Kines 162 Exam 1 Terms & Definitions for Physics
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Goals of Physics in Sport and Exercise
Performance improvement
technique improvement
equipment improvement
technique improvement
injury prevention and rehabilitation
Kinematics
Deals with the description of motion without considering the forces that cause motion.
Kinetics
Deals with the relationship between the motion of bodies and the forces acting upon them
length & distance
describes space in which movement occur
describes position of player, or how far they ran
Basic SI Units
Length = meter
Time = Sec
Mass = kilograms
Scalar
Magnitude only
mass, volume, density, distance & speed
Vector
magnitude & direction, orientation, point of application
displacement
force
velocity & acceleration
Time
Highly valuable metric in sports, exercise, physical activity, research
basic aspect for motion
Mass & Inertia
inertia is the property of an object to resist change in its motion
mass is the measurement of inertia
1 inch =
2.45 cm = 0.00254 m
1 foot =
30.48 cm = 0.3048 m
1 yard =
0.9144 m
1 mile =
1.609 km
1 cm =
10 mm
1 m =
100 cm
1000 m =
1 km
Qualitive
non numerical description
direct observation
Quantitive
numerical result
data from motion capture
reference system
necessary to specify position of the body, segment, or object so as to describe motion or identify whether any motion has occurred
linear kinematics variables
position refers to location of object in space relative to a reference system
distance refers to total path traveled
displacement refers to shortest path between start and end point
average vs instantaneous
change in time over certain distance, versus distinct value at specific point in time and space
stride length - stride rate relationship
at specific velocities stride lenght stops increasing
Position - velocity - acceleration
graphical representation/illustration
relationship of the tangential slope at each data point
dirivative
rate at which a value changes with respect to another value
components of projectile motion
any object that is thrown or projected into the air
they follow a curved path
horizontal motion
motion that is parallel to the ground
Vertical motion
any projectile thrown straight up in the air
has no forward motion
projectile motion in sport
time of flight, peak height, horizontal displacement
relative angle
included angle between two segments
absolute angle
angular orientation of a body segment with respect to a fixed line of reference
right hand rule
determines direction of rotations in terms of positive or negative
thumbs up positive
thumb down negative
planes and axes of motion
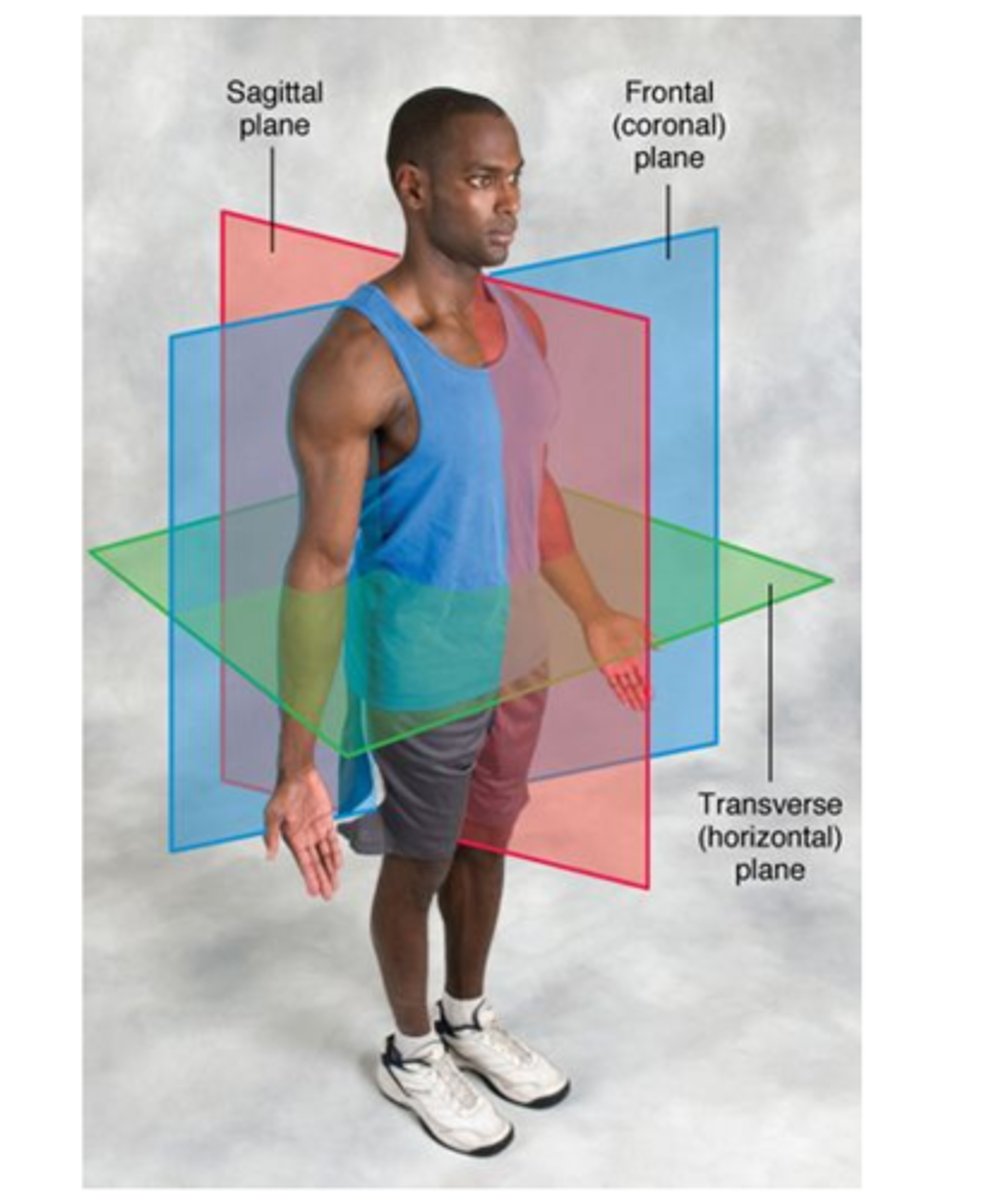
angular to linear relationship
angular motion of shoulder and wrist for softball swing
linear motion of the arm and the ball it hit.
3 main measurements
length/distance, time, mass/inertia