Neural Pathways and Motor Control: Corticobulbar, Spinal Tracts, and Reflexes
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
corticobulbar tract
Controls Muscles of the face, tongue, jaw, pharynx, etc. (voluntary control) (decussates)
- Runs parallel to the CST and ends at cranial nerves of the brainstem
Colliculospinal Tract
Involved in eye and head movements and connects superior colliculus to spinal cord (decussates)
reticulospinal tract
Modulates muscle tone, regulates the respiratory and sleep-wake cycles, and connects the reticular formation to the spinal cord.
Rubrospinal Tract
Limb movement, working with the CST. Axons from the red nucleus cross the midline and descend within the spinal cord. (decussates)
vestibulospinal tract
Maintains posture by connecting vestibular nuclei in the ear to the spinal cord.
internal capsule
A 'highway' for all tracts passing from the brainstem/spinal cord to the cortex.
What is the role of Lower Motor Neurons (LMN)?
innervate fibers directly, serving as the final common pathway that sends signals to body effectors.
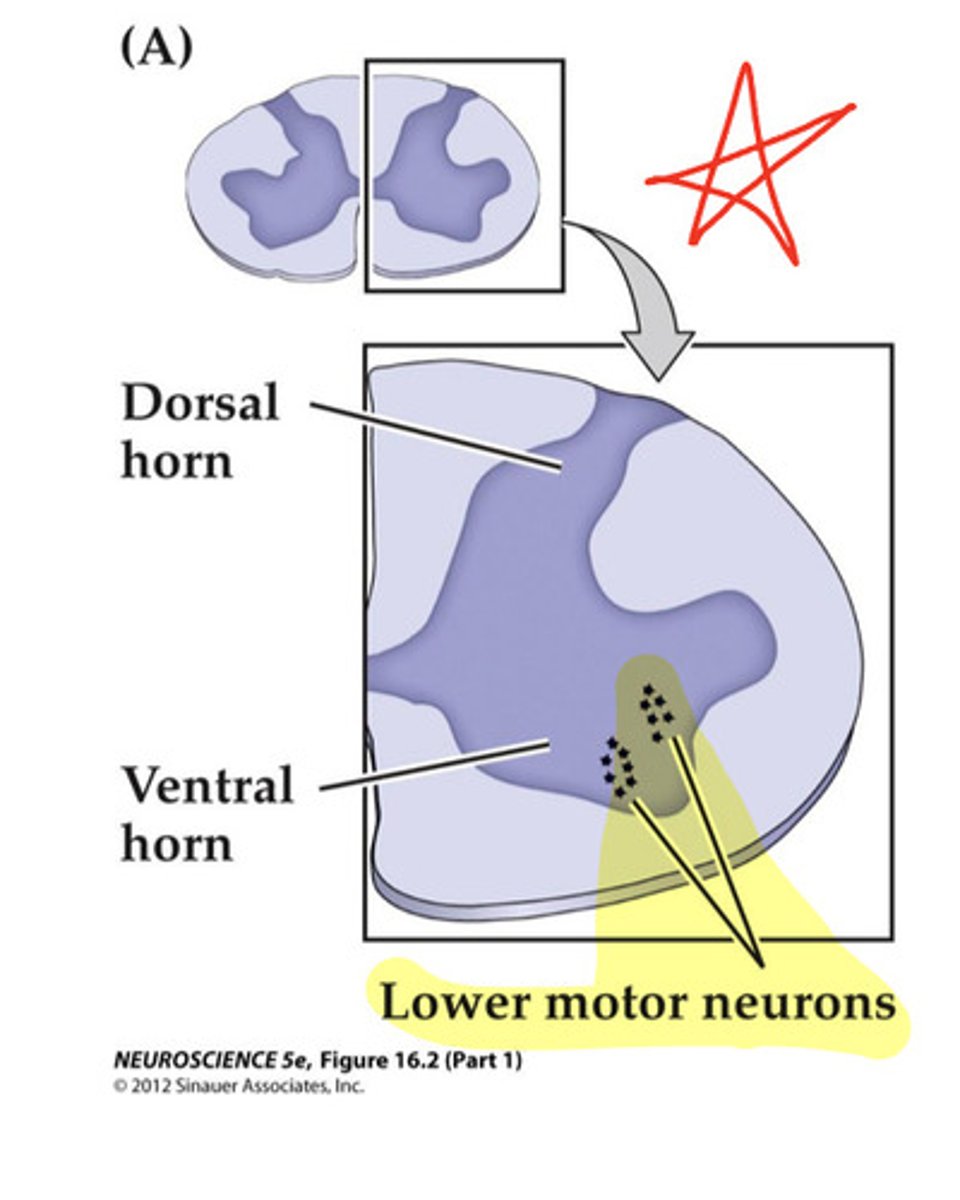
What is the role of upper motor neurons (UMN)?
Initiate and plan movement, while sending signals out to the body
Neuromuscular Junction
LMN connects directly to the muscle fibers, acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter released.
Alpha LMN
innervate extrafusal fibers for muscle contraction
Gamma LMN
intrafusal fibers, GTO's send signals to CNS about tension and length
What constitutes a Motor Unit?
A Lower Motor Neuron, its axon, and all the muscle fibers it innervates.
- variable in size (Territory), follows the "all or none principle"
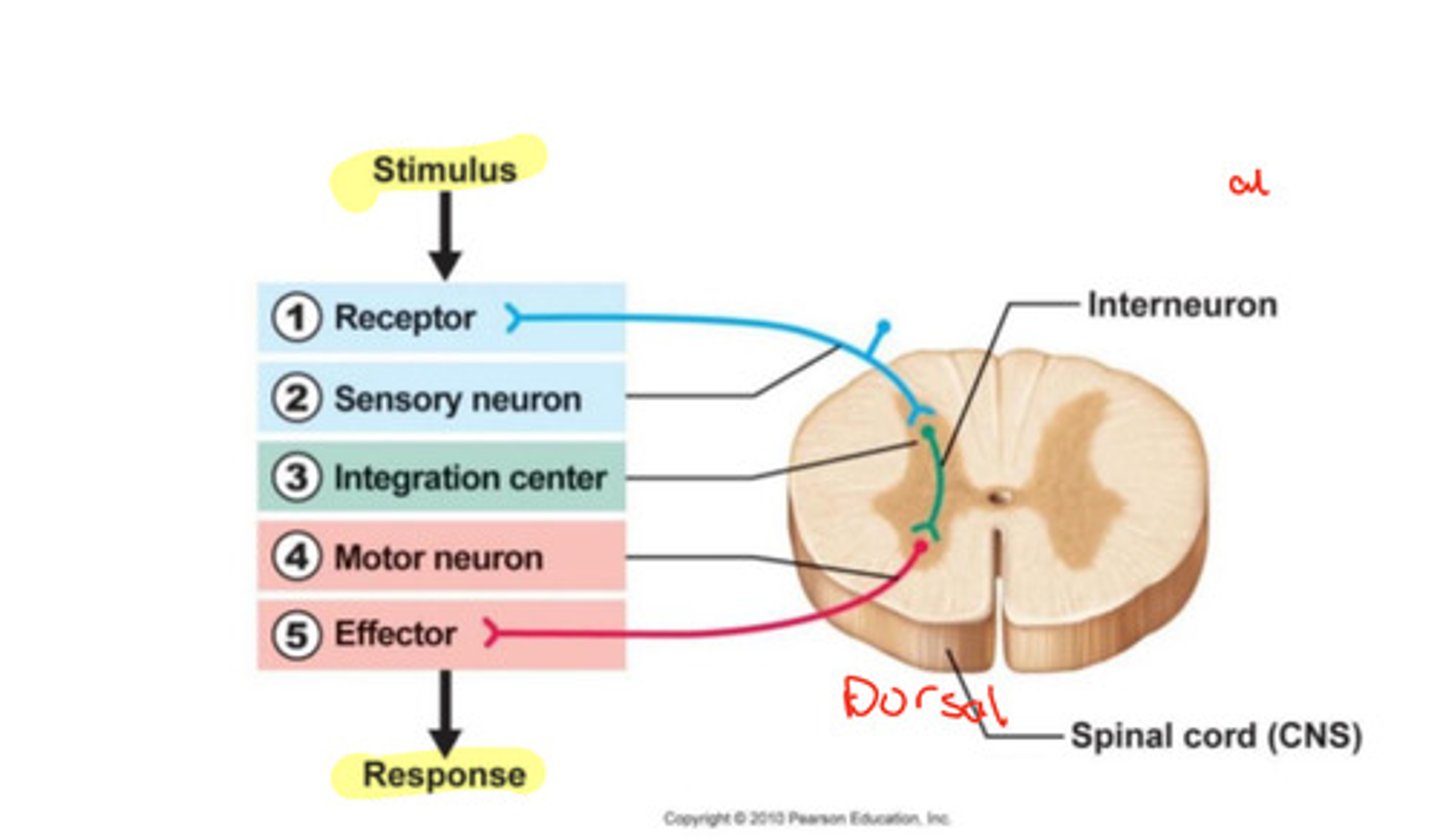
What is the Spinal Reflex?
A local circuit within the spinal cord that receives sensory information and mediates a motor response (reflex).
What are the components of a spinal reflex arc?
Receptor, sensory neuron, interneuron, motor neuron, and effector.
Corticospinal Tract
Involved in motor control (speed and agility of movement), carrying informational from the cortex to the spinal cord. (Decussates)
- Both lateral and anterior tracts pass through internal capsule
Lateral Corticospinal Tract
Fibers cross in medulla
Anterior Corticospinal Tract
Fibers cross at LMN
Pyramidal decussation
point at the junction of the medulla and spinal cord where motor fibers cross the midline.
Where are Betz cells located?
Layer 5 of M1 (primary motor cortex)
What is the significance of the Lawrence and Kuyper experiment?
It demonstrated the effects of damage versus healthy Corticospinal Tract pathways.