Lec 05: Assessment of Pain
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
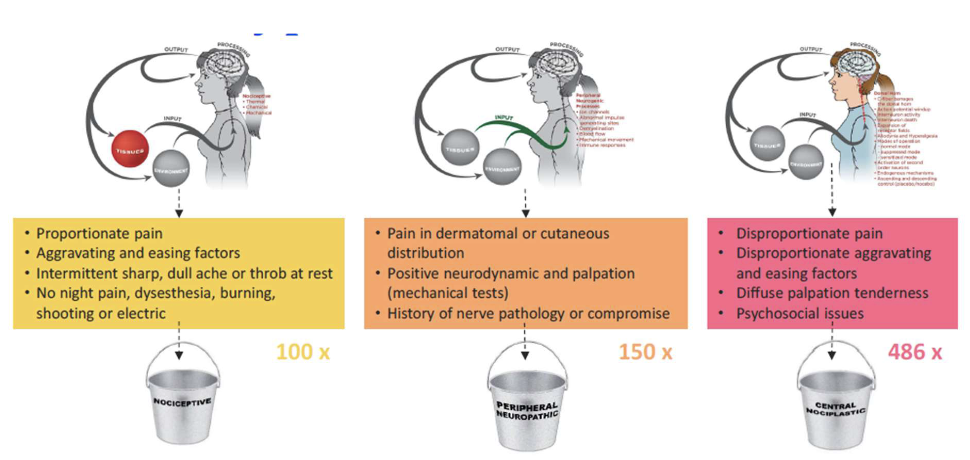
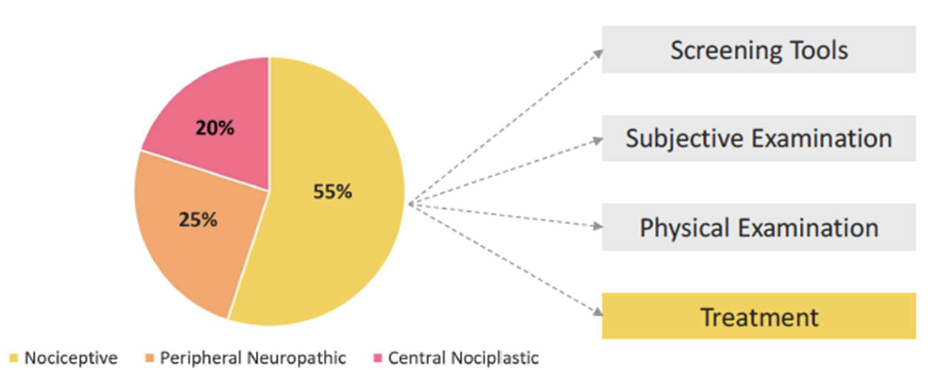
Pain Mechanisms – Review
Should drive ALL clinical decisions, tests and interventions
Pain Mechanisms
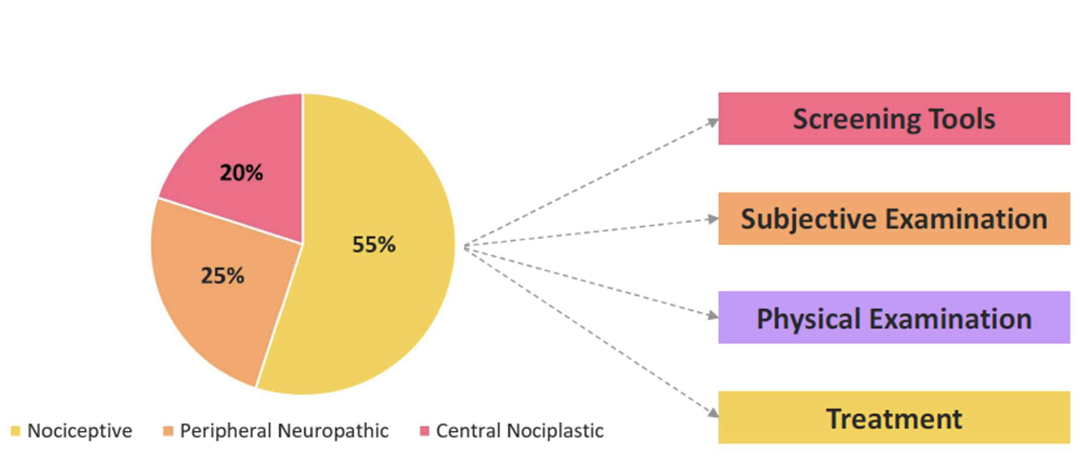
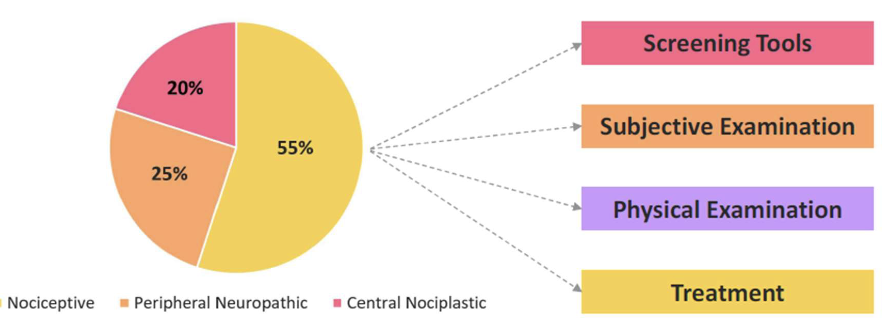
Step 1 - Screening Tools
Screen for Red Flags
– Review of systems
– Medical intake form
– Review of medical record
• Is the patient appropriate for PT?
OR
• Referral to another medical provider
Patient Safety
• Demographic info
• Insurance info
• Medical intake form
• Review of systems
• Pain Rating (VAS, Numeric)
• Fear Avoidance
– Fear Avoidance Belief Questionnaire
– Tamps Scale of Kinesiophobia
• Depression - PHQ
• Pain Catastrophizing Scale
Patient Screening
what are screening tools - pain scales?
face pain scale
numerical pain rating scale (NPRS)
visual analog scale (VAS)
McGill Pain Questionnaire
Central Sensitization Inventory (CSI)

– For use in children
Face Pain Scale
Numerical Pain Rating Scale (NPRS)
Screening Tools – Pain Scales
• Visual Analog Scale (VAS)
• Ruler to measure the distance in mm on a 10 cm line (0-100)
• Patients place mark on ruler
– 0-4 mm = no pain
– 5-44 mm = mild pain
– 45-74 = moderate pain
– 75-100 = severe pain
Screening Tools – Pain Scales
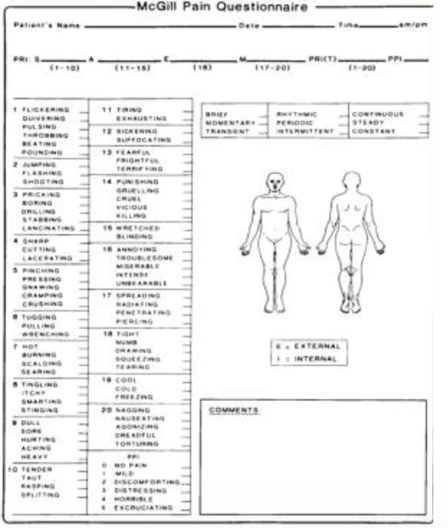
– Most frequently used multidimensional tool
– Sensory Intensity
– Emotional Impact
– Cognitive evaluation of pain
McGill Pain Questionnaire
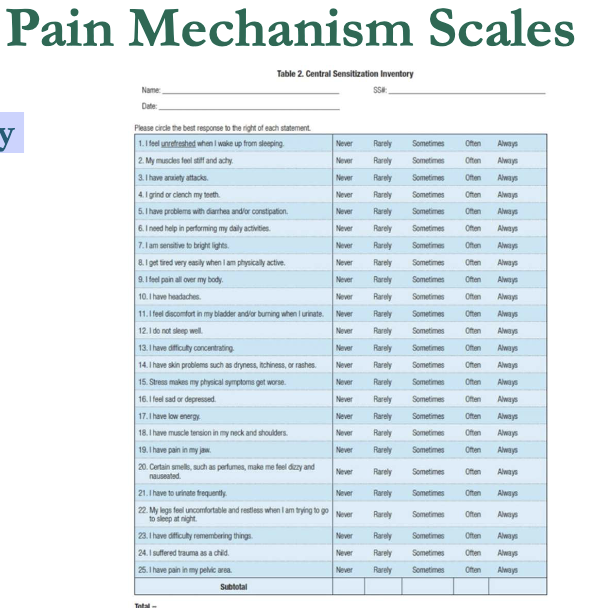
– 25 questions
– Score 0-100
– Score > 40 indicates central sensitization (nociplastic pain)
Central Sensitization Inventory (CSI)
what are screening tools - psychosocial assessment?
Fear avoidance beliefs questionnaire (FABQ)
tampa scale of kinesiophobia (TSK)
pain catastrophizing scale (PCS)
patient health questionnaire (PHQ)
StarTBACK
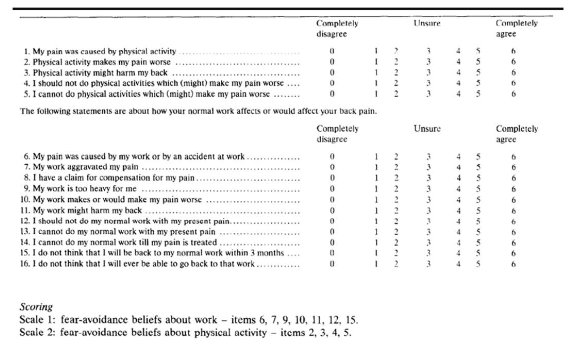
what is fear avoid ance beliefs questionnaire (FABQ)
– 16 items
– Includes physical activity (FABQ- PA) and work (FABQ-W) subscales
– FABQ-PA > 15 indicates fear avoidance
– FABQ-W > 34 indicates fear avoidance
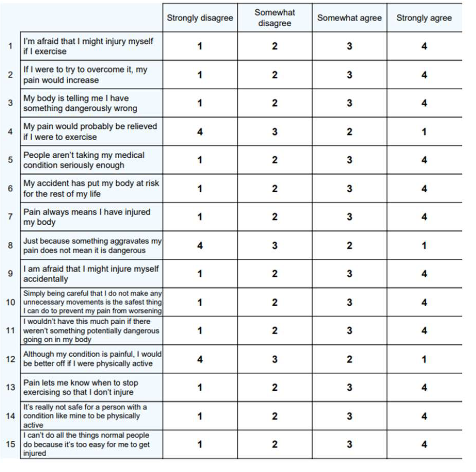
what is Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia (TSK)?
– Fear of physical activity or movement
– 17 items
– Score 17-68
– Higher scores indicate greater fear of movement and/or reinjury
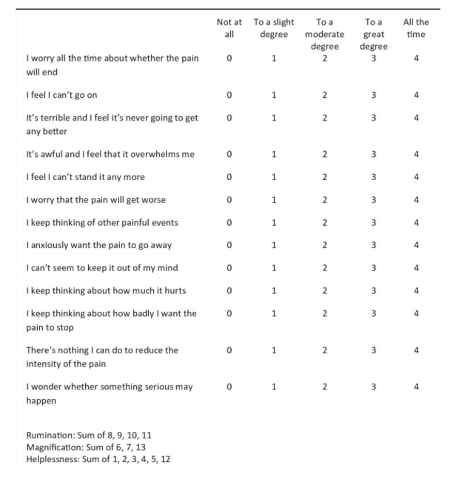
what is Pain Catastrophizing Scale (PCS)?
– 13 items
– 3 dimensions
• Rumination
• Magnification
• Hopelessness
– Score > 30/52 indicates catastrophizing in relation to pain
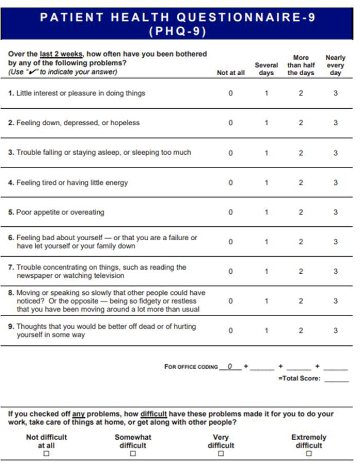
what is patient health questionnaire (PHQ) ?
– Depression scale
– PHQ-9
• 0-4 = no to minimal depression
• 5-9 = mild depression
• 10-14 = moderate depression
• 15-19 = moderately severe depression
• 20-27 = severe depression
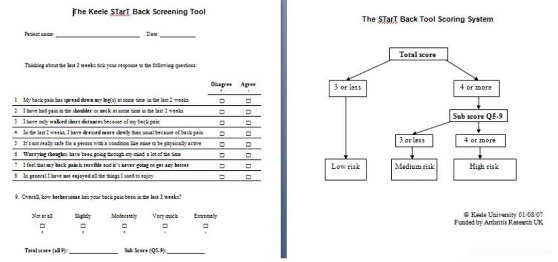
what is STarTBACK?
– 9 items
– Identifies patients who may be at risk for chronic low back pain
– Separates individuals into low and medium risk categories
– Distress subscale separates the medium risk subgroup into medium and high risk
Step 2 - Subjective Exam
what are types of subjective exams?
goal establish
S.I.N.S.S
what is goal establish
– Diagnosis
– Prognosis
– Screening for red flags
– Set PT/pt goals
– POC
– Treatment interventions
– Therapeutic Alliance
– Symptom of severity and irritability
what is S.I.N.S.S
– Severity
– Irritability
– Nature
– Stage
– Stability
what are types of Subjective Exam – Communication?
verbal
non-verbal
what is verbal communication?
– “Words the hurt and words that heal”
• “torn” “wear and tear” “ riped” “herniated” “congestive heart failure”
– Repeated pain rating
– Reassurance
• “You are going to be ok”
what is non-verbal communication?
– Physical signs of pain
• Grimace
• Stern look
• Dilated pupils
• Sweating
• Fast and shallow breathing
• Moving away from pain
• Unloading painful side
• Neglect

• Open Ended Questions
• Be receptive, open, and attentive
• Guide the Interview
• Speak clearly and slowly
Communication - Motivational Interviewing

Subjective Exam – 5 Areas
• Typical reasons for seeing a PT may include
– Pain
– limited movement
– range of motion
– Weakness
– Numbness
– decreased function
– fall risk
– etc
Type Of Disorder
categories of history?
disorder
treatment
what is disorder?
– How and when did this start?
– What kind of symptoms were present when it started?
– Did any of the symptoms spread anywhere else?
– What were you doing around the time of the onset?
– What do you think happened?
– Why do you think you hurt?
– Describe how (if any) the original symptoms have progressed over time.
– Since this initially started, is it getting better, worse, or staying the same?
what is treatment?
• What medical tests were done?
• Which providers have they seen?
• Medications prescribed and its effect?
• Current treatments, co-current treatment?
what is site of symtpoms?
pain location matter
body charts help patients visually communicate pain areas
body charts are valuable because they:
– Empower patients to express their pain
– May reveal neuroplastic changes (e.g., central sensitization, neglect)
– Help differentiate between peripheral and central pain mechanisms
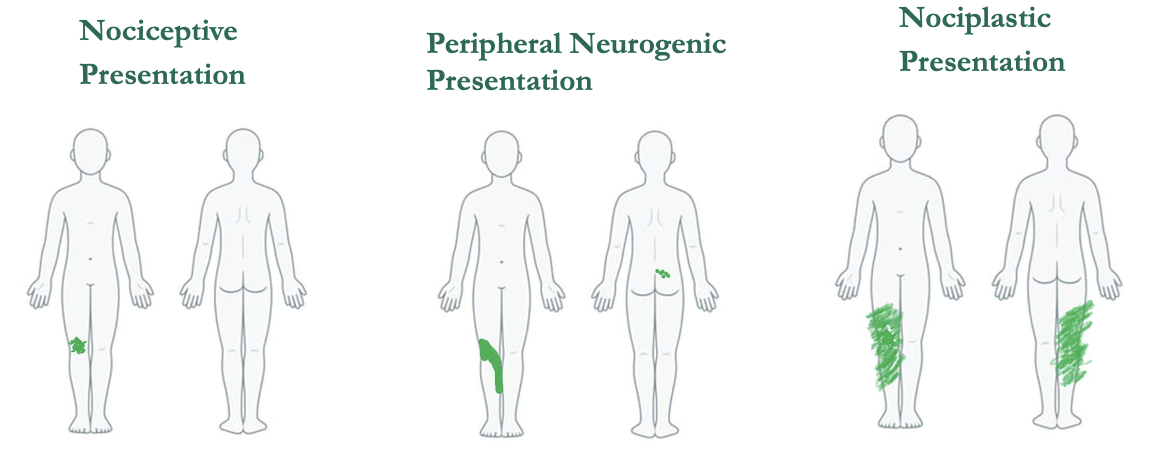
Patient Example – R Knee Pain
what is Behavior of Symptoms?
helps establish
symptom response
locus of control
what is helps establish?
– Diagnosis
– Pain mechanisms
– Precautions
– Contraindications
– Planning physical exam
– Treatment
what is symptom response?
– What increases symptoms?
– Decreases?
what is locus of control?
– What can you do for me?
Favors passive treatment techniques
what can i do for myself?
Favors active treatment techniques
what is Symptom Irritability?
hyperalgesia
allodynia
take away
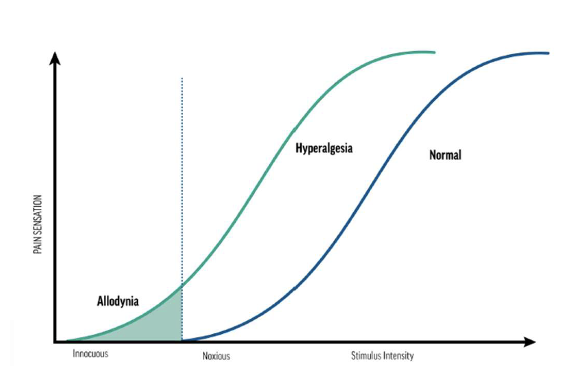
what is hyperalgesia?
Increased pain from a stimulus that normally provokes pain
what is allodynia?
Pain due to a stimulus that does not normally provoke pain
what is take away?
More irritable the condition, the less vigorous the tests and treatments should be.
what is Special Questions?
reviews the medical intake forms, and reviews systems, medical reports, or charts
aligned with a risk factor, precaution, or contraindication
ask additional questions to explore this further to determine if this needs further examination or referral to the doctor

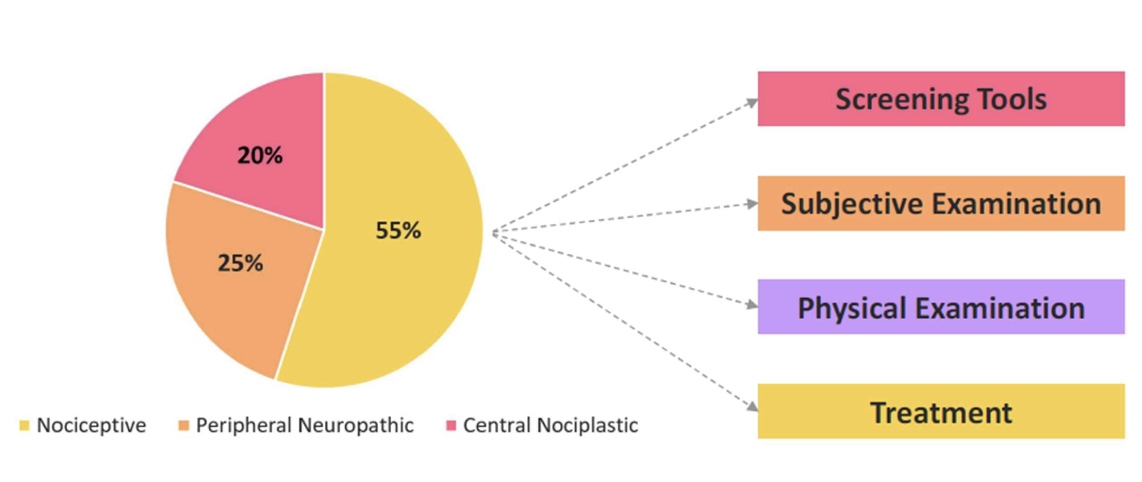
Subjective Info By Mechanism

Step 3 - Physical Exam
what is categories of Physical Exam?
planning the exam
conducting the exam
what is planning the exam ?
– What pain mechanism is dominant?
– What tests are definitely needed for today?
– Neurological evaluation needed?
– Safety tests
– Irritability level which may influence the number and vigor of tests
what is conducting the exam?
– Helps confirm the subjective hypothesis/diagnosis
– Establish a baseline of impairment
– Drive treatment choice
– Establish safety
– Patient expectations
– Create healing environment
• Pain with loading; relief with unloading (“on-off ” response)
• Pain matches complaint; typically sharp, dull, or intermittent
• End-range loading (e.g., over-pressure) is safe and useful
• Special tests
• Neuro screen needed to rule out nerve involvement
• Check strength, sensation, reflexes across relevant dermatomes/myotomes
Physical Exam - Nociceptive Dominant
what is Physical Exam - Peripheral Neuropathic?
neuro screen
mechanosensitivity
what is neuro screen?
sensation, strength, reflexes in dermatomes/cutaneous fields
what is mechanosensitivity?
nerve palpation
pressure algometry
neurodynamic tests
ULTT Median, Radial, Ulnar
SLR, Slump
what is Functional movement examination?
– Functional strength vs MMT
– Large functional movements
– Transfers, mobility
– Balance
– TUG or 1 minute sit/stand
– Limit Special Tests
what is Altered plasticity?
Laterality, 2-point discrimination, localization, graphesthesia
Thorough neuro screen
– Sensation
– Motor
– Reflex
what is sensitized nervous system?
– Neuro dynamics
• Active >Passive
– Nerve Palpation/PPT
• Local
• Remoteerality
Laterality tasks involve identifying the correct side of the body (left or right) when shown images of body parts
Performance on these tasks reflects the health of cortical body maps.
Laterality (Left/Right Judgement)
what is normative data of laterality?
– Hands and Feet:
• Accuracy: >80%
• Speed: 1.5–2.5 seconds per image
– Spine (neck/back movement direction):
• Accuracy: ~80%
• Speed: 1.1–2.1 seconds per image
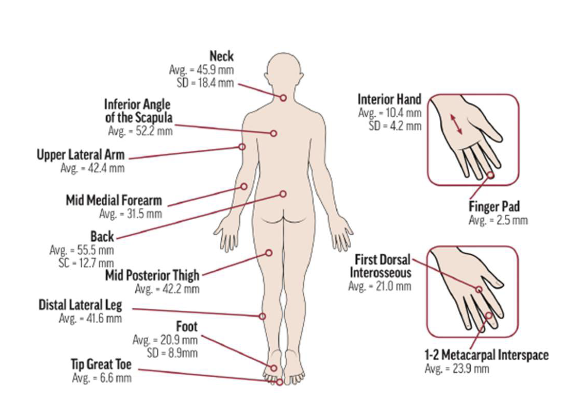
what is 2 Point Discrimination?
ability to distinguish two closely spaced points touching the skin as separate
Tactile acuity is often impaired in individuals experiencing pain
helps assess the integrity of the body’s sensory map
what is Localization?
the ability to accurately identify where on the body a tactile stimulus is applied
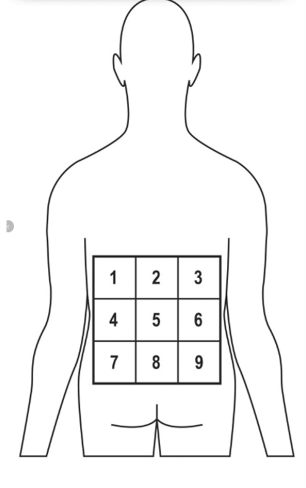
9-block or 12-block grid
Stimulate areas using a pencil eraser after instruction
Stimulate 20 areas and calculate percentage correct to assess accuracy
– 80% is suggested
Purpose:
To evaluate tactile localization accuracy and cortical sensory mapping in patients with low back pain.
Procedure:
1.Prepare the Grid:
Draw or place a 3x3 grid (9 blocks) over the lumbar region of the patient's back.
Ensure the grid is evenly spaced and covers the area of reported symptoms.
2.Instructions to Patient:
Inform the patient that you will lightly touch different areas within the grid and
they should identify the location of each stimulus.
3.Stimulus Application:
Use a pencil eraser or similar blunt object to gently touch one block at a time.
Randomize the order of stimulation to avoid pattern recognition.
4.Patient Response:
After each touch, ask the patient to point to or verbally identify the location
they felt the stimulus.
5.Scoring:
Record the number of correct responses out of 20. A score of ≥80% accuracy is
considered normal. Lower scores may indicate altered sensory processing or
central sensitization
9-Grid Localization for Low Back Assessment
what is Graphesthesia?
Ability to recognize writing on the skin purely by the sensation of touch
Helps assess sensory perception and cortical processing
somatosensory cortex
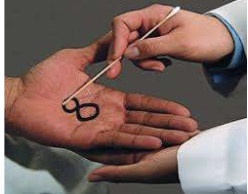
what is Graphesthesia procedure?
– clinician may trace a number or letter on a patient's palm or back using a blunt object (like the eraser end of a pencil)
– Without looking the patient must identify what was written
Pair Up
– Students form pairs (A and B).
Testing Phase (10 min):
– Student A closes eyes
– Student B uses a blunt object to trace a number or letter (A–Z, 0–9) on Student A’s palm
– Student A verbally identifies what was traced.
– Repeat 5–6 times, then switch roles
Graphesthesia Activity
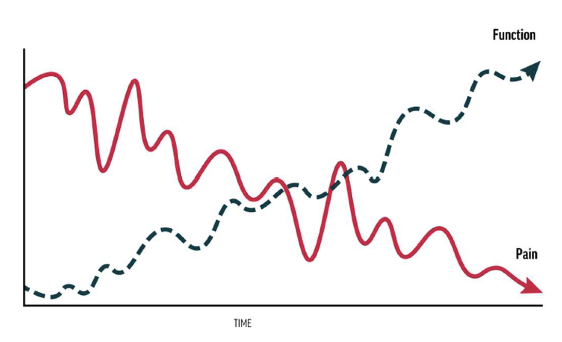
• Choose functional outcome measures that align closely with the primary concern
• evidence supports focusing on function rather than pain in treatment
– function tends to improve even when pain persists
• ultimate goal of PT is improved function despite ongoing pain.
Functional Outcome Measures
• Oswestry Disability Index (ODI)
• Neck Disability Index (NDI)
• Roland-Morris Disability Questionnaire (RMDQ)
• Lower Extremity Functional Scale (LEFS)
• Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH)
• Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC)
• Global Rating of Change (GROC)
• Patient Specific Functional Scale (PSFS)
Examples of Patient Reported Functional Outcome Measures
Step 4 Treatment – Overview
Traditional treatments
– Mobilization
– Manipulation
– Exercise
– Etc.Overpressure
Sustained, combined and repeated movement
High fear or pain catastrophizing: PNE
Treatment - Nociceptive Dominant
Commonly seen in therapy, i.e., radiculopathy
Traditional treatments – mobilization and manipulation
– Careful with overpressure
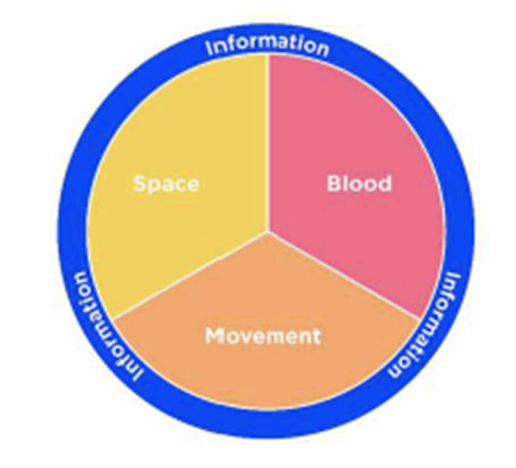
– Watch for latencyNeurodynamics:
– Sliders and Tensioners
– Space, movement and blood flow
– Pain neuroscience education
– Graded motor imagery
Treatment - Peripheral Neuropathic
what is neurodynamics?
– Sliders and Tensioners
– Space, movement and blood flow
– Pain neuroscience education
– Graded motor imagery
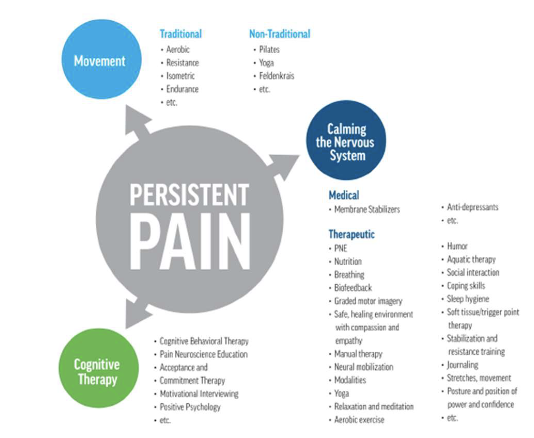
cognitive therapy
movement
calming the nervous system
Treatment – Nociplastic Dominant
what is under movement?
education, goal setting, pacing, and graded exposure
what is under calming the nervous system?
on-pharmacological alternatives such as mindfulness, meditation, sleep hygiene, and biofeedback