Psychology Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/133
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:06 AM on 1/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
3
New cards
What is psychology?
the scientific study of behavior and mental processes
4
New cards
What is the Scientific Method? Why would you use it?
A process for completing an experiment to collect and interpret data
5
New cards
What is the first step of the scientific method?
Form a question
6
New cards
What is the second step of the scientific method?
Form a hypothesis
7
New cards
What is the third step of the scientific method?
Test the hypothesis
8
New cards
What is the fourth step of the scientific method?
Analyze results
9
New cards
What is the fifth step of the scientific method?
conclusion
10
New cards
What is the sixth step of the scientific method?
replication
11
New cards
What is the last step in the scientific method?
New questions
12
New cards
Humanistic Perspective
**Humans need to self "actualize" and become the best we can be. People want to be helpful.**
Mr Jones has a low self esteem because he doesn't measure up to the smartest and richest people, so he is angry.
Mr Jones has a low self esteem because he doesn't measure up to the smartest and richest people, so he is angry.
13
New cards
Biological Perspective
**Behavior is the result of brain and nerve impulses, hormones and genetics**
Mr. Jones is a loud-mouthed, mean-spirited person. His children are too (genetic inheritance)
Mr. Jones is a loud-mouthed, mean-spirited person. His children are too (genetic inheritance)
14
New cards
Psychoanalytical Perspective
**Believe behavior is influenced by unconscious drives and childhood events**
The man was frustrated with his job, then that night he has a dream about quitting.
The man was frustrated with his job, then that night he has a dream about quitting.
15
New cards
Cognitive Perspective
**A psychological approach that emphasizes mental processes in perception, memory, language, problem solving, and what we think about ourselves affects our values**
One person said the same thing to two different people and they each took it a different way.
One person said the same thing to two different people and they each took it a different way.
16
New cards
Sigmund Freud
Psychoanalyst whose work focused on the unconscious causes of behavior and personality formation; founded psychoanalysis.
17
New cards
Alfred Adler
Psychoanalyst who introduced concept of "inferiority complex" and stressed the importance of birth order, realized that everyone felt inferior and everyone wanted to gain a feeling of belonging
18
New cards
BF Skinner
Learning Perspective, Operant Conditioning, decided peoples behaviors are trained through punishment and reward
19
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
Learning Perspective, discovered classical conditioning; trained dogs to salivate at the ringing of a bell
20
New cards
Carl Rogers
Humanistic Psychologist, we see an ideal persona and if we feel that we are like them then we feel good, if we don't feel like we are similar to them then we don't feel good
21
New cards
Abraham Maslow
Humanistic psychologist known for his "Hierarchy of Needs" and the concept of "self-actualization", people always wanna be better
22
New cards
John B. Watson
Behaviorist who was known for his Little Albert study (Would clang metal bars when albert saw something soft so he would be afraid of them)
23
New cards
Behavioral Perspective
Human behavior is caused by environmental conditions
24
New cards
Carl Jung
Psychoanalyst who was known for founding analytical psychology
25
New cards
Eric Erickson
Psychosocial, he believed you went through 8 stages from infancy to death
26
New cards
Piaget
Came up with the famous theory of cognitive development which explain how a child thinks and functions as they grow
27
New cards
Kohlberg
Believed in Moral Development, it said that people work through different stages of moral development and that is why they make certain decisions
28
New cards
Pie graph
used for percentages
29
New cards
Bar graph
used for comparing different things
30
New cards
Line graph
show one thing over time
31
New cards
Testing Method
giving your subjects psychological tests
32
New cards
Case Study
**an in depth look at one person or a small group** \n ^^Strengths- an in depth look at 1 person or small groups^^ \n ==Weaknesses- What you find out may not apply to anyone else, easy to get a close relationship==
33
New cards
Longitudinal Method
**take a small group of people and watch them for months/years** \n ^^Strengths- can get really in depth^^ \n ==Weaknesses- people quit or die before it is over==
34
New cards
Cross Sectional Method
**study people at different ages** \n ^^Strengths-Shorter and cheaper^^ \n ==Weaknesses- different experiences and abilities==
35
New cards
Natural Observation
**try to study people in their natural environment** \n ^^Strengths- tend to get a more "real" observation^^ \n ==Weaknesses- You can't control the conditions==
36
New cards
Laboratory Observation
**you study things in a controlled environment** \n ^^Strengths- You can control the conditions^^ \n ==Weaknesses- May affect behaviors==
37
New cards
Independent Variable
the factor that is changed by the researcher to determine the effect of change
38
New cards
Dependent Variable
change resulting from application of the independent variable
39
New cards
Control Group
doesn't receive independent variable, used for comparing how independent variables change the situation
40
New cards
Controlled Experiment
an experiment that uses an control group
41
New cards
Single Blind Study
do experiments on different groups and they don't know if they are the control group or the experiment group
42
New cards
Double Blind Study
neither the experimental group nor the observers know who is getting what so the observers cannot bias the experiment
43
New cards
What was the point of the Hawthorne experiment?
The effect of rest periods, workdays, and work weeks on productivity
44
New cards
What did we learn from the Hawthorne Experiment?
People perform better when they are being watched
\
\
45
New cards
Mean (central tendency)
average score
46
New cards
Median
the middle score
47
New cards
mode
most frequent score
48
New cards
Correlation
^^Positive-as one thing goes up/down so does the other^^ \n ==Negative- as one thing goes up/down another does opposite==
49
New cards
Ethics
standards for proper and responsible behavior
50
New cards
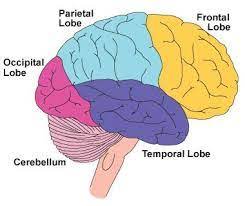
Occipital Lobe
back of the head, visual area
51
New cards
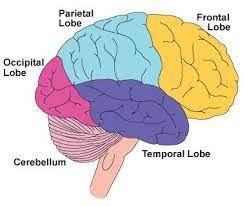
Temporal Lobe
On the side and below your ears, controls hearing
52
New cards
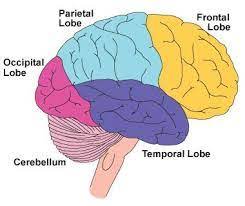
Parietal Lobe
Top rear of your head, handles skin senses
53
New cards
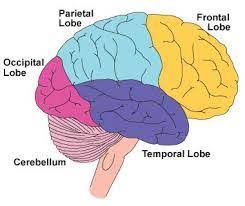
Frontal Lobe
behind the forehead, solves problems, makes plans, and makes decisions
54
New cards
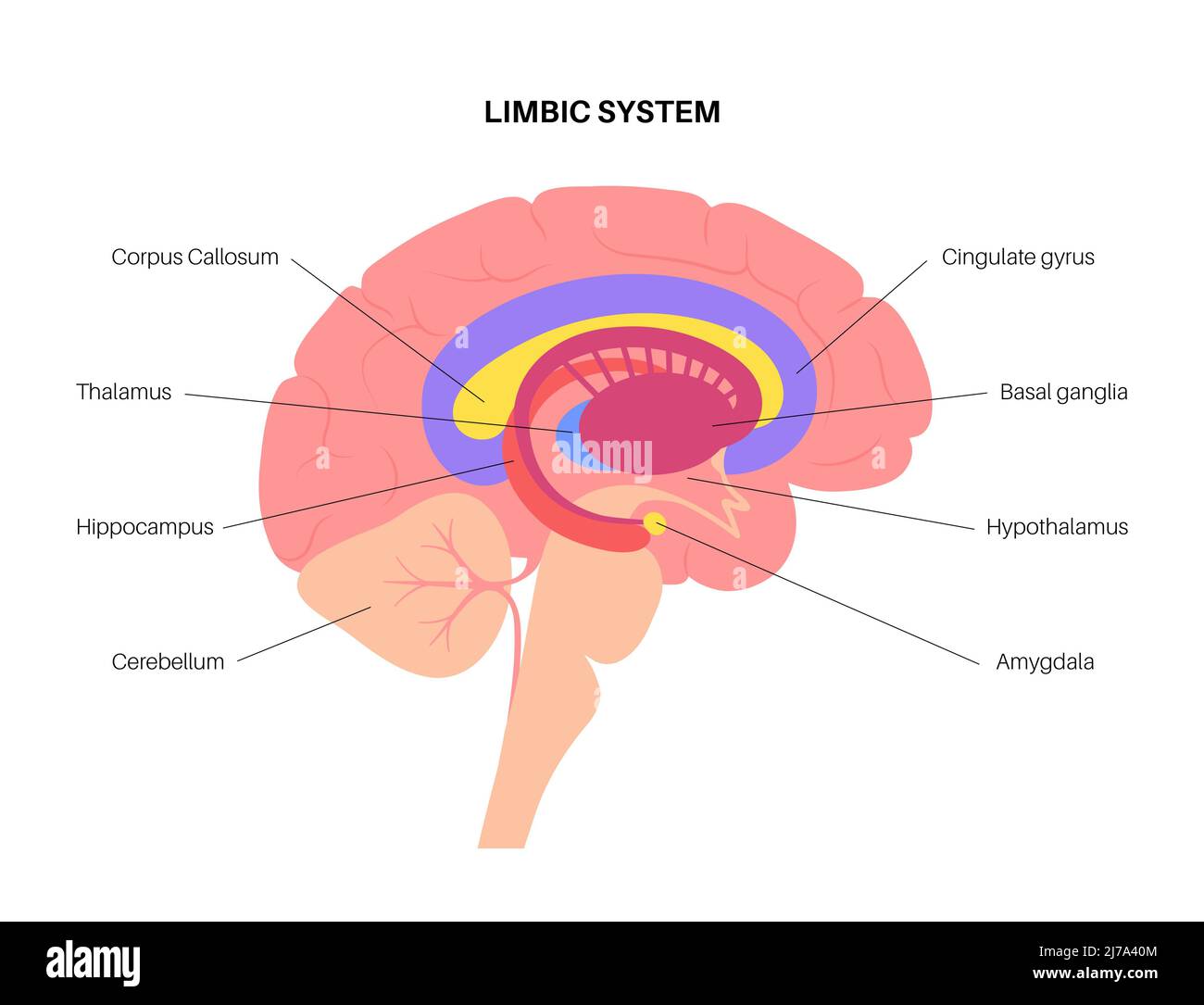
Thalamus
(Forebrain) a critical structure because it relays sensory information to the appropriate places
55
New cards
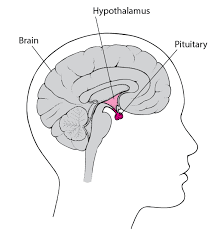
Hypothalamus
(Forebrain)below the thalamus (tiny). It regulates body temperature, stores nutrients, controls motivation and emotion. For example hunger, thirst, sexual behavior, caring for offspring, and aggression. Disturbances lead to unusual behaviors.
56
New cards
Pituitary Gland
sends out hormones including growth hormones which greatly affects children and pregnancy hormones
57
New cards
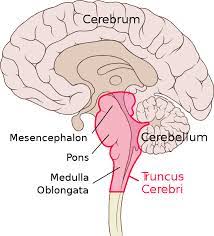
Brainstem
Controls things such as breathing, consciousness, blood pressure, heart rate, and sleep
58
New cards
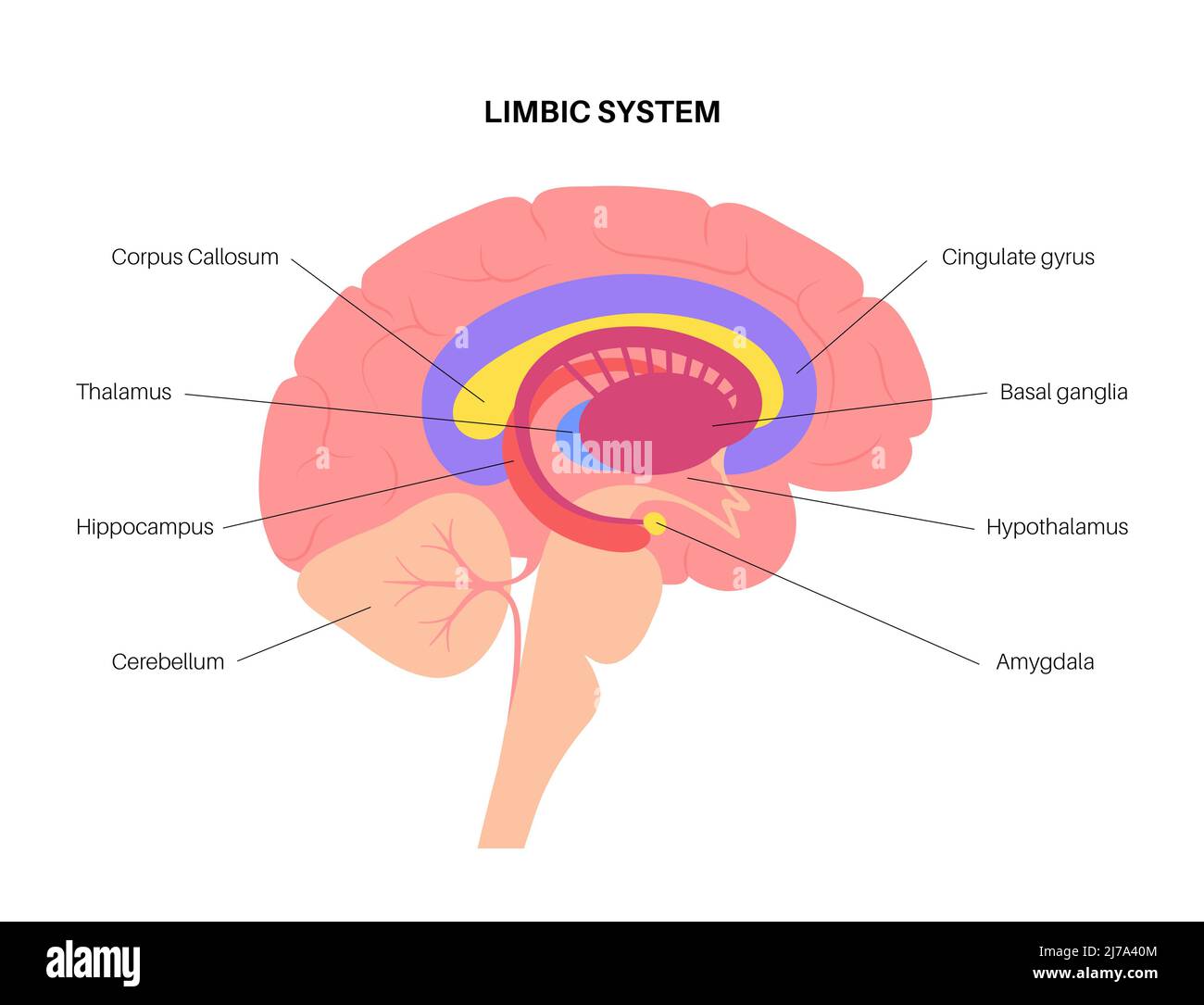
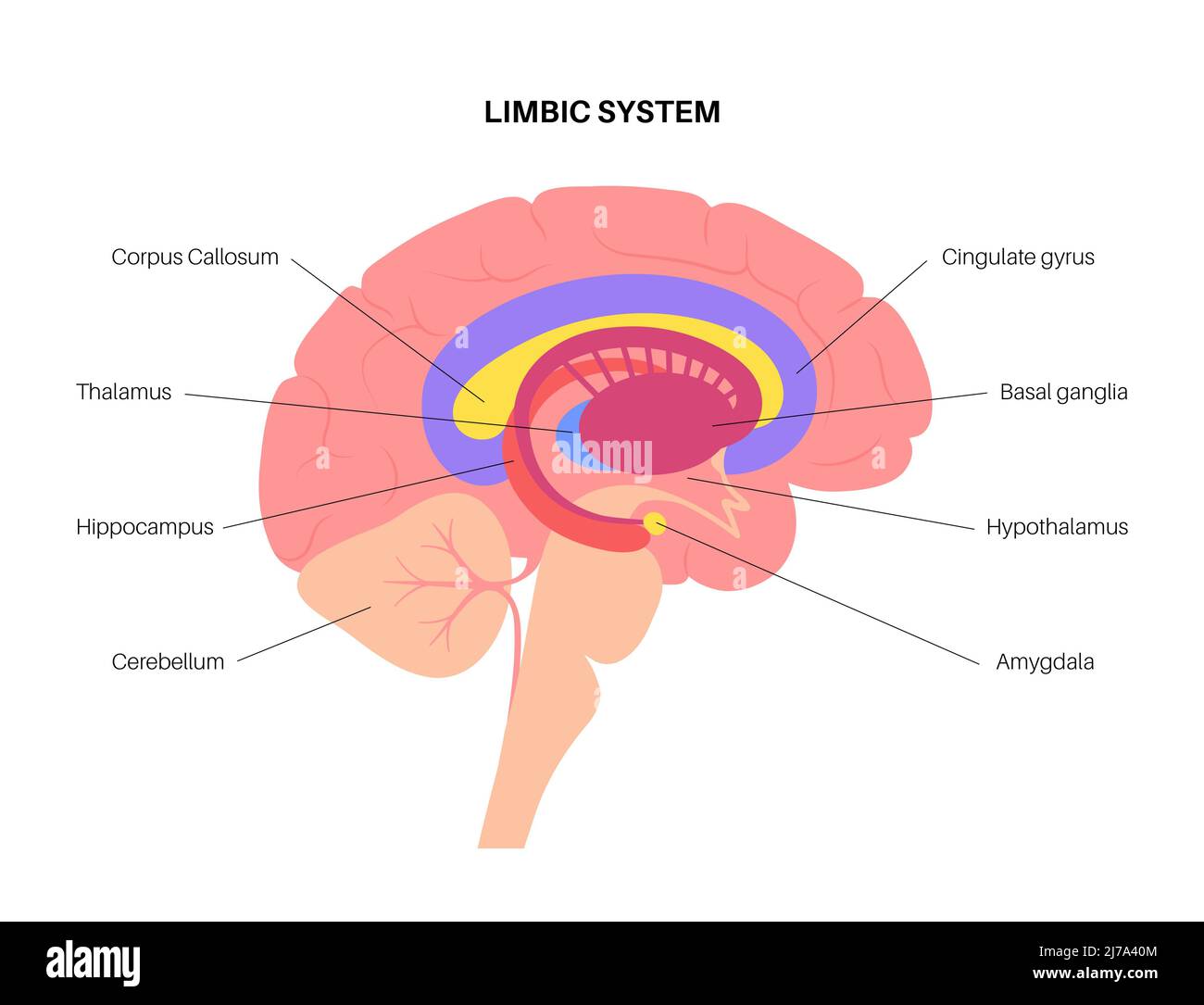
Cerebellum
(Hindbrain) takes care of balance and coordination
59
New cards
Corpus Callosum
a broad transverse nerve tract connecting the two cerebral hemispheres, aids the transfer of information
60
New cards
What does your "right brain" do?
creativity and artistic ability
61
New cards
What does your "left brain" do?
logic and problem solving
62
New cards
For right handed people language is based in the ______ hemisphere
Left
63
New cards
What glands produce chemicals?
Endocrine Glands
64
New cards
Stage 1 of sleep
lightest sleep, pulse slows down, brain waves slow, 30-40 mins, feels like you never slept
65
New cards
Stage 2 of sleep
Deeper version of Stage 1, lasts 15-30 mins
66
New cards
Stage 3 of Sleep
Deeper sleep yet 15-30mins
67
New cards
Stage 4 of sleep
Deepest sleep, very difficult to wake up, 30-40 mins
68
New cards
REM (rapid eye movement)
Occurs in stage 1 during second cycle, most vivid dreams, 50-80% of sleep time for babies, lack of REM results in behavioral changes
69
New cards
Hypnosis
A trance, deep state of relaxation, not everyone can be hypnotized
70
New cards
Meditiation
**narrowing of consciousness and focus on a small repetitive visual stimuli or sound** \n benefits-helps relax, less anxiety, lower blood pressure
71
New cards
Altered States of Consciousness
happens when one's sense of the world changes usually through sleep, drugs, meditation or hypnosis
72
New cards
3 Kinds of memory
Episodic, Semantic, and Implicit
73
New cards
Onset sleep (very first stage)
Pulse slows, temperature drops etc.
74
New cards
Episodic Memory
memory of a specific event or experience (flashbulb memories)
75
New cards
Semantic Memory
general knowledge that we remember but we don’t know exactly when we learned it (george washington was the 1st president)
76
New cards
Implicit
skills you can do like riding a bike
77
New cards
Encoding
the translation of information into a form in which it can be stored (remembering through a picture, sound)
78
New cards
Storage
Second process of memory, maintains encoded information over time (repeating information over and over again, relating information to something you already know, or filing system)
79
New cards
Retrieval
locating stored information and returning it to conscious thought (you remember something if you are in the place the memory happened, you remember details if you are in the same emotional state as you were when the memory occurred, tip of your tongue)
80
New cards
What are the three stages of memory?
==Sensory memory- useful info goes to short term memory, not useful information goes to trash==
^^Short-term Memory- 7-8 items at a time, we tend to remember first and last things in a series, useful info is stored into groups, non useful goes into trash^^
Long term Memory- Items categorized by common characteristics, no limit on how much can be stored
^^Short-term Memory- 7-8 items at a time, we tend to remember first and last things in a series, useful info is stored into groups, non useful goes into trash^^
Long term Memory- Items categorized by common characteristics, no limit on how much can be stored
81
New cards
Echoic Memory-
traces of things we have heard
82
New cards
Eidetic Imagery-
photographic memory. Super ironic memory. 5% of children have it. Fades with age
83
New cards
Iconic Memory
A snapshot or mental picture of something we saw
84
New cards
Primacy effect
we tend to remember the first few things in a series
85
New cards
Recency effect
we tend to remember the last items in a series
86
New cards
Chunking
organization of items into familiar or manageable units
87
New cards
Interference
is when new information pushes old information out of short term memory
88
New cards
Forgetting
Forgetting can occur during any of the 3 memory tasks
89
New cards
3 Memory Tasks-
Recognition-Identifying objects or events that have been encountered before
^^Recall- to bring something out of storage without seeing it^^
==Relearn- you can relearn things you once knew but forgot very quickly==
^^Recall- to bring something out of storage without seeing it^^
==Relearn- you can relearn things you once knew but forgot very quickly==
90
New cards
3 kinds of forgetting-
==Decay-a memory fades away if it isn’t used==
^^Repression- we forget painful memories (it helps us cope)^^
Amnesia- we forget what happened before age 3, forget trauma
^^Repression- we forget painful memories (it helps us cope)^^
Amnesia- we forget what happened before age 3, forget trauma
91
New cards
Learning
A change in behavior as a result of an experience
92
New cards
Who is Pavlov, and what did he do?
Psychologist who would train dogs to salivate at the sound of a bell through classical conditioning
93
New cards
What are the principles of classical conditioning?
Unconditioned Stimulus, Unconditioned Response, Conditioned Stimulus, and Conditioned Response
94
New cards
In Pavlov's Experiment what is the Unconditioned Stimulus?
Meat Powder
95
New cards
In Pavlov's Experiment what is the Unconditioned Response?
Dog drooling
96
New cards
In Pavlov's Experiment what is the conditioned stimulus?
Ringing of a Bell
97
New cards
In Pavlov's Experiment what is the conditioned response?
Dog drooling
98
New cards
Generalization
Responding to two or more stimuli in the same way
Ex: The dogs in Pavlov's experiment will drool at the sound of bells with high or low tones
Ex: The dogs in Pavlov's experiment will drool at the sound of bells with high or low tones
99
New cards
Extinction
The response to a conditioned stimulus weakens overtime after the unconditioned stimulus is removed
Ex: If a child is throwing a fit in the store and the parent doesn't give in, the child will most likely stop doing that
Ex: If a child is throwing a fit in the store and the parent doesn't give in, the child will most likely stop doing that
100
New cards
What is spontaneous recovery?
Revival of an response after a time of extinction
Ex: If pavlov stopped ringing the bell for his dog, then continued to ring the bell in a few days, they would still drool
Ex: If pavlov stopped ringing the bell for his dog, then continued to ring the bell in a few days, they would still drool