Lecture 5 v2
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Most recent version
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
When did sex with meiosis evolve in MRCA of all Eukaryotes?
1.5 bya
What is isogamy? Is it ancestral or derived?
A form of sexual reproduction where gametes are equal in size and morphology
ancestral/primitive
What is anisogamy? Is it ancestral or derived?
A derived reproductive system in which gametes differ in size—small, mobile sperm and large, nutrient-rich eggs.
derived
Which is ancestral—isogamy or anisogamy?
Isogamy is ancestral.
Which is derived—isogamy or anisogamy?
Anisogamy is derived.
What are dioecious or gonochoric species?
Species with distinct male and female individuals that produce anisogamous gametes.
What are monoecious or hermaphroditic species?
Species where individual bodies produce both types of anisogamous gametes.
What is reproductive investment?
The total physiological and energetic cost of producing gametes, finding mates, and providing parental care.
How does reproductive investment differ between sexes?
emales usually invest more per offspring; males often invest less, increasing variation in mating success.
What is Bateman’s Principle?
Males are limited by the number of mates, females by their fecundity (ability to produce and care for young).
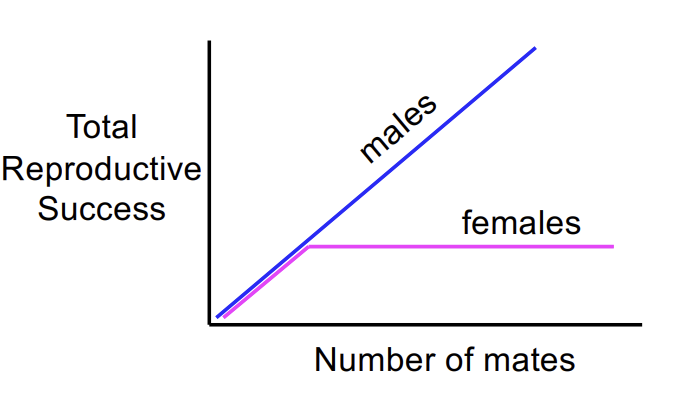
What does Bateman’s Principle predict about selection intensity?
Greater reproductive variance among males drives stronger sexual selection on males.
What are the four properties necessary for natural selection?
Variation in a trait
heritability
Variation in survival and fecundity
Correlation between survival and fecundity and the trait
What are the four properties necessary for sexual selection?
Variation in the trait
Heritability
Variation in mating/fertilization success
Correlation between the trait and mating/fertilization success
What is the outcome of sexual selection?
Evolution of secondary sexual characteristics.
According to Darwin, is sexual selection a subset of natural selection?
No—Darwin treated sexual selection as a separate evolutionary mechanism.
What are the five evolutionary mechanisms recognized in Bio 1040?
Mutation
Migration
Genetic Drift
Natural Selection
Sexual Selection
How does the modern definition of fitness differ from Darwin’s?
Modern fitness combines survival, fecundity, and mating success; Darwin’s referred only to survival and fecundity.
What is intrasexual selection?
Competition within one sex for control over mating or fertilization opportunities.
What traits often evolve under intrasexual selection?
Armaments and mechanisms of control (e.g., antlers, tusks, large body size).
What is an example of female-female intrasexual selection?
Wattled Jacanas—females compete for territories and mates and have spurs on their wings.
What is sperm competition?
Competition between sperm from different males to fertilize the same female’s eggs.
Can sperm competition occur in plants?
Yes, through pollen tube competition in the style.
What is intersexual selection?
Mate choice—selection by one sex for display traits in the other.
What traits evolve under intersexual selection?
Ornaments, songs, colors, and other display traits.
Who first described sexual selection by mate choice in detail?
Charles Darwin in The Descent of Man (1871).
What language did Darwin use to describe mate choice?
The language of aesthetics—"taste for the beautiful."
What was Alfred Russel Wallace’s critique of Darwin’s theory?
He argued ornamentation must correlate with health and vigor, not pure beauty.
What is the Darwinian (or Fisherian) view of mate choice?
Traits and preferences coevolve due to attraction—beauty itself drives selection (“arbitrary” choice).
What is the Wallacean (or adaptive) view of mate choice?
Ornaments evolve as indicators of good health or genes.
What is the Handicap Principle (Zahavi)?
Costly traits serve as honest signals of quality since only the fittest can afford them.
What are direct benefits in mate choice?
Immediate advantages such as food, territory, or parental care.
What are indirect benefits in mate choice?
Genetic advantages like “good genes” passed to offspring.
What is genetic covariance in mate choice?
When the trait and the preference for that trait become genetically correlated.
What is the line of equilibria in Fisherian models?
The trajectory along which trait and preference coevolve without natural selection constraints.
What does coevolution mean in sexual selection?
Reciprocal evolutionary change between traits in different sexes or species.
What is decadence in evolutionary terms?
When sexual selection decreases overall survival or fecundity but persists through preference feedback.
Why can decadence lead to extinction?
There is no inherent mechanism to stop the escalation of maladaptive traits.
What example illustrates sexual decadence?
Extreme ornamentation that lowers survival (e.g., overly large tail feathers).
Why did Darwin separate sexual from natural selection?
Because they can act in opposite directions—survival vs. attractiveness.
What is sexual conflict?
Divergence in evolutionary interests between males and females.
Over what can sexual conflict occur?
Mating frequency, partner choice, number of offspring, and parental investment.
What is sexual coercion?
Use of force or intimidation to increase fertilization probability.
In ducks, what drives sexual conflict?
Males attempt forced copulations; females resist to maintain mate choice.
How do female ducks resist forced copulation?
They evolve vaginal morphologies like clockwise spirals and blind pouches.
What is antagonistic coevolution?
Reciprocal adaptation and counteradaptation between sexes (e.g., genital arms races).
What is the effectiveness of female genital barriers in ducks?
Around 92–95% effective at preventing forced fertilization.
What is sexual autonomy?
The capacity to pursue mating preferences without coercion or threat.
Does sexual autonomy mean freedom from competition?
No—it means freedom from coercion, not from choice or competition.
How does sexual autonomy evolve?
Through mate choice and as a response to sexual coercion.
What species illustrate sexual autonomy through aesthetics?
Bowerbirds—females choose males based on artistic displays.
What is aesthetic remodeling?
Evolution of traits that enhance sexual autonomy or reduce coercion through mate choice.
How can aesthetic preferences promote diversity?
Freedom of choice fosters beauty and variation in traits.
What is an example of aesthetic remodeling in birds?
Blue Manakin cooperative courtship displays—social network structure predicts success.
What phrase summarizes aesthetic remodeling in manakins?
“Bromance before Romance.”
What does the “aesthetic view of life” emphasize?
Evolution is shaped by beauty and subjective choice, not only adaptation.
What is aesthetic deweaponization?
Reduction of coercive traits due to sexual autonomy and preference for nonviolent partners.
What is eugenics in evolutionary history?
A racist ideology using evolutionary theory to claim superiority of certain races.
How was “fitness” redefined during the eugenics era?
To merge sexual selection within natural selection for eugenic research purposes.
How can adopting a Darwinian definition of sexual selection help modern biology?
It separates evolutionary biology from eugenic conceptual origins.
What is the difference between secondary sexual and primary sexual traits?
Secondary traits aid in attraction or competition; primary traits involve reproductive organs.
Why is sexual selection a key driver of biodiversity?
It produces elaborate ornaments, behaviors, and coevolved preferences.
How do sexual and natural selection interact?
Adaptive mate choice links survival traits with attractiveness, but they can also conflict.
What is the evolutionary significance of pleasure in mate choice?
Pleasure reflects aesthetic agency—organisms seek experiences that reinforce selection for beauty.