Innate Immunity
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are PAMPS and give examples
Pathogen associated molecular patterns
Reconginsed by PRRs
→Bacteria: peptidoglycan, flagellin
→Fungi: zymosan
→Viruses: double stranded RNA
Describe the process of phagocytosis of bacteria
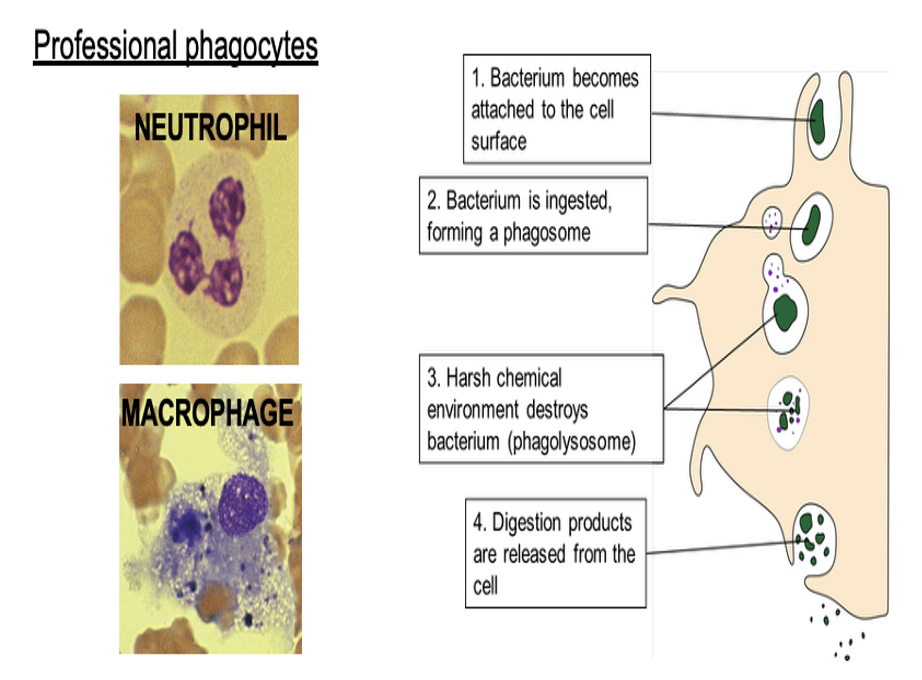
What are the key indicators of why micrboes are killed in the phagolysosome
low pH
H2O2 production
anti-microbiral peptides
NO production
proteases and lysozyme
What is a PRR drug
Imquidmod
PRR agonist against warts
State the components of the innate immune system
Barriers
Reconginition of conserved molecules expressed by microbes
Pathways and cells primed to activate in lack of missing self
What are the 3 outcomes of PAMP recognition
Direct cytoxicity
Opsonisation and phagoyctosis
Intracellular signalling and inflammation
What triggers opsonisation and phagocytosis of a cell
Coating the foreign body with host molecules that makes attractive to phagocytic cells of immune system e.g. C3b
Phagocytosis is the uptake of ingestion of particulate material by cells, purpose to destroy material through exposure to harsh chemicals
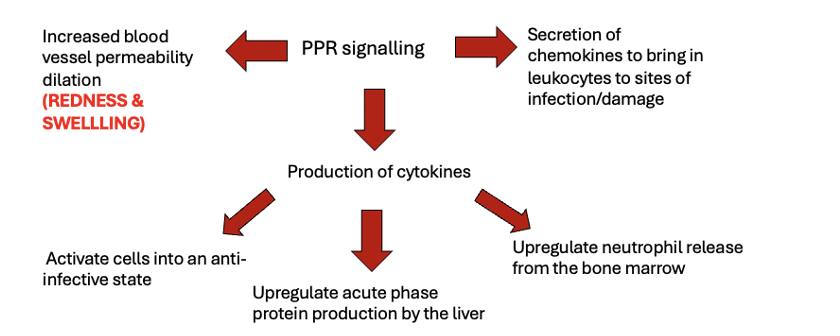
Explain how PRR signalling can trigger intracellular and inflammtion
-Liver: acute phase proteins (raised CRP level = release of cytokines)
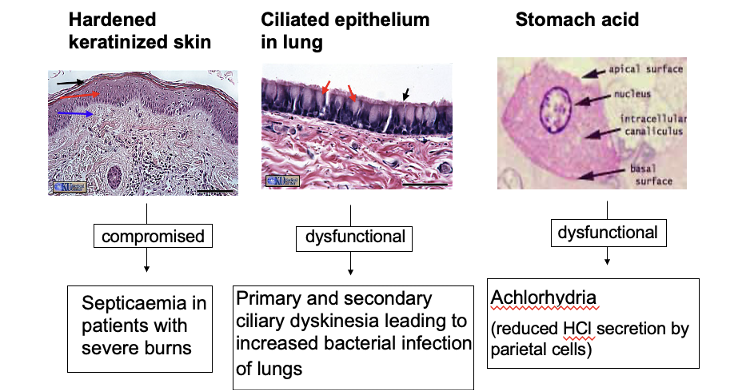
What are the 3 innate barriers and their key components to help protect
Keratinised skin
Ciliated epithelium in lung
Stomach acid
→exterior surfaces can also secrete proteins that protect those surfaces from colonisation (lysosome which breaks down peptidoglycan and anti-microbial peptides which disrupts the bacteria membrane)
What are DAMPS
Damage associated molecular patterns = trigger immune activation
increase exposure of phosphatidylserine on surface promotes phagocytosis
What is the complement system
Name given to a series of plasma proteins (zymogens) which co-operate to facilitate direct killing, opsonisation and inflammation
Can occur spontaneously but kept in check
Also driven by PAMPs and Ab from the adaptive immune system
Give an example of a PAMP
Mannose
List 2 complement defs
Hereditary angioedema (C1 inhibitor)
Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria (xs MAC pore formation)
What increase in the complement system indicates a bacterial infection
An increase in C3
also for fungal
Issues with C5 and MAC formation marks an increase vunerability to what
Nesseria infection
G-ve bacterial infection
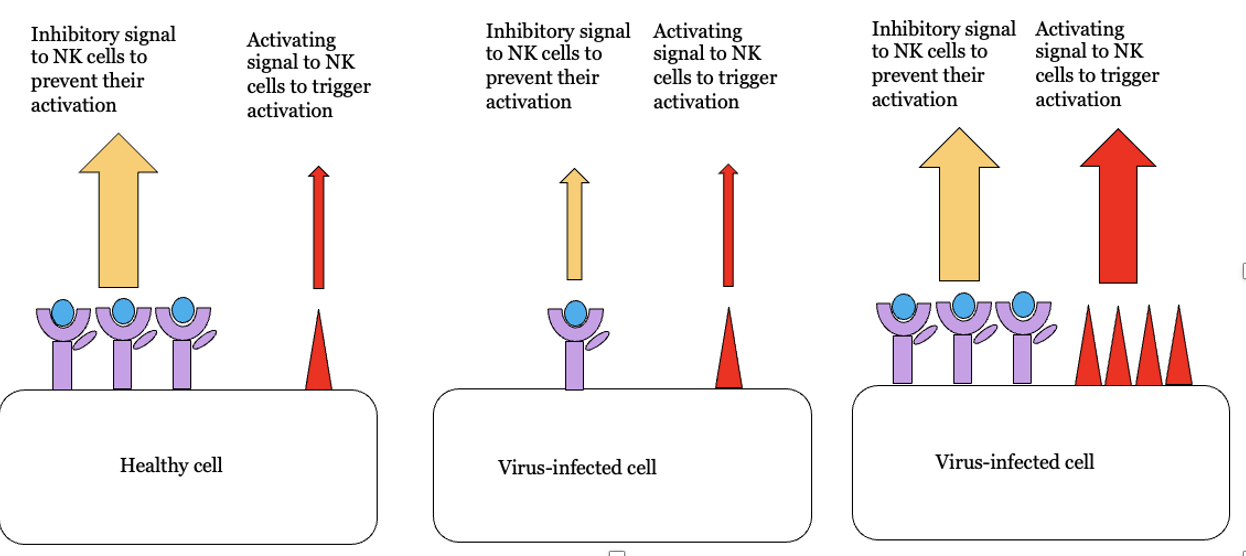
What are NK cells and their importance
not part of adaptive only innate !
Killing is direct contact with cell and realse of factors to trigger apoptosis
State the chemical barriers in the innate system
Low pH in stomach and urogential tract
Anti-microbial peptides on skin
Enzymes in secretion e.g tears
How is skin a barrier in the 1st line of defence
Dense keratinsed epitherlial cells
Secrete cytokines and TNF to alert immune cells in site of injury
Draw and descirbe the classical pathway
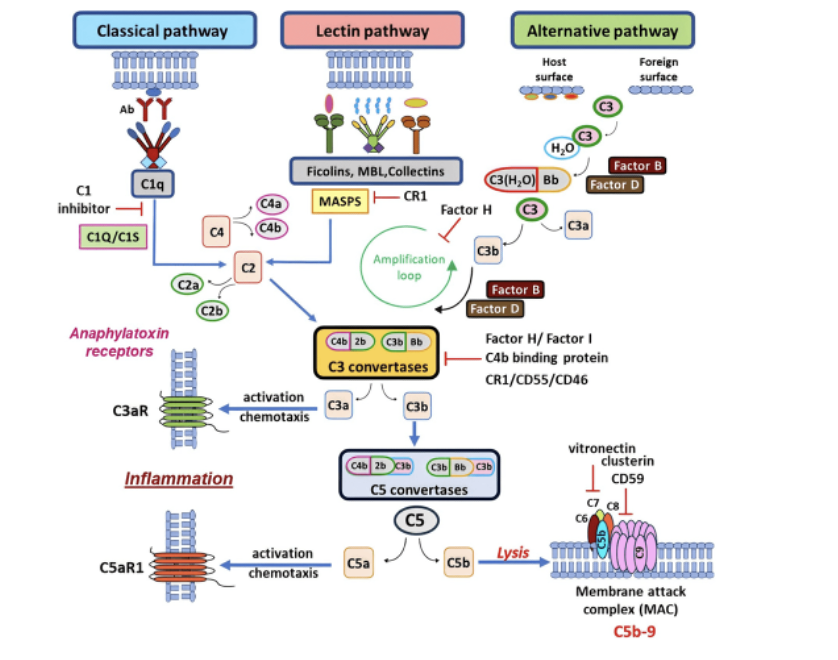
Draw and descirbe the terminal pathway
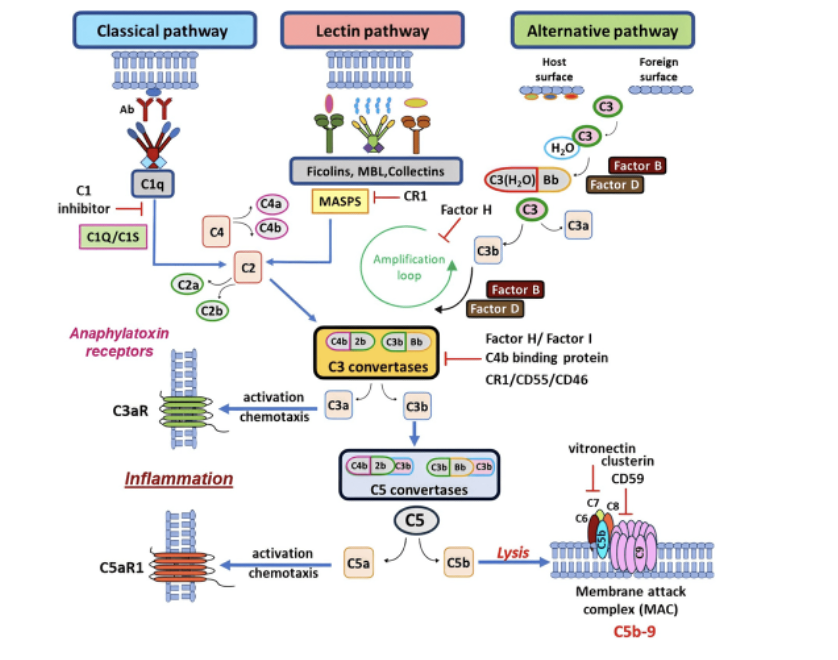
Draw and descirbe the alternate pathway
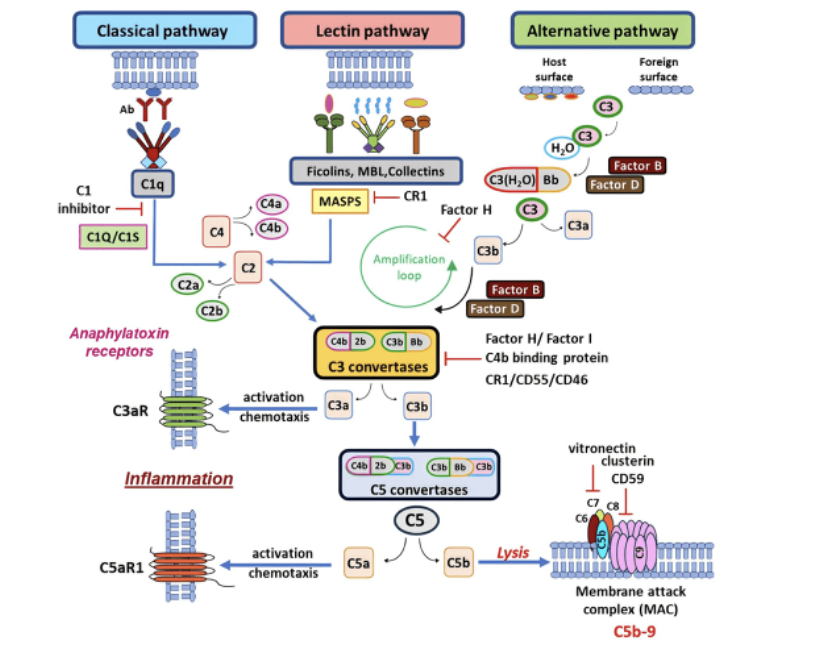
Describe the steps of the acute phase response
Local infection e.g. IL-6 reach liver and induce response
C-reactive protein is released and MBL = Complement system
What is the role of CRP
Bind to bacterial phospholipids from liver
Acting as opsonin to enhance phagocytosis