Nerves: Structure/Classification/Regeneration of nerve axons
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the structure of nerves?
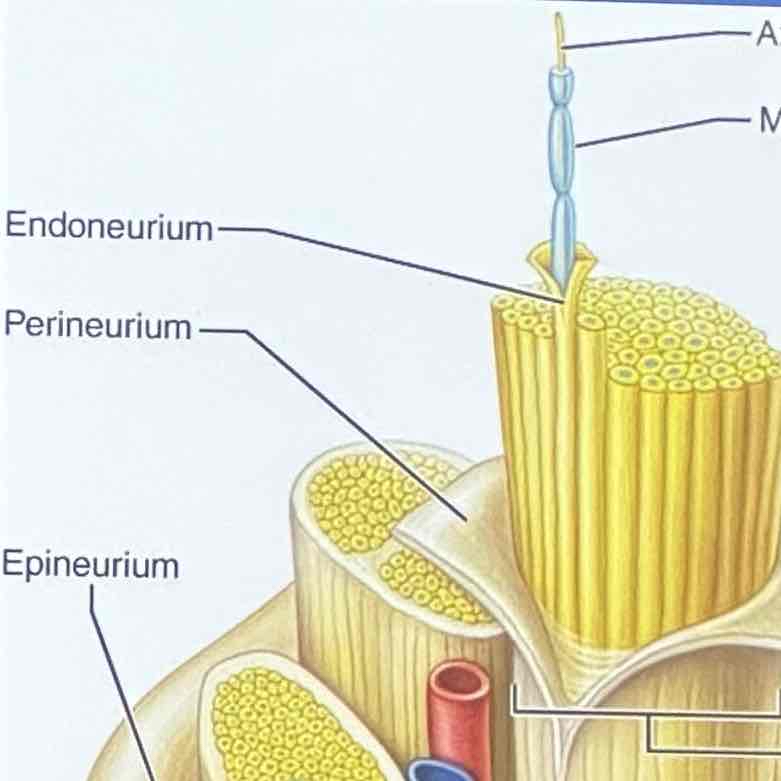
bundles of axons in the PNS encases within connective tissue wrappings
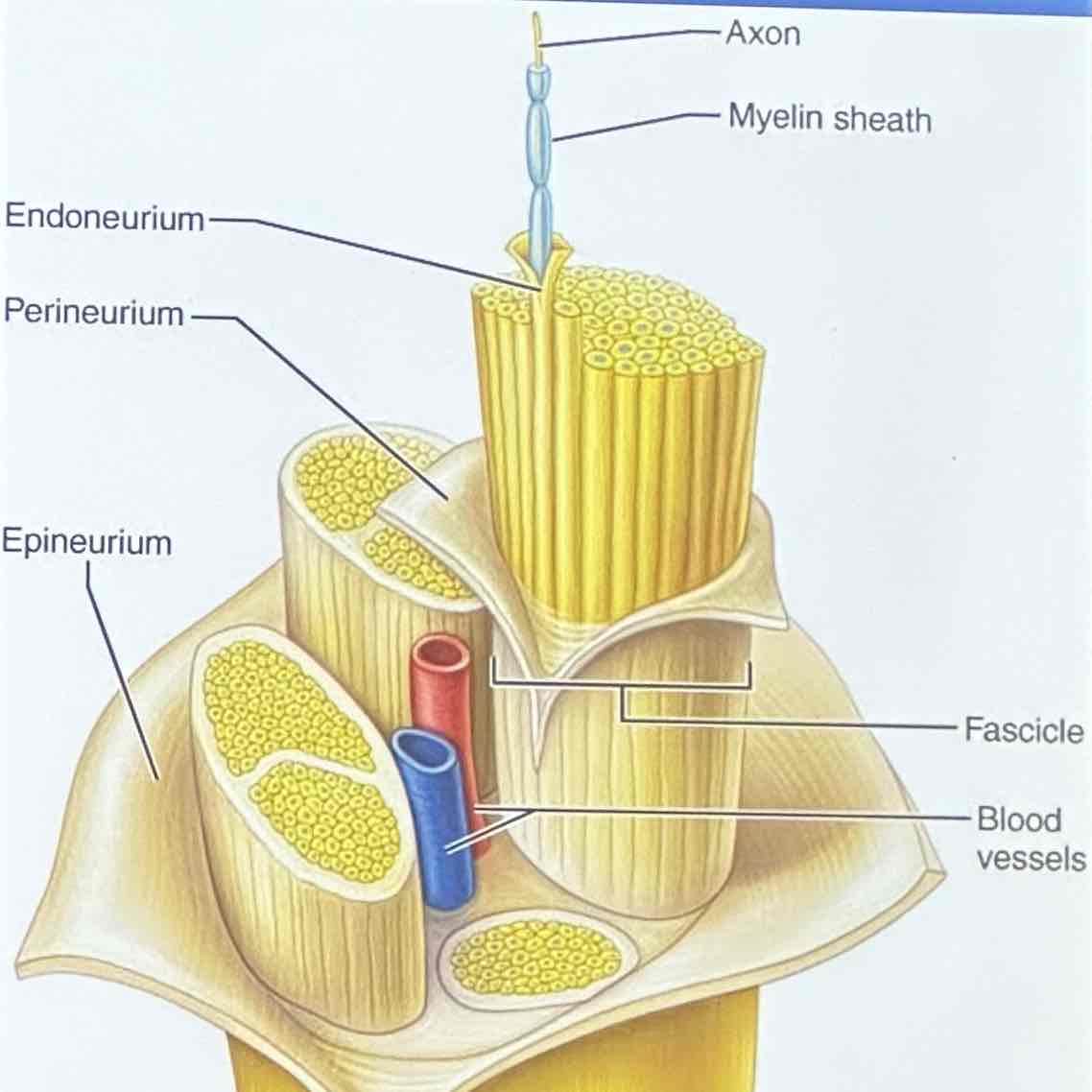
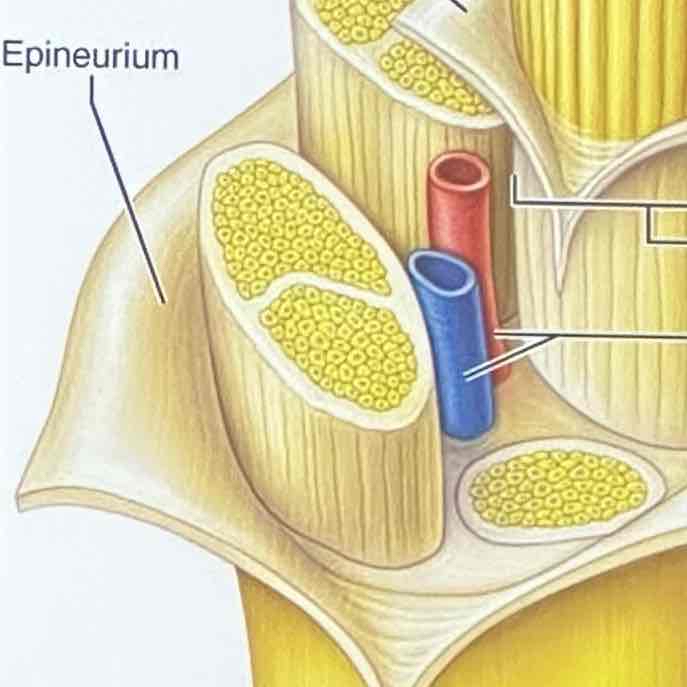
Structure: Epineurium
encloses fascicles that form the nerve
Structure: Perineurium
binds group of axons into bundles called fascicles
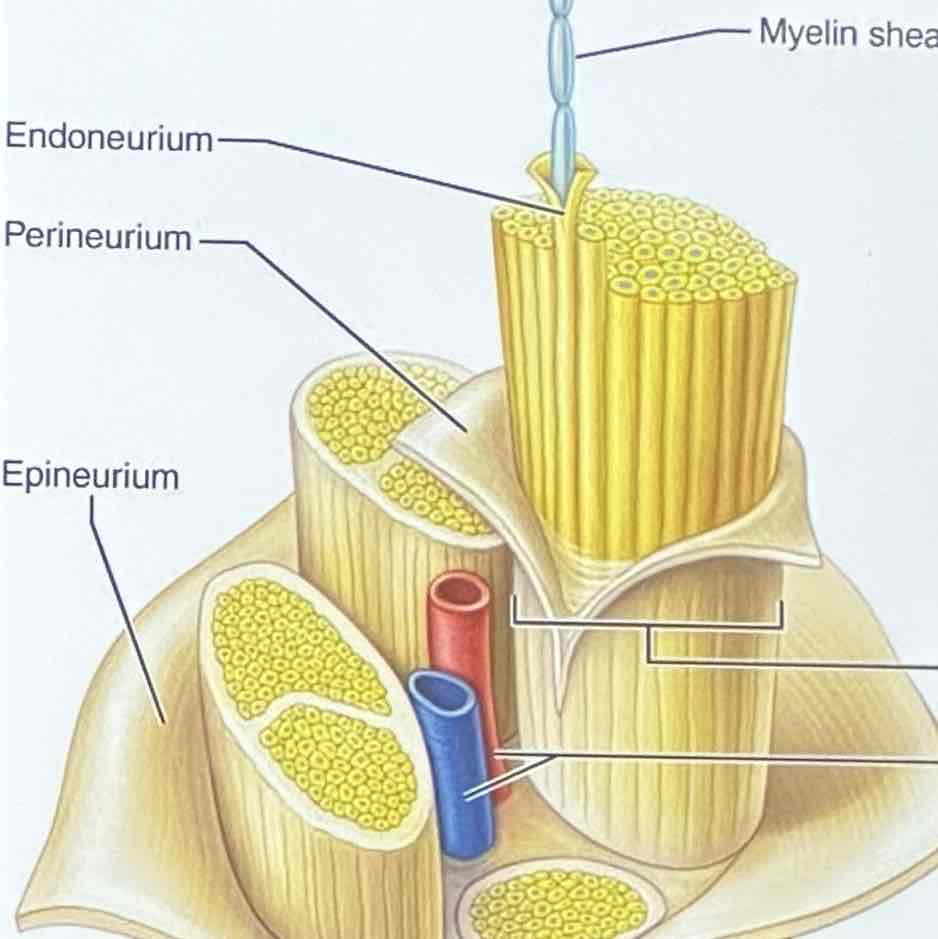
Structure: Endoneurium
encloses fibers associated with Schwann cells
Classification based on origin: Cranial nerves
originate from the brain
Classification based on origin: Spinal nerves
originate from the spinal cord
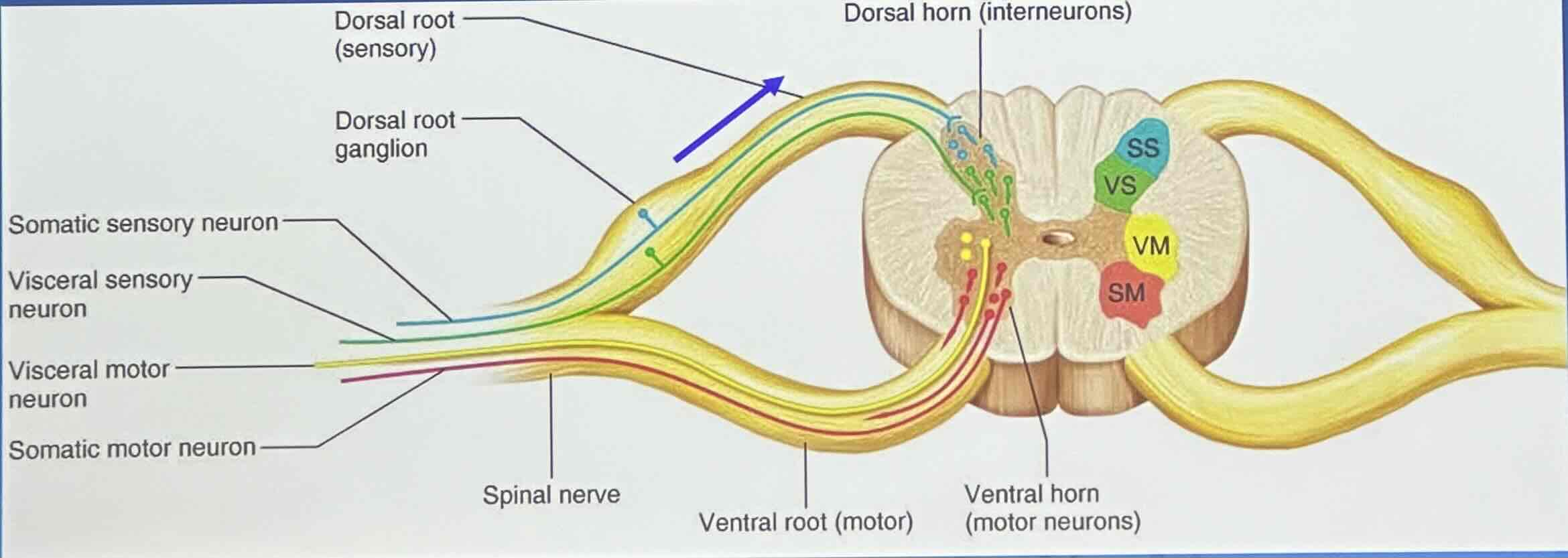
(C) Direction of impulse conduction: Sensory (afferent) nerves
conduct impulses toward the CNS
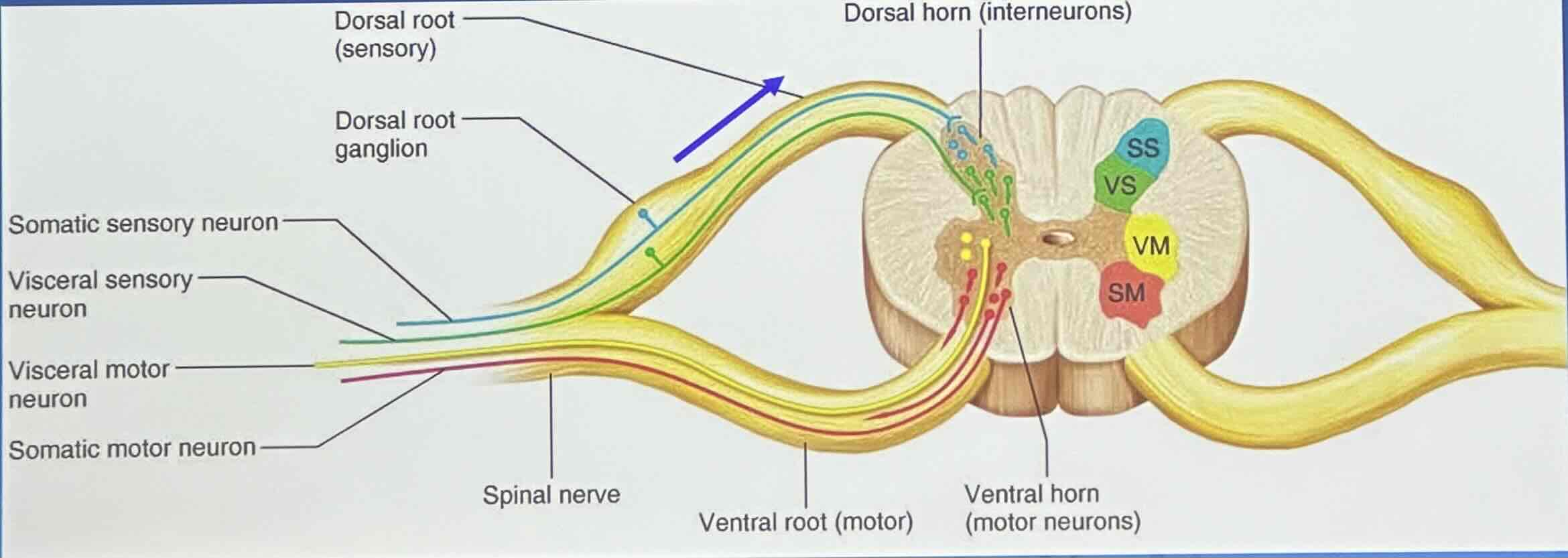
(C) Direction of impulse conduction: Motor (efferent) nerves
conduct impulses away from the CNS
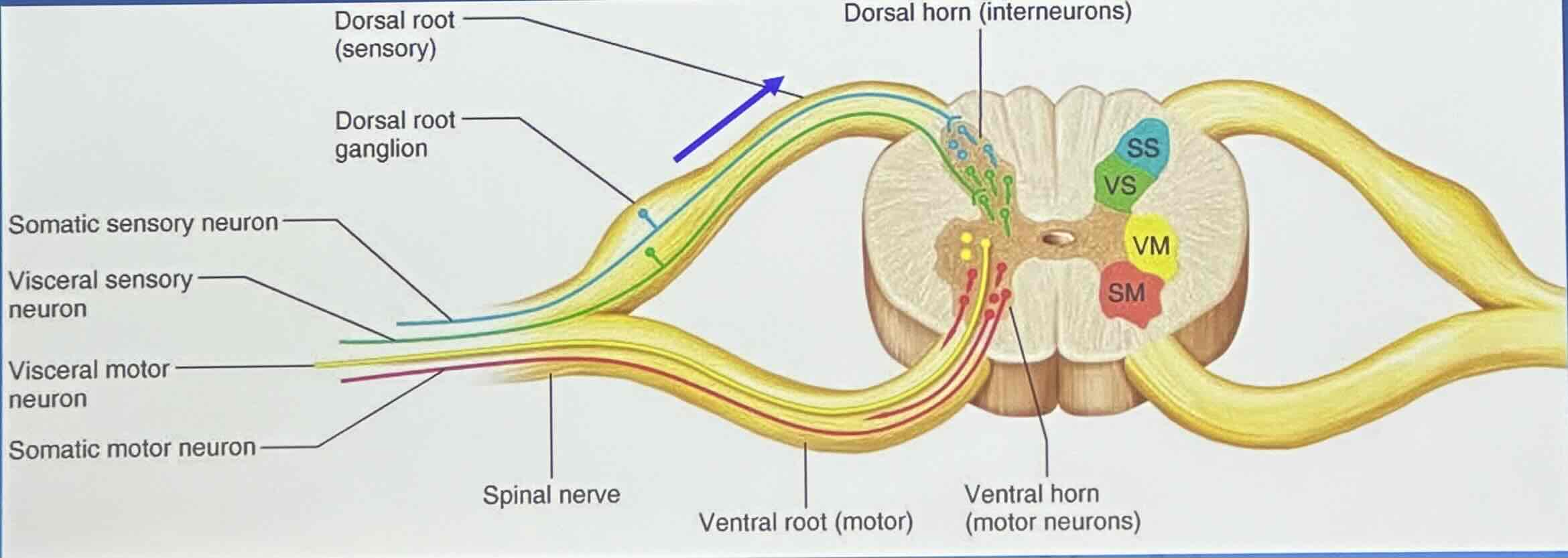
(C) Direction of impulse conduction: Mixed nerves contain both ____ and ____ fibers
afferent and efferent
Most/All cranial nerves are mixed
MOST cranial nerves are mixed
Most/All spinal nerves are mixed
ALL spinal nerves are mixed
Regeneration of nerve axons: CNS
Damaged CNS axons CANNOT regenerate (oligodendrocytes suppress axon regeneration)
What suppresses axon regeneration in the CNS?
oligodendrocytes
Regeneration of nerve axons: PNS
Damaged PNS axons can regenerate, but ONLY if body remains intact
When is the only case the PNS axons can regenerate?
IF the body remains intact
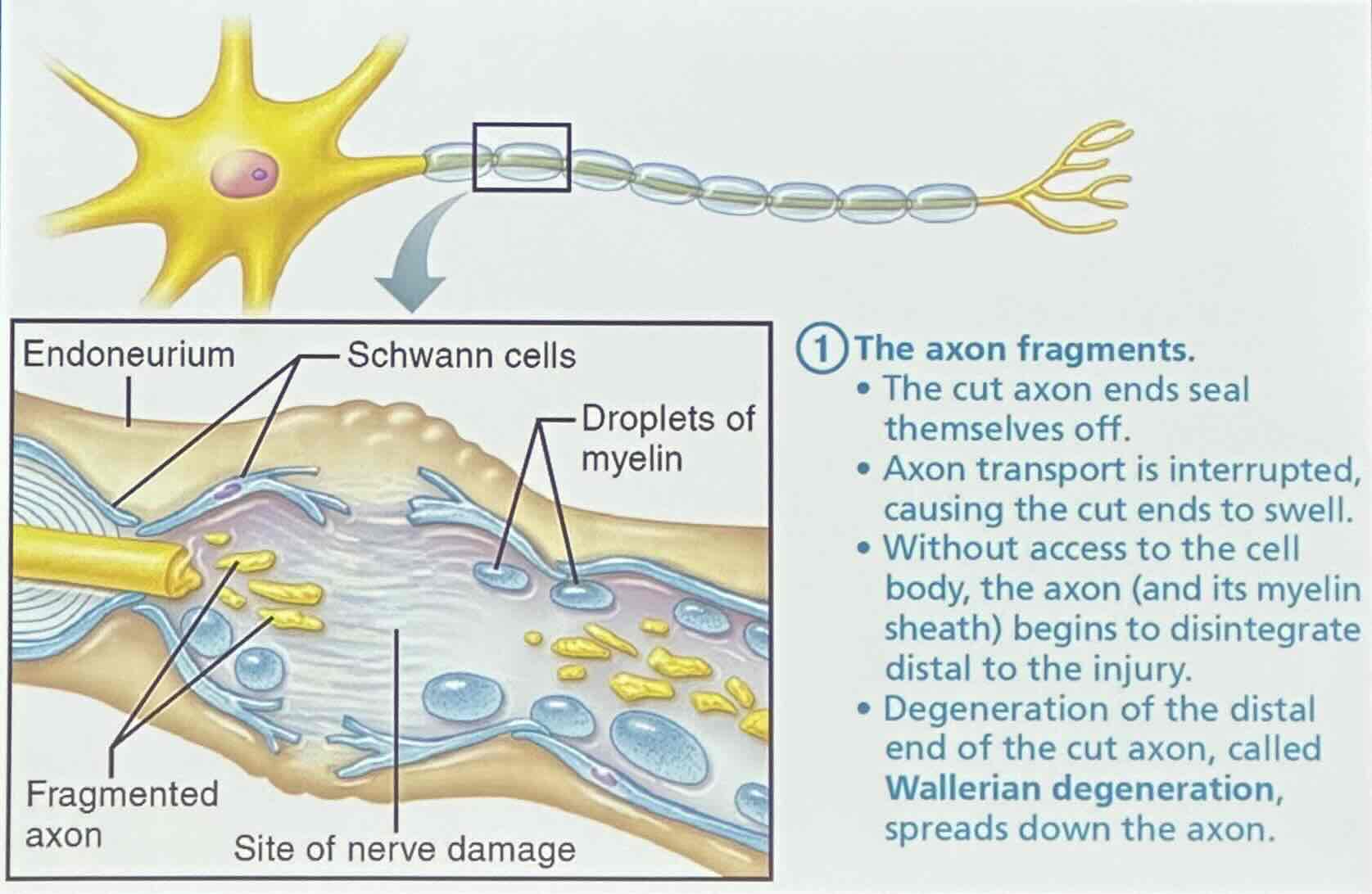
Regeneration of nerve axons: Step 1
The axon fragments
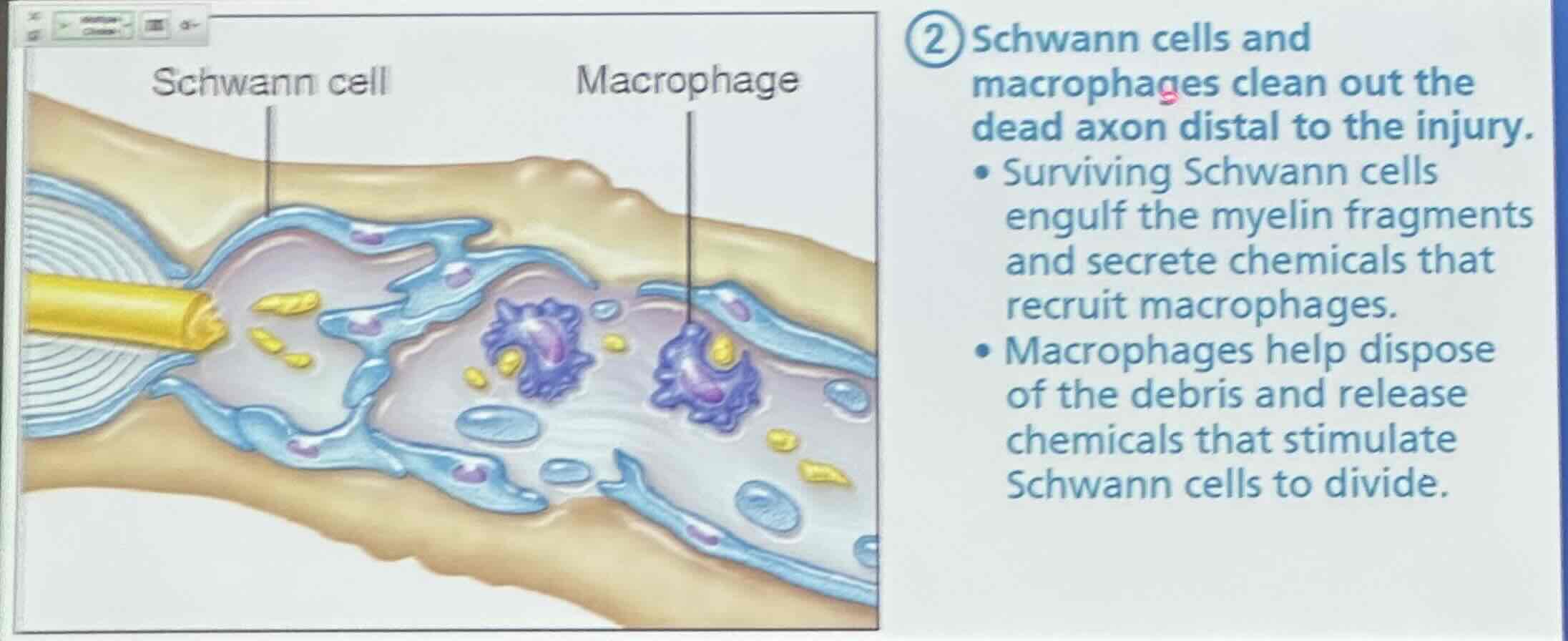
Regeneration of nerve axons: Step 2
Schwann cells and macrophages clean out the dead axon distal to the injury
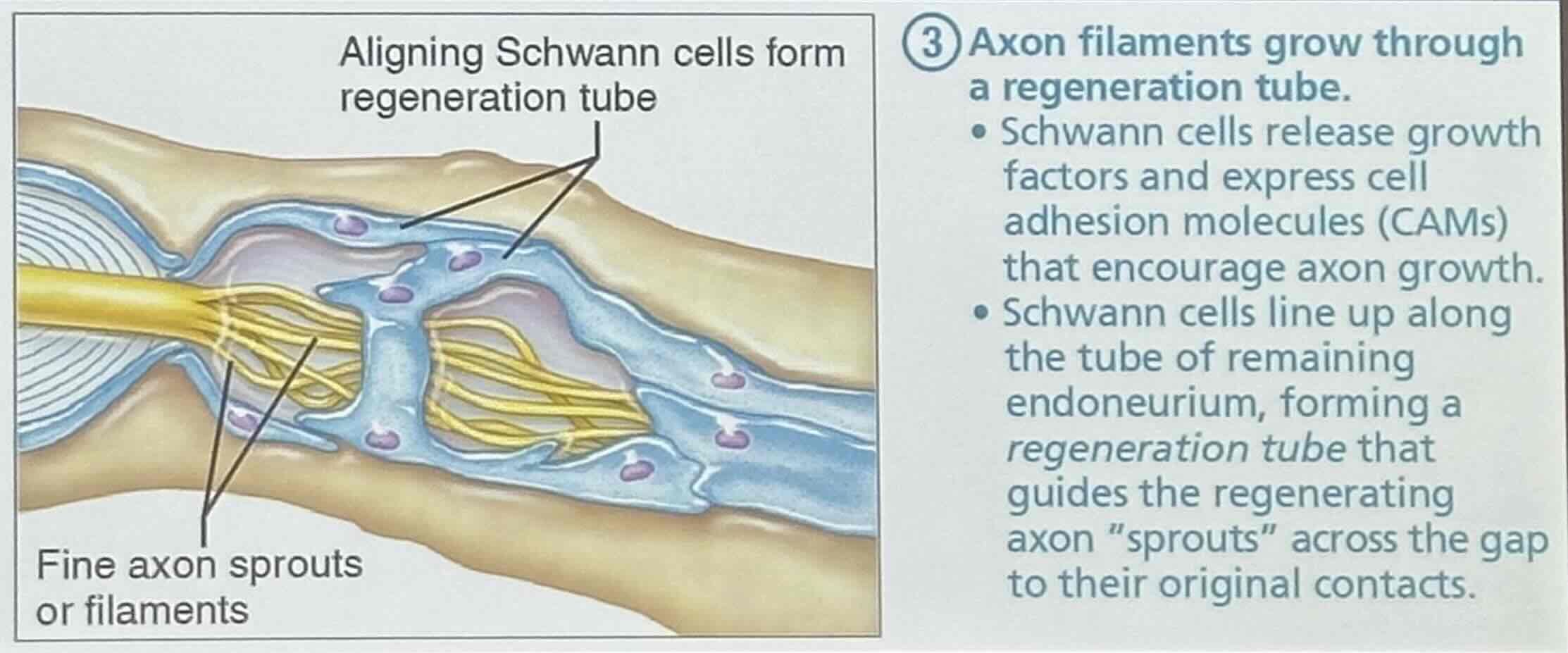
Regeneration of nerve axons: Step 3
Axon filaments grow through a regeneration tube
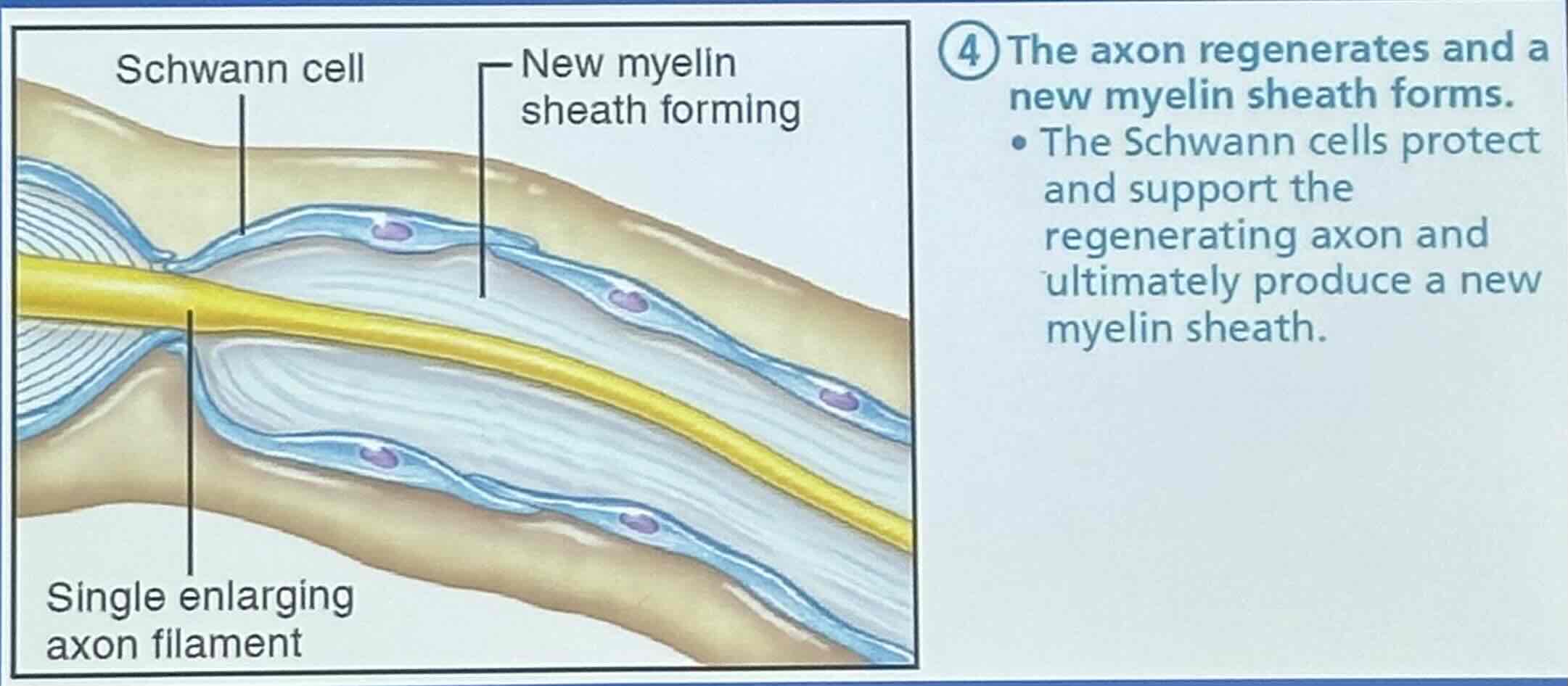
Regeneration of nerve axons: Step 4
The axon regenerates, and a new myelin sheath forms