Optics
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are the two conditions needed to see light?
1. A light source is needed
2. An obstruction (something for the light to bounce off of) is needed
Ray diagram
diagram that shows the path of light from one location to another with a light ray drawn in a straight line
What happens to "white light" when it passes through a prism?
Refraction → split into many colors
- colors have different wavelengths that bounce off of prism at slightly different angles
- will appear separated
Is it possible for an object viewed in red light to appear white?
No, there is no white light for the object to reflect in red light.
Using a flat mirror provides an ____________ reflection of the object.
exact
C (center of curvature)
C = 2f
center of sphere formed by lens/mirror
When an object is located between the focal point and concave mirror, the resulting image is...
virtual
upright
enlarged
When an object is located between the focal point and center of a concave mirror, the resulting image is...
real
inverted
enlarged
When an object is located beyond the center of a concave mirror, the resulting image is
real
inverted
reduced
When an object is placed at the center of curvature of a concave mirror, the resulting image is...
real
inverted
same size as object
Why are concave mirrors used as makeup mirrors?
- allow for magnification
- provide enlarged, upright images
- have large focal point, which will result in more magnified image
- move farther away → image will appear inverted
An image formed by a convex mirror is...
virtual
upright
reduced
An image formed by a plane mirror is...
virtual
Real images formed by concave mirrors are always...
inverted
Convenience stores have convex mirrors because...
- provide virtual, upright, reduced images
- allows wider view of store
- no need for expensive security camera system
Why might light rays change direction when moving from one type of material to another?
- material density
- index of refraction
index of refraction
C = nv, C = speed of light in vacuum = 3 * 10^8 m/s
measure of the bending of a ray of light when passing from a vacuum to a medium
Snell's law
sinθ1/sinθ2 = n2/n1
What happens when you submerge a glass in vegetable oil?
- have same index of refractions (~1.5)
- glass will appear to disappear when submerged in oil
Light bends away from the normal line when...
light is moving from a material with a higher index of refraction to a material with a lower index of refraction
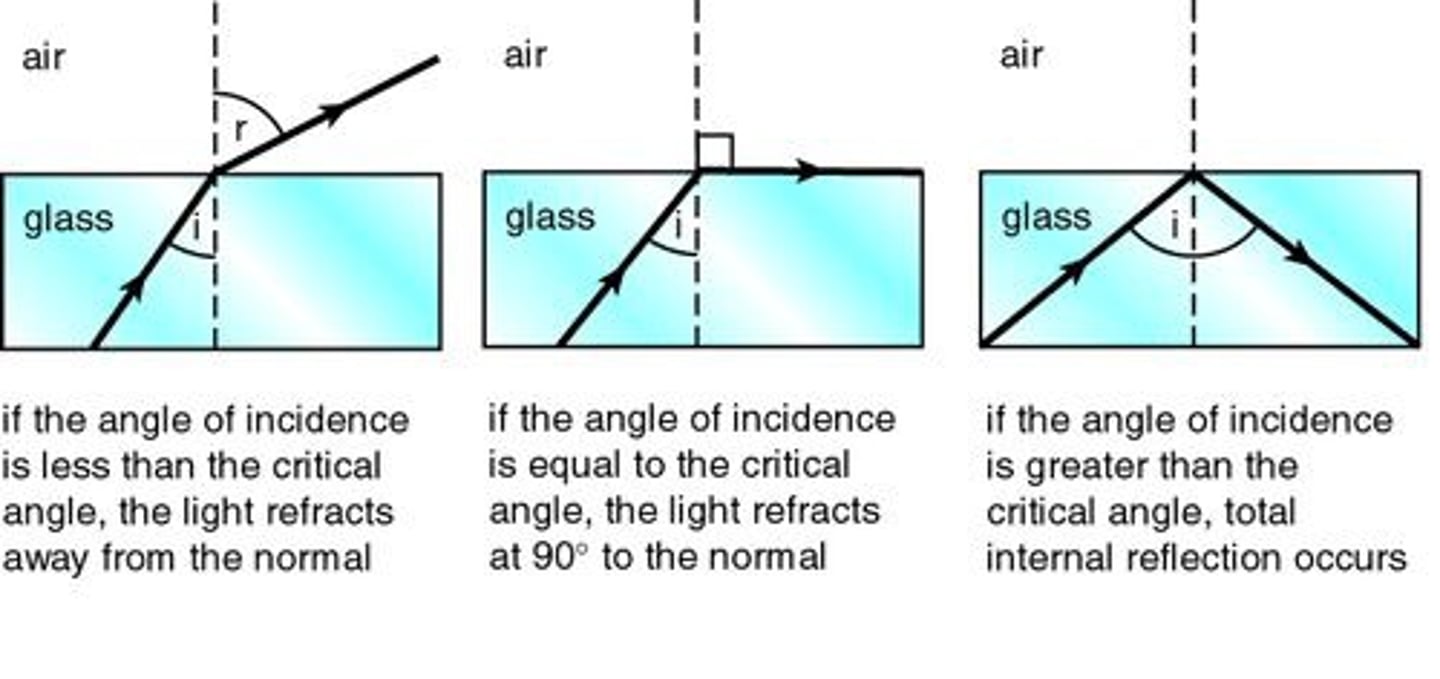
Critical angle
- greatest angle light can strike when traveling from one medium to another without being totally reflected in first medium
- going beyond critical = total internal reflection
- used in fiber optic glass and light pipes: light will internally reflect, will transmit digital signals without losses out the side of the wall of the fiber
Convex lens cause light rays to...
converge
concave lens cause light rays to...
diverge
Why do cameras and telescopes have two convex lens?
need second lens to make image upright
When an object is placed between the focal point and convex lens, the resulting image is...
virtual
upright
enlarged
When an object is placed between the focal point and center of a convex lens, the resulting image is...
real
inverted
enlarged
When an object is placed beyond the center of a convex lens, the resulting image is...
real
inverted
reduced
When an object is placed between the focal point and center of a concave lens, the resulting image is...
virtual
upright
reduced
Luminous source
source that produces light rays
Illuminated source
source that is lit by light rays
- becomes visible as a result of the light reflecting off it
- ask: "is light being reflected off of it and providing a light source?"
Extended source
a luminous source that emits light in all direction from each point on its surface
- if light illuminated from points perpendicular to surface, then some spots would be completely dark because light would not be able to reach those parts
Flat mirror
mirror with flat surface
normal line
perpendicular to mirror surface
reflected ray
ray reflected off mirror
incident ray
ray that strikes mirror
angle of incidence
the angle between the incident ray and the normal
angle of reflection
The angle between the reflected ray and the normal
law of reflection
the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
Image location
where the image is located relative to mirror
Object distance
distance from object to mirror
Image distance
distance from image to mirror
Virtual image
at any position where the paths of reflected rays seem to originate behind mirror
focal length (f)
distance from focal point to mirror/lens
focal point
location where parallel incident rays converge
real image
image that appears to come from a point where rays actually meet
virtual image
image that appears to come from a point where rays do not actually meet (need to extend rays)
mirror equation/thin lens equation
1/f = 1/do + 1/di
magnification equation
m = hi/ho = -di/do