionary theory.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Evolution
Heritable change in populations of organisms over time; descent with modification.
Natural Selection
Process in which environmental pressures lead to differential survival and reproduction of individuals with advantageous traits.
Scientific Revolution
A shift that replaces an existing idea about nature with a radically different one, such as evolution replacing special creation.
Special Creation
Historical belief that each species was independently created and unchanging.
Typological Thinking
View that species are fixed, perfect ‘types’ and variations are unimportant or misleading.
Plato
Greek philosopher who argued every organism is an unchanging, perfect essence.
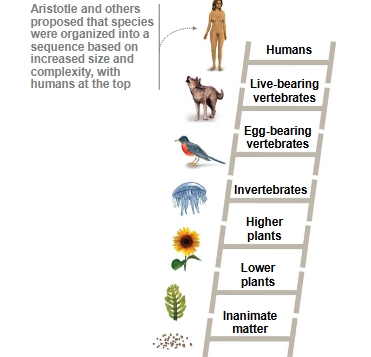
Aristotle’s Scala Naturae
Ancient concept arranging organisms in a linear sequence of increasing complexity, with humans at the top.
Fossil
Remains or traces of once-living organisms preserved in strata.
Strata
Layers of rock or sediment where fossils are found, indicating different time periods.
Paleontology
Scientific study of fossils; founded by Georges Cuvier.
Georges Cuvier
Paleontologist who documented extinction and changes in species across time.
Extinction
Permanent loss of a species from Earth, observed by Cuvier in the fossil record.
Jean Baptiste Lamarck
Early evolutionist who proposed inheritance of acquired characteristics and increasing complexity over time.
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
Lamarck’s idea that traits gained during an organism’s life can be passed to offspring; not supported by modern genetics.
Adaptation
Heritable trait that increases an individual’s fitness in a specific environment.
Charles Darwin
Naturalist who formulated the theory of evolution by natural selection after his voyage on HMS Beagle.
HMS Beagle
Ship on which Darwin served as naturalist during a five-year voyage that inspired his evolutionary ideas.
Descent with Modification
Darwin’s phrase for evolution: modern species arise from ancestral forms with changes over generations.
Fitness
Reproductive success of an individual relative to others in the population.
Artificial Selection
Selective breeding by humans to enhance desirable traits in domestic species.
Variation
Differences in phenotype among individuals, essential raw material for natural selection.
Mutation
Change in DNA sequence that can introduce new genetic variation into a population.
Macroevolution
Large-scale evolutionary changes that occur over long time spans, often involving speciation.
Speciation
Formation of one or more new species from an ancestral species.
Biological Species Concept
Defines species as groups of actually or potentially interbreeding populations that are reproductively isolated from others.
Allopatric Speciation
Speciation that occurs when populations are geographically separated, preventing gene flow.
Sympatric Speciation
Speciation that occurs within the same geographic area, without physical barriers.
Reproductive Isolation
Barriers that prevent gene flow between species, maintaining separate species boundaries.
Prezygotic Barrier
Reproductive isolation mechanism that acts before fertilization (e.g., temporal or behavioral differences).
Postzygotic Barrier
Reproductive isolation mechanism that acts after fertilization (e.g., hybrid sterility).
Ecological Isolation
Prezygotic barrier where species occupy different habitats within the same area.
Temporal Isolation
Prezygotic barrier where species breed at different times or seasons.
Behavioral Isolation
Prezygotic barrier where differences in courtship or mating behaviors prevent interbreeding.
Mechanical Isolation
Prezygotic barrier where differences in reproductive structures prevent successful mating.
Gametic Isolation
Prezygotic barrier where sperm of one species cannot fertilize eggs of another.
Hybrid Sterility
Postzygotic barrier where hybrid offspring survive but are infertile (e.g., mule).
Hybrid Inviability
Postzygotic barrier where hybrid embryos fail to develop or die early.
Hybrid Breakdown
Postzygotic barrier where hybrids are viable and fertile, but their offspring are weak or sterile.
Adaptive Trait
A heritable characteristic that increases an organism’s fitness in its environment.