Soil Science
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Explain the 3 main properties of soil and why this matters. water and interfaces
bent shape, positive and negative ends, forms hydrogen bonds that stick to themselves and other surfaces
this is important bc water now can stick to soil partices (adhesion) and itself (cohesion), this helps water move through small pores.
interfaces
water in soils is almost always touching air/soil particles
the forces that act on water are adhesion, cohesion and water
What are the 4 things water constantly moves between?
atmosphere
soil
groundwater
lakes, rivers, oceans
Capillary action? how does water climb up tiny vs large pores, and what equation is used for that?
in tiny pores like clay, gravity is less of a factor so water climbs up due to adhesion and cohesion overpowering gravity
in larger pores linke sand, rise is less because gravity wins
h=0.15/r
in sand there are bid pores so less capilary movement, in loam there is medium capillary movement, in clay there is less capillary movement,
Water content in soil- 2 ways of measuring water content. How to calculate depth equivalent of water? explain these 2 formulas 0m=Mv/Mm,0m=Vw/Vb
gravimetric water content (mass based)
0m=Mv/Mm Mv=(mass of wet-dry) Mm=mass of dry
Volumetric
0m=Vw/Vb (water volume/bulk volume of soil)
Depth equivalent
how deep layer of water youd get if you squeezed water out of soil
Dw=0vxDb (volumetric water content by depth of soil)
How to measure soil water content: Direct of without digging soil
direct
oven drying-accurate but destructuve
In situ methids
neutron pobe: meausre hydrogen atoms
TDR: Meaures how fast electrical signals travels: slower when more water is present
GPR: Uses radar to estimate water
what is water table? What is water potential? Why can it be positive or negative? 4 Basic components of total water potential, and explain if the compnent is negative/positive and where? Hydraulic Potential?
water table is where all pores are filled with water
how free water is to move
water always moves from high to low water potential
since its usually in reference to a reference point. if its more then the reference its positive if its less then its negative
Gravitational (if its above a reference point its postive. if ur 20 cm above reference point its +20)
Matric (attraction of soil, more forces pulling it up rather then down). this is about how water sucks water into pores. in unsaturated (above water table) there is a lot of empty pores to fill, so there is more suction or pull which is negative pressure. in saturated there is no pores to fill, so in saturated it would be 0
Osmotic potential-(this is when if you add salts, can water still move? solutes not too important)
Pressure potential-positive when more pressure is added to water (always positive. if you are 10m below, you have 10m of pressure). it can only occur below water table where pressure is present since above water table soil is holding it up.
Hydrolic Potential
above water table: gravitational +negative matic
below water: negative gravity+ pressure
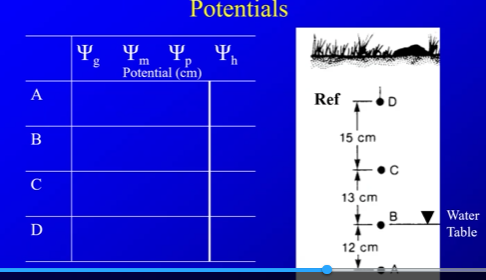
calculate the all the values, and what does all the h values mean? Why is this not realistic? water potential under non-equillibrium? Can you have pressure if you have matric? where does h values go?
all the h values being the same means that the water is not moving
its not relastic because water is always moving, so usually in non-equillibrium quesitons the matric will be given
you cant have portential if you have negative matric because negatic matric is above water table, and pressure above that is 0
water will always move from high potential (big number) to small number.
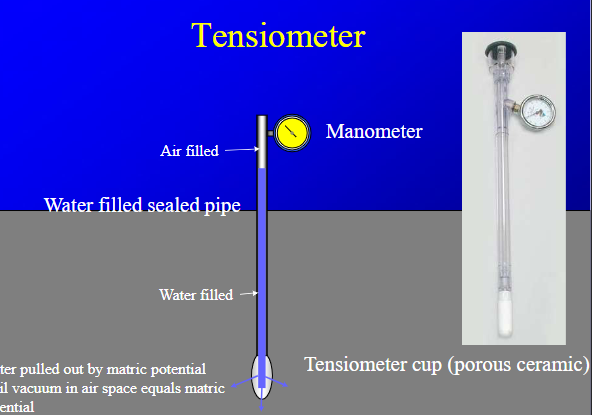
How to measure components of water potential? (matric, pressure, gravitational, osmotic)
Pressure
piezometer, or a well. measures at what depth water is sitting or water table, and measures how above or below someone is to find pressure
Gravitantional
use a ruler to find above or below you are from reference point
osmotic
salt concentration from one side to another, what is ion concentration of water one one side or another, which can be done by electric conductivrty which measured ion. more condvutivity, more ion
Matric (tensiometer)
imagine you have cup at bottom, forces (matric potential) will force water to be pulled out, creating a vaccum which shows a value on the scale
Describe relaitonship between water content and matric potential, describe this using sand textures.
biggest pores empty out first because they have lower matric potential. smaller pores epty later because they have greater matric potential
clay has larger matric potential then sand, because clay has smaller pores.
Soil water available to plants. Describe:
Field Capacity (FC)
Wilting Point (WP)-what has more availble water clay or loam
Availble Water (AW)
What will happen to WP, FC AW when organic matter is added?
Field Capacity (when free drainage has stopped)
water content where soil is holding as much water it can against gravity. this means big pores have emtied out because they cant hold against gravity, but the small pores are still filled. this means the big pores provide areation, so plants can breathe and are happy.
Wilting Point
soil is dry, causing pores to shrink so much that plants cant extract that water. clay has less plant availble water thenloam, because pores are smaller, harder to get.
Available Water
amount of water availble to plants is field capacty minus wilting point
Addition of organic matter?
when organic matter is added, more variation is pore size so small increase in wilting point, but mostly increas in field capacity, so FC will increase.
Hydraulic conductivuty. Why is it important?
the ability of soil to transmit liquid water through soil pores
Signficane
drainage
if water moves to fast, it can cause flooding
leaching, water that moves in quickly can carry nutrients and pollutants
septic fields and how much water is coming out of those fields
retention of water in canals

Darcys expiriment, Calculate flux rate
darcys experiment is when he took a tube filled with sand, poured water into one end, and measured how much water come out the other end, how long it took, and the difference in water height between the inlet and outlet
he found that if theres a greater water level before, it moves faster because theres a greater push,
and water moves faster is sand then clay cause theres bigger gaps.
The flux is a constant multipied by hydrolic potential over the the thickness of potential
Guelph Permeameter. why does water move faster in saturated soil?
maintains a contant pressure of water, untill you get a measurment of water leaving at constant state, which will tell you that water is at saturation
because in saturated soil all the pores are full, even the big pores, so water gets transferred easily and quickly
Hydrolic cycle and the water budget
water falls from the sky, adds water to the land, evapotrasnipiation from plants removes water from land, ruoff is water that flows downhill to lakes, infiltration is when water soaks into ground, and groundwater outflow is when water underground leaves underground and flows out to rivers, lakes or oceans.
water budget takes the gains P(in)-ET(out)-runoff(out)-groundwater(out)
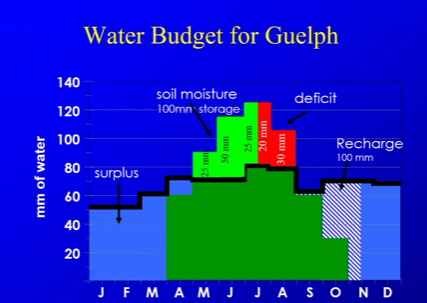
Water Budget? What factors are included. For the water budget in april may, you can see that there is high evapotranspiration potential,but plants in april may are still healthy. why?.what is evapotranspiration potential?
what impacts/increases evapotranspiration? How can you decrease the change from Evapotranpiration and potential (make more water present in soil)?
Evapotranspiration: actual amount of water lost by evaporation and plants
Evapotranspiration potential: amount of water that could be lost by evaporation and plant if water was always available. basically, how much water plant would like to have
in April may you have ground water that access so there’s not a large gap between water and water plants want
the water budget shows how much water guelph gets monthly, in winter you have more water in then out, from april to october plants have higher ability to store water, creating a deficit in august ish when plants need more then they have, and in rechange the water enters groundwater
more radiation, more evapotranspiration
Reduce gradient
have more organic matter that can create a larger field capacty, which can create more additional water
In ontario in early spring in fall we have excess water which means you are shrinking the growing season. what factors of excess water needs to be thought of before management?
the timing of excess water
causes of excess water
plant response. if excess doesnt impact plant response, why change it?
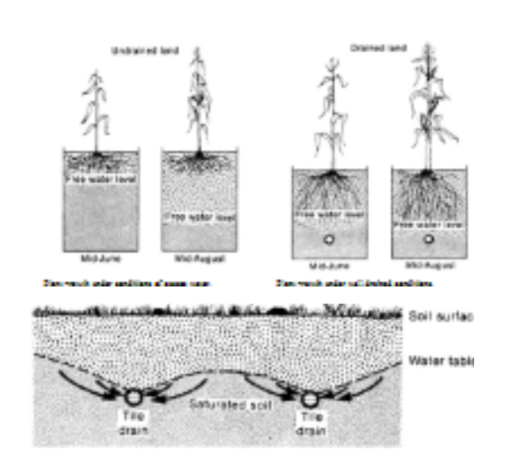
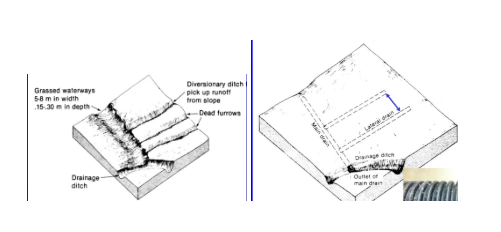
Strategies to remove excess water.
surface drainage
Tile drainage-size of main pipe based on steepness? Clay vs Plastic? When does tile drainge remove water? How does it reduce the water table?
How does machine that makes the pipe know how to lay the pipe at a constant height even though land has a different topography
Explain why its important for plants to have good drainage
main drain and little drains remove water from grounds top layer
pipes that are slightly more underground, but it is still the same layout as surface drains. big pipes for downhill since water is moving slower. Clay vs plastic? generally plastic is cheaper and easier to work with.
using GPS
tile drainage removes water after field capacity is reached. it lowers the water table because less pores are saturated because less water is present
in undrained plant, roots dont grow deep bc they suffucote and saturated soil, so when the water dries up they cant acess groundwater.
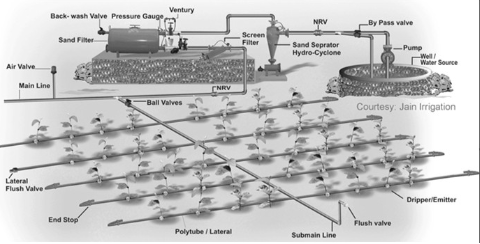
Water Deficit, and what factors need to be considered? talk about management systems like flood irrigation, trickle drip irrigation, lateral move, central pivot,Gun irrigation and the benefits and drawbacks.
Timing
if we have insuffucient water when we dont need to grow plants, its not importnat
if deficit happens in middle of growing season it might be important.
the reason why we dont irrigate everywhere is because its really expensive
Cause
excessive drainage, evapotranspiration, etc
Plant response
how plants deal with the change
Management
Flood irrigation
flooding the entire area which is good because weeds dont grow, you cant do this in areas with high topography because water moves.
Trickle/drip irrigation
main line and laterial dripping line. its good because it puts water in the root so less evapotranspiration, an ensures the plant doesnt get wet for too long
but its very expensive, and not super strong.
Gun irrigation
travelling gun, moves in a strip. its good because its long term and cheaper, but when water is empty you have to refill it.
Lateral move
moves laterally, moves across a field irrigating in a line. you can irrigate a large peice of land, but only in rectangular field.
Central pivot
it only irrigates in circles, so you always get a full range of motion.

This flashcard will take you through step by step the formaiton of Kaolinite (1:1)
2 building blocks of clay? silica tetrahedrom and alumninum octahedron? isomorphic substitution?
explain what happens when sillica tetrahedron forms a sheet, and when aluminum octahedron forms a sheet
Explain what happens when sheets of Si Tetrahedral and Al octahedral joined
How does clay structure (kaolinite) form? Discuss surface area and shrink swell
sillica tetrahedrom is a tiny pyramid building block with 4 silicon and 4 oxygen. isomorphic substitution is when one atom is swapped with a similar sized one like aluminum, making it negatively charged
aluminum octahedron is one alunimum and 5 OH. isomorphic substiution is when you have magnesium replacment causes a more negative charged.
Sheet
when sillica forms a sheet, looking from side its very flat, and all the oxygens are shared. since some O is not shared it will have a charge of -1
when alumniums forms a sheet, looking from the side every OH is shared (each ½ is split in half and shared), so it will have a 0 charge, so when a magnesium enters through isomorphic it becomes negative
Joined
oh bonds with O to create a bond. if no ismoprhic subsitiion, charge would be 0, but because of substitution, charge is negative.
Clay Structure
this is when the hydrogen from the Oh on the bonds start linking, a form of very strong hydrogen bonding, which start creating this structure
small surface area because they are all together now
low shrink swell becuase of strong hydrogen bonds, not a lot of water can enter

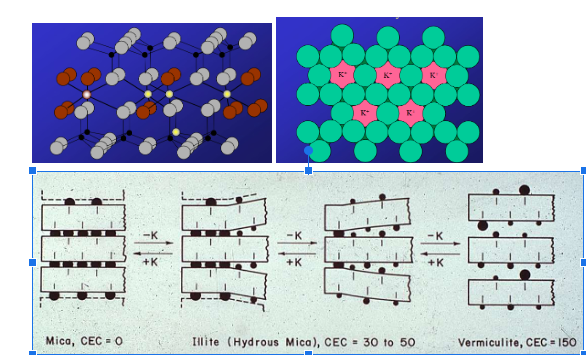
2:1 clay, illite? What does potassium do? surface area and shrink swell? What happens when potassium deteroiates and gets replaced by other cations? (vermiculite and smectite)
you have sillica, alunimum, sillica
in this structure, pockets are present where positively charged potassium can neutralize negative, and glue things together
so, this means theres also little shrink swell cause you have potassium glueing it together, and less surface area
when potassium deteroites it gets replaced by other cations that are in soluiton, have water in them, so sa increases, and water can go in and out creating a lot of shirnk and swell, so you have more negative charge because of more cations.
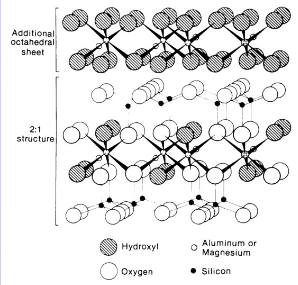
2:1:1 clay chlorite
silica aluminium sillica with extra octrahedral sheet on top making it small, little shrink swell
Cation Exchange Capacity-what does hydrogen do? Explain the CEC for Kaolinite, Illite, Vermiculite, and chlorite
negatively charged area (soil particle) always has cations around it, like cars parked in a parking spot
hydrogen will bump cations off, so that cations can be used for plant nutrients
CEC
Kaolinite is low because theres no isomorphic excahnge so no negative charge for cation, and no space for cations to sit
Illite has low CEC because its no space for cations and not too negative
vermeculite has high CEC because of the space in between for cations to go and more negative
chlororite has less space so less cec
explain how ph impacts cation exchange in clay vs organic?
on the ends of the clay layer structures you will have OH groups by itself. when ph increases, you reduce the amount of H, so you are only left with negative oxygens, which will increase cation exchange a little bit, because surface area is small
in organic matter, you have a much larger surface area, so a lot more negatively charged. so CEC increases a lot for organic, a little for clay
so its basically dependent on SA
How can we measure amount of cations coming in and out (measuring CEC)
So first, you flood negative area with a cation, for example sodium, so that all thr spaces in negatively charged space are filled with sodium
after, you add another caiton and see how many sodium come out of negative area.
Why does sodium have more dispersion in clay then calcium for example? (dont really need to focus on calcium, thats just an exampl). connect to champlain sea
sodium is surrounded by a lot of water that pushed clay plates apart
champlain sea has clay with a lot of sodium, so clays were really seperated. whenever you get a flood, all clay can dissolve creating bad effects of flooding, ccause the base of the houses and stuff just starts disperses.
What do we measure when we measure Ph? What are some ways to measure soil Ph? (name 2)
the negative log of Hydrogen, only hydrogen
Ph electrodes and coloured dyes
Sources of Soil Acidity-What is adding hydrogens to soils?
Natural:
decomposition
rainwater (interaction between carbonic acid and dioxide)
weathering of soil minerals
Anthropogenic sources-human activity
sulfer dioxide emissions of fertilizer create acid rain that creates more hydrogen-now there is legislation of fertilizers
Main issue with Acidic Soils? Major problems with basic soils
aluminum hydroxide gets reduced to just straight elemental aluminum which is toxic to soils. this reduces root elongation causes stubby roots
when ph reduces, calcium and magnesium is low, because they have been weathered out
Basic soil
availbility of nutrients, nutrients become less avialble
ammonia is in soil, can kill plants
nitrite is toxic to plants
CEC-What cations are present in the negative soil particles in ontario? think of cars in parking lot, what are the cars? there are 2 categories.
Acdic cations
H, AL3-
Base cations
ones that arent acidic like Ca, Mg
What relationship between base saturation and ph? What is buffer capacity, and how does CEC impact that. How to calculate base saturation, and what are the base cations?
when Ph lowers you have more hydrogens, so more hydrogens replace the base satuation, reducing the amount of bases present
buffer capacity is how much substance a soil can absrob before changing ph
something with a higher CEC has bigger buffer capacity because it can hold more hydrogen, so ph doesnt change as quickly as it would be in solution
base cations/total (Ca, K, Na, Mg)
Increasing soil Ph with Lime (for example calcite). Dolomite and carbonate have the same number of cations, so which will have a higher effect on ph? What factors (1) affect lime rate requirement?
when adding calcite to soil it reacts with water, releasing ant taking away hydrogens
dolomite weighs less, so it has a higher concentration and less mass so it has a greater effect on ph
Lime rate requirement
fine ground the soil is, more finely ground, more reactive
Soil Organic Matter? Which horizon is it mostly found? what is it main of? CEC is high? Related to that, why does Ph impact organic matter?
mostly found in Ah and Ap horizon
made of decoposed materials
as high CEC becuase it was a lot of negative sites bc of negatively charged particles (more parking lots for cars
when ph increases you lose hydrogen so it becomes a lot more negative, a larger CEC. because organic matter has a larger surface area then clays for example, these effects are a lot larget
Soil Organic Matter Capabilites- Capable of chelating metals (cheal-claw)
lets say iron is on its own in soil it wants to stick to CEC. but, it gets encapsulated by an organic material, and travels wherever the organic material goes, aka where water goes, so iron can now travel farther to plants that need its nutrients.
Transformaitons of carbon within a terrestrial ecosystem. What is the main aspect of this that impacts soils?
when plants and animals with carbon end up in soil, thats what we are interested in. over time the the materials will become more and more stabilize or takes longer to decompose.
Organic matter content of soil-rate of input vs rate of output. Why do tropics that have so much input, not have very organic soil?
how much organic matter is coming in vs leaving. the more you put in, the more thats gonna leave
because so much of their organic material is being decomposed so quick
What impacts the amount of organic matter created to soil in ontario? What impacts the amout of decompotisition in organic matter? Why do lower areas in field (it still has good drainage) have more soil organic matter?
more yield of crop, more organic matter because you have more residue
type of crop, when its planted can impact the organic matter.
Decomp
hotter, more decomp
more moisture helps decomp until field capacity, where after that the big pores start filling up, and theres not enough air to decompose it.
nature of material thats decomposable, some is more decomposable then other
neutral ph
more erosion, a level is gone where the organic matter is
Low lying areas
low lying areas have more water retention since extra water moves down, so more plants, more decomposition, more organic matter.
What are main types of organisms in SOM?
Heterotroughs-get energy from carbon from organic material
autotrophs(plants )-get energy from carbon from co2
Macrofauna (>2mm) -what do worms do?4 types. Microfauna, 2 types. Bacteria. Macroflora, Microflora
Macrofauna, >2mm
Vertebrates (groundhog)
Arthropods (insects)
Annelida (earthworms)
Burrowing will improve porosity
Improve aeration and water flow (preferential flow)
Mixing of organic matter
Mollusca (slugs and snails)
Microfauna
nematodes
Actinomycetes bacteria but fungal attributes
Bacteria like (single celled with no nuclear membrane) with Fungal attributes (netwrok of filaments)
Typically responsible for the soil smell
Bacterial
important for all soil organic processes
Macroflora (plants, mosses) autotrophs
Plants
Mosses
Microflora <0.2 mm
Algae
Blue green algae (cyanobacteria)
Contain chlorophyll
Some capable of fixing atmospheric N
Eutrophication
Autotrophic
Fungi
Decomposition and stabilization of soil structure
Mycorrhizae
Symbiosis that can improve
Plant nutrient uptake
Name some macronutrients (needed in large quantities) and micronutrients (needed in small quanitties). Whats special about selnium and how does that relate to a special characteristic of plant?
Macronutrient (needed in large quantities)
C, H, O
N, P, K
Ca, Mg, S (these are often called secondary nutrients)
Micronutrients (needed in small quantities)
Fe, Mn, Mo, B, Cu, Zn, Cl, Ni
Beneficial elements (Se, Si, Co, Na)
Something like selenium, as plant does not need BUT plants will take in ANYTHING in solution. Ultimately while plants do not require selenium, animals do and thus it gets used eventually.
plant can take up anything, even bad things.
Plant Nutrients: Uptake (Nitrogen)vs removal?
uptake is the nutrients plants are getting such as N in the form NH4 and convert to organic N
removal is when you harvest it, what nutrients are in the crop itself after it leaves the soil.
Take about the role of N,P,K in plants:
N
Chlorophyll formation
photosynthesis
amino acid and protieins
P
Energy transfer (ATP)
DNA, RNA
K
helps with movement of water in plant
stomata open and closing
translocation of carbohydrates
Nitrogen Cycling
(N2 fixation, lighting, haber, biological).
Decomp (once n2 is fixed it will be in parts of the plant, onece plant decomposes its locked in their bodies) -mineralization-immobilization
N2 from atmosphere is unusable by plants because the triple bond is very hard to break.
to break the bond, lighting strike can help N2 becomeNH3/NH4.
Haber process breaks N2 using a lot of heat and pressure to become ammonia and then goes through more pressure and CO2 to create fertilizer.
Some plants (legumes) create symbiotic relationship with bacteria that can break N2 bond. This only occurs in low oxygen environment, because the common enzyme in all legumes nitrogenase, gets destroyed bc of oxygen. but, there needs to be oxygen to break N2, so lehemoglobin is present and supplies small controlled amonts of oxygen so bacteria can still make enough energy to break N2.
Nitrogen Cycling Decomp (once n2 is fixed it will be in parts of the plant, onece plant decomposes its locked in their bodies)
Decomposition
Mineralization'-Decomp of OM by heterotrophic organisms to yield NH4, CO2, H20 AND other plant nutrients
Immobilization-if amount of N ingested from OM is less then microbes need, they will get N from soil (not locked in), so its still geting decomposed, but plant availble N is reduced.
Nitrogen Cycling Decomp minerlization-immobilization ratios. the first 2 ratios show that theres a lot less nitrogen to carbon then the ratio (1:8) that the microbes need, it doesnt seem like those 2 ratios are close together and it seem s that the microbes would ahve to much carbon
ok so basically,the amount of carbon nitrogen impacts if minerlization or immobilization will occur. if theres a lot of carbon the microbes will grow, but if theres not enough nitrgoen they will use the soil
C:N ration < 30:1 = mineralization
C:N ration > 35:1 = immobilization
C:N ration of soil microbes =~ 8:1
this is bascailly saying that the microbes are made of 8 parts carbon and 1 part nitrogen. if microbes eat something with a lot of carbon and nitrogen, they will poop out extra nitrogen. if theres not enough nitrogen, it will get it from soil thats already there.
but, the microbes use most of that carbon for respiration, then the ration becomes 9:1, which is pretty similar to 8:1.
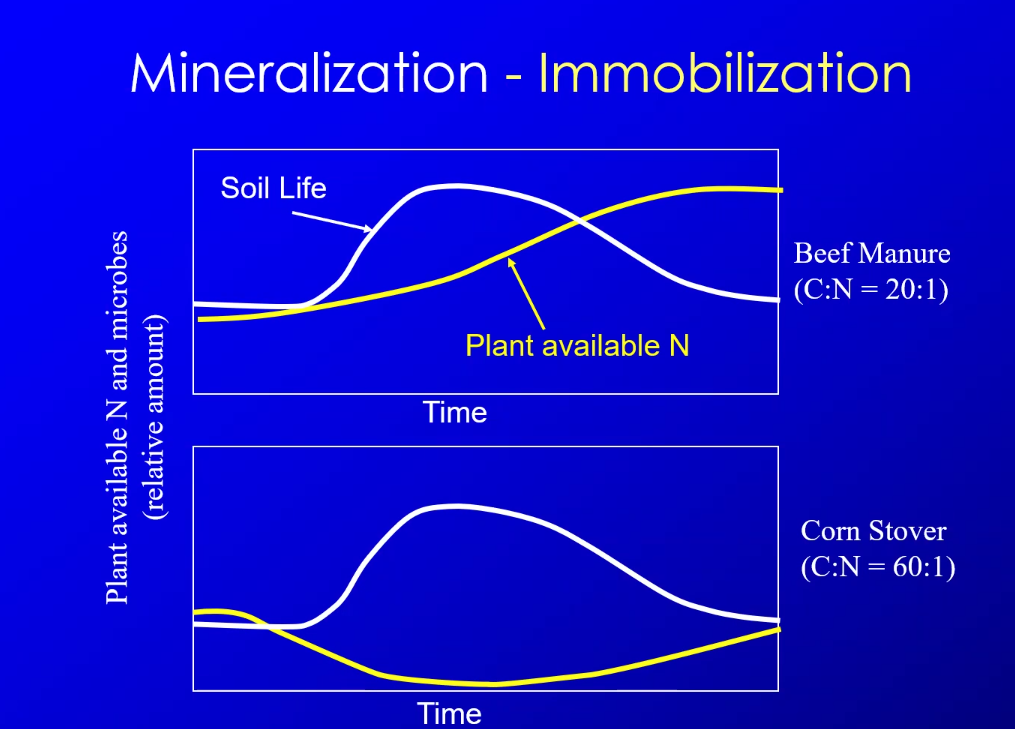
What is this saying?
for more carbon less nitrogen, microbes will use plant available ntrogen, which is why its down for corn compared to beef
Nitrification, write the 2 processes that are involved. What is the rate that effects nitrifcaition? (5). Once ot becomes NO3, its more readily available to be lost. Talk about leaching.
conversion of ammonium (NH4) to nitrate (NO2)
Effects Rate?
Temperature
you need ammonium and
you need oxygen
soil water content. Too much water not enough oxygen
soil ph-things can only exist in certain ph
Leaching
amount of nitrogen lost depends on how much nitroegne in soil, and the downward velcoty of water that carries nitrgoen

Blue baby syndrome (methemoglobinemia)
theres a lot of leaching, and nitrates in water that leach get coverted to nitrite which causes a lack of oxygen causing them to have issues
Denitrification (loss)-what enviornment does it need? how much oxygen. What factors affect the rate of denitrification? think about what bacteria needs to survive, and what leaching needs since its connected to this
NO3 converted to N2O gas by bacteria, it needs oxygen limited environments. this is because whern theres less oxygen other ions function as electron acceptors, which can be used to convert to gas. so you are loosing oxygen until you get to N2
factors
low oxygen
nitrogen
water for bacteria
carbon
temp and ph (same as leaching)
Ammonia Volatilization
where nitrogen is congerted to gaseous ammonia gas (NH3)
Why is low buffer soils important for ammonia volitilzation?
since low buffers dont have the protective features to protect from change. si they change into a gas quick
Environmental issues related to N. How to manage N to minimize leaching?
leaching to groundwater
emissions of N2O, a greenhouse gas
add N at rate time and place
What things are the same in nitrogen cycle and phosphorous cycle? whats difference
Same
minerlization, immobilization
Different
very small amount of phosphous leaves through leaching compared to nitrogen
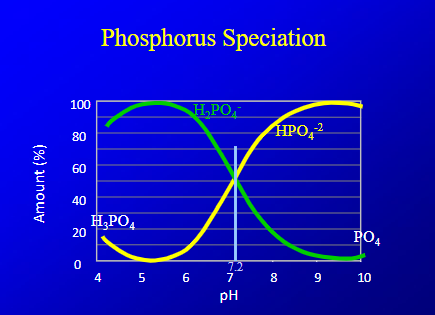
what does this chart show?
h2po4 has more hydrogen, lower ph more acidic, so most availbale amount of P
P mobility/immobility?
p that is locked in organic matter is converted into inorganic soluble form thats in soil.
P is converted into H2PO4, HPO4,
minerlaization is the process of microbes having a lot of phosphorous and pooping usable out creating H2PO4, HPO4, immobilization is when microbes take the good phosphourous
that H2PO4, HPO4, react with Ca Fe Al to produce insoluble precipitates, making it less availble for plants
So P does move down, but just very slowly.

Erosion in the P cycle?
P binds to soik particles, when soil moves O moves
Enviornmental issues with P
Algea blooms, p from soil gets eroded into lakes rivers, causes algae blooms
Can green farms continue to produce crops without phosphour fertilizer addtions?
no because you will have more losses then gains until no phosphour is present.

Potassium similarities?CAan you explain this?
mobilization, immobilization,
Potassium is in solution, it can become exchangable when its on negative clay like parking lot that can be exchanged, and then its in soil for something else. the fixed clay is that when its in soil its in between the layers so its hard to get out, so they cant access it right away. it leaches faster then P slower then N.
K fertilizer production
extract and purify potassium into KCL, then react it woth H2SO4 to make potasisum suphate, react with HNO3 to become KNO3
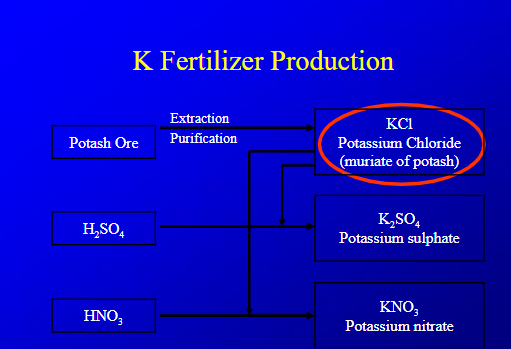
Environmental issues with K?
none except cost of extracting it
Defiency Symptoms of nitrogen (name effect of excess nitrogen) and phosphrous and potassium?
for nitrogen it would be yellowing. if theres too much nitrogen the plant woud tilt because theres so much nutrients
for phosphorous, the plant would be purple or green,
for potassium, the tips would dry and stalks would be weak
Upon completion of the soils course you are approached to work at Augusta (golf course)as the head greens keeper.
Your first task is to determine the fertilizer requirements for the fairways. The soil test results indicate a need for 50 kg P2O5 ha-1, 40 kg K2O ha-1 and a general recommendation indicates a need for 200 kg N ha-1. You have decided to apply the nutrients using a 20-10-10 fertilizer.
a) How much fertilizer do you need to apply to meet the needs of the turf-grass ?

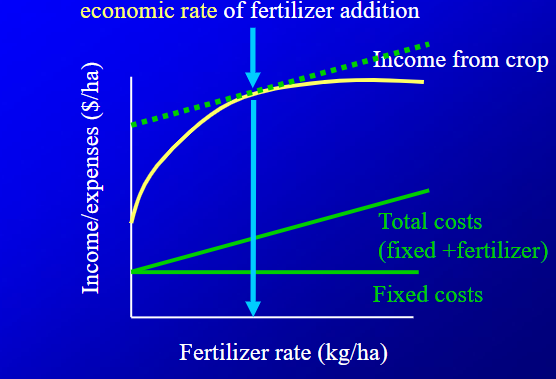
Explain what this graph is saying, and how to find out where the most income is made
its saying that for a nutrient defiicent crop that recieves a lot of nutirents will first go up a ton, but then will balance out eventually
to figure out where most income is made, you figure out where slopes of income from crop and total costs are the same.
Stock vs flow? Carrying capacity?
stock is non renewable, flow is non-renewable
carrying capacity is the max amount of resources that can be used before depeleting a source.
What do all forms of soil degredation result in? and what is the influence of soil degredation on carrying capacity, envrionemntal degredation, and costs?
all forms of soil degredation eventually lead to desertification, where soil cannot grow anything.
soil defredation decreases carrying capacity, because less resource can be used, the enviornment degreades, and costs increase to fix these issues.
soil degredation: Soil Erosion
the 4 erosion process. what kind of erosion occurs?
What are 4 factors that influence water erosion?
sheet vs gully formation
remedial measures of erosion? (try to name 3 main ones)
Wind erosion? what are the causes?the effect on horizons?
detachment-rainfall hits and soil falls apart
entrainment-sediment gets picked up
transport-sediment gets transported
deposit-sediment gets deposited.
Water erosion
slope
roots
rainfall
management
what soil is made of, some erode easier then others.
Sheet vs gully formaiton
sheet is a little bit of erosion everywhere
gully is a specific spot of erosion
Remedial measures of erosion?
adding crops after main crop season to protect soil
less tillage (less stirring of soil)
EC structuresss
reduce slope by figureing out how to plant crops better.
Winderosion
causes are high wind speed, finer particles, less water, less ground cover
it takes away the ah horizon
Soil degredation: Compaction, what are its effects and its management strategies?
loss of large pores, less aeration, less water infiltration
you can lower traffic and have more organic matter
Salinization? cause, imact, remdial measure. Acidificaiton, same thing
cause: becomes more salty, high salt contact. this causes plant to experience drought stress, and you can remediate this by improving drainage
Acidfication
cause is because of acid rain or fertilizers, it casuses toxicirt, and you can add lime to help