Unit 1 - Physical Growth and Development
1/437
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
438 Terms
What does status mean?
stage of maturity someone is at pre/post puberty
What are some examples of status?
physical size, maturation, performance levels
What does progress mean?
rate of development
What is an example of progress?
how fast a child grows in weight/height
Is rate of change constant or variable?
variable
When is rate of change crucial?
during development
What does comparison mean?
showing of data between others
What does prediction mean?
guessing something
What is an example of comparison?
height between peers
What is an example of prediction?
abnormalities
What does physical performance goals mean?
how realistic physical performance goals are
What does physical activity mean?
best age/time to train children
What are the 4 things that are relevant to growth/development?
status
progress
comparison/prediction
physical activity/performance
What are examples of practical applications?
maturity related behaviour
individual developmental readiness
response to performance pressures
sex differences
maturational considerations
skill development
safety issues
sensitive/critical periods
What does maturity related behaviour mean?
what the child’s stage looks like physically, psychologically, and socially
What is an example of maturity related behaviour?
a child that is 11 years old acts like a 6 year old
What does individual developmental readiness mean?
the child being prepared for whatever will come at their age
What is an example of individual developmental readiness?
a child born in January will be more prepared to start school than a child born in December
What does response to performance pressures mean?
how children respond to playing sports under certain bands/directions
What is an example of response to performance pressures?
not keeping score in a game for children under the age of 12 (focus on enjoyment)
What does sex difference mean?
the different abilities physically, psychologically, and socially between sexes
What is an example of sex differences?
girls hit puberty before boys do
What does bio banding mean?
having a maturity band instead of a biological band
What type of advantage does bio banding have?
theoretical
What does maturational considerations mean?
keeping children in a similar group even with different maturity levels
What does skill development mean?
timing and sequences of teaching in components
What does safety/liability issues mean?
making sure there is physically and environmentally a good spot for children to experience activities
What is an example of safety issues?
maintaining contact/violence before a certain age
What does sensitive/critical periods mean?
things that need to happen at a specific age or there will be consequences later
What is an example of a critical period?
learning stages
When can bone mass be grown?
during the growing period
Does bone always grow throughout life?
no
Does the rate of bone growth increase or decrease with time?
decrease
Is bone maintained after the growing period?
yes
What are common research challenges with children?
ethical
methodological issues
variability
generalizability
What is an example of ethical challenges?
needing consent for invasive techniques
What are examples of methodological issues?
different maturation stages
different body sizes (specifically muscle)
different attention spans than adults
What is an example of generalizability?
difficulty to make conclusions with different ages/genders
What some examples of variability?
all children are different
needing more child testing to come to conclusions
What are the 2 types of study designs?
cross sectional
longitudinal
What is cross sectional study design?
comparing 2 or more group
What is an advantage of cross sectional studies?
efficient and not costly
What is a disadvantage of cross sectional studies?
cannot see genetic differences
What is longitudinal study design?
a study over a long period of time
What is an advantage of longitudinal studies?
can see change over time and reduces variability
What is a disadvantage of longitudinal studies?
costly and not very efficient, also potential dropouts from study
What are plastic processes of development?
nutrition
childhood disease
physical activity
environmental stress
What does ‘plastic’ mean?
the ability to change
Does everyone have the same reaction to plastic processes?
no
Why does everyone react differently to plastic processes?
biological variation due to everyone’s individual genes
What do factors interact with
genes
What are 2 things that a part of development?
growth and maturation
What type of aspect is growth?
physical
What type of aspect is maturation?
functional
What age is prenatal?
conception to birth
What age is infancy?
birth to 2 years
What age is childhood?
2 years to 12 years
What age is adolescence for females?
11 years to 18 years
What age is adolescence for males?
13 years to 18 years
What age is adulthood?
over 18 years
What age group goes through puberty?
adolescence
What age group are children clinically?
under 18 years
What age group are children medically?
before puberty
What does hyperplasia mean?
increase in cell number
What does hypertrophy mean?
increase in cell size
What does accretion mean?
increase in intercellular substance (mainly with bone growth)
When does hyperplasia mainly occur?
early in development (prenatal/infancy)
When does hypertrophy mainly occur?
after hyperplasia
What is the distance curve?
change in height over age
What is the velocity curve?
change in rate of height over age
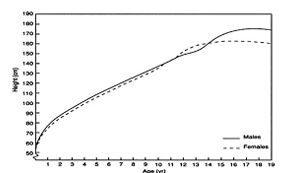
What is this a photo of?
distance curve
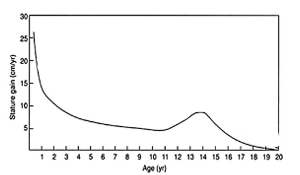
What is this a photo of?
velocity curve
What is developed within the first 2 weeks of prenatal?
egg
What is developed between weeks 2-8 of prenatal?
embryo
What is developed between weeks 9-40 of prenatal?
fetus
What happens during the egg stage?
cell division and differentiation
What happens during the embryo stage?
cell number and differentiation
What happens during the fetus stage?
cell size and mass
During which prenatal stage are organ systems formed but not functional?
embryo
During which prenatal stage are organ systems formed and functional?
fetus
Is fetal growth linear?
no
When does mass increase in pregnancy?
late in pregnancy
Are proportion changes immediate?
no
What is the major change in the fetus?
head
What sex is more active in the fetus?
male
How long does it take the heart to develop?
4 weeks
How long does it take the limbs to develop?
6-9 weeks
How long does it take reflexes to develop?
36 weeks
What can affect fetal activity?
motherly environment
What is a strong indicator of newborn and maternal health?
birth weight
What happens when there is a low birth weight?
increased risk of diseases
What happens when there is low physical activity as a child?
it decreases even more throughout adulthood
What does alcohol affect prenatally?
nervous system
What factors affect prenatal growth and development?
nutrition
smoking
alcohol
sex
caffeine
recreational drugs
What affects exercise capability?
gestational and post natal undernutrition
What does smoking affect in a baby?
size and cognitive activity
What does SES stand for?
socioeconomic stress
How much physical activity is recommended when pregnant?
more than 150 minutes
What is the difference from pre and post natal growth?
final size
rate of growth
Are growth rates the same between all individuals?
no